Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsTonometry Clin Op
Tonometry Clin Op
Uploaded by
Vero VillamorThe document discusses tonometry, which is the objective measurement of intraocular pressure used to assist in diagnosing glaucoma, describing the Goldmann applanation tonometer as the contemporary standard method that involves flattening a small area of the cornea to measure the force required and convert it to millimeters of mercury. Potential sources of error in tonometry measurements are also reviewed, such as corneal thickness, pressure on the eye during measurement, corneal edema, and incorrect calibration of the tonometer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pocket Reference For ICUDocument63 pagesPocket Reference For ICUtostc100% (6)
- Steel-Ply Concrete Forming SystemDocument72 pagesSteel-Ply Concrete Forming SystembetopagoadaNo ratings yet
- Intra Ocular Pressure AyuDocument16 pagesIntra Ocular Pressure AyuAndi Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- Tonometry 161031160527Document33 pagesTonometry 161031160527Student ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Index 9Document3 pagesIndex 9Lucas HoldereggerNo ratings yet
- Tonometry and Gonioscopy: Presented by 1 Year PG Student Department of Ophthalmology ST - John's Medical CollegeDocument71 pagesTonometry and Gonioscopy: Presented by 1 Year PG Student Department of Ophthalmology ST - John's Medical CollegeJoel AntonyNo ratings yet
- Open Angle GlaucomaDocument114 pagesOpen Angle Glaucomahassan qureshiNo ratings yet
- How To Measure Intraocular Pressure: Applanation Tonometry: PreparationDocument1 pageHow To Measure Intraocular Pressure: Applanation Tonometry: Preparationpqwoeifjpakou134No ratings yet
- Goldmann TonometryDocument22 pagesGoldmann TonometrySyeda MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 4 Ocular TonometryDocument3 pages4 Ocular Tonometrymajd danNo ratings yet
- TonometryDocument27 pagesTonometryTikaNo ratings yet
- TonometriiDocument5 pagesTonometriireza salzabellaNo ratings yet
- Basics of GlaucomaDocument12 pagesBasics of GlaucomaJatinderBaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Document45 pagesAdvanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Danielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- Para311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeDocument6 pagesPara311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeMarinel GaniaNo ratings yet
- Applanation TonometerDocument15 pagesApplanation TonometerMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- @tonometryDocument49 pages@tonometryabhishek tNo ratings yet
- Biometry..Iol CalculationDocument86 pagesBiometry..Iol CalculationSristi Thakur0% (1)
- Shiotz Tonometer - UpdatedDocument8 pagesShiotz Tonometer - UpdatedRAHILNo ratings yet
- Part 1. General Instrumentation Concepts: Reading Assignment: Chapter 1 in Our TextbookDocument115 pagesPart 1. General Instrumentation Concepts: Reading Assignment: Chapter 1 in Our TextbookGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of VisionDocument119 pagesAnatomy of VisionjaheerNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Optical Constants of The EyeDocument33 pagesMeasurements of Optical Constants of The Eyesakina kutbuddinNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma and LensDocument4 pagesGlaucoma and Lenssarguss14No ratings yet
- A Scan BiometryDocument37 pagesA Scan BiometryAnonymous Wb2LoZv9c100% (1)
- Tonometry 1Document4 pagesTonometry 1Ashty RzgarNo ratings yet
- Tonometry and Care of Tonometers PDFDocument7 pagesTonometry and Care of Tonometers PDFAnni MuharomahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Intraocular Pressure Measurements TonomDocument16 pagesPediatric Intraocular Pressure Measurements TonomJust ShareNo ratings yet
- TonometerDocument29 pagesTonometerNavya SriNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2023 12547532Document6 pagesMUCLecture 2023 12547532sedeeqadel96No ratings yet
- Tonometer EditedDocument107 pagesTonometer EditedANUSAYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Tonomet RI Tonomet RI: Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang Syawali Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliDocument12 pagesTonomet RI Tonomet RI: Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang Syawali Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliIbnu Gilang SyawaliNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma at Glance - ASCDocument35 pagesGlaucoma at Glance - ASCYA MAAPNo ratings yet
- Lecture1-Human Eye SystemDocument29 pagesLecture1-Human Eye SystemPrajakta KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Inst. Lec3 PDFDocument16 pagesBiomedical Inst. Lec3 PDFLari EvergardenNo ratings yet
- Accesory Eqipment TabulationDocument11 pagesAccesory Eqipment TabulationNER CARLO SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Whitacre1993 TONOMETROSDocument30 pagesWhitacre1993 TONOMETROSVicky ObandoNo ratings yet
- Tonometry Dan PacymetriDocument9 pagesTonometry Dan PacymetriGusti Zidni FahmiNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument5 pagesGlaucomaspringdingNo ratings yet
- Detectors & DosemetersDocument6 pagesDetectors & DosemeterssingstimNo ratings yet
- To No Me TryDocument23 pagesTo No Me Trynmanasa8035No ratings yet
- Computer Vision - Human Visual SystemDocument81 pagesComputer Vision - Human Visual SystemNguyễn Anh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDDocument20 pagesOcular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDMalek AldawimehNo ratings yet
- Tonometer... Aashikat 2nd Yr BoptomDocument38 pagesTonometer... Aashikat 2nd Yr BoptomAashimaha thalapathiNo ratings yet
- Visual Field Testing AND Interpretation: Hira Nath DahalDocument82 pagesVisual Field Testing AND Interpretation: Hira Nath DahalSaurabh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFDocument5 pagesBiometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFJavier Andrés Pinochet SantoroNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Lesson 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicroPara Lesson 2 Reviewerrobelynjoy.alparo.cvtNo ratings yet
- Faradic Current: Masood Abdullah Hussein MSC PhysiotherapyDocument30 pagesFaradic Current: Masood Abdullah Hussein MSC PhysiotherapyZA IDNo ratings yet
- Intro - To - Visual InspectionDocument63 pagesIntro - To - Visual InspectionNoman Saeed100% (1)
- OPTO 307 SynoptophoreDocument4 pagesOPTO 307 SynoptophorecaponsharranerizaNo ratings yet
- OPT 424 Lectures1 To 3 - RGP Fitting Basics by Prof OriowoDocument67 pagesOPT 424 Lectures1 To 3 - RGP Fitting Basics by Prof Oriowoteamtruth50No ratings yet
- Tonometrybyarun 120727210025 Phpapp02Document98 pagesTonometrybyarun 120727210025 Phpapp02Sayoki GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gonioscopy: Aao ReadingDocument34 pagesGonioscopy: Aao ReadingTakwinNo ratings yet
- Tonometry: DR - Mehreen Afzal PGR Eye Unit IiDocument34 pagesTonometry: DR - Mehreen Afzal PGR Eye Unit IiUsman Imtiaz0% (1)
- Oxford Specialty Training: Training in Ophthalmology: Second EditionDocument37 pagesOxford Specialty Training: Training in Ophthalmology: Second EditionMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics: Force, Fluid Flow SensorsDocument40 pagesMechatronics: Force, Fluid Flow SensorsKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Part 1 MicroscopeDocument24 pagesWeek 2 Part 1 Microscopekimmynemil80No ratings yet
- Trial Frame RefractionDocument2 pagesTrial Frame RefractionJaneNo ratings yet
- Eye 2Document5 pagesEye 2Nadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionDocument16 pagesLecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Aberrometry NotesDocument3 pagesAberrometry NotesVero VillamorNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Origins of InequalitiesDocument1 pageOrigins of InequalitiesDuvNo ratings yet
- Broiler Analysis For 100 BroilersDocument18 pagesBroiler Analysis For 100 BroilersannmarieNo ratings yet
- Environmental Human Health123Document34 pagesEnvironmental Human Health123Sameer KsNo ratings yet
- Seven Zoe Back From Excerpt1Document3 pagesSeven Zoe Back From Excerpt1Jonathan VetromileNo ratings yet
- CHO-KLAT Version2.0 - Young2013Document5 pagesCHO-KLAT Version2.0 - Young2013Nay AungNo ratings yet
- Revised Crop Diseases - FormattedDocument98 pagesRevised Crop Diseases - FormattedMona ElsayedNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument5 pagesInterviewGracie S. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Hospital Staff ListDocument2 pagesHospital Staff ListOsheen KhanNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Growth-Democracy and Human CapitalDocument15 pagesThe Political Economy of Growth-Democracy and Human CapitalArchietasari NindyamurtiNo ratings yet
- Manual FFHH Oaci (Ingles)Document335 pagesManual FFHH Oaci (Ingles)Pran Antonio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Statistics Concepts and Controversies 9th Edition Moore Test Bank DownloadDocument11 pagesStatistics Concepts and Controversies 9th Edition Moore Test Bank DownloadKirk Neri100% (20)
- Let Me Be ClearDocument15 pagesLet Me Be ClearCrown Publishing Group85% (13)
- Kimera Exosomes, Kimera Labs, Inc. - 649343 - 09:01:2023 - FDADocument1 pageKimera Exosomes, Kimera Labs, Inc. - 649343 - 09:01:2023 - FDAseenfgNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Control of Microbial GrowthDocument10 pagesCh. 7 Control of Microbial GrowthYousef DosouqiNo ratings yet
- Dark Purple Woman Photo Customer Service Resume PDFDocument1 pageDark Purple Woman Photo Customer Service Resume PDFSamuel ZendNo ratings yet
- Rhesus Iso-ImmunizationDocument20 pagesRhesus Iso-Immunizationahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- Coursework For PsychiatristDocument7 pagesCoursework For Psychiatristafjwoamzdxwmct100% (2)
- Live Litbing Utbk 2 Feb 2024Document14 pagesLive Litbing Utbk 2 Feb 2024marettaNo ratings yet
- Msds Citrapure - DryDocument2 pagesMsds Citrapure - DryKyle MccoyNo ratings yet
- Pashupalan Nirdeshika EnglishDocument122 pagesPashupalan Nirdeshika EnglishdpanickerNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument27 pagesFINALSAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Brochure XGENIA ENGDocument2 pagesBrochure XGENIA ENGTaherNo ratings yet
- Personal StatementDocument2 pagesPersonal StatementTom Hayes67% (3)
- Elektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDocument71 pagesElektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityNadyaNo ratings yet
- Cycloplegic Effect of 0.5%tropicamide and 0.5%phenylephrine Mixed Eye Drops - Objective Assessment in Japanese Schoolchildren With MyopiaDocument5 pagesCycloplegic Effect of 0.5%tropicamide and 0.5%phenylephrine Mixed Eye Drops - Objective Assessment in Japanese Schoolchildren With Myopiaal_dhi_01No ratings yet
- The Versatility of Cow Ghee An AyurvedaperspectiveDocument7 pagesThe Versatility of Cow Ghee An AyurvedaperspectivekapsicumadNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAscorbic Acid Drug StudyJam Mohammad100% (5)
- Ross, C. (2020) - PTSD As A Future-Oriented Survival Strategy. Richardson The Colin A. Ross Institute For Psychological TraumaDocument5 pagesRoss, C. (2020) - PTSD As A Future-Oriented Survival Strategy. Richardson The Colin A. Ross Institute For Psychological TraumaEraNo ratings yet
Tonometry Clin Op
Tonometry Clin Op
Uploaded by
Vero Villamor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesThe document discusses tonometry, which is the objective measurement of intraocular pressure used to assist in diagnosing glaucoma, describing the Goldmann applanation tonometer as the contemporary standard method that involves flattening a small area of the cornea to measure the force required and convert it to millimeters of mercury. Potential sources of error in tonometry measurements are also reviewed, such as corneal thickness, pressure on the eye during measurement, corneal edema, and incorrect calibration of the tonometer.
Original Description:
Original Title
tonometry clin op
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses tonometry, which is the objective measurement of intraocular pressure used to assist in diagnosing glaucoma, describing the Goldmann applanation tonometer as the contemporary standard method that involves flattening a small area of the cornea to measure the force required and convert it to millimeters of mercury. Potential sources of error in tonometry measurements are also reviewed, such as corneal thickness, pressure on the eye during measurement, corneal edema, and incorrect calibration of the tonometer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesTonometry Clin Op
Tonometry Clin Op
Uploaded by
Vero VillamorThe document discusses tonometry, which is the objective measurement of intraocular pressure used to assist in diagnosing glaucoma, describing the Goldmann applanation tonometer as the contemporary standard method that involves flattening a small area of the cornea to measure the force required and convert it to millimeters of mercury. Potential sources of error in tonometry measurements are also reviewed, such as corneal thickness, pressure on the eye during measurement, corneal edema, and incorrect calibration of the tonometer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Clinical Optometry Practice: Tonometry
features glaucoma Normal range of IOP notes
Objective measurement Silent thief of sight Average: 15.5 mmHg Simple applanation devices
of intraocular pressure • First introduced in 1867
(IOP) Most common form is Normal range: 10-22 • Based on principle that two
• Based most painless and insidious mmHg (Moses, 1975) spheres in contact with one
commonly on the in its destruction of another share a flat surface only
force required to visual field IOP is not constant within if the internal pressures of the
flatten the cornea an individual spheres are identical
• Degree of corneal Defined by triad of: • Arterial pulse: 2-3 o Flatten a small area of the
indentation produced • High IOP mmHg central cornea and measure
by a fixed force • Optic nerve • Erect or supine the amount of force required
Has been performed damage position of px: 2-4
since the latter part of the • Loss of visual mmHg Impression/Indentation Tonometers
19th century field • Time of day: 5 • Involves a weighted free-
mmHg moving plunger that indents
Used to assist in the Early detection by rather than flattens the cornea
diagnosis of glaucoma tonometry • Data is then translated into IOP
readings
Can be divided into those • Perfected by Schiotz in 1905
instruments that • Elevated the IOP significantly
applanate (flatten) and and are influenced by scleral
those that indent the rigidity
cornea o Via weights and a
nomogram, a reasonably
accurate determination of
IOP can be done
• Time consuming compared with
applanation tonometers that are
internally calibrated and easier
for the patient and clinician
Goldmann Applanating Device
Contemporary standard for applanation tonometry
features procedure interpretation
Based on Imbert-Fick Law Fluorescein + local anesthetic is applied to the eye Tonometer is too low
• A perfect sphere has its topically
internal pressure equally • Anesthetic maintains patient comfort
distributed and that the • Patient is in primary gaze
external force needed to • Dial is preset between 1 and 2
flatten a known area of
that sphere is directly Fluorescein spreads into the tear film and forms a Tonometer is too close
proportional to the meniscus surrounding the area of contact between the
internal pressure of the probe tip and corneal surface
sphere
• Intraocular pressure is Tangential to the probe is the light source, with a cobalt Too much fluorescein
equal to the tonometer blue filter in place
weight divided by the
applanated area Clinician views the illuminated probe through the
microscope
assumes that the eye is a
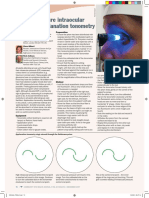
perfect sphere A circular field shows two faint white arcs that indicate
proximity to the patient’s cornea Too little fluorescein
Area of contact between the • Grossly center these two arcs
tip of the tonometer and the
cornea is constant When the probe tip touches the cornea
• Two yellow-green glowing semicircles are seen
Force required to maintain • Semicircles represents the doubled image of the
the contact area is converted circular applanated area Advantages
into millimeters of mercury Clinician adjusts the force applied to the globe 1. Gold standard for IOP
(mmHg) • Inner limit of the fluorescent meniscus has been measurement
doubled by the fixed prism 2. Accurate & precise
Measures the force needed • Diameter of the contact area is at 3.06mm
to flatten a 3.06mm Disadvantages
diameter circular area of the Fluorescence is visualized by using cobalt-filtered 1. Only provides valid
cornea to provide a measure illumination of the flat end of the Goldmann probe as it measurements for
of the pressure in the eye rests against the corneal surface corneas with near
o Diameter chosen average thickness
because it was found Tension dial is adjusted so that the inner edges of the - Thick corneas, IOP
that at such a diameter, semicircles become coincident overestimated
the surface tension • Thickness of each semicircle should be - Thin corneas, IOP
attraction of the probe approximately 1/10 of the diameter underestimated
was equal and opposite • Too thick semicircles, IOP is overestimated 2. Cornea is anesthesized
to the force required to • Too thin, IOP is underestimated 3. Needs a slit lamp but a
counteract corneal handheld version has
• Calibrated in grams, with each gram of force
rigidity for an average been developed
equivalent to 10mmHg IOP
thickness cornea
notes disinfection Potential errors
Corneal curvature may Wipe the probe clean and Inappropriate fluorescein pattern
influence the reading soak the tip in • Resulting from excessive fluorescein will make the
• Measurement of IOP • 1:10 dilution of semicircles too thick and the radius too small
in eyes with corneal household bleach • Insufficient fluorescein will make the semicircles too
astigmatism exceeding • 3% hydrogen peroxide thin and the radius too large
4D should be made • 70% ethanol or Pressure on the globe
approximately 45 isopropanol • By the examiner or the patient squeezing the eyelids,
degrees from the • Accomplishes high- and restricted EOM may result in an artificially high
flattest meridian level disinfection reading
• Alcohol soaks cause
rapid damage to the Cornea edema
probe • May result in artificially low IOP by as much as 10
mmHg compared with the true pressure
Reducing the risk of cross • Hydrogen peroxide is
infection less destructive than Corneal thickness
• Avoiding tonometry in diluted bleach • If the cornea is thinner, underestimation of IOP may
individuals with overt • Most wipe with alcohol result and if thicker, an overestimation
infection swab • Individuals with ocular hypertension tend to have
• Using a disposable corneas thicker than normal; normal-tension
sleeve which covers the glaucoma tend to have thinner corneas
tip of the tonometer
• Swabbing the tonometer Incorrect calibration
tip thoroughly with an • Can result in an incorrect reading
alcohol prep pad and • Check the calibration at regular intervals
allowing it to dry for
approximately 10 Other factors
minutes • Tight collar, which obstructs venous return and
causes IOP to rise
• Anxiety
Schiotz (indentation) tonometer
features procedure Advantages n dis notes
Local anesthetic is used 1. Patient must be reclined Advantages Cleaning
2. Drop of anesthetic 1. Portability • Entire instrument
Patient’s head is reclined instilled to both eyes 2. Reduced cost must be cleaned to
3. Instruct patient to open compared to Goldmann avoid spread of
Practitioner applies the both eyes and look at tonometer infection
tonometer to the corneal the ceiling (inexpensive) o Isoprophyl
apex 4. Hold gently the patients 3. Autoclavable alcohol
• Simple mechanical eye lids apart anchoring instrument o Steam
device that employs them against the orbital sterilization
weight to press a rim Disadvantages o Noncorrosive
freely moving plunger 5. Gently lower the 1. Cornea is anesthetized chemical
against the cornea, tonometer on the 2. Accurate data is disinfection
indenting it patient's eye (foot plate difficult to obtain • Disassemble prior to
rest on the center of the 3. Due to repeated cleaning
Reading taken has a scale cornea) indentation of the • Dry thoroughly on a
value that is translated into 6. Take the reading 3 times cornea sterile pad
an IOP reading using a and get the average - Clarity may be • Reassemble in reverse
nomogram disrupted order
• Calculated on the 4. Supine position of the
basis of average patient may influence Calibration
scleral rigidity IOP • Checked by resting
• Readings obtained 5. Indentation of the the tonometer
using standard 5.5g cornea forces aqueous perpendicularly on the
weight from the anterior test block
chamber • Needle should
Three readings taken for - Underestimation of indicate zero
more accurate measurement IOP with successive
readings
• If it does not, a small
screw at the base of
the needle can be
loosened to rezero the
needle. Don’t bend the
needle
Other tonometers
Non-contact tonometers
Features Advantages n dis interpretations
Based on the principle of applanation Advantages Too close to px
but instead of using a prism, the 1. No disinfection necessary
central part of the cornea is flattened 2. No topical anesthesia required
by a jet of air 3. Easier to perform
Time required to sufficiently flatten Disadvantages
the cornea relates directly to the level 1. More expensive and less portable Too far from the px
of IOP 2. Accurate reading depends on precise
alignment of targets with patient’s eye
Instrument is easy to use and does not - Can be used for screening
require topical anesthesia - For high, unequal or increased IOP, use
GAT
Main advantage is that it is accurate 3. Distance of device from corneal apex is
only within the low to middle range critical Focused
- Not for uncooperative patients
Jet of air can startle the patient both 4. Can overestimate the IOP compared with
with its apparent force and noise Goldmann technique
May be non-portable or portable
Tono-pen
Features Calibrating procedure notes
Hand-held, self-contained 1. Hold the instrument 1. Anesthetic in both eyes Common errors
battery powered, portable with the tip down, the 2. Px is instructed to look • High IOP because of
contact tonometer black button is quickly straight ahead and keep patient apprehension
pressed twice both eyes open • Pressing on the globe
Probe tip contains a 2. CAL will appear on the 3. Button is pressed once while holding the
transducer that measures window to activate the eyelids open
the applied force 3. The button is depressed instrument. (beep • Too tight shirt collars
once, after a few sound) • Patient holding their
Microprocessor analyses seconds, UP will appear 4. Tip is repeatedly breaths
the force/time curve 4. Instrument is then touched to the cornea • Repeating the
generated by the transducer inverted with the tip up. 5. Ask the patient not to applanation
during corneal indentation GOOD or BAD will move their eyes o Reduces IOP due to
to calculate IOP appear tonographic effect
5. Calibration check
should be done only at
Correlates well with the beginning of each Advantages
Goldmann tonometry day 1. Portable
although it slightly 2. Patient can be sitting
overestimates a low IOP up or lying down
and underestimates a high
IOP Disadvantages
1. Less stable than slit
Main advantage involves lamp mounted
the ability to measure IOP instrument
in eyes with distorted or 2. Does not allow for
edematous corneas as well examining the cornea
as through a bandage before and after the test
contact lens
Other other tonometers
APPLANATION TONOMETER
Goldmann
• GAT Disadvantages
• Standard method for measuring IOP • High level of skill to operate
• Measurement of the force required to compress the • Inability to measure in supine patients
cornea over a given area • Need for topical anesthesia
• Topic anesthetic + Fluorescein dye + Cobalt blue • Decreased accuracy on an irregular or scarred
filter cornea
Perkins applanation tono
• Hand-held tonometer Disadvantages
• Same mechanism of applanation as the Goldmann • High level of skill to operate
• Portable • Decrease in stability with a handheld
• Useful in settings where a slit lamp is not instrument
feasible • Need for topical anesthesia
• Can be used in uptight or supine patient • Decreased accuracy on an irregular or
scarred cornea
Non-contact tonometer
• Also known as “air puff” tonometer Disadvantages
• Use a small puff of air directed at the cornea • Less accurate method than GAT
• Returning air from the surface of the cornea is
measured by a membrane that records the force,
converted to IOP
• No topical anesthesia needed
• Useful for children and adults unable to tolerate
contact methods
Ocular response analyer (ora)
• Non contact tonometer • Designed to improve IOP accuracy
• Utilizes a column of air as the applanating force to • Allows clinicians to account for the
deform the cornea variability in corneal biomechanical
• Based on the force of airflow and the rate of properties seen among patients
recovery from deformation • Disadvantage
• Corneal hysteresis • Cannot be used on supine patients
• Ability of the cornea to absorb and
dissipate applied forces based on its
viscoelastic properties
INDENTATION TONOMETER
Tono-pen indentation/applanation tonometer
• Electronic hand held device that uses a small Disadvantages
plunger to record the force needed to applanate the • Requires daily recalibration
cornea • Topical anesthesia required
• Averages multiple readings of this small force
converted to IOP
• Useful in portable screenings
• Ability to measure over soft CL, on an irregular
corneal surface
• Potential to measure at peripheral cornea
• Patient can be supine or upright
Pneumatonometer
• Uses a stream of air to indent the cornea with a Disadvantage
5mm diameter silicone tip • Hand held probe attached to a table
• Force of air that indents the cornea is recorded and mounted device
converted to IOP
• Can measure irregular cornea surfaces, over soft
CL, at the peripheral cornea
• Patient can be supine or upright
Schiotz tonometer
• Portable tonometer Disadvantages
• Consists of a weighted plunger attached to a • Patient must be supine
footplate positioned on a cornea • Topical anesthesia is required
• Weights are stacked onto the probe to cause
depression of the cornea
• Number of weights stacked onto the probe
correlates to a calibrated IOP
REBOUND TONOMETER
I-care tonometer
• Portable Disadvantages
• Simple to use hand held device using a small • Cannot be used on supine patients
probe that bounces off the cornea in the horizontal • Accuracy decreases in the setting of
plane corneal edema
• Deceleration of the probe produces a level of
voltage that is converted to IOP
• The faster the rate of deceleration against the
cornea, the higher the pressure
• No anesthesia required
• Patients who are not tolerant of contact methods
DYNAMIC CONTOUR TONOMETER (DCT)
Pascale DCT
• Utilizes a contour-matched, piezoelectric sensor to Disadvantages
measure minuscule dynamic pulsations in IOP at • Requires topical anesthesia
the cornea • Less accurate on irregular corneas
• Allows measurement of IOP without deforming
the cornea
• Readings are independent of corneal thickness
• More accurate method on regularly shaped corneas
You might also like
- Pocket Reference For ICUDocument63 pagesPocket Reference For ICUtostc100% (6)
- Steel-Ply Concrete Forming SystemDocument72 pagesSteel-Ply Concrete Forming SystembetopagoadaNo ratings yet
- Intra Ocular Pressure AyuDocument16 pagesIntra Ocular Pressure AyuAndi Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- Tonometry 161031160527Document33 pagesTonometry 161031160527Student ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Index 9Document3 pagesIndex 9Lucas HoldereggerNo ratings yet
- Tonometry and Gonioscopy: Presented by 1 Year PG Student Department of Ophthalmology ST - John's Medical CollegeDocument71 pagesTonometry and Gonioscopy: Presented by 1 Year PG Student Department of Ophthalmology ST - John's Medical CollegeJoel AntonyNo ratings yet
- Open Angle GlaucomaDocument114 pagesOpen Angle Glaucomahassan qureshiNo ratings yet
- How To Measure Intraocular Pressure: Applanation Tonometry: PreparationDocument1 pageHow To Measure Intraocular Pressure: Applanation Tonometry: Preparationpqwoeifjpakou134No ratings yet
- Goldmann TonometryDocument22 pagesGoldmann TonometrySyeda MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 4 Ocular TonometryDocument3 pages4 Ocular Tonometrymajd danNo ratings yet
- TonometryDocument27 pagesTonometryTikaNo ratings yet
- TonometriiDocument5 pagesTonometriireza salzabellaNo ratings yet
- Basics of GlaucomaDocument12 pagesBasics of GlaucomaJatinderBaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Document45 pagesAdvanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Danielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- Para311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeDocument6 pagesPara311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeMarinel GaniaNo ratings yet
- Applanation TonometerDocument15 pagesApplanation TonometerMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- @tonometryDocument49 pages@tonometryabhishek tNo ratings yet
- Biometry..Iol CalculationDocument86 pagesBiometry..Iol CalculationSristi Thakur0% (1)
- Shiotz Tonometer - UpdatedDocument8 pagesShiotz Tonometer - UpdatedRAHILNo ratings yet
- Part 1. General Instrumentation Concepts: Reading Assignment: Chapter 1 in Our TextbookDocument115 pagesPart 1. General Instrumentation Concepts: Reading Assignment: Chapter 1 in Our TextbookGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of VisionDocument119 pagesAnatomy of VisionjaheerNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Optical Constants of The EyeDocument33 pagesMeasurements of Optical Constants of The Eyesakina kutbuddinNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma and LensDocument4 pagesGlaucoma and Lenssarguss14No ratings yet
- A Scan BiometryDocument37 pagesA Scan BiometryAnonymous Wb2LoZv9c100% (1)
- Tonometry 1Document4 pagesTonometry 1Ashty RzgarNo ratings yet
- Tonometry and Care of Tonometers PDFDocument7 pagesTonometry and Care of Tonometers PDFAnni MuharomahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Intraocular Pressure Measurements TonomDocument16 pagesPediatric Intraocular Pressure Measurements TonomJust ShareNo ratings yet
- TonometerDocument29 pagesTonometerNavya SriNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2023 12547532Document6 pagesMUCLecture 2023 12547532sedeeqadel96No ratings yet
- Tonometer EditedDocument107 pagesTonometer EditedANUSAYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Tonomet RI Tonomet RI: Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang Syawali Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliDocument12 pagesTonomet RI Tonomet RI: Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang Syawali Oleh: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliIbnu Gilang SyawaliNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma at Glance - ASCDocument35 pagesGlaucoma at Glance - ASCYA MAAPNo ratings yet
- Lecture1-Human Eye SystemDocument29 pagesLecture1-Human Eye SystemPrajakta KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Inst. Lec3 PDFDocument16 pagesBiomedical Inst. Lec3 PDFLari EvergardenNo ratings yet
- Accesory Eqipment TabulationDocument11 pagesAccesory Eqipment TabulationNER CARLO SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Whitacre1993 TONOMETROSDocument30 pagesWhitacre1993 TONOMETROSVicky ObandoNo ratings yet
- Tonometry Dan PacymetriDocument9 pagesTonometry Dan PacymetriGusti Zidni FahmiNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument5 pagesGlaucomaspringdingNo ratings yet
- Detectors & DosemetersDocument6 pagesDetectors & DosemeterssingstimNo ratings yet
- To No Me TryDocument23 pagesTo No Me Trynmanasa8035No ratings yet
- Computer Vision - Human Visual SystemDocument81 pagesComputer Vision - Human Visual SystemNguyễn Anh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDDocument20 pagesOcular Anatomy and Physiology: Mera Haddad BSC MSC PHDMalek AldawimehNo ratings yet
- Tonometer... Aashikat 2nd Yr BoptomDocument38 pagesTonometer... Aashikat 2nd Yr BoptomAashimaha thalapathiNo ratings yet
- Visual Field Testing AND Interpretation: Hira Nath DahalDocument82 pagesVisual Field Testing AND Interpretation: Hira Nath DahalSaurabh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFDocument5 pagesBiometry by Suryakant Jha and Wangchuk Doma PDFJavier Andrés Pinochet SantoroNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Lesson 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicroPara Lesson 2 Reviewerrobelynjoy.alparo.cvtNo ratings yet
- Faradic Current: Masood Abdullah Hussein MSC PhysiotherapyDocument30 pagesFaradic Current: Masood Abdullah Hussein MSC PhysiotherapyZA IDNo ratings yet
- Intro - To - Visual InspectionDocument63 pagesIntro - To - Visual InspectionNoman Saeed100% (1)
- OPTO 307 SynoptophoreDocument4 pagesOPTO 307 SynoptophorecaponsharranerizaNo ratings yet
- OPT 424 Lectures1 To 3 - RGP Fitting Basics by Prof OriowoDocument67 pagesOPT 424 Lectures1 To 3 - RGP Fitting Basics by Prof Oriowoteamtruth50No ratings yet
- Tonometrybyarun 120727210025 Phpapp02Document98 pagesTonometrybyarun 120727210025 Phpapp02Sayoki GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gonioscopy: Aao ReadingDocument34 pagesGonioscopy: Aao ReadingTakwinNo ratings yet
- Tonometry: DR - Mehreen Afzal PGR Eye Unit IiDocument34 pagesTonometry: DR - Mehreen Afzal PGR Eye Unit IiUsman Imtiaz0% (1)
- Oxford Specialty Training: Training in Ophthalmology: Second EditionDocument37 pagesOxford Specialty Training: Training in Ophthalmology: Second EditionMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics: Force, Fluid Flow SensorsDocument40 pagesMechatronics: Force, Fluid Flow SensorsKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Part 1 MicroscopeDocument24 pagesWeek 2 Part 1 Microscopekimmynemil80No ratings yet
- Trial Frame RefractionDocument2 pagesTrial Frame RefractionJaneNo ratings yet
- Eye 2Document5 pagesEye 2Nadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionDocument16 pagesLecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Aberrometry NotesDocument3 pagesAberrometry NotesVero VillamorNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Origins of InequalitiesDocument1 pageOrigins of InequalitiesDuvNo ratings yet
- Broiler Analysis For 100 BroilersDocument18 pagesBroiler Analysis For 100 BroilersannmarieNo ratings yet
- Environmental Human Health123Document34 pagesEnvironmental Human Health123Sameer KsNo ratings yet
- Seven Zoe Back From Excerpt1Document3 pagesSeven Zoe Back From Excerpt1Jonathan VetromileNo ratings yet
- CHO-KLAT Version2.0 - Young2013Document5 pagesCHO-KLAT Version2.0 - Young2013Nay AungNo ratings yet
- Revised Crop Diseases - FormattedDocument98 pagesRevised Crop Diseases - FormattedMona ElsayedNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument5 pagesInterviewGracie S. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Hospital Staff ListDocument2 pagesHospital Staff ListOsheen KhanNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Growth-Democracy and Human CapitalDocument15 pagesThe Political Economy of Growth-Democracy and Human CapitalArchietasari NindyamurtiNo ratings yet
- Manual FFHH Oaci (Ingles)Document335 pagesManual FFHH Oaci (Ingles)Pran Antonio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Statistics Concepts and Controversies 9th Edition Moore Test Bank DownloadDocument11 pagesStatistics Concepts and Controversies 9th Edition Moore Test Bank DownloadKirk Neri100% (20)
- Let Me Be ClearDocument15 pagesLet Me Be ClearCrown Publishing Group85% (13)
- Kimera Exosomes, Kimera Labs, Inc. - 649343 - 09:01:2023 - FDADocument1 pageKimera Exosomes, Kimera Labs, Inc. - 649343 - 09:01:2023 - FDAseenfgNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 Control of Microbial GrowthDocument10 pagesCh. 7 Control of Microbial GrowthYousef DosouqiNo ratings yet
- Dark Purple Woman Photo Customer Service Resume PDFDocument1 pageDark Purple Woman Photo Customer Service Resume PDFSamuel ZendNo ratings yet
- Rhesus Iso-ImmunizationDocument20 pagesRhesus Iso-Immunizationahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- Coursework For PsychiatristDocument7 pagesCoursework For Psychiatristafjwoamzdxwmct100% (2)
- Live Litbing Utbk 2 Feb 2024Document14 pagesLive Litbing Utbk 2 Feb 2024marettaNo ratings yet
- Msds Citrapure - DryDocument2 pagesMsds Citrapure - DryKyle MccoyNo ratings yet
- Pashupalan Nirdeshika EnglishDocument122 pagesPashupalan Nirdeshika EnglishdpanickerNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument27 pagesFINALSAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Brochure XGENIA ENGDocument2 pagesBrochure XGENIA ENGTaherNo ratings yet
- Personal StatementDocument2 pagesPersonal StatementTom Hayes67% (3)
- Elektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDocument71 pagesElektrokardiografi: DR - Dr. Zaenal Muttaqien Sofro,, AIFM, Sport & Circ - Med School of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityNadyaNo ratings yet
- Cycloplegic Effect of 0.5%tropicamide and 0.5%phenylephrine Mixed Eye Drops - Objective Assessment in Japanese Schoolchildren With MyopiaDocument5 pagesCycloplegic Effect of 0.5%tropicamide and 0.5%phenylephrine Mixed Eye Drops - Objective Assessment in Japanese Schoolchildren With Myopiaal_dhi_01No ratings yet
- The Versatility of Cow Ghee An AyurvedaperspectiveDocument7 pagesThe Versatility of Cow Ghee An AyurvedaperspectivekapsicumadNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAscorbic Acid Drug StudyJam Mohammad100% (5)
- Ross, C. (2020) - PTSD As A Future-Oriented Survival Strategy. Richardson The Colin A. Ross Institute For Psychological TraumaDocument5 pagesRoss, C. (2020) - PTSD As A Future-Oriented Survival Strategy. Richardson The Colin A. Ross Institute For Psychological TraumaEraNo ratings yet