Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sigma
Sigma
Uploaded by
tkiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sigma
Sigma
Uploaded by
tkiCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Notes: Sigma
Definition and Concept:
Sigma (Σ) is the 18th letter of the Greek alphabet, often used as a symbol in
various fields, including mathematics, statistics, science, and engineering.
In mathematics, sigma represents the summation notation, indicating the sum of
a sequence of numbers.
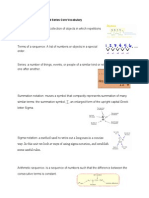
Summation Notation:
Σ (Sigma) notation is a concise way to represent the sum of a series of terms.
It involves an expression written below the sigma symbol, indicating the terms
to be summed, and the range of values for which the sum is taken.
Components of Σ Notation:
The expression to the right of the sigma represents the term to be summed.
The variable below the sigma indicates the starting value of the summation.
The upper limit of the summation is usually indicated above the sigma symbol.
The symbol 'n' is commonly used as the variable, but other letters can be used
as well.
Examples:
∑(i = 1 to 5) i
This notation represents the sum of integers from 1 to 5: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
= 15.
∑(k = 0 to 3) 2^k
This represents the sum of the powers of 2 for k ranging from 0 to 3: 2^0 +
2^1 + 2^2 + 2^3 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 = 15.
∑(j = 1 to n) j^2
This represents the sum of squares of integers from 1 to n.
Applications:
Sigma notation is used to simplify and represent complex sums in mathematics,
physics, and engineering.
It's commonly used to calculate the total value of sequences, series, and
mathematical expressions involving summation.
Common Properties:
The order of the terms in the sum does not affect the final result.
A constant factor can be taken out of the sum: ∑(i = 1 to n) c * f(i) = c * ∑(i
= 1 to n) f(i).
Conclusion:
Sigma notation, represented by the Greek letter Σ, is a powerful tool in
mathematics for expressing and calculating the sums of sequences and series.
It simplifies the representation of complex mathematical expressions involving
summation.
You might also like
- Summation: Tal. If Numbers Are Added Sequentially From Left To Right, IDocument6 pagesSummation: Tal. If Numbers Are Added Sequentially From Left To Right, INelly GómezNo ratings yet
- 2012 Acjc Paper 1Document5 pages2012 Acjc Paper 1Aditya KNo ratings yet
- Arithmos, Meaning "Number," and Technē, Referring To An Art or Skill. Thus, Arithmetic Means The Art of Numbers. The Numbers Used in ArithmeticDocument1 pageArithmos, Meaning "Number," and Technē, Referring To An Art or Skill. Thus, Arithmetic Means The Art of Numbers. The Numbers Used in ArithmeticRhoda Grace Agustin IlisanNo ratings yet
- Notes Sum OperatorDocument2 pagesNotes Sum OperatorMariusTestNo ratings yet
- On Net Regular Signed GraphsDocument8 pagesOn Net Regular Signed GraphsMia AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Sequences and Series Core VocabularyDocument3 pagesChapter 8 Sequences and Series Core Vocabularyapi-288055619No ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Sigma NotationDocument11 pagesPre Calculus Sigma NotationStudy BunnyNo ratings yet
- 1Document26 pages1rbsingh1967No ratings yet
- Arithmetic Ang Geometric SequencesDocument7 pagesArithmetic Ang Geometric SequencesAngelica LaraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12Document1 pageMathematics GR 12reacharunkNo ratings yet
- Series and Sigma NotationDocument7 pagesSeries and Sigma NotationCaren Pelayo JonelasNo ratings yet
- Summation NotesDocument9 pagesSummation NotesnunterhunterNo ratings yet
- HILL, Lester S. - Cryptography in An Algebraic AlphabetDocument8 pagesHILL, Lester S. - Cryptography in An Algebraic AlphabetDouglas DanielNo ratings yet
- Bks MaaSL Ccuu Syov XxaannDocument14 pagesBks MaaSL Ccuu Syov XxaannGametogameNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument45 pagesInformation SecurityAryan Akshay VerduNo ratings yet
- Rudiments of Io AnalysisDocument18 pagesRudiments of Io AnalysisJay-ar MiraNo ratings yet
- Important Rules For Solving Arithmetic OperationsDocument8 pagesImportant Rules For Solving Arithmetic OperationsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences and SumsDocument4 pagesArithmetic Sequences and SumsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- SigmaDocument10 pagesSigmaAlphaNo ratings yet
- Explaination and AnalysisDocument5 pagesExplaination and AnalysisMOHAMAD AKMAL MOHAMAD ZAINALNo ratings yet
- Bottom Schur FunctionsDocument16 pagesBottom Schur Functionsapi-26401608No ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Document3 pagesSequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Sharon RivaniNo ratings yet
- 2014 Ensenar A Investigar Una Didactica Nueva de La Investigacion en Ciencias Sociales y HumanasDocument17 pages2014 Ensenar A Investigar Una Didactica Nueva de La Investigacion en Ciencias Sociales y HumanasMica ElaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27Document4 pagesLecture 27Syeda Farkhanda Batool NaqviNo ratings yet
- Practical No-1: AIM: Write and Implement A Program To Simulate Deterministic Finite Automata TheoryDocument9 pagesPractical No-1: AIM: Write and Implement A Program To Simulate Deterministic Finite Automata TheoryAtharvaNo ratings yet
- Final Report 6500Document4 pagesFinal Report 6500Dipesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Find Terms of Sequences Given The General or NTH Term. Convert Between Sigma Notation and Other Notation For A SeriesDocument99 pagesFind Terms of Sequences Given The General or NTH Term. Convert Between Sigma Notation and Other Notation For A SeriesChristina Aguila NavarroNo ratings yet
- Graph Thoery Lecture 3Document20 pagesGraph Thoery Lecture 3Vishnu Kumar Reddy BobbitiNo ratings yet
- Geometric Sequences: ExampleDocument5 pagesGeometric Sequences: ExampleSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 R MathematicsDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 R MathematicsShreya YadavNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences & SeriesDocument5 pagesArithmetic Sequences & SerieswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Guttman 1934Document9 pagesGuttman 1934Liridon1804No ratings yet
- Arithmetical StructureDocument19 pagesArithmetical StructureMarcelo Marcy Majstruk CimilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Prerequisites: 1.1 Operations On Complex NumbersDocument6 pagesMathematical Prerequisites: 1.1 Operations On Complex NumbersDennis Mads MakhandiaNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryDocument4 pagesArithmetic and Geometric Progressions APGP SummaryGyoWool EunNo ratings yet
- APGPDocument51 pagesAPGPMuskaan AvasthiNo ratings yet
- AlzebraDocument3 pagesAlzebrareachudaycNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For It/Computing: By: Rodgers KimeraDocument55 pagesMathematics For It/Computing: By: Rodgers KimeraellykamcodeNo ratings yet
- ACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 1Ken JiaNo ratings yet
- Maths AA Ib TopicsDocument3 pagesMaths AA Ib TopicsSofia MarinoNo ratings yet
- Centered Triangular Sum Labeling of Graphs: S. Murugesan D. Jayaraman J. ShiamaDocument4 pagesCentered Triangular Sum Labeling of Graphs: S. Murugesan D. Jayaraman J. ShiamaJenisha I.B.No ratings yet
- Group 06Document16 pagesGroup 06indula123No ratings yet
- YaywyeyfoDocument9 pagesYaywyeyfoClaire GubatNo ratings yet
- List of Mathematical Symbols - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesList of Mathematical Symbols - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlexis SinghNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 8-9 Pre-CalculusDocument15 pagesQ2 Week 8-9 Pre-CalculusJONELL PADONGAONo ratings yet
- Access Denied Your Page Is Blocked Due To A KIET IT Security Policy That Prohibits Access To Category DefaultDocument10 pagesAccess Denied Your Page Is Blocked Due To A KIET IT Security Policy That Prohibits Access To Category DefaultakttripathiNo ratings yet
- cs330 10 Notes PDFDocument204 pagescs330 10 Notes PDFasifmechengrNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World 3Document19 pagesMathematics in The Modern World 3CFCST CCPNo ratings yet
- Module Sigma NotationDocument9 pagesModule Sigma NotationJoan Adelaide BigleteNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document40 pagesModule 6Kshitiz GoyalNo ratings yet
- On The Modulus of The Riemann Zeta Funct-1Document29 pagesOn The Modulus of The Riemann Zeta Funct-1MikeNo ratings yet
- 10.3934 Math.2023051 1Document15 pages10.3934 Math.2023051 1Znar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Math Review: 1 Notation and DefinitionsDocument24 pagesMath Review: 1 Notation and DefinitionssafowanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Glossary For Teachers in Key Stages 1 To 4: January 2001Document40 pagesMathematics Glossary For Teachers in Key Stages 1 To 4: January 2001zeohuntNo ratings yet
- Maths FinalDocument27 pagesMaths FinalLakshay BooraNo ratings yet
- Sigma Notation: 1. 2 2. Some Examples 3 3. Writing A Long Sum in Sigma Notation 5 4. Rules For Use With Sigma Notation 6Document10 pagesSigma Notation: 1. 2 2. Some Examples 3 3. Writing A Long Sum in Sigma Notation 5 4. Rules For Use With Sigma Notation 6DarwinNo ratings yet
- Digital TextbookDocument16 pagesDigital TextbookAnonymous s8adxPdNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument11 pagesComplex NumbersOmkar SawantNo ratings yet