Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Syllabus
Maths Syllabus
Uploaded by
Arpit VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Schaum's Outline of Advanced Calculus, Third EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Advanced Calculus, Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Ceramic Forming TechniquesDocument26 pagesCeramic Forming TechniquesBorith pangNo ratings yet
- Course DetailsDocument22 pagesCourse DetailsSubham MaityNo ratings yet
- Course of Study M.A/M.Sc, Mathematics Semester-I, Ii, Iii & IvDocument19 pagesCourse of Study M.A/M.Sc, Mathematics Semester-I, Ii, Iii & IvNidhiNo ratings yet
- UG MathDocument6 pagesUG MathVishak H PillaiNo ratings yet
- Loyola College PG Mathematics 1Document27 pagesLoyola College PG Mathematics 1Prasoon SurendranNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusKunjal DasNo ratings yet
- Sust Math SyllabusDocument12 pagesSust Math SyllabusMohanned KhairyNo ratings yet
- NEP - Syllabus M.a.& M.sc. Mathematics (2022-2023) PDFDocument5 pagesNEP - Syllabus M.a.& M.sc. Mathematics (2022-2023) PDFtoufiquealam7985No ratings yet
- M SC MathematicsDocument16 pagesM SC MathematicsprabhumarchNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis & CalculusDocument2 pagesReal Analysis & CalculusHelloNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Semester II 2022-24Document5 pagesSyllabus Semester II 2022-24Rebel SachinNo ratings yet
- MSC Maths Syllabus 2018-19 PDFDocument28 pagesMSC Maths Syllabus 2018-19 PDFGovind Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Syl MSC Stats PDFDocument16 pagesSyl MSC Stats PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- M.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Document25 pagesM.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Hitesh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument8 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaGargi SarkarNo ratings yet
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Upperwala RaiNo ratings yet
- M.A. M. Sc. Mathematics (Part-II)Document37 pagesM.A. M. Sc. Mathematics (Part-II)Ashok MundeNo ratings yet
- MTH165Document1 pageMTH165Khalid HusenNo ratings yet
- MSC Sem 1 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMSC Sem 1 SyllabusM Afshan FaridiNo ratings yet
- M. A. / M. Sc. (Mathematics) First Semester Paper-I (Advanced Abstract Algebra-I) Time: Max. Marks: Unit 1Document24 pagesM. A. / M. Sc. (Mathematics) First Semester Paper-I (Advanced Abstract Algebra-I) Time: Max. Marks: Unit 1Vinaykumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Syllabus First Year First SemesterDocument7 pagesSyllabus First Year First Semestersnehasispal.spNo ratings yet
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Najeeb FatimaNo ratings yet
- Annuxure IiiDocument14 pagesAnnuxure IiiNamoNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1,2,3Document4 pagesCalculus 1,2,3Naveed100% (1)
- Calculus: Pre-Requisite: Single Variable CalculusDocument1 pageCalculus: Pre-Requisite: Single Variable CalculusSunil GuptaNo ratings yet
- M - Phil (Maths) CET - Syllabus-19-20Document8 pagesM - Phil (Maths) CET - Syllabus-19-20Prajakta BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- BS Fall 2019 5th SemesterDocument5 pagesBS Fall 2019 5th SemesterAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- BSC SyllabusDocument11 pagesBSC SyllabusMandar Priya PhatakNo ratings yet
- Anu Syllabus of M.phil-PhDocument1 pageAnu Syllabus of M.phil-PhDAVIDNo ratings yet
- Ma 6003Document2 pagesMa 6003bt20103080 Rijul SinglaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (1)Document2 pagesMathematics (1)Vaishali PawarNo ratings yet
- Common Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences, June 2019Document2 pagesCommon Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences, June 2019SWETHA LATHANo ratings yet
- Syllabus-PGT - Math FDocument5 pagesSyllabus-PGT - Math Fsahudebashis2000No ratings yet
- Detailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsDocument5 pagesDetailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsmiscNo ratings yet
- MSC MathematicsDocument20 pagesMSC MathematicsAIM INSTITUTENo ratings yet
- Stat Syllabus StatisticsDocument26 pagesStat Syllabus StatisticsAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Annexure-79. (GE For BA and BCom (Prog) (REVISED)Document2 pagesAnnexure-79. (GE For BA and BCom (Prog) (REVISED)raykrishan806No ratings yet
- MSC Iitpkd SyllabusDocument28 pagesMSC Iitpkd SyllabusSeshan SahooNo ratings yet
- M.sc. MathsDocument23 pagesM.sc. MathsRavi Sekhar100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument4 pagesMathematicsamjadNo ratings yet
- B.SC Part II ExamCode 05Document87 pagesB.SC Part II ExamCode 05swayangdash2003No ratings yet
- M.SC Syllabus Xyz (MATHS)Document18 pagesM.SC Syllabus Xyz (MATHS)Ldrago TerrorincarnatedNo ratings yet
- Objective: This Is A Preliminary Course For The Basic Courses in Mathematics Like, AbstractDocument5 pagesObjective: This Is A Preliminary Course For The Basic Courses in Mathematics Like, Abstractsairam patnaikNo ratings yet
- MTH3104 Linear Algebra IIDocument2 pagesMTH3104 Linear Algebra IIRonald EmanuelNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument7 pagesMATHEMATICSMohit SinghNo ratings yet
- (I) Syllabus On Algebra and Number TheoryDocument12 pages(I) Syllabus On Algebra and Number TheoryDeepNo ratings yet
- Course Outline (2021-2025)Document50 pagesCourse Outline (2021-2025)Amir Nawaz100% (1)
- Mathematics Course Alagappa UniversityDocument10 pagesMathematics Course Alagappa UniversityTirthajit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Aero Syllabus 12Document5 pagesAero Syllabus 12ae00505No ratings yet
- Maths VIDocument4 pagesMaths VIMohitNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus M-301 Ece-1Document5 pagesRevised Syllabus M-301 Ece-1Sayan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument1 pageAlgebraAN0% (1)
- 21 Syllabus M.SC Mathematics SyllabusDocument32 pages21 Syllabus M.SC Mathematics SyllabusShubhamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SyllabusDocument13 pagesMathematics SyllabusSARTHAK SHARMANo ratings yet
- Real Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountableDocument3 pagesReal Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountablelukasNo ratings yet
- GE Mathematics SyllabusDocument2 pagesGE Mathematics Syllabussoumyaliku14No ratings yet
- MSC Math Syllabus 2023-24Document31 pagesMSC Math Syllabus 2023-24Soumi MaityNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Linear Algebra and Differential EquationsFrom EverandIntroduction to Linear Algebra and Differential EquationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- GRL+Prosp - EDocument2 pagesGRL+Prosp - Ethoma111sNo ratings yet
- Graphical Analysis of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraphical Analysis of Motion WorksheetAnnNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Energy and The Electric PotentialDocument33 pagesElectric Potential Energy and The Electric PotentialJekjek LobatonNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Heat TransferDocument6 pagesFundamental Heat TransferCham SurendNo ratings yet
- Resuscitaire RW82-1Document7 pagesResuscitaire RW82-1Alexandra JanicNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideDocument146 pagesClinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideNacko Stavreski67% (3)
- Varian Leak Detection BrochureDocument42 pagesVarian Leak Detection BrochureKarthikeyan SankarrajanNo ratings yet
- Solution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Document14 pagesSolution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Prabhat JhaNo ratings yet
- M. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIDocument15 pagesM. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIFaturrachmanNo ratings yet
- Che 311-HW3 PDFDocument3 pagesChe 311-HW3 PDFYaren ErelNo ratings yet
- GCS 5910 - Lighting (20091231)Document16 pagesGCS 5910 - Lighting (20091231)Mosa Elnaid ElnaidNo ratings yet
- Ölflex® Classic 110 LT: Product InformationDocument4 pagesÖlflex® Classic 110 LT: Product InformationPhaniNo ratings yet
- ME582 CH 06Document30 pagesME582 CH 06Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum EorDocument5 pagesXanthan Gum EorTanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Tank Calculation: Project Name Design by Client Reviewed by Date Std/Code: Asme Viii & AiscDocument6 pagesRectangular Tank Calculation: Project Name Design by Client Reviewed by Date Std/Code: Asme Viii & AiscRubi HerwinNo ratings yet
- Fricton Loss in Valves & FittingsDocument3 pagesFricton Loss in Valves & FittingsBen LimNo ratings yet
- MIT Physics 8.02: Electricity & Magnetism: Course NotesDocument539 pagesMIT Physics 8.02: Electricity & Magnetism: Course NotesAnh Lương QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life of Packaged Bakery Goods-A ReviewDocument23 pagesShelf Life of Packaged Bakery Goods-A ReviewMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- L14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDocument3 pagesL14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDipto MahmudNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of MetalsAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Very ImportantDocument9 pagesCircuit Breaker Very ImportantHytham Ramdan El BardecyNo ratings yet
- Shukrun Farrell Et Al 2020 3d Printing of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Complex StructuresDocument8 pagesShukrun Farrell Et Al 2020 3d Printing of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Complex StructuresEmiliano AmbrosinoNo ratings yet
- Ampl F 600L WH Nb-A2 TG SD: LED Floodlight Luminaire "AMAZE PLUS"Document6 pagesAmpl F 600L WH Nb-A2 TG SD: LED Floodlight Luminaire "AMAZE PLUS"Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- CHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsJane Eilyza Aballa100% (1)
- QUIZ 2 RIGID MOTION Master 9 THDocument3 pagesQUIZ 2 RIGID MOTION Master 9 THBombasticNo ratings yet
- Bond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtDocument23 pagesBond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtdhanushNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Reading Comprehension Worksheet: Thomas Edison - The Inventor of The Light BulbDocument2 pagesGrade 3 Reading Comprehension Worksheet: Thomas Edison - The Inventor of The Light Bulbhoneylibra9378100% (3)
- Utp Ledurit 65Document1 pageUtp Ledurit 65brayanNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Tanks 4 Year Civil: Rectangular Tanks By: Abdel Hamid ZaghwDocument30 pagesReinforced Concrete Tanks 4 Year Civil: Rectangular Tanks By: Abdel Hamid ZaghwjabbarNo ratings yet
Maths Syllabus
Maths Syllabus
Uploaded by
Arpit VermaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Syllabus
Maths Syllabus
Uploaded by
Arpit VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
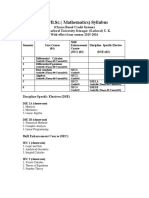
UG SEMESTER- I
(For students with Mathematics as a minor subject)
Applicable Mathematics– I
Credit: 4 T:04
Course Outcomes:
1. To compute the rank of a matrix and its applications in finding solutions
of system of equations, computing Eigen values and Eigen vectors and their
applications.
2. To Know the concepts of calculus, namely, limits, continuity,
differentiability of functions and their applications in the form of mean
value theorem and Taylor’s theorem.
3. To understand the concept of double and triple integration and their
applications in finding length surfaces and volumes etc.
4. To understand the concepts of vector calculus.
UNIT I
Types of matrices, elementary operations on matrices, rank of a matrix, echelon and
normal forms of a matrix, inverse of a matrix by elementary operations, systems of
linear homogeneous and non - homogeneous equations, consistency of linear system
of equations, eigenvalues, eigenvectors and characteristic equation of a square
matrix, Cayley - Hamilton theorem and its application in finding the inverse of a
matrix.
UNIT II
Limit, continuity and differentiability of functions of single variable, successive
differentiation, Leibnitz's theorem, Rolle's theorem, Lagrange's and Cauchy's mean
value theorems, Taylor's and Maclaurins's series with various forms of remainders.
UNIT III
Limit, continuity and differentiability of functions of two variables, partial derivatives,
Euler's theorem for homogeneous functions, total derivative, Taylor's and Maclaurins's
theorem for functions of two variables, extrema of functions of two variables,
Lagrange's method of unknown multipliers, Jacobian.
UNIT IV
Double and triple integration, change of order of integration, application of integration
to length, surface and volumes (only Cartesian coordinates), beta, gamma and
Dirichlet’s integral – basic properties with applications, vector differentiation, gradient,
divergence and curl with their physical interpretations, tangent and normal on a
surface, directional derivative, line, surface and volume integrals, applications of
Green's, Stoke's and Gauss' divergence theorems (without proofs).
References:
Textbooks
1. Linear Algebra by K. Hoffman and R. Kunze.
2. Calculus, Volumes I & II by T. M. Apostol.
3. Mathematical Analysis by S.C. Malik and S. Arora, New Age International
Limited, New Delhi.
Suggested Books
1. R. R. Goldberg : Methods of Real Analysis, Oxford & IBH Pub. Co. Pvt. Ltd.
2. R. G. Bartle, The Elements of Real Analysis, Wiley International Edition.
UG SEMESTER- II
(For students with Mathematics as a minor subject)
Applicable Mathematics– II
Credit: 4 T:04
Course Outcomes:
1. To understand the concepts of groups, subgroups, cyclic groups, quotient
groups and homomorphism of groups.
2. To Know the concepts of rings, subrings, ideals, quotient rings and
homomorphism of rings.
3. To know the concept of vector spaces, its basis and dimension, quotient
space and linear transformations.
4. To learn sequences and various tests to check convergence of an infinite
series.
UNIT I
Equivalence relations and partitions, congruence modulo n, groups, subgroups, cyclic
groups, coset decomposition, Lagrange’s theorem, Fermat’s & Euler’s theorems,
normal subgroups, quotient groups, homomorphism and homomorphism theorems.
UNIT II
Rings, types of rings - commutative rings, rings with unity, division rings, integral
domains and fields, subrings, ideals and quotient rings, ring homomorphism and
homomorphism theorems, characteristic of a ring, Polynomial rings.
UNIT III
Vector spaces, subspaces, linear independence and dependence, basis and dimension,
quotient space, linear transformations and their representation as matrices, rank -
nullity theorem.
UNIT IV
Sequences, limit of a sequence, convergence, divergence and oscillation of a sequence,
infinite series and its convergence, geometric and harmonic series, tests for
convergence and divergence - comparison test, Cauchy integral test, D’alembert’s ratio
test, Cauchy’s nth root test, Raabe’s logarithmic test, DeMorgan and Bertrand’s test,
alternating series, absolute and conditional convergence, Leibnitz’s theorem (without
proof).
References:
Textbooks
1. V. Sahai & V. Bist : Algebra, Narosa.
2. J.A. Gallian : Contemporary Abstract Algebra, Narosa.
3. R.G. Bartle : Introduction to Real Analysis, Wiley.
Suggested books
1. J.B. Fraleigh : A First course in Abstract Algebra, Pearson.
2. D.S. Dummit & R.M. Foote : Abstract Algebra, Wiley International edition.
You might also like
- Schaum's Outline of Advanced Calculus, Third EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Advanced Calculus, Third EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Ceramic Forming TechniquesDocument26 pagesCeramic Forming TechniquesBorith pangNo ratings yet
- Course DetailsDocument22 pagesCourse DetailsSubham MaityNo ratings yet
- Course of Study M.A/M.Sc, Mathematics Semester-I, Ii, Iii & IvDocument19 pagesCourse of Study M.A/M.Sc, Mathematics Semester-I, Ii, Iii & IvNidhiNo ratings yet
- UG MathDocument6 pagesUG MathVishak H PillaiNo ratings yet
- Loyola College PG Mathematics 1Document27 pagesLoyola College PG Mathematics 1Prasoon SurendranNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusKunjal DasNo ratings yet
- Sust Math SyllabusDocument12 pagesSust Math SyllabusMohanned KhairyNo ratings yet
- NEP - Syllabus M.a.& M.sc. Mathematics (2022-2023) PDFDocument5 pagesNEP - Syllabus M.a.& M.sc. Mathematics (2022-2023) PDFtoufiquealam7985No ratings yet
- M SC MathematicsDocument16 pagesM SC MathematicsprabhumarchNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis & CalculusDocument2 pagesReal Analysis & CalculusHelloNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Semester II 2022-24Document5 pagesSyllabus Semester II 2022-24Rebel SachinNo ratings yet
- MSC Maths Syllabus 2018-19 PDFDocument28 pagesMSC Maths Syllabus 2018-19 PDFGovind Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Syl MSC Stats PDFDocument16 pagesSyl MSC Stats PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- M.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Document25 pagesM.a.M.sc. Part I Mathematics (Ext - Reg I) 09Hitesh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument8 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology PatnaGargi SarkarNo ratings yet
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Upperwala RaiNo ratings yet
- M.A. M. Sc. Mathematics (Part-II)Document37 pagesM.A. M. Sc. Mathematics (Part-II)Ashok MundeNo ratings yet
- MTH165Document1 pageMTH165Khalid HusenNo ratings yet
- MSC Sem 1 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMSC Sem 1 SyllabusM Afshan FaridiNo ratings yet
- M. A. / M. Sc. (Mathematics) First Semester Paper-I (Advanced Abstract Algebra-I) Time: Max. Marks: Unit 1Document24 pagesM. A. / M. Sc. (Mathematics) First Semester Paper-I (Advanced Abstract Algebra-I) Time: Max. Marks: Unit 1Vinaykumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Syllabus First Year First SemesterDocument7 pagesSyllabus First Year First Semestersnehasispal.spNo ratings yet
- B.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Document10 pagesB.A. /B.Sc. - Part I (Mathematics)Najeeb FatimaNo ratings yet
- Annuxure IiiDocument14 pagesAnnuxure IiiNamoNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1,2,3Document4 pagesCalculus 1,2,3Naveed100% (1)
- Calculus: Pre-Requisite: Single Variable CalculusDocument1 pageCalculus: Pre-Requisite: Single Variable CalculusSunil GuptaNo ratings yet
- M - Phil (Maths) CET - Syllabus-19-20Document8 pagesM - Phil (Maths) CET - Syllabus-19-20Prajakta BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- BS Fall 2019 5th SemesterDocument5 pagesBS Fall 2019 5th SemesterAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- BSC SyllabusDocument11 pagesBSC SyllabusMandar Priya PhatakNo ratings yet
- Anu Syllabus of M.phil-PhDocument1 pageAnu Syllabus of M.phil-PhDAVIDNo ratings yet
- Ma 6003Document2 pagesMa 6003bt20103080 Rijul SinglaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (1)Document2 pagesMathematics (1)Vaishali PawarNo ratings yet
- Common Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences, June 2019Document2 pagesCommon Syllabus For Part B' and C' Mathematical Sciences, June 2019SWETHA LATHANo ratings yet
- Syllabus-PGT - Math FDocument5 pagesSyllabus-PGT - Math Fsahudebashis2000No ratings yet
- Detailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsDocument5 pagesDetailes Syllabus Lecturer in MathsmiscNo ratings yet
- MSC MathematicsDocument20 pagesMSC MathematicsAIM INSTITUTENo ratings yet
- Stat Syllabus StatisticsDocument26 pagesStat Syllabus StatisticsAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Annexure-79. (GE For BA and BCom (Prog) (REVISED)Document2 pagesAnnexure-79. (GE For BA and BCom (Prog) (REVISED)raykrishan806No ratings yet
- MSC Iitpkd SyllabusDocument28 pagesMSC Iitpkd SyllabusSeshan SahooNo ratings yet
- M.sc. MathsDocument23 pagesM.sc. MathsRavi Sekhar100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument4 pagesMathematicsamjadNo ratings yet
- B.SC Part II ExamCode 05Document87 pagesB.SC Part II ExamCode 05swayangdash2003No ratings yet
- M.SC Syllabus Xyz (MATHS)Document18 pagesM.SC Syllabus Xyz (MATHS)Ldrago TerrorincarnatedNo ratings yet
- Objective: This Is A Preliminary Course For The Basic Courses in Mathematics Like, AbstractDocument5 pagesObjective: This Is A Preliminary Course For The Basic Courses in Mathematics Like, Abstractsairam patnaikNo ratings yet
- MTH3104 Linear Algebra IIDocument2 pagesMTH3104 Linear Algebra IIRonald EmanuelNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument7 pagesMATHEMATICSMohit SinghNo ratings yet
- (I) Syllabus On Algebra and Number TheoryDocument12 pages(I) Syllabus On Algebra and Number TheoryDeepNo ratings yet
- Course Outline (2021-2025)Document50 pagesCourse Outline (2021-2025)Amir Nawaz100% (1)
- Mathematics Course Alagappa UniversityDocument10 pagesMathematics Course Alagappa UniversityTirthajit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Aero Syllabus 12Document5 pagesAero Syllabus 12ae00505No ratings yet
- Maths VIDocument4 pagesMaths VIMohitNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus M-301 Ece-1Document5 pagesRevised Syllabus M-301 Ece-1Sayan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument1 pageAlgebraAN0% (1)
- 21 Syllabus M.SC Mathematics SyllabusDocument32 pages21 Syllabus M.SC Mathematics SyllabusShubhamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SyllabusDocument13 pagesMathematics SyllabusSARTHAK SHARMANo ratings yet
- Real Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountableDocument3 pagesReal Analysis: (Review: Elementary Set Theory, Finite, CountablelukasNo ratings yet
- GE Mathematics SyllabusDocument2 pagesGE Mathematics Syllabussoumyaliku14No ratings yet
- MSC Math Syllabus 2023-24Document31 pagesMSC Math Syllabus 2023-24Soumi MaityNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Linear Algebra and Differential EquationsFrom EverandIntroduction to Linear Algebra and Differential EquationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- GRL+Prosp - EDocument2 pagesGRL+Prosp - Ethoma111sNo ratings yet
- Graphical Analysis of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraphical Analysis of Motion WorksheetAnnNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Energy and The Electric PotentialDocument33 pagesElectric Potential Energy and The Electric PotentialJekjek LobatonNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Heat TransferDocument6 pagesFundamental Heat TransferCham SurendNo ratings yet
- Resuscitaire RW82-1Document7 pagesResuscitaire RW82-1Alexandra JanicNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideDocument146 pagesClinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideNacko Stavreski67% (3)
- Varian Leak Detection BrochureDocument42 pagesVarian Leak Detection BrochureKarthikeyan SankarrajanNo ratings yet
- Solution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Document14 pagesSolution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Prabhat JhaNo ratings yet
- M. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIDocument15 pagesM. Fatur - H1C018040 - PETROLOGIFaturrachmanNo ratings yet
- Che 311-HW3 PDFDocument3 pagesChe 311-HW3 PDFYaren ErelNo ratings yet
- GCS 5910 - Lighting (20091231)Document16 pagesGCS 5910 - Lighting (20091231)Mosa Elnaid ElnaidNo ratings yet
- Ölflex® Classic 110 LT: Product InformationDocument4 pagesÖlflex® Classic 110 LT: Product InformationPhaniNo ratings yet
- ME582 CH 06Document30 pagesME582 CH 06Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum EorDocument5 pagesXanthan Gum EorTanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Tank Calculation: Project Name Design by Client Reviewed by Date Std/Code: Asme Viii & AiscDocument6 pagesRectangular Tank Calculation: Project Name Design by Client Reviewed by Date Std/Code: Asme Viii & AiscRubi HerwinNo ratings yet
- Fricton Loss in Valves & FittingsDocument3 pagesFricton Loss in Valves & FittingsBen LimNo ratings yet
- MIT Physics 8.02: Electricity & Magnetism: Course NotesDocument539 pagesMIT Physics 8.02: Electricity & Magnetism: Course NotesAnh Lương QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life of Packaged Bakery Goods-A ReviewDocument23 pagesShelf Life of Packaged Bakery Goods-A ReviewMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- L14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDocument3 pagesL14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDipto MahmudNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of MetalsAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Very ImportantDocument9 pagesCircuit Breaker Very ImportantHytham Ramdan El BardecyNo ratings yet
- Shukrun Farrell Et Al 2020 3d Printing of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Complex StructuresDocument8 pagesShukrun Farrell Et Al 2020 3d Printing of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Complex StructuresEmiliano AmbrosinoNo ratings yet
- Ampl F 600L WH Nb-A2 TG SD: LED Floodlight Luminaire "AMAZE PLUS"Document6 pagesAmpl F 600L WH Nb-A2 TG SD: LED Floodlight Luminaire "AMAZE PLUS"Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- CHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHE 509 - Past Exam QuestionsJane Eilyza Aballa100% (1)
- QUIZ 2 RIGID MOTION Master 9 THDocument3 pagesQUIZ 2 RIGID MOTION Master 9 THBombasticNo ratings yet
- Bond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtDocument23 pagesBond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtdhanushNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Reading Comprehension Worksheet: Thomas Edison - The Inventor of The Light BulbDocument2 pagesGrade 3 Reading Comprehension Worksheet: Thomas Edison - The Inventor of The Light Bulbhoneylibra9378100% (3)
- Utp Ledurit 65Document1 pageUtp Ledurit 65brayanNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Tanks 4 Year Civil: Rectangular Tanks By: Abdel Hamid ZaghwDocument30 pagesReinforced Concrete Tanks 4 Year Civil: Rectangular Tanks By: Abdel Hamid ZaghwjabbarNo ratings yet