Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Uploaded by
boneyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells AnswersDocument3 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Answersboney75% (4)
- Evolution EvidenceDocument7 pagesEvolution EvidenceMiljoy DelegadoNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Companion For How To Read A Codon ChartDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Companion For How To Read A Codon ChartThảo VânNo ratings yet
- Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesAmoeba SistersSvetlana Hunn100% (2)
- Kami Export - CellStructureSEDocument3 pagesKami Export - CellStructureSEDohnovan RankinsNo ratings yet
- LAB - Meiosis ModelingDocument7 pagesLAB - Meiosis ModelingDaniel CondreayNo ratings yet
- Types of Evolution Worksheet: Description Convergen T Divergen T Coevolutio NDocument3 pagesTypes of Evolution Worksheet: Description Convergen T Divergen T Coevolutio NElizabeth100% (1)
- Dyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry PaperworkDocument7 pagesDyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry Paperworkapi-250608665No ratings yet
- Dihybrid ProblemsDocument7 pagesDihybrid Problemsbrenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development in Vocational and Technical Education: Planning, Content, and Implementation (5th Edition)Document7 pagesCurriculum Development in Vocational and Technical Education: Planning, Content, and Implementation (5th Edition)Syafril NaguzaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Review ActivityDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Review ActivityAngelica PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitcesarNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- Biology DefinitionsDocument6 pagesBiology DefinitionsSixtine MorinNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cells Alive WebquestDocument2 pagesKami Export - Cells Alive WebquestRainNo ratings yet
- 9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3Document32 pages9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3syztqNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Exam QDocument29 pagesInheritance Exam Qapi-422428700100% (1)
- Evidence of Evolution Lab AnalysisDocument4 pagesEvidence of Evolution Lab AnalysisDiego GuardadoNo ratings yet
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument82 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- 02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSDocument35 pages02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSRitik Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFDocument50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFRozel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument9 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functionapi-517602393No ratings yet
- Cells WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Webquestapi-347555363No ratings yet
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Al Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesAl Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeNicayne RamnarineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Speciation NotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Speciation NotesCHIENG PEI WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KeyDocument7 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet KeyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pages63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersSean WongNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument20 pagesCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pagesReproduction in PlantsTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPNo ratings yet
- Bio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYDocument2 pagesBio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Active Transport in Root Hair CellsDocument3 pagesActive Transport in Root Hair CellsBetty GlamourousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Darwin's Natural SelectionDocument2 pagesDarwin's Natural Selectionsofia alamiaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Radiation and Speciation LabDocument2 pagesAdaptive Radiation and Speciation LabzacharyNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument79 pagesHeredity and VariationNathiya100% (1)
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsLea IoaNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant System NotesDocument2 pages1 Plant System NotesAdeyemi AdamsNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 pagesCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riNo ratings yet
- LQ: What Is The Role of Enzymes?Document19 pagesLQ: What Is The Role of Enzymes?NabeelNo ratings yet
- F2C4 BiDocument8 pagesF2C4 BiJeanShuenNo ratings yet
- 4 2Document4 pages4 2isabella gonzalezNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Ap Biology Mid Term PretestDocument30 pagesAp Biology Mid Term PretestKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyAnna MontiniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 InvertebratesDocument8 pagesWorksheet 7 InvertebratesAbdulla Saleem100% (1)
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 pagesNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Guided Reading Chapter 16Document5 pagesGuided Reading Chapter 16Tara Gambetta50% (4)
- Ecology WorksheetDocument12 pagesEcology WorksheetManongdo Allan0% (1)
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Evolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictDocument21 pagesEvolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictEfimios Neos100% (2)
- Ecology 2Document18 pagesEcology 2ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Bio IpassDocument15 pagesBio IpassmonreNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Review WorksheetMae SilogNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Daily Calorie RequirementDocument4 pagesDaily Calorie RequirementpenguinpowerrrrNo ratings yet
- Genurile Aloinopsis, Nananthus Si Titanopsis PDFDocument34 pagesGenurile Aloinopsis, Nananthus Si Titanopsis PDFKty FloreaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Propagation - Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesSexual Propagation - Advantages and DisadvantagesKlint VanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Coconut Tree Genetic Divergence by Compound Sample RAPD Marker AnalysisDocument8 pagesAssessment of Coconut Tree Genetic Divergence by Compound Sample RAPD Marker Analysisspullc26No ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade4fl Performance TaskDocument10 pagesSecond Quarter Grade4fl Performance TaskMark angelo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Anthem Biosciences - OverviewDocument29 pagesAnthem Biosciences - OverviewNitish JondhaleNo ratings yet
- Back From The Bluez - 01 - Overview of DepressionDocument9 pagesBack From The Bluez - 01 - Overview of DepressionsusanasotogarridoNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingDocument11 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingRyo LamNo ratings yet
- Journal Comprehensive Pharmacokinetic Model of Insulin Glargine and Other Insulin FormulationsDocument12 pagesJournal Comprehensive Pharmacokinetic Model of Insulin Glargine and Other Insulin FormulationsAnkgoeh GhoebawaNo ratings yet
- Swasthvritta Prabhat Tiwari Ed. 2024 NCISM Syllabus PresentationDocument31 pagesSwasthvritta Prabhat Tiwari Ed. 2024 NCISM Syllabus Presentationpawan9889niravaliNo ratings yet
- 1.8 InvestigationsDocument4 pages1.8 InvestigationsJessie QianNo ratings yet
- 0610 s13 QP 63 PDFDocument16 pages0610 s13 QP 63 PDFHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Origin of LanguangeDocument94 pagesOrigin of LanguangeDarkk Sunn0% (1)
- Origin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZDocument26 pagesOrigin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZSri Naharindah NingNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Electron Transport ChainDocument2 pages4 4 Electron Transport ChainKai JieNo ratings yet
- Department of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusDocument1 pageDepartment of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) Virusshoaib chNo ratings yet
- Weiss JurmainDocument14 pagesWeiss JurmainLM AdrianneNo ratings yet
- Perdev QuestionsDocument1 pagePerdev QuestionsajNo ratings yet
- BIOA01 F2021 SyllabusDocument10 pagesBIOA01 F2021 Syllabusthisis throwawayxDNo ratings yet
- Animal Parts QuizDocument13 pagesAnimal Parts QuizLarisa M.No ratings yet
- Child and AdolescentDocument2 pagesChild and AdolescentOrmon Angel AndesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PersonalityDocument66 pagesChapter 9 Personalitysp-hazaranaz.mohdaslamNo ratings yet
- Needleman-Wunsch and Smith-Waterman AlgorithmDocument19 pagesNeedleman-Wunsch and Smith-Waterman Algorithmgayu_positive67% (9)
- Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteDocument39 pagesCulturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteGela16No ratings yet
- Body Forms of FishesDocument12 pagesBody Forms of Fishesrano khanNo ratings yet
- 6th Bio Final Term 2021-2022.Document3 pages6th Bio Final Term 2021-2022.Navya ChaplotNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDinkey AlegadoNo ratings yet
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Uploaded by
boneyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Uploaded by
boneyCopyright:
Available Formats
Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotes are microscopic single-celled organisms. Prokaryotic cells don’t have a distinct nucleus
with a membrane. Correctly label the following prokaryotic cell structures.
Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid
Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes Cytoplasm
Briefly explain the function of each labeled structure.
Cell Membrane
Cell Wall
Capsule
Pili
Plasmid
Flagella
Nucleoid Region
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Resource created by Tobie T.
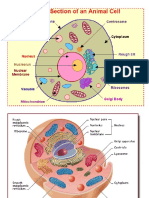
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotes are organisms that can be both unicellular and multicellular. The genetic material is DNA
which is contained within a distinct nucleus. Correctly label the following eukaryotic cell
structures.
Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes
Mitochondria Lysosome Vacuole Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi apparatus
Briefly explain the function of each labeled structure.
Nucleus
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Lysosome
Vacuole
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
Resource created by Tobie T.
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant
and Animal cells are both eukaryotic cells. While they contain many of the same
organelles, there are significant differences between them.
Write the number of the correct corresponding structure in the table below. Then,
distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by writing either a tick or cross in the
boxes.
1.
5.
2.
6.
3.
4.
7.
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Organelle Number of Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells
Structure
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Vacuole
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
DNA free in
cytoplasm
Resource created by Tobie T.
You might also like
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells AnswersDocument3 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Answersboney75% (4)
- Evolution EvidenceDocument7 pagesEvolution EvidenceMiljoy DelegadoNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Companion For How To Read A Codon ChartDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Companion For How To Read A Codon ChartThảo VânNo ratings yet
- Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesAmoeba SistersSvetlana Hunn100% (2)
- Kami Export - CellStructureSEDocument3 pagesKami Export - CellStructureSEDohnovan RankinsNo ratings yet
- LAB - Meiosis ModelingDocument7 pagesLAB - Meiosis ModelingDaniel CondreayNo ratings yet
- Types of Evolution Worksheet: Description Convergen T Divergen T Coevolutio NDocument3 pagesTypes of Evolution Worksheet: Description Convergen T Divergen T Coevolutio NElizabeth100% (1)
- Dyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry PaperworkDocument7 pagesDyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry Paperworkapi-250608665No ratings yet
- Dihybrid ProblemsDocument7 pagesDihybrid Problemsbrenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development in Vocational and Technical Education: Planning, Content, and Implementation (5th Edition)Document7 pagesCurriculum Development in Vocational and Technical Education: Planning, Content, and Implementation (5th Edition)Syafril NaguzaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Review ActivityDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Review ActivityAngelica PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitcesarNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocument38 pagesNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezNo ratings yet
- Biology DefinitionsDocument6 pagesBiology DefinitionsSixtine MorinNo ratings yet
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cells Alive WebquestDocument2 pagesKami Export - Cells Alive WebquestRainNo ratings yet
- 9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3Document32 pages9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3syztqNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Exam QDocument29 pagesInheritance Exam Qapi-422428700100% (1)
- Evidence of Evolution Lab AnalysisDocument4 pagesEvidence of Evolution Lab AnalysisDiego GuardadoNo ratings yet
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument82 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- 02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSDocument35 pages02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSRitik Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFDocument50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis PDFRozel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument9 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functionapi-517602393No ratings yet
- Cells WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Webquestapi-347555363No ratings yet
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Al Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesAl Rowad International School, Riyadh: Biology IGCSE CambridgeNicayne RamnarineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Speciation NotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Speciation NotesCHIENG PEI WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KeyDocument7 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet KeyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pages63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersSean WongNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument20 pagesCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pagesReproduction in PlantsTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPNo ratings yet
- Bio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYDocument2 pagesBio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Active Transport in Root Hair CellsDocument3 pagesActive Transport in Root Hair CellsBetty GlamourousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Darwin's Natural SelectionDocument2 pagesDarwin's Natural Selectionsofia alamiaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Radiation and Speciation LabDocument2 pagesAdaptive Radiation and Speciation LabzacharyNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument79 pagesHeredity and VariationNathiya100% (1)
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsLea IoaNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant System NotesDocument2 pages1 Plant System NotesAdeyemi AdamsNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDocument10 pagesCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riNo ratings yet
- LQ: What Is The Role of Enzymes?Document19 pagesLQ: What Is The Role of Enzymes?NabeelNo ratings yet
- F2C4 BiDocument8 pagesF2C4 BiJeanShuenNo ratings yet
- 4 2Document4 pages4 2isabella gonzalezNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Ap Biology Mid Term PretestDocument30 pagesAp Biology Mid Term PretestKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyAnna MontiniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 InvertebratesDocument8 pagesWorksheet 7 InvertebratesAbdulla Saleem100% (1)
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 pagesNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Guided Reading Chapter 16Document5 pagesGuided Reading Chapter 16Tara Gambetta50% (4)
- Ecology WorksheetDocument12 pagesEcology WorksheetManongdo Allan0% (1)
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Evolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictDocument21 pagesEvolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictEfimios Neos100% (2)
- Ecology 2Document18 pagesEcology 2ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Bio IpassDocument15 pagesBio IpassmonreNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Review WorksheetMae SilogNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Daily Calorie RequirementDocument4 pagesDaily Calorie RequirementpenguinpowerrrrNo ratings yet
- Genurile Aloinopsis, Nananthus Si Titanopsis PDFDocument34 pagesGenurile Aloinopsis, Nananthus Si Titanopsis PDFKty FloreaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Propagation - Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesSexual Propagation - Advantages and DisadvantagesKlint VanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Coconut Tree Genetic Divergence by Compound Sample RAPD Marker AnalysisDocument8 pagesAssessment of Coconut Tree Genetic Divergence by Compound Sample RAPD Marker Analysisspullc26No ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade4fl Performance TaskDocument10 pagesSecond Quarter Grade4fl Performance TaskMark angelo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Anthem Biosciences - OverviewDocument29 pagesAnthem Biosciences - OverviewNitish JondhaleNo ratings yet
- Back From The Bluez - 01 - Overview of DepressionDocument9 pagesBack From The Bluez - 01 - Overview of DepressionsusanasotogarridoNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingDocument11 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell Membrane: A. Concept CheckingRyo LamNo ratings yet
- Journal Comprehensive Pharmacokinetic Model of Insulin Glargine and Other Insulin FormulationsDocument12 pagesJournal Comprehensive Pharmacokinetic Model of Insulin Glargine and Other Insulin FormulationsAnkgoeh GhoebawaNo ratings yet
- Swasthvritta Prabhat Tiwari Ed. 2024 NCISM Syllabus PresentationDocument31 pagesSwasthvritta Prabhat Tiwari Ed. 2024 NCISM Syllabus Presentationpawan9889niravaliNo ratings yet
- 1.8 InvestigationsDocument4 pages1.8 InvestigationsJessie QianNo ratings yet
- 0610 s13 QP 63 PDFDocument16 pages0610 s13 QP 63 PDFHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Origin of LanguangeDocument94 pagesOrigin of LanguangeDarkk Sunn0% (1)
- Origin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZDocument26 pagesOrigin of Lymphoid Neoplasms: CLP: BLB: NBC: MC: GC: MZSri Naharindah NingNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Electron Transport ChainDocument2 pages4 4 Electron Transport ChainKai JieNo ratings yet
- Department of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) VirusDocument1 pageDepartment of Molecular Virology: COVID-19 (Corona) Virusshoaib chNo ratings yet
- Weiss JurmainDocument14 pagesWeiss JurmainLM AdrianneNo ratings yet
- Perdev QuestionsDocument1 pagePerdev QuestionsajNo ratings yet
- BIOA01 F2021 SyllabusDocument10 pagesBIOA01 F2021 Syllabusthisis throwawayxDNo ratings yet
- Animal Parts QuizDocument13 pagesAnimal Parts QuizLarisa M.No ratings yet
- Child and AdolescentDocument2 pagesChild and AdolescentOrmon Angel AndesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PersonalityDocument66 pagesChapter 9 Personalitysp-hazaranaz.mohdaslamNo ratings yet
- Needleman-Wunsch and Smith-Waterman AlgorithmDocument19 pagesNeedleman-Wunsch and Smith-Waterman Algorithmgayu_positive67% (9)
- Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteDocument39 pagesCulturable Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated With A Laboratory Culture of Botryococcus Braunii, A Colonial Oil-Producing Green Alga From Paoay Lake, Ilocos NorteGela16No ratings yet
- Body Forms of FishesDocument12 pagesBody Forms of Fishesrano khanNo ratings yet
- 6th Bio Final Term 2021-2022.Document3 pages6th Bio Final Term 2021-2022.Navya ChaplotNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDinkey AlegadoNo ratings yet