Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Uploaded by
Shahrukh123456789Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Financial Model of ACCDocument13 pagesFinancial Model of ACCYash AhujaNo ratings yet
- 5.well PerforationDocument13 pages5.well Perforationakshitppe11100% (1)
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesNuclear Power PlantlintangellaNo ratings yet
- Battery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextDocument13 pagesBattery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerplantDocument5 pagesNuclear PowerplantAri HariNo ratings yet
- Sumit BhardwajDocument8 pagesSumit BhardwajER Publications, IndiaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1Document7 pagesSteam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1RichardNo ratings yet
- E-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMDocument9 pagesE-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMnidhidgowda185No ratings yet
- Hydro Power GenerationDocument15 pagesHydro Power GenerationEngr Lanre MajekNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument10 pagesUnit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Colour)Document44 pagesPower Plant Colour)Er Anoop GuptaNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument71 pagesHYDRO Power Plant Presentationfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Power Plants: Dept. of Mech & Mfg. EnggDocument12 pagesPower Plants: Dept. of Mech & Mfg. EnggomkardashetwarNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power NotesDocument14 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power Notes1ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1Document16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument24 pagesNuclear Power Plantvkumar_345287No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument7 pagesNuclear Power PlantzzaanNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument35 pagesHYDRO Power Plant PresentationM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringC SelvenNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDocument27 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionDocument35 pagesIV SolutionAnonymous t3GcHwKMBNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power: An Insider'S ViewDocument2 pagesNuclear Power: An Insider'S ViewrollramsNo ratings yet
- Micro Hydro Electricity BasicsDocument13 pagesMicro Hydro Electricity Basicssebascian100% (1)
- Chapter-1: 1.1.induction GeneratorDocument12 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.induction GeneratorSURAJNo ratings yet
- Chimoio, Maio de 2021Document15 pagesChimoio, Maio de 2021Demítrio G. PioNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantDocument12 pagesTypes of Power PlantJonaz CruzNo ratings yet
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Document3 pagesWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- SPP1 4209-Hydro Power TechniquesDocument5 pagesSPP1 4209-Hydro Power TechniquesShariff Oluoch OdiwuorNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument4 pagesWorking Principle of Hydroelectric Power PlantGummadi AmarNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument35 pagesHYDRO Power Plant Presentationhannyjberchmans100% (1)
- Hydroelectric Power Plants - Principles of Operation - EE Power SchoolDocument14 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants - Principles of Operation - EE Power Schoolharshitsingh.m99No ratings yet
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternDocument3 pagesPressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternAnkit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Paper-Oil Transformers and The Requirement For High Quality Adsorbing Desiccants To Prolong Transformer LifeDocument5 pagesElectrical Paper-Oil Transformers and The Requirement For High Quality Adsorbing Desiccants To Prolong Transformer LifekamaladonNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument12 pagesPowerplant EngineeringBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantVinay Rai100% (3)
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument22 pagesNuclear Power PlantMuhammad Ahkam KhanNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-5Document26 pagesBEE Unit-5gunasundar choppaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Final AssignmentDocument6 pagesDistribution Final AssignmentGabrielGrecoNo ratings yet
- Report of Project PGS 2Document16 pagesReport of Project PGS 2Safdar ali AlmaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plants - 2018 PDFDocument71 pagesTypes of Power Plants - 2018 PDFJeff Justine GeragaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantmaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantADocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantAtheunsung tale100% (1)
- Electrical Energy Generation, Utilization and ConsrevationDocument132 pagesElectrical Energy Generation, Utilization and Consrevationvarunflyhigh50% (2)
- Lec 1 - Mod 1.2Document127 pagesLec 1 - Mod 1.2Ar. Soumya P SNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant - WikipediaDocument21 pagesNuclear Power Plant - Wikipediahasan.the.great420No ratings yet
- For Power PlantDocument224 pagesFor Power PlantIrene Mununi100% (2)
- M4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFDocument5 pagesM4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument5 pagesRADIOACTIVITYYusra KhanNo ratings yet
- Mid 2Document164 pagesMid 2Asif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDocument15 pagesNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioNo ratings yet
- Principle of Power GenerationDocument36 pagesPrinciple of Power Generationbilyaminu hamisu b/zNo ratings yet
- Foebe Bee2093 Chapter2Document36 pagesFoebe Bee2093 Chapter2Mwindjou MhoumadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument6 pagesNuclear Power PlantDr. Lenin V RNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaFrom EverandIntroduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaNo ratings yet
- Brake & Clutch Fluid Dot 3 PDFDocument6 pagesBrake & Clutch Fluid Dot 3 PDFBryan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hempadur XP 87550: DescriptionDocument2 pagesHempadur XP 87550: DescriptionEngTamer50% (4)
- 12 - Sucker Rod Pumping - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringDocument20 pages12 - Sucker Rod Pumping - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringmissaouiNo ratings yet
- EAW-Nisbit Submittal - 01152013Document56 pagesEAW-Nisbit Submittal - 01152013StCharlesCSNo ratings yet
- Pcie Link TrainingDocument3 pagesPcie Link TrainingChinmay100% (1)
- Solid Shell Connection in Finite Element AnalysisDocument21 pagesSolid Shell Connection in Finite Element AnalysisvilukNo ratings yet
- Cinnetic 2014 PDFDocument60 pagesCinnetic 2014 PDFOscar SpinningaliciaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 10 - HSE Facility Standard of SECLDocument27 pagesAppendix 10 - HSE Facility Standard of SECLMurtadda MohammedNo ratings yet
- Communication ProtocolDocument6 pagesCommunication Protocolgemni7No ratings yet
- Ram Concrete AnalysisDocument94 pagesRam Concrete AnalysisTom CurryNo ratings yet
- 2018IBM BPMOverview AprilDocument12 pages2018IBM BPMOverview AprilsaluyumugiNo ratings yet
- VoriconazoleDocument3 pagesVoriconazoleWH PANDWNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tenses - 10 TextsDocument9 pagesMixed Tenses - 10 TextsRamon Gabriel100% (1)
- Map UgDocument1,856 pagesMap Ughanif0404100% (1)
- NyquistDocument12 pagesNyquistOsel Novandi WitohendroNo ratings yet
- Uninstalling and Reinstalling The Windows 2012R2 Failover Clustering FeatureDocument6 pagesUninstalling and Reinstalling The Windows 2012R2 Failover Clustering FeatureNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Assessment ChecklistDocument28 pagesLaboratory Assessment ChecklistPanneer Selvam100% (2)
- CCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st EditionDocument531 pagesCCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st Editionmansoorali_af100% (2)
- AdvantageCalibration Quick Ref CardDocument36 pagesAdvantageCalibration Quick Ref CardDario Fernando Flores Cotto100% (1)
- Notes: General Steel Fabrication Notes: Carbon Steel Fabrication Notes: Stainless Steel FabricationDocument6 pagesNotes: General Steel Fabrication Notes: Carbon Steel Fabrication Notes: Stainless Steel FabricationAquiles MartinezNo ratings yet
- OltremareDocument1 pageOltremareAfraz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Book Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDocument57 pagesBook Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDanny OxinaNo ratings yet
- Technology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameDocument15 pagesTechnology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameMoses MussNo ratings yet
- Marks of ESE 2023 Qualified CandidatesDocument10 pagesMarks of ESE 2023 Qualified Candidatesthunderbuddy2222No ratings yet
- Daewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFDocument62 pagesDaewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFdann222No ratings yet
- Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesBonding in SolidsMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Column in Limit State MethodDocument7 pagesDesign of Column in Limit State MethodRicardo BermudezNo ratings yet
- Design and Thermal Analysis of Segmental Baffle and Helical Baffle in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Using Kern MethodDocument7 pagesDesign and Thermal Analysis of Segmental Baffle and Helical Baffle in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Using Kern MethodIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Uploaded by
Shahrukh123456789Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Power Technology: 1. What Is Breaker?
Uploaded by
Shahrukh123456789Copyright:
Available Formats
Assignment on:-
POWER TECHNOLOGY
1. What is breaker?
A switch that automatically interrupts the flow of electric current if the current exceeds a preset limit, measured in amperes. Circuit breakers are used most often as a safety precaution where excessive current through a circuit could be hazardous. Unlike fuses, they can usually be reset and reused.
Page: 1
TYPES:There are three common types of circuit breakers. The basic parts of a circuit breaker are the switch and a moving, conductive contact plate that moves the switch when electricity comes into contact with it. In the circuit box the contact plate is connected to a stationary plate that allows electricity to flow; but if the circuit is overloaded the contact plate will force the switch to flip and break the electrical flow. A magnetic circuit breaker uses electromagnetism to break the circuit. The electromagnet on this circuit breaker gets stronger with the flow of electricity. When the electrical load exceeds the prescribed currency the electromagnet will be powerful enough to force the circuit breaker lever down and move the contact plate which flips the switch. Another kind of circuit breaker is the thermal circuit breaker which uses heat to break the circuit. With a bimetallic strip (two types of metal; one on each side) this circuit breaker responds to the extreme heat of the electrical current. Each type of metal expands differently to bend the strip. When the electricity is too strong then the strip is bent at an angle which will turn over the contact plate and break the circuit. The third type of circuit breaker combines electromagnetism and heat. This device has an electromagnet that protects against sudden surges in the electrical load and a bimetallic strip that protects against prolonged electrical overload and overheating. When purchasing circuit breakers for your home you will need to discuss your options with your electrician and select the best type of circuit breaker for your needs.
Page: 2
2. NUCLEAR PLANT:-
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. Nuclear power plants are base load stations, which work best when the power output is constant.
Page: 3
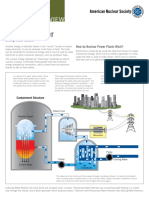
SYSTEM The conversion to electrical energy takes place indirectly, as in conventional thermal power plants. The heat is produced by fission in a nuclear reactor (in a coal power plant it would correspond to the boiler) and given to a heat transfer fluid usually water (for a standard type light water reactor). Directly or indirectly water vaporsteam is produced. The pressurized steam is then usually fed to a multi-stage steam turbine. Steam turbines in Western nuclear power plants are among the largest steam turbines ever. After the steam turbine has expanded and partially condensed the steam, the remaining vapor is condensed in a condenser. The condenser is a heat exchanger which is connected to secondary side such as a river or a cooling tower. The water then pumped back into the nuclear reactor and the cycle begins again.
*Nuclear reactors:-
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The most common use of nuclear reactors is for the generation of electric energy and for the propulsion of ships. The nuclear reactor is the heart of the plant. In its central part, the reactor cores heat is generated by controlled nuclear fission. With this heat, a coolant is heated as it is pumped through the reactor and thereby removes the energy from the reactor. Heat from nuclear fission is used to raise steam, which runs through turbines, which in turn powers either ships propellers or electrical generators. Since nuclear fission creates radioactivity, the reactor core is surrounded by a protective shield. This containment absorbs radiation and prevents radioactive material from being released into the environment. In addition, many reactors are equipped with a dome of concrete to protect the reactor against external impacts. In nuclear power plants, different types of reactors, nuclear fuels, and cooling circuits and moderators are sometimes used.
Page: 4
*Steam turbine:-
The object of the steam turbine is to convert the heat contained in steam into rotational energy. The engine house with the steam turbine is usually structurally separated from the main reactor building. It is aligned to prevent debris from the destruction of a turbine in operation from flying towards the reactor In the case of a pressurized water reactor, the steam turbine hermetically separated from the nuclear system. To detect a leak in the steam generator and thus the passage of radioactive water at an early stage is the outlet steam of the steam generator mounted an activity meter. In contrast, boiling water reactors and the steam turbine with radioactive water applied and therefore part of the control area of the nuclear power plant.
*Generator:The generator converts kinetic energy supplied by the turbine into electrical energy. Low-pole AC synchronous generators of high rated power are used.
*Main coolant pump (PWR) and forced circulation pump (BWR):The reactor coolant pump in the case of the DWR has the task to circulate the coolant between the reactor and steam generators. In western nuclear power plants, the nuclear reactor is fed with four redundant pumps (loops), each separated by Redundancy structurally accommodated in the reactor building. The design of the pump corresponds to a Centrifugal with a one-piece forged body. The throughput is up to 10,000 l / s at a pressure of 175 bar and a maximum allowable temperature of 350 C.[13] The increase in pressure through the main coolant pump when DWR indicates pressure loss in the reactor, steam generators and piping system. Even after the failure of the main coolant pumps (RESA is the result of) the circulation and thus the heat dissipation is by so-called Natural circulation guaranteed. In the case of boiling water reactor are the reactor pressure vessel forced circulation pumps to avoid core wings attached to their interpretation is approximately equal to those in a PWR. You are responsible for the safety of the plant is not absolutely necessary.
Page: 5
*Safety valves:The pressure in the reactor pressure vessel at an incident, to limit upward, two independent safety valves are available. The pressure relief prevents bursting of pipes or reactor. The valves are in their capacity designed so that they can derive all of the supplied flow rates with little increase in pressure. In the case of the BWR, the steam is directed into the condensate chamber and condenses there. The chambers are on heat exchanger connected to the intermediate cooling circuit.
*Feedwater pump:The Feedwater pump have the task of the water from the feedwater tank to the vapor pressure in the reactor and the steam generator to bring and promote a water with approximately 2200 kg / s. The power required amounts here to about 20 MW per pump. About the feed water system, the water level in the steam generator and nuclear reactor is controlled. Emergency power supply [Edit] The Emergency power supply a nuclear power plant is several times redundant built up by diesel generators and battery buffers. The battery backup provides uninterrupted coupling of the diesel units in the network secure. If necessary, the emergency power supply allows the safe descent down the nuclear reactor. Less important auxiliary systems such as, for example, heat tracing of pipelines are not receiving it. The majority of the required power is used to supply the feed pumps and Notspeisepumpen order to shut down the nuclear reactor, the Decay heat even with a Failure of the power system, A Blackout permanently dissipate.
Page: 6
3. HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANT:-
To define hydroelectric power plants means to have an up close glimpse as far as the role of hydroelectric power plants in the world that we belong in. It is not an easy task for a power generating source like this to perform its ultimate task of providing an energy that is non-hazardous and to make energy conservation a thing to be look forward to and not just a thing of the past. This article aims not only to define hydroelectric power plants, but to enlighten the readers about its benefits and its accompanying limitations not only environmentally but also economically. Hydroelectricity plants are intricate and complex installations which are being employed to convert energy. It is consists of a sequence of chain of hydraulic engineering equipments which has the needed water flow, thereby creating a head, along with a power-generating equipment for transforming water energy that is under pressure thereby converted to mechanical energy of rotation Afterwards, it is transformed to electrical energy for human use. Meanwhile, hydropower stations are built to make the supply of hydroelectricity a continuous process. Some countries in the world like Australia and New Zealand have the most modernized and sophisticated hydroelectric stations today. In fact, Australia has already launched their first ever hydropower plants just recently. According to the
North Head Sewerage, this hydroelectric powered station will really benefit the environment because of its green energy. Actually, this hydroelectric sewerage will definitely decrease the emission of toxic gases. This can be possible by trapping energy from treated waste water which falls down a 60 meter shaft. Likewise, its green energy will be able to power up almost 1,000 houses for a period of one year. The great thing about their hydroelectricity project is that it can significantly diminish gas emissions at a significant percentage, averaging to 12,000 tons per year. Due to the demanding and ever-growing needs of man, engineers have decided to build the largest hydroelectric dam in the world that is found in Rogun, Tajikistan. It stands about 1,000 feet tall. However, engineers have to consider the hydroelectric power plant locations. The proper place of this hydroelectric energy plants is necessary in order to generate the adequate amount of hydroelectric energy needed in a given area or territory. It has to be in proximity of valleys and rivers. Why is this necessary? It is because there are locations that will not be suited to build these hydroelectric generated plants. As to the suitable location, it is best to build hydroelectric facilities where the land is like a slope and not flat. On another side, hydroelectric energy is advantageous. Primarily, it can lower the cost of electric consumption and generate millions of dollars to boost the economy. Though, it will endanger our marine resources, environmental safeguards are being created to ensure the safety of human life and our ecosystem as a whole in the years ahead. Truly, the creation of hydroelectric energy makes life easy and convenient.
X--------------X----------------X
Page: 7
You might also like
- Financial Model of ACCDocument13 pagesFinancial Model of ACCYash AhujaNo ratings yet
- 5.well PerforationDocument13 pages5.well Perforationakshitppe11100% (1)
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesNuclear Power PlantlintangellaNo ratings yet
- Battery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextDocument13 pagesBattery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerplantDocument5 pagesNuclear PowerplantAri HariNo ratings yet
- Sumit BhardwajDocument8 pagesSumit BhardwajER Publications, IndiaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1Document7 pagesSteam Turbine Electrical Generator Condensed Condenser: Part C Unit 1RichardNo ratings yet
- E-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMDocument9 pagesE-Note 19058 Content Attachment1 20240425024156PMnidhidgowda185No ratings yet
- Hydro Power GenerationDocument15 pagesHydro Power GenerationEngr Lanre MajekNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument10 pagesUnit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Colour)Document44 pagesPower Plant Colour)Er Anoop GuptaNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument71 pagesHYDRO Power Plant Presentationfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- Power Plants: Dept. of Mech & Mfg. EnggDocument12 pagesPower Plants: Dept. of Mech & Mfg. EnggomkardashetwarNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power NotesDocument14 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power Notes1ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1Document16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument24 pagesNuclear Power Plantvkumar_345287No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument7 pagesNuclear Power PlantzzaanNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument35 pagesHYDRO Power Plant PresentationM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringC SelvenNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDocument27 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- IV SolutionDocument35 pagesIV SolutionAnonymous t3GcHwKMBNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power: An Insider'S ViewDocument2 pagesNuclear Power: An Insider'S ViewrollramsNo ratings yet
- Micro Hydro Electricity BasicsDocument13 pagesMicro Hydro Electricity Basicssebascian100% (1)
- Chapter-1: 1.1.induction GeneratorDocument12 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.induction GeneratorSURAJNo ratings yet
- Chimoio, Maio de 2021Document15 pagesChimoio, Maio de 2021Demítrio G. PioNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantDocument12 pagesTypes of Power PlantJonaz CruzNo ratings yet
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Document3 pagesWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- SPP1 4209-Hydro Power TechniquesDocument5 pagesSPP1 4209-Hydro Power TechniquesShariff Oluoch OdiwuorNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument4 pagesWorking Principle of Hydroelectric Power PlantGummadi AmarNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- HYDRO Power Plant PresentationDocument35 pagesHYDRO Power Plant Presentationhannyjberchmans100% (1)
- Hydroelectric Power Plants - Principles of Operation - EE Power SchoolDocument14 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants - Principles of Operation - EE Power Schoolharshitsingh.m99No ratings yet
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternDocument3 pagesPressurized Water Reactors (PWRS) Constitute The Large Majority of All WesternAnkit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Paper-Oil Transformers and The Requirement For High Quality Adsorbing Desiccants To Prolong Transformer LifeDocument5 pagesElectrical Paper-Oil Transformers and The Requirement For High Quality Adsorbing Desiccants To Prolong Transformer LifekamaladonNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument12 pagesPowerplant EngineeringBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantVinay Rai100% (3)
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument22 pagesNuclear Power PlantMuhammad Ahkam KhanNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-5Document26 pagesBEE Unit-5gunasundar choppaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Final AssignmentDocument6 pagesDistribution Final AssignmentGabrielGrecoNo ratings yet
- Report of Project PGS 2Document16 pagesReport of Project PGS 2Safdar ali AlmaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plants - 2018 PDFDocument71 pagesTypes of Power Plants - 2018 PDFJeff Justine GeragaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Power Plants and Boilers: Layout of Steam Power PlantmaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantADocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantAtheunsung tale100% (1)
- Electrical Energy Generation, Utilization and ConsrevationDocument132 pagesElectrical Energy Generation, Utilization and Consrevationvarunflyhigh50% (2)
- Lec 1 - Mod 1.2Document127 pagesLec 1 - Mod 1.2Ar. Soumya P SNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant - WikipediaDocument21 pagesNuclear Power Plant - Wikipediahasan.the.great420No ratings yet
- For Power PlantDocument224 pagesFor Power PlantIrene Mununi100% (2)
- M4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFDocument5 pagesM4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument5 pagesRADIOACTIVITYYusra KhanNo ratings yet
- Mid 2Document164 pagesMid 2Asif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDocument15 pagesNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioNo ratings yet
- Principle of Power GenerationDocument36 pagesPrinciple of Power Generationbilyaminu hamisu b/zNo ratings yet
- Foebe Bee2093 Chapter2Document36 pagesFoebe Bee2093 Chapter2Mwindjou MhoumadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by Alebachew TZerihun PaulosNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument6 pagesNuclear Power PlantDr. Lenin V RNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaFrom EverandIntroduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaNo ratings yet
- Brake & Clutch Fluid Dot 3 PDFDocument6 pagesBrake & Clutch Fluid Dot 3 PDFBryan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hempadur XP 87550: DescriptionDocument2 pagesHempadur XP 87550: DescriptionEngTamer50% (4)
- 12 - Sucker Rod Pumping - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringDocument20 pages12 - Sucker Rod Pumping - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringmissaouiNo ratings yet
- EAW-Nisbit Submittal - 01152013Document56 pagesEAW-Nisbit Submittal - 01152013StCharlesCSNo ratings yet
- Pcie Link TrainingDocument3 pagesPcie Link TrainingChinmay100% (1)
- Solid Shell Connection in Finite Element AnalysisDocument21 pagesSolid Shell Connection in Finite Element AnalysisvilukNo ratings yet
- Cinnetic 2014 PDFDocument60 pagesCinnetic 2014 PDFOscar SpinningaliciaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 10 - HSE Facility Standard of SECLDocument27 pagesAppendix 10 - HSE Facility Standard of SECLMurtadda MohammedNo ratings yet
- Communication ProtocolDocument6 pagesCommunication Protocolgemni7No ratings yet
- Ram Concrete AnalysisDocument94 pagesRam Concrete AnalysisTom CurryNo ratings yet
- 2018IBM BPMOverview AprilDocument12 pages2018IBM BPMOverview AprilsaluyumugiNo ratings yet
- VoriconazoleDocument3 pagesVoriconazoleWH PANDWNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tenses - 10 TextsDocument9 pagesMixed Tenses - 10 TextsRamon Gabriel100% (1)
- Map UgDocument1,856 pagesMap Ughanif0404100% (1)
- NyquistDocument12 pagesNyquistOsel Novandi WitohendroNo ratings yet
- Uninstalling and Reinstalling The Windows 2012R2 Failover Clustering FeatureDocument6 pagesUninstalling and Reinstalling The Windows 2012R2 Failover Clustering FeatureNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Assessment ChecklistDocument28 pagesLaboratory Assessment ChecklistPanneer Selvam100% (2)
- CCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st EditionDocument531 pagesCCNP ROUTEComplete Guide 1st Editionmansoorali_af100% (2)
- AdvantageCalibration Quick Ref CardDocument36 pagesAdvantageCalibration Quick Ref CardDario Fernando Flores Cotto100% (1)
- Notes: General Steel Fabrication Notes: Carbon Steel Fabrication Notes: Stainless Steel FabricationDocument6 pagesNotes: General Steel Fabrication Notes: Carbon Steel Fabrication Notes: Stainless Steel FabricationAquiles MartinezNo ratings yet
- OltremareDocument1 pageOltremareAfraz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Book Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDocument57 pagesBook Review of Communication System by Roy BlakeDanny OxinaNo ratings yet
- Technology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameDocument15 pagesTechnology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameMoses MussNo ratings yet
- Marks of ESE 2023 Qualified CandidatesDocument10 pagesMarks of ESE 2023 Qualified Candidatesthunderbuddy2222No ratings yet
- Daewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFDocument62 pagesDaewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFdann222No ratings yet
- Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesBonding in SolidsMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Column in Limit State MethodDocument7 pagesDesign of Column in Limit State MethodRicardo BermudezNo ratings yet
- Design and Thermal Analysis of Segmental Baffle and Helical Baffle in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Using Kern MethodDocument7 pagesDesign and Thermal Analysis of Segmental Baffle and Helical Baffle in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Using Kern MethodIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet