Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HISTORY
HISTORY
Uploaded by
Fun ExplorerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DBQ PRT 2Document3 pagesDBQ PRT 2FrankAulettiNo ratings yet
- Do We Have Special Moral Duties To Our Fellow Countrymen?Document14 pagesDo We Have Special Moral Duties To Our Fellow Countrymen?Frosen91No ratings yet
- Social Psychology PSYC250Document21 pagesSocial Psychology PSYC250pazucenaNo ratings yet
- DCCDocument1 pageDCCBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Bonilla. o LiberalismoDocument24 pagesBonilla. o LiberalismoJhéssica LuaraNo ratings yet
- NAAB Student Performance Criteria Matrix For The Professional M.Arch. Degree at SDSUDocument1 pageNAAB Student Performance Criteria Matrix For The Professional M.Arch. Degree at SDSUSally AlaslamiNo ratings yet
- Adp-Ksa-Sol-Dwg-El-Td-Det-419 Cafe Counter Detail 2 - Rev.01Document1 pageAdp-Ksa-Sol-Dwg-El-Td-Det-419 Cafe Counter Detail 2 - Rev.01ekhaa.awal1No ratings yet
- 170156-001 (Rev-) Existing Site PlanDocument1 page170156-001 (Rev-) Existing Site PlanDaniel TelphiaNo ratings yet
- Madac SD El Fa BF 504Document1 pageMadac SD El Fa BF 504shoaibNo ratings yet
- UPU Živogošće Blato 2.1 PrometDocument1 pageUPU Živogošće Blato 2.1 PrometNikola MiljkoNo ratings yet
- DR - Majd and Dr. Dima Shop Drawing Reference 256 Date 12.08.23Document54 pagesDR - Majd and Dr. Dima Shop Drawing Reference 256 Date 12.08.230988624395hamzaNo ratings yet
- FS0654-DOD-ZZ-XX-DR-M-2013 - Domestic Water Distribution Schematic - Construction - C01 - 0Document1 pageFS0654-DOD-ZZ-XX-DR-M-2013 - Domestic Water Distribution Schematic - Construction - C01 - 0mvrisleyNo ratings yet
- Notes: Rear Elevation Side ElevationDocument1 pageNotes: Rear Elevation Side ElevationVarietta LusingaNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar - 2021Document2 pagesAmit Kumar - 2021Amit MalikNo ratings yet
- In This ChapterDocument24 pagesIn This ChapterabcNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson Z800i - V800 - V802se - SchematicsDocument39 pagesSony Ericsson Z800i - V800 - V802se - Schematicsfranklin quispe floresNo ratings yet
- Mapa Metamórfico de Colombia: Mario MayaDocument2 pagesMapa Metamórfico de Colombia: Mario MayaNicolas GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Jess 403Document10 pagesJess 403yomanNo ratings yet
- Jess 403Document10 pagesJess 403PracKillerNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Librando Janry Design 5 Condominium ResearchDocument14 pagesLibrando Janry Design 5 Condominium ResearchJanryLibrandoNo ratings yet
- Estrutural Divisa - R00-FL01Document1 pageEstrutural Divisa - R00-FL01Pablo LimaNo ratings yet
- P8 5.5.0-P85.5.4 Patch Compatibility Matrix 6Document16 pagesP8 5.5.0-P85.5.4 Patch Compatibility Matrix 6Fouad ELMNo ratings yet
- Rcompany Monthly: Assignment 1Document8 pagesRcompany Monthly: Assignment 1ANJALINo ratings yet
- Rapporto Sulla Domanda Di Banda LargaDocument61 pagesRapporto Sulla Domanda Di Banda LargaLuigi ReggiNo ratings yet
- Siemens WT46W560gB09 - INSTMANUAL - (EN)Document10 pagesSiemens WT46W560gB09 - INSTMANUAL - (EN)Jeancarlos DominguezNo ratings yet
- Bhopal Tamil Sangam Brochure INDIA July 2022Document11 pagesBhopal Tamil Sangam Brochure INDIA July 2022US Soy CouncilNo ratings yet
- FAJA MARGINAL PropuestaDocument1 pageFAJA MARGINAL PropuestaDemetrio VargasNo ratings yet
- LS Fence 1Document1 pageLS Fence 1jimNo ratings yet
- 6 Architectural Plans Part 3 of 3 1800 Sheppard Avenue EastDocument11 pages6 Architectural Plans Part 3 of 3 1800 Sheppard Avenue EastBhushanNo ratings yet
- Pile SectionDocument1 pagePile Sectionsam_antony2005No ratings yet
- Pronorm Einbaukuchen GMBHDocument1 pagePronorm Einbaukuchen GMBHatulkundariaNo ratings yet
- Arhitectura Comunităţii Ca Arhitectură Integrată-Analiză Comparativă Şi Sinteză A Teoriilor Lui John F.C. Turner, John Habraken Şi Christopher Alexander/ COMMUNITY ARCHITECTURE AS..Document21 pagesArhitectura Comunităţii Ca Arhitectură Integrată-Analiză Comparativă Şi Sinteză A Teoriilor Lui John F.C. Turner, John Habraken Şi Christopher Alexander/ COMMUNITY ARCHITECTURE AS..ViorelNo ratings yet
- Typeset Using Lilypond by Steve Dunlop - Reference: Mutopia-2008/01/13-1235 Sheet Music From Mutopiaproject - Free To Download, With The Freedom To Distribute, Modify and PerformDocument1 pageTypeset Using Lilypond by Steve Dunlop - Reference: Mutopia-2008/01/13-1235 Sheet Music From Mutopiaproject - Free To Download, With The Freedom To Distribute, Modify and PerforminfobitsNo ratings yet
- 3 - Quaid-e-Azam Aor Aaj Ka PakistanDocument12 pages3 - Quaid-e-Azam Aor Aaj Ka PakistanA Wakeel HijaziNo ratings yet
- 2024 Annual ReportDocument102 pages2024 Annual ReportmaqsoumiNo ratings yet
- DMT Hvac PetsnackDocument1 pageDMT Hvac PetsnackYunus 12345No ratings yet
- PR A TD MLCP FP 202 Basement 1Document1 pagePR A TD MLCP FP 202 Basement 1shaikhtauqeir749No ratings yet
- Modular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseDocument2 pagesModular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseakinravNo ratings yet
- Hs CD 23 00187-Landscape General Arrangement Plan 1 of 4-952020Document1 pageHs CD 23 00187-Landscape General Arrangement Plan 1 of 4-952020api-193778159No ratings yet
- Facilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksDocument3 pagesFacilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksmichaelNo ratings yet
- Separators in The Cement IndustryDocument5 pagesSeparators in The Cement Industryzane truesdaleNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesassis alihNo ratings yet
- Diwali Gala 2010: J S O T IDocument9 pagesDiwali Gala 2010: J S O T ISuparshNo ratings yet
- Снимок экрана 2021-05-10 в 15.24.13Document1 pageСнимок экрана 2021-05-10 в 15.24.13captmarlenNo ratings yet
- AVR-I-102.4B-FF-R.C.P Dimension Plan-10.03.2022Document1 pageAVR-I-102.4B-FF-R.C.P Dimension Plan-10.03.2022IqRa JaVedNo ratings yet
- A02.10-D - Overall Floor Plan - Level 07Document1 pageA02.10-D - Overall Floor Plan - Level 07Aakanksha Pandit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Issued For Construction: For Kitchen Equipment Power Connection Refer Dwg. 1308-Mob-E-709Document1 pageIssued For Construction: For Kitchen Equipment Power Connection Refer Dwg. 1308-Mob-E-709Motaleb BijoyNo ratings yet
- Credit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit TransactionsDocument1 pageCredit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit TransactionsDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Enamelled WireDocument20 pagesEnamelled WireNesya LaxmithaNo ratings yet
- 5th Floor Plan-Layout1Document1 page5th Floor Plan-Layout1yadvikram7No ratings yet
- φDocument1 pageφantonisdachliNo ratings yet
- DELE STRUCTURAL-Fdn. FTDocument1 pageDELE STRUCTURAL-Fdn. FTuche ekeNo ratings yet
- Swept Path Analysis For Delivery TruckDocument1 pageSwept Path Analysis For Delivery TruckGladdelyn PiencenavesNo ratings yet
- Kyoto Bus MapDocument1 pageKyoto Bus MapAndrew WongNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL SCHEMATICS - H&C B70 V6-Base 71Document1 pageMECHANICAL SCHEMATICS - H&C B70 V6-Base 71Slobodan HristovNo ratings yet
- Yatta Foundation RevDocument1 pageYatta Foundation RevKevin Lil'Vokez MulimaNo ratings yet
- P103 DWG STR 001Document1 pageP103 DWG STR 001RJNo ratings yet
- SR28C84196 B Main BoardDocument2 pagesSR28C84196 B Main BoardArthur AntoniolliNo ratings yet
- Makeni FootingDocument3 pagesMakeni FootingJack HaamboteNo ratings yet
- Everyday Life in ByzantiumDocument244 pagesEveryday Life in ByzantiumJovana Mitic Savic100% (11)
- Airport BoardDocument2 pagesAirport BoardcamiayoungNo ratings yet
- White Shade: The Real-World Primer for the Black Professional WomanFrom EverandWhite Shade: The Real-World Primer for the Black Professional WomanNo ratings yet
- Christian Education For Social ChangeDocument2 pagesChristian Education For Social ChangeAlan83% (6)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument6 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-206950621No ratings yet
- Barrier Free Architecture: Prof. Subodh ShankarDocument41 pagesBarrier Free Architecture: Prof. Subodh Shankarsubodh shankar100% (2)
- Opposition To The Ku Klux Klan in The Early 1920s: The Beginnings of Disaffection in Richmond, IndianaDocument25 pagesOpposition To The Ku Klux Klan in The Early 1920s: The Beginnings of Disaffection in Richmond, IndianaNicolas MartinNo ratings yet
- Mayoor School, Noida HALF YEARLY EXAM (2019-20) Political Science Class-Xi Set A Marking Scheme TIME: 3 Hour M.M: 80 DateDocument9 pagesMayoor School, Noida HALF YEARLY EXAM (2019-20) Political Science Class-Xi Set A Marking Scheme TIME: 3 Hour M.M: 80 DateKanupriya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Black Skins - and White Masks - Comic Books and The Secret of RaceDocument14 pagesBlack Skins - and White Masks - Comic Books and The Secret of RaceRose OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Latest Social Science Reviewer Part 11Document7 pagesLatest Social Science Reviewer Part 11Rubelin Dagohoy AmitNo ratings yet
- Representation in The Sun - GenderDocument40 pagesRepresentation in The Sun - GenderDee WatsonNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisAnonymous DwRqrHSXs3No ratings yet
- Asian American WomenDocument9 pagesAsian American Womenapi-247035267No ratings yet
- SADC SummaryDocument5 pagesSADC SummaryFaye JacobsNo ratings yet
- The Lesbianism Aspects in The Main Character of Novel "The Color Purple" by Alice Walker: A Feminist ApproachDocument7 pagesThe Lesbianism Aspects in The Main Character of Novel "The Color Purple" by Alice Walker: A Feminist ApproachElisua Kenniar AdhidaivataNo ratings yet
- Noah's SF 181 With Attached DocumentsDocument16 pagesNoah's SF 181 With Attached DocumentsEMPRESS_OM100% (4)
- Diversity in Organizations (Organizational Behavior Summary - Judge, Robins)Document3 pagesDiversity in Organizations (Organizational Behavior Summary - Judge, Robins)Kobe MaestreNo ratings yet
- FKB Learn-Sight-Words-Print Friendly-Dont Be A BullyDocument21 pagesFKB Learn-Sight-Words-Print Friendly-Dont Be A Bullysan ovNo ratings yet
- g9 q3 Module 1 - Differentiating Biases From PrejudicesDocument40 pagesg9 q3 Module 1 - Differentiating Biases From PrejudicesGeraldine MartinNo ratings yet
- Mainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 SlidesDocument50 pagesMainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 Slidestilahunthm100% (1)
- The female colonizer and othered woman in Isak Dinesen's Out of Africa, Jean Rhys's Wide Sargasso Sea, Tayeb Salih's Season of migration to the north, and Paule Marshall's The chosen place, the timeless peopleDocument81 pagesThe female colonizer and othered woman in Isak Dinesen's Out of Africa, Jean Rhys's Wide Sargasso Sea, Tayeb Salih's Season of migration to the north, and Paule Marshall's The chosen place, the timeless peopleAilen AlmaNo ratings yet
- Race 5tabloidDocument2 pagesRace 5tabloidMarcus RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cedar Park Assembly of God of Kirkland, Washington V KreidlerDocument22 pagesCedar Park Assembly of God of Kirkland, Washington V KreidlerAnonymous HiNeTxLMNo ratings yet
- LHOD and Her HSC English Extension 1 EssayDocument3 pagesLHOD and Her HSC English Extension 1 EssayFrank Enstein FeiNo ratings yet
- Gujrat Riots PDFDocument13 pagesGujrat Riots PDFaditya_2kNo ratings yet
- SAT 2hr DiagnosticDocument58 pagesSAT 2hr Diagnostic劉又綺 EuniceNo ratings yet
- Romantic Love Is A Moral IssueDocument4 pagesRomantic Love Is A Moral Issuemshiran7No ratings yet
- Tattoos and Piercings Are They Compatible in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesTattoos and Piercings Are They Compatible in The WorkplaceOkoth WilliamNo ratings yet
- Morality, Disgust, and Countertransference in PsychotherapyDocument4 pagesMorality, Disgust, and Countertransference in PsychotherapyJohn GavazziNo ratings yet
HISTORY
HISTORY
Uploaded by
Fun ExplorerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTORY
HISTORY
Uploaded by
Fun ExplorerCopyright:
Available Formats
Despite these challenges, many Italian workers settled in
Canadian cities like Toronto and Montréal, allowing Italian
communities to grow and establish businesses.
Eventually, the Black workers organized their own union, as
white unions continued to refuse their membership until 1919. The TRC continues to work to build respectful relationships
between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal communities.
From 1902 to 1912, Italian dock and freight workers frequently
fought strikes, often violently, due to harsh working conditions
and job security. Only some Black workers were rehired, but they received no
compensation. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada (TRC)
gathered evidence from 2008 to 2015 and educated
In 2013, only 22 out of the league's 690 players were Black. In February 1912, male sewing machine operators were told Canadians on the experiences of residential school survivors.
They provided care during high-risk situations and during
they would have to sew in coat linings, but they were not paid Their relationships with employers grew tense due to their wartime. In 1899, the Canadian Army Nursing Service was
for this extra task. In protest, 65 machine operators went on lower-end jobs and limited pay. The Liberal government was accused of racism for not established, with women receiving the same rank and pay as
strike. supporting the Black porters. Support from Christian missionaries helped maintain army lieutenants.
traditions. The last residential school in Canada closed in 1996, but the The government opened up the cleared land to new settlers,
The Coloured Hockey League of the Maritimes was founded to
effects of abuse still affect former students today. impacting the Doukhobors and their established communities.
provide opportunities for Black hockey players, and the The All People's Mission in Winnipeg, a Methodist organization,
National Hockey League (NHL) has since seen a slow increase Stereotypes and discrimination against Italian workers were provided free kindergarten and English classes to Eastern
in Black hockey players. Toronto's Timothy Eaton Company, a powerful employer, had evident, as they needed to survive and send money back They rallied behind the workers, contacting newspapers and The Victorian Order of Nurses was created to address the European immigrants in a poor neighborhood.
Jewish garment workers make up 80% of its workforce. home. politicians to make the discrimination public.opic The government proposed removing their First Nations status First Nations communities resisted the ban by secretly holding healthcare crisis in rural areas, training young women to Diverse perspectives from other groups also hindered unity. This unofficial approach to immigration was based on personal
They organized their own union, but white unions refused their and making them Canadian citizens, dividing the reserve land potlatches, including the Haida, disguised as European Many died from abuse, abuse, or forced escape. become visiting nurses. James Mavor protested, leading to the Doukhobors' relocation belief rather than government policy.
membership until 1919. among Songhees families. holidays. to British Columbia in 1908. Mostly only one of the family members could afford to come to
the overpopulated place they lived in became know as New Canada because of the head tax, leaving the rest of the family
Segregated schools, poor farmland, and lower wages were Leaders like Reverend Woodsworth influenced Canada's social Jerusalem They work and earn money from farms in Canada and then at China.
common experiences for Black children. n 1914, a group of young Chinese men founded the Chinese Jewish garment workers faced workplace challenges like low They were given temporary jobs in railway, mining, shipping, In 1898, the railway fired Black workers, causing outrage Unity with other women's groups was challenging, as and political landscape, with organizations like the Canadian
send it to their families at home When arrived at Canada they were not allowed entry
Canadian Club, providing activities for Chinese youth, including pay and unsafe conditions, affecting male, female, and child Jewish workers' actions raised public awareness about and lumber industries, but faced seasonal work and poor among Black churches. Students faced abuse, lack of food, and isolation from their Lady Aberdeen, wife of Governor General Lord Aberdeen, The Woman's Christian Temperance Union emphasized the temperance movement members criticized NCWC for allowing Woman's Christian Temperance Union supporting the Between 1896 and 1914, around 170,000 Ukrainian This allowed new immigrants to help each other start their This allowed new immigrants to help each other start their Some government agents, including W.D. Scott, admitted to
sports and book clubs, marking the first time the term was workers. sweatshops and introduced a generation to the labour treatment from their employers. The Liberal government was accused of racism, and some In Victoria, a Songhees reserve was located near Victoria's The event included feasts, dancing, and singing, often involving families. founded women's organizations like the National Council of importance of banning alcohol to address family violence and Gentle sports like rowing, skating, and golf were considered wine at dinners, while temperance women sought suffrage and movement. Hoodless devoted her life to educating the public about food immigrants settled in Canada. Peter Svarich's memoir compares the journey to Canada's farms and be surrounded by familiar people, languages, Oliver began reclaiming land from the Doukhobors in Good relations with the Cree helped the Doukhobors farms and be surrounded by familiar people, languages, Oliver used the Act to take farmland from the Doukhobors in ignoring requests and spreading information to discourage
The club provided winter clothing, volunteered, and helped
used to identify Canadian-born people of Chinese descent. movement, but Canadians still held prejudices against non- Black workers were rehired but not compensated. inner harbor, where they hunted, fished, and canoed. host destruction to show superiority. Women of Canada. crime rates. appropriate, while team sports like hockey, field hockey, alcohol bans. safety, nutrition, and hygiene, forming a new area of study In 1899, over 7500 Doukhobors arrived in Canada, highlighting advertising. religions, and customs. Saskatchewan, but their communal farming practices led to overcome new settlement challenges. religions, and customs. 1908. They began to discriminate and be racist Black immigrants.
found the Union United Church, Montréal's oldest Black
northern European immigrants. baseball, and lacrosse were considered unsuitable. called domestic science. their desire to escape their oppressive situation in Russia. Many Jewish people ended up living in slums land confiscation. Chinse workers only earned $1.00 per day for a life
In cities, Black people faced restrictions in dining, theaters, and church. These organizations raised the profile of Black women In 1911, a Black farmer in Oklahoma requested entry to
He made people give speeches in England about all the The Canadian government used immigration posters to get They were taken from orphanages The continuous journey made it nearly impossible for Asian threatening job Riot began in China town
neighborhood living. They were paid lower wages and had longer hours, often Established in Saint John, New Brunswick, it provided safe, in Montréal. Canada, but the superintendent denied his request.
opportunities Canada provided people from other countries to settle in Canada immigrants to come to Canada
However, unions like the Canadian branches of the Thousands of Italian immigrants, including Greeks and Italians, working with only three hours of sleep. Despite their harsh The government continued to open more residential schools, affordable housing, supervised boarding houses, and job The social gospel movement gained popularity in English Dr. Joseph Oleskiw, a Ukrainian man, aimed to promote
They spoke the language, understood their parents' culture, International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union helped maintain arrived in Canada seeking better opportunities. They were not allowed to join unions, leading to their firing in working conditions, Black porters were not allowed to join Sir Richard McBride, the premier, sought control of all First Potlatch, a gift-giving ceremony, strengthened relationships In 1911, the deal was finalized, and Chief Cooper made teaching household, farming, and trade skills but not providing training schools. Stowe, who was denied medical school admission in Toronto, Women's suffrage and alcohol abuse were key goals, as Lady Aberdeen believed the National Council of Women of Canada, promoting the idea that society could be improved by Canadian homesteads and encourage Ukrainians to settle in The first Doukhobors arrived in Canada in 1900. The Svarich Farmland in the Prairies was divided into 65-ha land grants, The Doukhobors arrived in Canada without horses, but Cree Farmland in the Prairies was divided into 65-ha land grants, Frank Oliver introduced the Immigration Act in 1906, Many Canadians British though they posed threat in their life. The Canadian government did not enact any official
and adapted to Anglo-Canadian culture through English- their culture. Struggling workers quit, Eaton Company refused to hire Jewish 1898. unions that could have protected them. Nations reserve land to create more settlement and and allowed communities to pass on meaningful traditions to McBride an honorary Songhees chief. much academic education. pledged to improve Canadian women's lives. national church conferences supported them by 1914. Typically, only middle-class women or female students had the Canada should support Hoodless's domestic science, arts, and working together and applying Protestant values. Unpasteurized milk was not common during this time, leading the Prairies. They faced persecution and faced threats, including The advertisement in Figure 7.7 differs from the government's family from Ukraine immigrated to the Canadian Prairies in These violent riots resulted in the deaths of around 50 people, Immigrants in Canada hoped for better opportunities and They also faced a lot of discriminations because of their with bloc settlements allowing groups of people from the same He claimed the Doukhobors refused to sign an oath of farmer Jim Greyeyes provided four horses and a worker to with bloc settlements allowing groups of people from the same increasing government power to restrict immigration, deport, regulations against immigration, but some government
speaking schools. workers, only a few allowed. development areas. younger generations. opportunity to participate. help society by working together on these issues. to many deaths. imprisonment or exile. promotion of Canada in other European regions. 1900, arriving in Winnipeg in April. prompting some Jewish people to leave Russia. freedom of religion. religion cultural group to settle on farms. allegiance and were not allowed to settle in communities. help the women. cultural group to settle on farms. They were between the age of 8 and 16 and target undesirable groups. The head tax was $50 in 1855 but increased steadily employees used indirect methods to discourage it. people were protesting on immigration and targeting Japanese
In Canada, Black people faced discrimination in both rural and n the 1890s and 1900s, women's organizations primarily The Immigration Act did not explicitly ban specific nationalities
He helped moving people from England to Canada The government offered 160 acres of free farmland to settlers The passengers were mostly sikh and male and Canadians
urban areas from the late 1800s onwards. focused on white, upper- and middle-class women, with few or ethnic groups from entering Canada, but parts like the
Canada's economy improved in the early 1900s, prompting the The Canadian Young Women's Christian Association (YWCA) reaching out to Black women. Toronto's Young Women's Canadian immigrants often farmed communally or "continuous journey" regulation could be used to bar certain When immigration flooded into Canada from different parts of By 1912, Black immigration to Alberta had halted, but
n the early 1900s, Canada's garment industry employed many government to hire temporary workers. In the late 1800s, the Intercolonial Railway (ICR) employed In the late 1800s, the Intercolonial Railway (ICR) employed The 43 Songhees families received cash payments for their However, schools often did not respect or cooperate with their Industrialization and urban growth led to more working-class was formed in 1870 to address the growing number of single The Canadian Women's Suffrage Association, led by Dr. Emily The social gospel movement aimed to improve society by Christian Association provided housing for single Black Early 1900s saw women's church involvement in social lives, Hoodless founded the first Women's Institute in 1897, leading Canada attracted immigrants from various countries by cooperatively before arriving, with 65-ha land grants and bloc immigrants. In 1908, the regulation required immigrants to the world, not only did immigrates speak British, French and established communities like Amber Valley grew, with 300
Chinese youth in Canada faced racism and discrimination, but Jewish immigrants, who faced anti-Semitism when seeking jobs In 1912, 65 male sewing machine operators went on strike due SuUnion strike pay ran out by mid-April; little support in media Black men as porters, working in harsh conditions and with many Black men as porters, working on first-class passenger British Columbia's First Nations reserves were limited to a First Nations communities defied federal laws banning reserve land, moving to a new reserve, and receiving land, families. women seeking city jobs, often as domestic servants or young women in cities. Stowe, aimed to help women gain the right to vote and study in securing government funding for social gospel programs. women, while the Coloured Women's Club of Montréal was Suffragettes encouraged women to participate in sports by the Despite social gospel, suffrage, and temperance movements, but societal changes led to poverty, crime, and unemployment, n 1889, Adelaide Hoodless's son John died from meningitis to over 500 institutes and colleges in Canada, promoting offering free land, attracting people from Britain, Ukraine, The Doukhobors, farmers in Russia, were pacifists who From 1900 to 1911, over 90,000 British and European women The journey from Europe to Canada was long, requiring Europe experienced growing anti-Semitism, leading to mob Rising political and social tensions in Europe led to violence New Jewish immigrants couldn't speak English or French and Immigrants in Canada often farmed communally or settlements allowing cultural group cooperation and In 1905, Frank Oliver replaced Sifton as minister of the interior, In 1909, a friendship between the Cree and Doukhobors in Immigrants in Canada often farmed communally or Between 1867 and 1984 100 000 British children's were sent travel by continuous journey from their country of origin to Sifton's immigration policy encouraged diverse immigration to Head tax was a fee chinse immigrants had to pay before Aboriginal but many other languages and practiced different Between 1905 and 1911, 1500 US Black farmers settled in Oklahoma immigrants immigrating in 1910 to escape
grew up in Canada, integrating into two societies. outside the industry. to unpaid coat linings. and business.btopic limited sleep. cars. small portion, often near growing cities or mineral-rich land. traditional ceremonies, such as potlatch, in 1884. fishing, and hunting rights. factories. universities. founded in 1902 to fight poverty and discrimination. 1800s, focusing on health benefits. disputes remained on empowering women. impacting church importance. from contaminated milk. domestic science education for women. He had a big role with immigration getting alot Hungary, Romania, Germany, opposed military service due to religious and political beliefs. immigrated to Canada for work as domestic servants. multiple boats, trains, and wagons. attacks on Jewish neighborhoods in Russia in 1881. and discrimination based on heritage or religion. The population of Canada grew and more people needed food had difficulties in communication cooperatively before arriving. familiarity. aiming to reclaim farmland cleared by Doukhobors. Saskatchewan began in 1909. cooperatively before arriving. to live in Canadian's farm The Komagata Maru was a Japanese steam ship Canada. Canada. entering Canada religions. Western Canada. discrimination. Japanese Canadian grocery store was destroyed
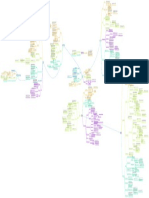
n the early 1900s, First Nations families fought against DEVELOPMENT OF THE YOUNG WOMEN’S CHRISTIAN SOCIAL GOSPEL, WOMEN’S SUFFRAGE, AND TEMPERANCE:
CREATING BLACK COMMUNITY ORGANIZATIONS Chinese Canadian Club JEWISH GARMENT WORKERS PROTEST Moblizing a Commuinty CONSEQUENCES OF THE PROTESTS ITALIAN WORKERS GO ON STRIKE
CREATING CHINESE COMMUNITY ORGANIZATONS Black Churches help railways SONGHEES REFUSE TO SELL THEIR LAND RESISTING THE POTLATCH LAW NEGOTIATING WITH THE GOVERNMENT residential school policies, gaining consent from chiefs in 1902. Working in cites ASSOCIATION IMPROVING SOCIAL STATUS COMMON GOALS SUPPORTING BLACK WOMEN PARTICIPATING IN SPORTS WORKING TOGETHER FOLLOWING THE SOCIAL GOSPEL MOVEMENT ESTABLISHING THE DOMESTIC SCIENCES THE WOMEN’S INSTITUTES Clifford Sifton's plan Escaping poverty The Doukhobors Seeking workers Seeking a better future Jewish Immigrants Feeling persecutions There was need for more farmers Jewish Commuintes Ukraine Commuinties Challenges on settling on farms Broken Promises Doukhobors LIVING IN BLOC SETTLEMENTS Home children Komagata maru THE CONTINUOUS JOURNEY REGULATION The immigration act The Chinese Head Tax Criticizing Immigration policy Discouraging immigration Responding to black immigration in Alberta Protesting immagration
Topic 1 Topic 2 RESISTANCE FROM FAMILIES Topic 3 Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4
Chapter 8 HISTORY Chapter 7
You might also like
- DBQ PRT 2Document3 pagesDBQ PRT 2FrankAulettiNo ratings yet
- Do We Have Special Moral Duties To Our Fellow Countrymen?Document14 pagesDo We Have Special Moral Duties To Our Fellow Countrymen?Frosen91No ratings yet
- Social Psychology PSYC250Document21 pagesSocial Psychology PSYC250pazucenaNo ratings yet
- DCCDocument1 pageDCCBrat WurstNo ratings yet
- Bonilla. o LiberalismoDocument24 pagesBonilla. o LiberalismoJhéssica LuaraNo ratings yet
- NAAB Student Performance Criteria Matrix For The Professional M.Arch. Degree at SDSUDocument1 pageNAAB Student Performance Criteria Matrix For The Professional M.Arch. Degree at SDSUSally AlaslamiNo ratings yet
- Adp-Ksa-Sol-Dwg-El-Td-Det-419 Cafe Counter Detail 2 - Rev.01Document1 pageAdp-Ksa-Sol-Dwg-El-Td-Det-419 Cafe Counter Detail 2 - Rev.01ekhaa.awal1No ratings yet
- 170156-001 (Rev-) Existing Site PlanDocument1 page170156-001 (Rev-) Existing Site PlanDaniel TelphiaNo ratings yet
- Madac SD El Fa BF 504Document1 pageMadac SD El Fa BF 504shoaibNo ratings yet
- UPU Živogošće Blato 2.1 PrometDocument1 pageUPU Živogošće Blato 2.1 PrometNikola MiljkoNo ratings yet
- DR - Majd and Dr. Dima Shop Drawing Reference 256 Date 12.08.23Document54 pagesDR - Majd and Dr. Dima Shop Drawing Reference 256 Date 12.08.230988624395hamzaNo ratings yet
- FS0654-DOD-ZZ-XX-DR-M-2013 - Domestic Water Distribution Schematic - Construction - C01 - 0Document1 pageFS0654-DOD-ZZ-XX-DR-M-2013 - Domestic Water Distribution Schematic - Construction - C01 - 0mvrisleyNo ratings yet
- Notes: Rear Elevation Side ElevationDocument1 pageNotes: Rear Elevation Side ElevationVarietta LusingaNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar - 2021Document2 pagesAmit Kumar - 2021Amit MalikNo ratings yet
- In This ChapterDocument24 pagesIn This ChapterabcNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson Z800i - V800 - V802se - SchematicsDocument39 pagesSony Ericsson Z800i - V800 - V802se - Schematicsfranklin quispe floresNo ratings yet
- Mapa Metamórfico de Colombia: Mario MayaDocument2 pagesMapa Metamórfico de Colombia: Mario MayaNicolas GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Jess 403Document10 pagesJess 403yomanNo ratings yet
- Jess 403Document10 pagesJess 403PracKillerNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- Librando Janry Design 5 Condominium ResearchDocument14 pagesLibrando Janry Design 5 Condominium ResearchJanryLibrandoNo ratings yet
- Estrutural Divisa - R00-FL01Document1 pageEstrutural Divisa - R00-FL01Pablo LimaNo ratings yet
- P8 5.5.0-P85.5.4 Patch Compatibility Matrix 6Document16 pagesP8 5.5.0-P85.5.4 Patch Compatibility Matrix 6Fouad ELMNo ratings yet
- Rcompany Monthly: Assignment 1Document8 pagesRcompany Monthly: Assignment 1ANJALINo ratings yet
- Rapporto Sulla Domanda Di Banda LargaDocument61 pagesRapporto Sulla Domanda Di Banda LargaLuigi ReggiNo ratings yet
- Siemens WT46W560gB09 - INSTMANUAL - (EN)Document10 pagesSiemens WT46W560gB09 - INSTMANUAL - (EN)Jeancarlos DominguezNo ratings yet
- Bhopal Tamil Sangam Brochure INDIA July 2022Document11 pagesBhopal Tamil Sangam Brochure INDIA July 2022US Soy CouncilNo ratings yet
- FAJA MARGINAL PropuestaDocument1 pageFAJA MARGINAL PropuestaDemetrio VargasNo ratings yet
- LS Fence 1Document1 pageLS Fence 1jimNo ratings yet
- 6 Architectural Plans Part 3 of 3 1800 Sheppard Avenue EastDocument11 pages6 Architectural Plans Part 3 of 3 1800 Sheppard Avenue EastBhushanNo ratings yet
- Pile SectionDocument1 pagePile Sectionsam_antony2005No ratings yet
- Pronorm Einbaukuchen GMBHDocument1 pagePronorm Einbaukuchen GMBHatulkundariaNo ratings yet
- Arhitectura Comunităţii Ca Arhitectură Integrată-Analiză Comparativă Şi Sinteză A Teoriilor Lui John F.C. Turner, John Habraken Şi Christopher Alexander/ COMMUNITY ARCHITECTURE AS..Document21 pagesArhitectura Comunităţii Ca Arhitectură Integrată-Analiză Comparativă Şi Sinteză A Teoriilor Lui John F.C. Turner, John Habraken Şi Christopher Alexander/ COMMUNITY ARCHITECTURE AS..ViorelNo ratings yet
- Typeset Using Lilypond by Steve Dunlop - Reference: Mutopia-2008/01/13-1235 Sheet Music From Mutopiaproject - Free To Download, With The Freedom To Distribute, Modify and PerformDocument1 pageTypeset Using Lilypond by Steve Dunlop - Reference: Mutopia-2008/01/13-1235 Sheet Music From Mutopiaproject - Free To Download, With The Freedom To Distribute, Modify and PerforminfobitsNo ratings yet
- 3 - Quaid-e-Azam Aor Aaj Ka PakistanDocument12 pages3 - Quaid-e-Azam Aor Aaj Ka PakistanA Wakeel HijaziNo ratings yet
- 2024 Annual ReportDocument102 pages2024 Annual ReportmaqsoumiNo ratings yet
- DMT Hvac PetsnackDocument1 pageDMT Hvac PetsnackYunus 12345No ratings yet
- PR A TD MLCP FP 202 Basement 1Document1 pagePR A TD MLCP FP 202 Basement 1shaikhtauqeir749No ratings yet
- Modular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseDocument2 pagesModular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseakinravNo ratings yet
- Hs CD 23 00187-Landscape General Arrangement Plan 1 of 4-952020Document1 pageHs CD 23 00187-Landscape General Arrangement Plan 1 of 4-952020api-193778159No ratings yet
- Facilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksDocument3 pagesFacilities/Machinery/ Equipment Mode of Acquisition Year Acquired Brand/ Model Condition/ RemarksmichaelNo ratings yet
- Separators in The Cement IndustryDocument5 pagesSeparators in The Cement Industryzane truesdaleNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesassis alihNo ratings yet
- Diwali Gala 2010: J S O T IDocument9 pagesDiwali Gala 2010: J S O T ISuparshNo ratings yet
- Снимок экрана 2021-05-10 в 15.24.13Document1 pageСнимок экрана 2021-05-10 в 15.24.13captmarlenNo ratings yet
- AVR-I-102.4B-FF-R.C.P Dimension Plan-10.03.2022Document1 pageAVR-I-102.4B-FF-R.C.P Dimension Plan-10.03.2022IqRa JaVedNo ratings yet
- A02.10-D - Overall Floor Plan - Level 07Document1 pageA02.10-D - Overall Floor Plan - Level 07Aakanksha Pandit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Issued For Construction: For Kitchen Equipment Power Connection Refer Dwg. 1308-Mob-E-709Document1 pageIssued For Construction: For Kitchen Equipment Power Connection Refer Dwg. 1308-Mob-E-709Motaleb BijoyNo ratings yet
- Credit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit TransactionsDocument1 pageCredit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit TransactionsDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Enamelled WireDocument20 pagesEnamelled WireNesya LaxmithaNo ratings yet
- 5th Floor Plan-Layout1Document1 page5th Floor Plan-Layout1yadvikram7No ratings yet
- φDocument1 pageφantonisdachliNo ratings yet
- DELE STRUCTURAL-Fdn. FTDocument1 pageDELE STRUCTURAL-Fdn. FTuche ekeNo ratings yet
- Swept Path Analysis For Delivery TruckDocument1 pageSwept Path Analysis For Delivery TruckGladdelyn PiencenavesNo ratings yet
- Kyoto Bus MapDocument1 pageKyoto Bus MapAndrew WongNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL SCHEMATICS - H&C B70 V6-Base 71Document1 pageMECHANICAL SCHEMATICS - H&C B70 V6-Base 71Slobodan HristovNo ratings yet
- Yatta Foundation RevDocument1 pageYatta Foundation RevKevin Lil'Vokez MulimaNo ratings yet
- P103 DWG STR 001Document1 pageP103 DWG STR 001RJNo ratings yet
- SR28C84196 B Main BoardDocument2 pagesSR28C84196 B Main BoardArthur AntoniolliNo ratings yet
- Makeni FootingDocument3 pagesMakeni FootingJack HaamboteNo ratings yet
- Everyday Life in ByzantiumDocument244 pagesEveryday Life in ByzantiumJovana Mitic Savic100% (11)
- Airport BoardDocument2 pagesAirport BoardcamiayoungNo ratings yet
- White Shade: The Real-World Primer for the Black Professional WomanFrom EverandWhite Shade: The Real-World Primer for the Black Professional WomanNo ratings yet
- Christian Education For Social ChangeDocument2 pagesChristian Education For Social ChangeAlan83% (6)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument6 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-206950621No ratings yet
- Barrier Free Architecture: Prof. Subodh ShankarDocument41 pagesBarrier Free Architecture: Prof. Subodh Shankarsubodh shankar100% (2)
- Opposition To The Ku Klux Klan in The Early 1920s: The Beginnings of Disaffection in Richmond, IndianaDocument25 pagesOpposition To The Ku Klux Klan in The Early 1920s: The Beginnings of Disaffection in Richmond, IndianaNicolas MartinNo ratings yet
- Mayoor School, Noida HALF YEARLY EXAM (2019-20) Political Science Class-Xi Set A Marking Scheme TIME: 3 Hour M.M: 80 DateDocument9 pagesMayoor School, Noida HALF YEARLY EXAM (2019-20) Political Science Class-Xi Set A Marking Scheme TIME: 3 Hour M.M: 80 DateKanupriya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Black Skins - and White Masks - Comic Books and The Secret of RaceDocument14 pagesBlack Skins - and White Masks - Comic Books and The Secret of RaceRose OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Latest Social Science Reviewer Part 11Document7 pagesLatest Social Science Reviewer Part 11Rubelin Dagohoy AmitNo ratings yet
- Representation in The Sun - GenderDocument40 pagesRepresentation in The Sun - GenderDee WatsonNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisAnonymous DwRqrHSXs3No ratings yet
- Asian American WomenDocument9 pagesAsian American Womenapi-247035267No ratings yet
- SADC SummaryDocument5 pagesSADC SummaryFaye JacobsNo ratings yet
- The Lesbianism Aspects in The Main Character of Novel "The Color Purple" by Alice Walker: A Feminist ApproachDocument7 pagesThe Lesbianism Aspects in The Main Character of Novel "The Color Purple" by Alice Walker: A Feminist ApproachElisua Kenniar AdhidaivataNo ratings yet
- Noah's SF 181 With Attached DocumentsDocument16 pagesNoah's SF 181 With Attached DocumentsEMPRESS_OM100% (4)
- Diversity in Organizations (Organizational Behavior Summary - Judge, Robins)Document3 pagesDiversity in Organizations (Organizational Behavior Summary - Judge, Robins)Kobe MaestreNo ratings yet
- FKB Learn-Sight-Words-Print Friendly-Dont Be A BullyDocument21 pagesFKB Learn-Sight-Words-Print Friendly-Dont Be A Bullysan ovNo ratings yet
- g9 q3 Module 1 - Differentiating Biases From PrejudicesDocument40 pagesg9 q3 Module 1 - Differentiating Biases From PrejudicesGeraldine MartinNo ratings yet
- Mainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 SlidesDocument50 pagesMainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 Slidestilahunthm100% (1)
- The female colonizer and othered woman in Isak Dinesen's Out of Africa, Jean Rhys's Wide Sargasso Sea, Tayeb Salih's Season of migration to the north, and Paule Marshall's The chosen place, the timeless peopleDocument81 pagesThe female colonizer and othered woman in Isak Dinesen's Out of Africa, Jean Rhys's Wide Sargasso Sea, Tayeb Salih's Season of migration to the north, and Paule Marshall's The chosen place, the timeless peopleAilen AlmaNo ratings yet
- Race 5tabloidDocument2 pagesRace 5tabloidMarcus RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cedar Park Assembly of God of Kirkland, Washington V KreidlerDocument22 pagesCedar Park Assembly of God of Kirkland, Washington V KreidlerAnonymous HiNeTxLMNo ratings yet
- LHOD and Her HSC English Extension 1 EssayDocument3 pagesLHOD and Her HSC English Extension 1 EssayFrank Enstein FeiNo ratings yet
- Gujrat Riots PDFDocument13 pagesGujrat Riots PDFaditya_2kNo ratings yet
- SAT 2hr DiagnosticDocument58 pagesSAT 2hr Diagnostic劉又綺 EuniceNo ratings yet
- Romantic Love Is A Moral IssueDocument4 pagesRomantic Love Is A Moral Issuemshiran7No ratings yet
- Tattoos and Piercings Are They Compatible in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesTattoos and Piercings Are They Compatible in The WorkplaceOkoth WilliamNo ratings yet
- Morality, Disgust, and Countertransference in PsychotherapyDocument4 pagesMorality, Disgust, and Countertransference in PsychotherapyJohn GavazziNo ratings yet