Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE O Level Magnetism-Notes
IGCSE O Level Magnetism-Notes
Uploaded by
SajidMansoorKuriyedam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views4 pages1. A magnet produces a magnetic field and has stronger magnetic poles at its ends.
2. Magnetic materials like iron are attracted to magnets, while non-magnetic materials like plastic are not.
3. Permanent magnets retain magnetism, while temporary magnets only become magnetic near a permanent magnet or when electricity is applied.
Original Description:
IGCSE O level magnetism-notes
Original Title
IGCSE O level magnetism-notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. A magnet produces a magnetic field and has stronger magnetic poles at its ends.
2. Magnetic materials like iron are attracted to magnets, while non-magnetic materials like plastic are not.
3. Permanent magnets retain magnetism, while temporary magnets only become magnetic near a permanent magnet or when electricity is applied.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views4 pagesIGCSE O Level Magnetism-Notes
IGCSE O Level Magnetism-Notes
Uploaded by
SajidMansoorKuriyedam1. A magnet produces a magnetic field and has stronger magnetic poles at its ends.
2. Magnetic materials like iron are attracted to magnets, while non-magnetic materials like plastic are not.
3. Permanent magnets retain magnetism, while temporary magnets only become magnetic near a permanent magnet or when electricity is applied.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Magnetism
A magnet is an object that produces magnetic force.
Properties of magnet
1. A magnet has a magnetic field around it.
2. When freely suspended, a magnet aligns in the N-S direction of earth.
3. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
4. Magnetic strength is strongest at the poles.
Magnetic and non-magnetic materials
The materials to which magnets are attracted are called magnetic materials.
Eg: iron, steel, cobalt, nickel etc.….
The materials to which magnets are not attracted are called non-magnetic materials.
Eg: Copper, Aluminum, Lead, Brass, Rubber, Wood, Plastic
Permanent and temporary magnet
A magnet that retains its magnetic properties after the removal of the magnetizing force is
called Permanent magnet.
Eg: Bar magnet
A material that does not retain its magnetic property after the removal of the magnetizing
force is called temporary magnet.
Eg: paper clips attracted to magnet, electromagnet (solenoid)
Induced magnetism
When a piece of unmagnetized material is brought near a permanent magnet, it becomes a
temporary magnet by itself is called induced magnetism.
Ferromagnets
The metals or alloys which are strongly magnetized are called ferromagnets. They mainly
contain iron, nickel and cobalt.
Hard and Soft magnetic materials
Magnetic materials which are difficult to magnetize and demagnetize are called Hard
magnetic materials. It is used to make permanent magnets.
Eg: Steel, Alnico
Magnetic materials which are easy to magnetize and demagnetize are called Soft magnetic
materials. It is used as core in the transformer.
Eg: iron
Magnetization
The process that makes a magnetic material magnetic is called magnetization. The removal of
magnetic property of a magnet is called De-magnetization.
Magnetization methods
1. Stroking- The magnetic material is stroked with the same pole of the magnet.
The magnet is lifted and again bring the same pole to starting end. The process is
repeated until it becomes a magnet.
2. Electrical method- keep the magnet inside a long coil of wire and pass a large DC into it.
De-Magnetization methods
1. Heating the magnet.
2. Hammering the magnet.
3. Electrical method- keep the magnet inside a long coil of wire and pass AC into it.
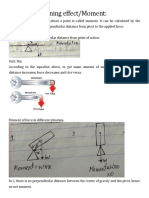
Magnetic Field
It is the region around a magnet where it experiences a force due to another magnet or
magnetic material.
Magnetic Field Lines: the imaginary lines around a magnet which represent a magnetic field.
Properties of Magnetic Field
1. It is always directed from N to S.
2. Near the poles, the field lines are crowded. This gives rise to a strong magnetic field
near the poles.
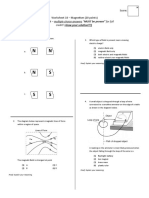
Draw magnetic field patterns for the following cases
a. Single Bar magnet
b. When the bar magnets attract each other
c. Bar magnets repel each other
Solenoid
A solenoid (electromagnet) is a straight conductor/ wire wound in the form of a cylinder.
The magnetic field around a solenoid (a long coil) is identical to the magnetic field of a bar
magnet.
A solenoid with a soft iron core is nearly 1000 times stronger than that of a solenoid without
a core.
The strength of an electromagnet’s magnetic field may be increased by:
• Increasing the current in the coil.
• Inserting a soft iron into the coil.
• Adding more turns to the coil.
Electromagnets have an advantage over permanent magnets as they can be
a. turned on and off
b. the magnetic field strength can be changed.
You might also like
- Introduction To Industrial Automation PDFDocument458 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Automation PDFEr Amarsinh R93% (15)
- Uganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursDocument4 pagesUganda Certificate of Education Physics Paper 4 Time: 2 HoursTamale John PaulNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity - Notes PDFDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity - Notes PDFsabastian johnsNo ratings yet
- Light Prism Pandathe Test2 Question PaperDocument4 pagesLight Prism Pandathe Test2 Question Paperboltu100% (1)
- GSM g20 Alarm System ManualDocument14 pagesGSM g20 Alarm System Manualmartig87No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current ExerciseDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current Exercisemaatla monkge100% (1)
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-P2.01 Energy Stores, Transfers and ConservationDocument21 pagesChapter-2-P2.01 Energy Stores, Transfers and ConservationMicheal XavierNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument13 pagesMagnetism Notesmaatla monkge100% (1)
- 2ND Term S2 Physics - 2Document39 pages2ND Term S2 Physics - 2Adelowo DanielNo ratings yet
- Theory Workbook (TE) Chapter 2Document24 pagesTheory Workbook (TE) Chapter 2scribduser0811972No ratings yet
- Show All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Document1 pageShow All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Yzelle SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Phy Unit 2 Notes: Mains ElectricityDocument9 pagesPhy Unit 2 Notes: Mains Electricityarin ahmedNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForceDocument4 pagesTurning Effect of ForceIbrahim Khurram100% (1)
- A Level Notes On Group 1 and 2Document16 pagesA Level Notes On Group 1 and 2kmoiz427No ratings yet
- Pendulum ExpDocument4 pagesPendulum ExpRoyston EbenezerNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field.Document32 pages3.2 Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field.Ishraqi IlyasNo ratings yet
- Q1L7 ElectricityDocument61 pagesQ1L7 ElectricityCarmella Raguindin100% (2)
- 4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsDocument9 pages4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsIshraque MahmudNo ratings yet
- Magnet 4 DocDocument4 pagesMagnet 4 DocMIS NURUL IMAN JakbarNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersDocument2 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersVicious core100% (1)
- Turning Effects of Forces PDFDocument6 pagesTurning Effects of Forces PDFMazharul SamiNo ratings yet
- F Ma FrictionDocument5 pagesF Ma FrictionBen100% (1)
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Document4 pagesO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic EffectsDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic EffectsTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Document12 pagesWaves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Khushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document22 pagesTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 6 - Turning Effect of ForcesDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 6 - Turning Effect of ForcesFatimah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds For MYP 3Document18 pagesElements and Compounds For MYP 3Maira ButtNo ratings yet
- Physics DC CircuitsDocument24 pagesPhysics DC CircuitsJenessaNo ratings yet
- G Field PDFDocument25 pagesG Field PDFmughees_itcompNo ratings yet
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-20 Magnetic Effect PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-20 Magnetic Effect PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Document4 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Sharuvindan Nair100% (1)
- PHYSICS - 10 First Term ExaminationDocument11 pagesPHYSICS - 10 First Term ExaminationFatima MohammadNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument5 pagesICSE Class 10 Physicssudhir_narang_3No ratings yet
- Chem Energetics TestDocument7 pagesChem Energetics TestJkaurbhsNo ratings yet
- Igcse Sound Physics PowerpointDocument28 pagesIgcse Sound Physics Powerpointmaryam2024igcseNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionzaira_rq3551No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11AdeenaNo ratings yet
- Momentum MCQ 211Document4 pagesMomentum MCQ 211Kariem Mohamed Ragab Hamed100% (1)
- UNIT 6 Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument16 pagesUNIT 6 Magnetism & ElectromagnetismT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- 8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIDocument13 pages8.1-Transport - in - Plants - Igcse-Cie-Biology - Solved OLIAmber TeacherNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDocument2 pagesRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument184 pagesPhysicsPiyush BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Topic-18: Static Electricity: Electrostatic PhenomenaDocument9 pagesTopic-18: Static Electricity: Electrostatic Phenomenamuhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 12Document7 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 12Ekam KaurNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentkunalNo ratings yet
- Moment of Forces WorksheetDocument4 pagesMoment of Forces WorksheetjessicaNo ratings yet
- 4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Document31 pages4003 Physics Section Revision Guide-1Noel MakambaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - 1 Name of The Student: - Class:-10 Sec - Academic YearDocument4 pagesWork Sheet - 1 Name of The Student: - Class:-10 Sec - Academic YearunniNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Conceptual QuestionsDocument1 pageVectors - Conceptual QuestionsMalaika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 9701 w02 QP 4Document12 pages9701 w02 QP 4Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- A2 Physics DefinitionsDocument4 pagesA2 Physics DefinitionssallyohhNo ratings yet
- IGCSE PHYSICS MagnetismDocument30 pagesIGCSE PHYSICS MagnetismSajidMansoorKuriyedamNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetic FieldsDocument12 pagesMagnetism: Magnetic FieldsShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument7 pagesMagnetismNaeem MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: K30 ES, K30 Vario, K30 CompetitionDocument20 pagesOperating Instructions: K30 ES, K30 Vario, K30 CompetitionIgor RamosNo ratings yet
- Determining The Initial States in Forward-Backward LteringDocument8 pagesDetermining The Initial States in Forward-Backward LteringgimmiNo ratings yet
- Hand-Book-2018-2019 WayabaDocument62 pagesHand-Book-2018-2019 WayabaNisala DulajNo ratings yet
- Fpga Implementation of Fir Filter in Signal Processing: AbstractDocument4 pagesFpga Implementation of Fir Filter in Signal Processing: AbstractShafiullaShaikNo ratings yet
- RCA 14M041 Service ManualDocument34 pagesRCA 14M041 Service ManualferdialvascribdNo ratings yet
- TK-C Transmitter PDFDocument4 pagesTK-C Transmitter PDFGopal HegdeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PheripheralsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To PheripheralsIris OnidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Msbte Asked QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Msbte Asked Questionsrutu surve (Ru.)No ratings yet
- Appnote Trf796x Pwramp 4wDocument24 pagesAppnote Trf796x Pwramp 4wchiase83No ratings yet
- BA 211 Exercise 4Document3 pagesBA 211 Exercise 4Eden Mae DeGuzmanNo ratings yet
- Powerful Open Software Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesPowerful Open Software Key FeaturesCristian SmarandacheNo ratings yet
- OM Narada NPFC Series Li Ion 0423 V8Document26 pagesOM Narada NPFC Series Li Ion 0423 V8UnstoppableNo ratings yet
- Digsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionDocument17 pagesDigsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionBra BicabaNo ratings yet
- MF COMPACT-OPTIMUM EN E03.12Document102 pagesMF COMPACT-OPTIMUM EN E03.12felix camusNo ratings yet
- Elective I (Math)Document2 pagesElective I (Math)RajulNo ratings yet
- DSD Lab 10Document8 pagesDSD Lab 10Shayan AmjadNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: PCG-GRS150/GRS170Document12 pagesService Manual: PCG-GRS150/GRS170Andrei RadulescuNo ratings yet
- (Install) Aerisa 1250D IpureairDocument2 pages(Install) Aerisa 1250D IpureairChad100% (1)
- DDX 2100Document18 pagesDDX 2100Octavio RamirezNo ratings yet
- MP Viva QuestionDocument7 pagesMP Viva QuestionShreerama Samartha G BhattaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Bus Bar Protection: GE MultilinDocument92 pagesFundamentals of Bus Bar Protection: GE Multilinsonu200186100% (1)
- GUI GuideDocument606 pagesGUI GuideAnLeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Instruments Catalogue GFUVE ElectronicsDocument172 pagesElectrical Instruments Catalogue GFUVE ElectronicsMuhd Nu'man HNo ratings yet
- BIRDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDocument44 pagesBIRDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDAnne Mary FabregasNo ratings yet
- UENR88640001 EVC600I Automatic Voltage Regulator (UENR8864-01)Document9 pagesUENR88640001 EVC600I Automatic Voltage Regulator (UENR8864-01)Carlos U. CallirgosNo ratings yet
- 81211M Position 05-2021 EngDocument19 pages81211M Position 05-2021 Engperop123No ratings yet
- Rancangan Dan Uji Coba Otomatisasi Irigasi Kendi DDocument15 pagesRancangan Dan Uji Coba Otomatisasi Irigasi Kendi DridhodiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Synchronous Sequential CircuitsDocument56 pagesChapter 06 Synchronous Sequential Circuitskidgod2111No ratings yet