Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lipids
Lipids
Uploaded by
Cyra Bantillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesLipids are a diverse group of nonpolar compounds that function for long-term energy storage and provide insulation. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids have a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. Fats may be saturated or unsaturated, with saturated fats containing only single bonds between carbons and unsaturated containing one or more double bonds.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLipids are a diverse group of nonpolar compounds that function for long-term energy storage and provide insulation. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids have a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. Fats may be saturated or unsaturated, with saturated fats containing only single bonds between carbons and unsaturated containing one or more double bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesLipids
Lipids
Uploaded by
Cyra BantilloLipids are a diverse group of nonpolar compounds that function for long-term energy storage and provide insulation. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids have a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group. Fats may be saturated or unsaturated, with saturated fats containing only single bonds between carbons and unsaturated containing one or more double bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
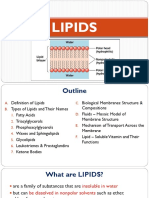
LIPIDS
Include a diverse group of compounds that are nonpolar in nature
They are hydrocarbons that include mostly only nonpolar carbon-carbon or
carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Lipids functions for long-term energy storage
Also provide insulation from the environment for plants and animals
Also are building blocks of many hormones and are important constituent of
all cellular membranes
Include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
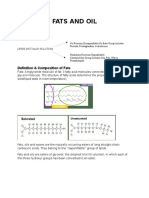
FATS and OILS
A fat molecule has two main components- glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five
hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups
Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl group is
attached
The ester linkage released water molecules
Fats are also called triaclyglycerols or triglycerides.
Some fatty acids have common names that specify their origin:
Palmitic acid- a saturated fatty acid derived from palm tree
Arachidic acid- derived from Arachis hypogea
Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated
Saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acid (trans or cis)
Saturated
Have only single bonds between neighboring carbons in the hydrocarbon
chain
Saturated with hydrogen
Has no double bonds thus no more hydrogen may be added to the carbon
atoms of the chain
Animal fats with stearic and palmitic acid and the fat with butyric acid
(common in butter) are examples
Mammals store fats as adipocytes
In plants they are stored in seeds
Unsaturated
Contains one or more double bonds
Oleic acid is an example
Are liquid at room temperature and are called oils
Monounsaturated- one double bond in the molecule (olive oil)
Polyunsaturated- has more than one double bond in the molecule (canola oil)
Can be cis and trans
Cis- if the hydrogens are present in the same plane
Trans- if the hydrogens are on different planes.
You might also like
- Notes On Lipids Mam BarramedaDocument16 pagesNotes On Lipids Mam Barramedasshh bartolata100% (1)
- Lipid Molecules: LipidsDocument23 pagesLipid Molecules: LipidsKlimpoy WatashiewaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument6 pagesLipidsMUHAMMAD SHOAIB MUNAWARNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 LipidsDocument28 pagesQuarter 4 LipidsLeoniz Victoria GomitoNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS - (Biomolecules - For Grade 10)Document46 pagesLIPIDS - (Biomolecules - For Grade 10)Fame Iverette GalapiaNo ratings yet
- The Lipids What Are Lipids?Document16 pagesThe Lipids What Are Lipids?Sire100% (1)
- FatsDocument45 pagesFatsManshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- TriglyceridesDocument1 pageTriglyceridesAnthony AsendenteNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Units (Lectures)Document113 pagesBiochemistry Units (Lectures)Tundup NamgailNo ratings yet
- Lipids BSC II Sem Notes by Darshan KumarDocument14 pagesLipids BSC II Sem Notes by Darshan Kumardarshan kumar tNo ratings yet
- Lipids 2-1Document68 pagesLipids 2-1akintunjiNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument2 pagesLIPIDSAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Fat - WikipediaDocument29 pagesFat - WikipediaWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument22 pagesLipidsMary Grace CaasiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter Five: Lipids: Department of Industrial ChemistryDocument18 pagesBiochemistry (Ichem.3052) Chapter Five: Lipids: Department of Industrial ChemistryBizuayehu Ze GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lipid PDFDocument5 pagesLipid PDFKhổng Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Lipids Classification and TypesDocument4 pagesLipids Classification and TypesDesiree Roxanne DiamzonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LipidsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To LipidsBharaniDeepan50% (2)
- 2 LipidsDocument40 pages2 LipidsMike AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: PresentDocument4 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Presentsamantha laurenthNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument56 pagesLipidsIris BallajNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compopsition of The CellDocument14 pagesChemical Compopsition of The Cellmarwani mat nasirNo ratings yet
- Lipids NoteDocument4 pagesLipids NoteOgunsina olabodeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry V. LiipidsDocument50 pagesBiochemistry V. LiipidsAlthea De TorresNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Class Of: LipidsDocument53 pagesWelcome To Class Of: LipidsMarinela DaumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Lipids: Preethi S Department of BiochemistryDocument37 pagesChemistry of Lipids: Preethi S Department of BiochemistryRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument172 pagesLipidsK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- Beige Minimal Professional Business Project PresentationDocument47 pagesBeige Minimal Professional Business Project PresentationBhagwat KaurNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NotesDocument3 pagesBiochemistry NotesMike AbellanaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS ReportDocument38 pagesLIPIDS ReportcharmsterNo ratings yet
- Oils & Fats - 3Document25 pagesOils & Fats - 3Aleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fats & Oils IntroductionDocument12 pagesFats & Oils IntroductionShibbu GangwarNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument3 pagesLipidsAbdul MaalikNo ratings yet
- Cog 13 LipidsDocument27 pagesCog 13 LipidsTahpehs PhiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: LIPIDSDocument23 pagesChapter V: LIPIDSGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 LipidsDocument4 pagesLesson 8 LipidsJanet Floreno VillasanaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsDocument8 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsMehran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARADocument65 pagesFats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARANaveenNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument30 pagesLipidsima mhammedNo ratings yet
- Module 3 LipidsDocument8 pagesModule 3 LipidsAiza OrdonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document65 pagesChapter 1maya adamNo ratings yet
- CHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsDocument93 pagesCHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsMevil Jane MabrasNo ratings yet
- Sample 62Document9 pagesSample 62Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument4 pagesLipidsAshley ArnoldNo ratings yet
- 7 LipidsDocument19 pages7 LipidsAnxi XiNo ratings yet
- C46 Lec6 LipidsDocument91 pagesC46 Lec6 LipidsMary Aniderf Cagape Maturan-GumanoyNo ratings yet
- Classification of LipidsDocument2 pagesClassification of LipidsChiel PajaresNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids and GlyceridesDocument17 pagesFatty Acids and GlyceridesAngelia PedrenoNo ratings yet
- General Biochemistry (BCH 201) Section: Chemistry of Lipids Course OutlineDocument28 pagesGeneral Biochemistry (BCH 201) Section: Chemistry of Lipids Course OutlineOjo OluwafunkeNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument20 pagesLipidsbam yeontanieNo ratings yet
- Lipids FatsDocument21 pagesLipids FatsMona Riza PagtabonanNo ratings yet
- Structure of LipidDocument11 pagesStructure of LipidAfrah Alatas100% (1)
- Lecture 5 Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesLecture 5 Biological MoleculesMuhammad FurrukhNo ratings yet
- 1A (111) LipidsDocument4 pages1A (111) Lipidsenakshi perusingheNo ratings yet
- Fats and LipidsDocument31 pagesFats and LipidsKaye Danielle HilomenNo ratings yet
- The Lipids PowerpointDocument13 pagesThe Lipids PowerpointyselleamNo ratings yet
- BPD02181028 (Introduction To Lipids)Document8 pagesBPD02181028 (Introduction To Lipids)ChaudryNomiNo ratings yet
- Lipids (Jigsaw)Document33 pagesLipids (Jigsaw)Milimo JingsawNo ratings yet
- Classification of LipidsDocument18 pagesClassification of LipidsD Kaur100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Math ResearchDocument35 pagesMath ResearchCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Freedom of The Human PersonDocument3 pagesFreedom of The Human PersonCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Homeroom 3Document4 pagesHomeroom 3Cyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- PAGBASADocument8 pagesPAGBASACyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Oral Com ReportDocument4 pagesOral Com ReportCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Homeroom 2Document4 pagesHomeroom 2Cyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Glennelyn 1Document1 pageGlennelyn 1Cyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever Wondered How The Universe Was MadeDocument7 pagesHave You Ever Wondered How The Universe Was MadeCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- LifeDocument5 pagesLifeCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- T DistributionDocument9 pagesT DistributionCyra BantilloNo ratings yet