Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology 4
Biology 4
Uploaded by
Nitin DassCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Human Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFPrince Maurya89% (9)
- Renal Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesRenal Physiology Notescipa920% (1)
- Excretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesDocument2 pagesExcretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BIO235 Sp18 Lecture SyllabusDocument3 pagesBIO235 Sp18 Lecture Syllabusdrig0nNo ratings yet
- 2 - Renal PhysiologyDocument8 pages2 - Renal PhysiologyKunware TropaNo ratings yet
- Venture: An Initiative by Iitians, For Future Iitians !!!Document17 pagesVenture: An Initiative by Iitians, For Future Iitians !!!varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Excretory Products & Their Elimination Finsl Reviewed 1Document59 pagesMind Map Excretory Products & Their Elimination Finsl Reviewed 1vvzpf7k92sNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument7 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationKajal SinghNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document1 pageExcretion 1dianahwilliam33No ratings yet
- Biology 3Document10 pagesBiology 3Nitin DassNo ratings yet
- Aubf LecDocument97 pagesAubf Lechinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- VII - Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesVII - Urinary SystemGael QuingNo ratings yet
- 3 Renal SystemDocument30 pages3 Renal SystemgsnehaaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemJake SimNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Excretion - Humans & Plants - OriginalDocument36 pagesLife Processes - Excretion - Humans & Plants - Originalnouraft.07No ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument56 pagesExcretionChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument8 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationsinghsad8282No ratings yet
- Excretory System 2.0Document6 pagesExcretory System 2.0Kim DahyunNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PearsonsDocument13 pagesUrinary System Pearsonsblando.shaneNo ratings yet
- Vipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument55 pagesVipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationvanshpatelssisNo ratings yet
- EXCRETION PPT-teaching Note.Document62 pagesEXCRETION PPT-teaching Note.safeggNo ratings yet
- Renal PhsyiologyDocument9 pagesRenal PhsyiologyRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans IgcseDocument30 pagesExcretion in Humans Igcse20I1190 G-7CNo ratings yet
- Lec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerDocument12 pagesLec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerProfessor GhoulNo ratings yet
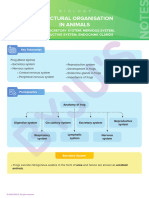
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Frog - Excretory System, Nervous System, Reproductive System, Endocrine GlandsDocument8 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Frog - Excretory System, Nervous System, Reproductive System, Endocrine GlandsKali Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint #5: Honors BiologyDocument19 pagesPowerpoint #5: Honors BiologyNylan AnyerNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec Renal Function I PDFDocument4 pagesAUBF Lec Renal Function I PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Sciences 2: Renal SystemDocument38 pagesBasic Medical Sciences 2: Renal Systemblessed23No ratings yet
- Renal FunctionDocument5 pagesRenal Functionchayiezen0301No ratings yet
- Ch-13 Excretion in HumansDocument7 pagesCh-13 Excretion in Humansdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemJM MatiasNo ratings yet
- Urinary System FinalsDocument7 pagesUrinary System Finalskatrinabondoc03No ratings yet
- REVIEWER Excretory SystemDocument2 pagesREVIEWER Excretory SystemLYSEA GINAULINo ratings yet
- Life Processes - ExcretionDocument18 pagesLife Processes - ExcretionraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- 12 ExcretionDocument4 pages12 ExcretionvedikaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Excretory System: OutlineDocument5 pagesHistology of Excretory System: Outlinekang seulgi can set me on fire with her gaze aloneNo ratings yet
- The Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.Document60 pagesThe Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.john ronald PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDocument46 pagesChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Bio 208 Urinary SystemDocument121 pagesBio 208 Urinary SystemNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- Excretory-SystemDocument90 pagesExcretory-SystemArchitaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument116 pagesUrinary SystemKiana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pha618 Lab ExcretoryDocument11 pagesPha618 Lab ExcretoryKirsten Shayne ManingasNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 pagesY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJNo ratings yet
- CROSS SECTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEYS (Autosaved)Document26 pagesCROSS SECTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEYS (Autosaved)Abraham Dawson machachaNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionsDocument1 pageKidney FunctionsShania DawnNo ratings yet
- QUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecDocument8 pagesQUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- 030722the Physiology of MicturitionDocument3 pages030722the Physiology of MicturitionAnnizah Paramitha100% (1)
- The Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCDocument29 pagesThe Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCHeaven SolNo ratings yet
- B2U3 Excretorysystem Notes 06Document5 pagesB2U3 Excretorysystem Notes 06Kudakwashe ChikazheNo ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalDocument22 pagesAnaphy FinalMa Sofiya Yazmin OroñaNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans IgcseDocument30 pagesExcretion in Humans IgcseAdrian KW NGNo ratings yet
- Excretion and Homeostatsis NotesDocument12 pagesExcretion and Homeostatsis NotesrissNo ratings yet
- 1A HISTO 2M Urinary TractDocument13 pages1A HISTO 2M Urinary TractallaineNo ratings yet
- Excretion NotesDocument5 pagesExcretion NoteskuluNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Finals Trans URINARYDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab Finals Trans URINARYJaisel Meris Ado-anNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Excretory System PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Excretory System PDFErica Ann Ical100% (1)
- Urinary EliminationDocument5 pagesUrinary EliminationClarence ViboraNo ratings yet
- Regulations of Body FluidsDocument26 pagesRegulations of Body FluidsMarcStep De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per PageDocument8 pagesLecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per Pageroselyn_061001No ratings yet
- PyelonephritisDocument59 pagesPyelonephritisGheyl GabrielNo ratings yet
- Kelim Rate of Drug Elimination From The Plasma T Time: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesKelim Rate of Drug Elimination From The Plasma T Time: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 6ravi2likeNo ratings yet
- Etextbook For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesEtextbook For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Full Chapter PDFchanndmoz100% (5)
- Kidney and Urine FormationDocument19 pagesKidney and Urine FormationXee JayNo ratings yet
- Aubf Review UermDocument18 pagesAubf Review UermZhiddah Japzon0% (1)
- Team Four: Activity 12Document81 pagesTeam Four: Activity 12Aura Naera Dandan Magarang100% (1)
- Drugs and Kidney Dec 28 2012Document43 pagesDrugs and Kidney Dec 28 2012Vin BitzNo ratings yet
- Ncert Line by Line MCQDocument9 pagesNcert Line by Line MCQyashpawarpatil4No ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24Document28 pagesX Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24chaitanya100% (3)
- Urinary FinalsDocument4 pagesUrinary FinalsAlliana Pauline AbanNo ratings yet
- Vet. Internal Medicine Text BookDocument674 pagesVet. Internal Medicine Text Bookuhgl hgluvtm100% (5)
- Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesUrinary SystemFlyEngineer100% (2)
- The Urinary System & Fluid BalanceDocument8 pagesThe Urinary System & Fluid BalanceMarianne DugosNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Cert Single Award Biol SOW KBI0 CVRDocument31 pagesEdexcel Cert Single Award Biol SOW KBI0 CVRFathimath IrashaNo ratings yet
- Aubf BrunzelDocument42 pagesAubf Brunzelabigail lausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document7 pagesChapter 26jess waldenNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument25 pagesCIE IGCSE Biologytgdzbspikio.comNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Class 11Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Class 11AlfaazNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument8 pagesEndocrine System IntroductionAlchemi Mij PoolscanNo ratings yet
- 6.1. AntihipertensiDocument52 pages6.1. AntihipertensiDada DoniNo ratings yet
- Case 8 GUS - AKIDocument210 pagesCase 8 GUS - AKIGroup 12 Sofia HanaNo ratings yet
- Biopharm Module Unit-7Document14 pagesBiopharm Module Unit-7Mitz Evan TabaranzaNo ratings yet
- QC JUli Abal2Document52 pagesQC JUli Abal2Rahayu HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysDocument106 pagesChapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysAlvinTercianoVitugNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 Ob Physical and Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument57 pagesChapter14 Ob Physical and Physiological Changes During Pregnancyth233No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Principles of Anatomy Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Gerard J Tortora Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Principles of Anatomy Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Gerard J Tortora Online PDF All Chapterjoeeeenhaeeey945100% (4)
Biology 4
Biology 4
Uploaded by
Nitin DassOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology 4
Biology 4
Uploaded by
Nitin DassCopyright:
Available Formats
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
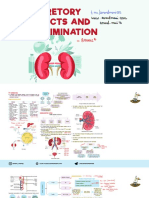
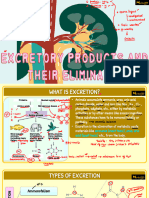
EXCRETION
4
CHAPTER
E
T
CONTENTS EXCRETION IN HUMAN BEING
• Excretion A pair of kidney is the main excretory organ in
U
human.
• Waste products
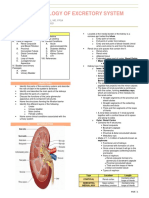
Structure and Function of Kidney in Human :
IT
• Excretion in Human Being • There are two bean shaped, dark red coloured
•
kidney placed just below the stomach, one on
Structure of Nephron each side of the mid dorsal line.
T
• Mechanism of urine formation • The depression is called hilus from where the
ureter originates and the renal artery and renal
• Excretion in Plant
S vein go in and out here.
Adrenal gland
IN
EXCRETION Inferior Renal gland
Vena cava
Renal vein
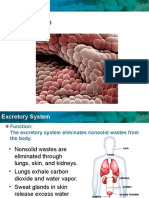
Excretion is the elimination of metabolic waste Pelvis
products from the body.
Medulla Kidney
WASTE PRODUCTS
E
Cortex
• Nitrogenous Waste Products. They are the Dorsal aorta
N
major waste products which are formed during Ureter
breakdown of extra amino acids, nucleic acids and
alkaloids. The important nitrogenous waste
-O
products are urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine
Urinary bladder
and ammonia.
• Non-nitrogenous Waste Products - Oxalic acid, Urethra
lactic acid. Figure : HUMAN URINARY SYSTEM
• Excess Chemicals - Excess minerals, drugs,
pigments, vitamins, hormones, cholesterol, etc. • Ureter entering through hilus expands. Medula on
A
inner side has cone like structure called renal
• Bile Pigments - Bilirubin, biliverdin and urochrome.
pyramids. Each kidney contains about one million
• CO2 nephrons. The functional unit of the kidney is the
• Excess water.
nephron.
Excretion 24
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
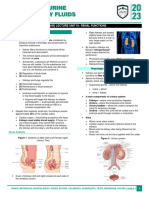
STRUCTURE OF NEPHRON MECHANISM OF URINE FORMATION
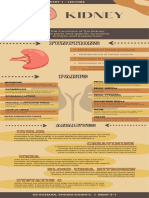
• Each nephron consists of a round malpighian It has four steps - ultra filtration, selective
body formed by Bowman’s capsule filled with reabsorption, secretion and concentration.
capillary net work afferent and efferent arterioles. (i) Ultra Filtration. Blood flows inside glomerulus
Afferent means incoming, Efferent means under pressure due to narrowness of efferent
E
outgoing called Glomerulus or Malpighian arteriole. As a result it undergoes pressure
corpuscles. The malpighian tubule is divided into filtration or ultrafiltration. All small volume
T
3 parts forming a shaped convoluted tubule. solutes (e.g., urea, uric acid, amino acids,
hormones, glucose, ions, vitamins) and water are
(A) The proximal tubule - Nearest Bowman’s
filtered out and enter the Bowmans' capsule. The
U
capsule.
product is called nephric or glomerular filtrate.
(B) Henle loop - It is a 'U' shape thin tube like Its volume is 125 ml/min (180 litres/day).
IT
structure.
(ii) Reabsorption. Nephric filtrate is also called
(C) Distal tubule - Join collecting tuble. primary urine. It passes into proximal convoluted
tubule. The same is surrounded by peritubular
capillaries. The latter reabsorb all the useful
T
Efferent components of nephric filtrate, e.g, glucose,
Afferent arteriole arteriole
amino acids, vitamins C, calcium, potassium,
Glomerulus
Bowman's
S sodium, chloride, bicarbonate and water (75%).
capsule Proximal Selective absorption also occurs in the region of
IN
convoluted
distal convoluted tubule.
tubule
(iii) Secretion (Augmentation). It occurs mostly in
Collecting
duct the distal convoluted tubule which is also
Descending surrounded by peritubular capillaries. Smaller
limp of loop
of Henle amount of tubular secretion also takes palce in the
E
Ascending area of proximal convoluted tubule. Tubular
Limp of loop secretion is active secretion of waste products by
of Henle
N
the blood capillaries. It cause removal of all the
Vasa recta
waste products from blood, viz. urea, uric acid,
creatinine. Extra salts, K+ and H+ are also secreted
-O
Figure : REPRESENTATION OF A NEPHRON
into urinary tubule to maintain a proper
concentration and pH of the urine.
The ascending limb of Henle’s loop again gives
(iv) Concentration of the Urine. 75% of water
second convoluted tubule opening into collecting content of nephric filtrate is reabsorbed in the
tubule and finally into lager tubule known as duct region of proximal convoluted tubule. Some 10%
of Bellini, which opens into the pelvis of ureter
A
of water passes out of the filtrate through osmosis
at the apex of renal pyramids. The entire kidney in the area of loop of Henle. It is because loops of
tubule is surrounded by blood capillaries called Henle are immersed in hyper-osmotic interstitial
vasa recta. fluid. Further concentration takes place
Excretion 25
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
(v) Resins. They are oxidation products of
aromatic oils.
(vi) Gums. They are degradation products of cell
wall.
Mechanism of Excretion in Plante:
Plants do not have any mechanism to collect,
E
transport and throw out their waste products. They
have adopted varied strategies to protect their
T
living cell from waste products.
(i) Old Leaves. Waste products are stored in older
leaves which soon fall off.
U
(ii) Old Xylem. Resins, gums, tannins and other
in the area of collecting tubule in the presence of
waste products are deposited in the old xyem
hormone called antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or
which soon becomes nonfunctional e.g. Hard
IT
vasopressin. Absence of Antidiuretic hormone
wood.
produces a dilute urine. Hormone action,
(iii) Bark. Bark consists of dead cells which is
therefore, maintains osmotic concentration of
peeled off periodically. Tannins and other wastes
body fluids. Deficiency of ADH causes excessive,
T
are deposited in the bark. Incidentally, tannins are
repeated dilute urination (diabetes insipidus).
raw material for dyes and inks.
The process of passes urine in called Micturition.
(iv) Central Vacuole. Most plant waste products
EXCRETION IN PLANTS
S are stored in central vacuole of their cells. They
are unable to influence the working of cytoplasm
IN
Plants do not produce nitrogeneous wastes like due to presence of a selectively permeable
urea and uric acid because extra amino acids and membrane called tonoplast.
nucleotides are not formed. They produce other (v) Root Excretion. Some waste substances are
types of waste products, called secondary actually excreted by the plants in the region of
metabolites, e.g., alkaloids, tannins, aromatic oils. their roots.
(i) Nitrogenous Waste Products. They are (vi) Detoxification. The toxi oxalic acid is
E
byproducts of general metabolism. The common detoxified by formation of calcium oxalate which
ones are alkaloids, e.g., quinine, morphine, gets crystallized into needles (raphides), prism
N
atropine. (prismatic crystals), stars (sphaeraphides) and
(ii) Organic Acids. They are metabolic crystal sand. Excess of calcium is also
intermediates. Some of them are without any other precipitated as calcium carbonate crystals, e.g.
-O
use. Rather on accumulation they may prove toxic, cystolith.
e.g., oxalic acid. (vii) Salt Glands. They excrete excess salts
(iii) Tannins. They are complex aromatic obtained from the habitat.
compounds which are formed as secondary
metabolites.
(iv) Latex. It is an emulsion of varied
A
composition which is exereted by special tubular
cells called laticifers.
Excretion 26
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
EXERCISE # 1
A. Single Choice Type Questions Q.9 A mammal excretes nitrogen in the form of -
(A) Ammonium ions (B) Amino acids
Q.1 Useful materials filtered out in nephric filtrate (C) Urea (D) Uric acid
are mostly reabsorbed in the area of -
E
(A) Bowman's capsule Q.10 Which one of the following sets of animals
(B) Distal convoluted tubule produces the same substances as their chief
(C) Loop of Henle excretory product ?
T
(D) Proximal convoluted tubule (A) Cockroach, camel and lizard
(B) Man, dog and camel
Q.2 Contractile vacuole of Amoeba takes part in -
U
(C) Amoeba, ant and antelope
(A) Locomotion
(D) Fowl, fish and frog
(B) Digestion of food
(C) Ingestion of food Q.11 A Malpighian tubule empties urine into the
IT
(D) Osmoregulation (A) Gut (B) Coelom
(C) Lymph (D) Ureters
Q.3 Tannins are deposited in -
(A) Bark (B) Old xylem Q.12 Kidneys are not only organs of excretion.Their
T
(C) Sieve tubes (D) Both A and B work is supplemented by -
(A) Liver (B) Heart
Q.4 Every plant cell has a dump for waste
(C) Large intestine (D) Skin
products. It is -
(A) Cytoplasm (B) Central vacuole
S Q.13 The conversin of protein waste, the ammonia
(C) Golgi apparatus (D) Lysosome into urea occurs mainly in -
IN
Q.5 Basic filteration unit of kidney is - (A) Kidney (B) Lungs
(A) Ureter (B) Glomerulus (C) Liver (D) Intestine
(C) Urethra (D) Collecting tubule Q.14 The Bowman's capsule functions as a
Q.6 Dilution of concentration of urine is (A) Filter
determined by availability of - (B) Suction pump
E
(A) Hormone thyroxine (C) Egestion
(B) Hormone thymosine (D) All of the above
N
(C) Hormone ADH Q.15 Which of the following is the part of kidney ?
(D) Both A and B (A) Pelvis (B) Ileum
Q.7 Excretion means - (C) Fibula (D) Henle loop
-O
(A) Removal of substances present in excess
Q.16 The basic unit of a vertebrate kidney is the -
(B) Formation of those substances that have
(A) Ureter
some role in the body
(B) Nephron
(C) Removal of such substances that have
(C) Malpighian tubule
never been part of the body
(D) Islets of langerhans
(D) All of the above
Q.17 Excess of water in urine resulting from
A
Q.8 Ureotelic animals are those that eliminate the
kidney failure is known as -
nitrogenous wastes predominatly in the form (D) Diabetes
of - (A) Ureotelic
(B) Uricotelic insipidus
(A) Uric acid (B) Ammonia
(C) Amino acids (D) Urea (C) Diabetes Malitus
Excretion 27
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
A ONE INSTITUTE – A SYNONYM TO SUCCESS, OFFICE – SCO 322, SECTOR 40 D, CHANDIGARH
PRE - FOUNDATION
EXERCISE # 2
A. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.20 Describe the mechanism of urine formation.
Q.1 Define excretion ?
E
Q.21 Describe the mechanism by which human
Q.2 What are waste products ? beings are able to regulate the concentration
of urine.
T
Q.3 What is excretory system ?
Q.4 What is the function of ADH ?
C. Long Answer Type Questions
U
Q.5 What is unit of human kidney ? Q.22 Describe the various components of urinary
system of man.
IT
Q.6 What is glomerulus ?
Q.23 Explain the structure of nephron with the help
Q.7 Name the components of a Malpighian of a labelled diagram.
capsule.
T
Q.24 Draw a diagram of the human urinary system
Q.8 Name the structure which absorb glucose in and label in it
nephron. (i) Kidney (ii) Ureter (iii) Urinary bladder
Q.9 Define micturition.
S (iv) Urethra.
IN
Q.10 What is Bownman's capsule ?
Q.11 Name a waste product of plants which is used
as medicine.
Q.12 Where is urine stored in the body ?
E
Q.13 Write the name of membrane of vacuole.
N
B. Short Answer Type Questions
-O
Q.14 Enumerate functions of kidney.
Q.15 Named the various waste products produced
in human beings.
Q.16 Named the different waste products by plants.
Q.17 How are plants able to manage their waste
A
products ?
Q.18 Write a short note on ultra filteration.
Q.19 Write a short note on secretion.
Excretion 28
A – ONE INSTITUTE OF COMPETITIONS, PH – 9872662038, 9872642264
You might also like
- Human Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFPrince Maurya89% (9)
- Renal Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesRenal Physiology Notescipa920% (1)
- Excretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesDocument2 pagesExcretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BIO235 Sp18 Lecture SyllabusDocument3 pagesBIO235 Sp18 Lecture Syllabusdrig0nNo ratings yet
- 2 - Renal PhysiologyDocument8 pages2 - Renal PhysiologyKunware TropaNo ratings yet
- Venture: An Initiative by Iitians, For Future Iitians !!!Document17 pagesVenture: An Initiative by Iitians, For Future Iitians !!!varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Excretory Products & Their Elimination Finsl Reviewed 1Document59 pagesMind Map Excretory Products & Their Elimination Finsl Reviewed 1vvzpf7k92sNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument7 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationKajal SinghNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document1 pageExcretion 1dianahwilliam33No ratings yet
- Biology 3Document10 pagesBiology 3Nitin DassNo ratings yet
- Aubf LecDocument97 pagesAubf Lechinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- VII - Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesVII - Urinary SystemGael QuingNo ratings yet
- 3 Renal SystemDocument30 pages3 Renal SystemgsnehaaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemJake SimNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Excretion - Humans & Plants - OriginalDocument36 pagesLife Processes - Excretion - Humans & Plants - Originalnouraft.07No ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument56 pagesExcretionChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument8 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationsinghsad8282No ratings yet
- Excretory System 2.0Document6 pagesExcretory System 2.0Kim DahyunNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PearsonsDocument13 pagesUrinary System Pearsonsblando.shaneNo ratings yet
- Vipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument55 pagesVipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationvanshpatelssisNo ratings yet
- EXCRETION PPT-teaching Note.Document62 pagesEXCRETION PPT-teaching Note.safeggNo ratings yet
- Renal PhsyiologyDocument9 pagesRenal PhsyiologyRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans IgcseDocument30 pagesExcretion in Humans Igcse20I1190 G-7CNo ratings yet
- Lec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerDocument12 pagesLec-1h-Excretory System ReviewerProfessor GhoulNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Frog - Excretory System, Nervous System, Reproductive System, Endocrine GlandsDocument8 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Frog - Excretory System, Nervous System, Reproductive System, Endocrine GlandsKali Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint #5: Honors BiologyDocument19 pagesPowerpoint #5: Honors BiologyNylan AnyerNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec Renal Function I PDFDocument4 pagesAUBF Lec Renal Function I PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Sciences 2: Renal SystemDocument38 pagesBasic Medical Sciences 2: Renal Systemblessed23No ratings yet
- Renal FunctionDocument5 pagesRenal Functionchayiezen0301No ratings yet
- Ch-13 Excretion in HumansDocument7 pagesCh-13 Excretion in Humansdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemJM MatiasNo ratings yet
- Urinary System FinalsDocument7 pagesUrinary System Finalskatrinabondoc03No ratings yet
- REVIEWER Excretory SystemDocument2 pagesREVIEWER Excretory SystemLYSEA GINAULINo ratings yet
- Life Processes - ExcretionDocument18 pagesLife Processes - ExcretionraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- 12 ExcretionDocument4 pages12 ExcretionvedikaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Excretory System: OutlineDocument5 pagesHistology of Excretory System: Outlinekang seulgi can set me on fire with her gaze aloneNo ratings yet
- The Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.Document60 pagesThe Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.john ronald PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDocument46 pagesChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Bio 208 Urinary SystemDocument121 pagesBio 208 Urinary SystemNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- Excretory-SystemDocument90 pagesExcretory-SystemArchitaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument116 pagesUrinary SystemKiana RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pha618 Lab ExcretoryDocument11 pagesPha618 Lab ExcretoryKirsten Shayne ManingasNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 pagesY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJNo ratings yet
- CROSS SECTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEYS (Autosaved)Document26 pagesCROSS SECTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE KIDNEYS (Autosaved)Abraham Dawson machachaNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionsDocument1 pageKidney FunctionsShania DawnNo ratings yet
- QUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecDocument8 pagesQUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- 030722the Physiology of MicturitionDocument3 pages030722the Physiology of MicturitionAnnizah Paramitha100% (1)
- The Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCDocument29 pagesThe Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCHeaven SolNo ratings yet
- B2U3 Excretorysystem Notes 06Document5 pagesB2U3 Excretorysystem Notes 06Kudakwashe ChikazheNo ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalDocument22 pagesAnaphy FinalMa Sofiya Yazmin OroñaNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans IgcseDocument30 pagesExcretion in Humans IgcseAdrian KW NGNo ratings yet
- Excretion and Homeostatsis NotesDocument12 pagesExcretion and Homeostatsis NotesrissNo ratings yet
- 1A HISTO 2M Urinary TractDocument13 pages1A HISTO 2M Urinary TractallaineNo ratings yet
- Excretion NotesDocument5 pagesExcretion NoteskuluNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Finals Trans URINARYDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab Finals Trans URINARYJaisel Meris Ado-anNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Excretory System PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Excretory System PDFErica Ann Ical100% (1)
- Urinary EliminationDocument5 pagesUrinary EliminationClarence ViboraNo ratings yet
- Regulations of Body FluidsDocument26 pagesRegulations of Body FluidsMarcStep De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per PageDocument8 pagesLecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per Pageroselyn_061001No ratings yet
- PyelonephritisDocument59 pagesPyelonephritisGheyl GabrielNo ratings yet
- Kelim Rate of Drug Elimination From The Plasma T Time: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesKelim Rate of Drug Elimination From The Plasma T Time: Pharmacology Semester 1 Page 1 of 6ravi2likeNo ratings yet
- Etextbook For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesEtextbook For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Full Chapter PDFchanndmoz100% (5)
- Kidney and Urine FormationDocument19 pagesKidney and Urine FormationXee JayNo ratings yet
- Aubf Review UermDocument18 pagesAubf Review UermZhiddah Japzon0% (1)
- Team Four: Activity 12Document81 pagesTeam Four: Activity 12Aura Naera Dandan Magarang100% (1)
- Drugs and Kidney Dec 28 2012Document43 pagesDrugs and Kidney Dec 28 2012Vin BitzNo ratings yet
- Ncert Line by Line MCQDocument9 pagesNcert Line by Line MCQyashpawarpatil4No ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24Document28 pagesX Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24chaitanya100% (3)
- Urinary FinalsDocument4 pagesUrinary FinalsAlliana Pauline AbanNo ratings yet
- Vet. Internal Medicine Text BookDocument674 pagesVet. Internal Medicine Text Bookuhgl hgluvtm100% (5)
- Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesUrinary SystemFlyEngineer100% (2)
- The Urinary System & Fluid BalanceDocument8 pagesThe Urinary System & Fluid BalanceMarianne DugosNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Cert Single Award Biol SOW KBI0 CVRDocument31 pagesEdexcel Cert Single Award Biol SOW KBI0 CVRFathimath IrashaNo ratings yet
- Aubf BrunzelDocument42 pagesAubf Brunzelabigail lausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document7 pagesChapter 26jess waldenNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE BiologyDocument25 pagesCIE IGCSE Biologytgdzbspikio.comNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Class 11Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Class 11AlfaazNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument8 pagesEndocrine System IntroductionAlchemi Mij PoolscanNo ratings yet
- 6.1. AntihipertensiDocument52 pages6.1. AntihipertensiDada DoniNo ratings yet
- Case 8 GUS - AKIDocument210 pagesCase 8 GUS - AKIGroup 12 Sofia HanaNo ratings yet
- Biopharm Module Unit-7Document14 pagesBiopharm Module Unit-7Mitz Evan TabaranzaNo ratings yet
- QC JUli Abal2Document52 pagesQC JUli Abal2Rahayu HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysDocument106 pagesChapter 18 URINARY SYSTEM SeeleysAlvinTercianoVitugNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 Ob Physical and Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument57 pagesChapter14 Ob Physical and Physiological Changes During Pregnancyth233No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Principles of Anatomy Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Gerard J Tortora Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Principles of Anatomy Physiology 2Nd Asia Pacific Edition Gerard J Tortora Online PDF All Chapterjoeeeenhaeeey945100% (4)