Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsNOTESmidterm
NOTESmidterm
Uploaded by
Alexis Jhan MagoThe document defines cash and cash equivalents as highly liquid assets that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash, such as money, bank deposits and short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less. It also discusses the classification, measurement and presentation of cash and cash equivalents in the financial statements, as well as accounting treatments for bank overdrafts, compensating balances, and cash shortages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFJade Gomez100% (1)
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- NC Iii Bookkeeping ReviewerDocument18 pagesNC Iii Bookkeeping ReviewerJoseph Dhune Batoctoy100% (2)
- Accounting NotesDocument20 pagesAccounting NotesAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJUST KINGNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lessons - Far 1Document23 pagesCompiled Lessons - Far 1Gwyn OliverNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- C7 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesC7 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- 10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pages10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsuncianojhezrhyllemhaeNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsbona jirahNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- and Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashDocument3 pagesand Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Audit of CashDocument6 pagesAudit of Cashannebernadette watanNo ratings yet
- CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerDocument2 pagesCASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerhelloangelodavidNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesSummary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMhico Mateo100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentGiyah UsiNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentDarwyn HonaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCamille Joyce Corpuz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- FAR LectureDocument6 pagesFAR Lecturewingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument47 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument34 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- (Studocu) Int Acc Chapter 1 - Valix, Robles, Empleo, MillanDocument3 pages(Studocu) Int Acc Chapter 1 - Valix, Robles, Empleo, MillanHufana, ShelleyNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheDocument4 pagesCash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheannyeongNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument32 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerMaliha KansiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument32 pagesModule 3 Cash and Cash Equivalentschuchu tv100% (1)
- Cash and ReceivablesDocument25 pagesCash and ReceivablesOjv FgjNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsshe lacks wordsNo ratings yet
- 02 Cash Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 Cash Cash EquivalentalteregoNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting NotesDocument7 pagesIntermediate Accounting NotesKyle Angela IlanNo ratings yet
- C and CE NotesDocument4 pagesC and CE NotesFrancine PimentelNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCLEAR MELODY VILLARANNo ratings yet
- Aud 1&2 - CceDocument6 pagesAud 1&2 - Ccecherish melwinNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2Document19 pagesModule 1.2Althea mary kate MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cash Part1Document7 pagesCash Part1cuaresmamonicaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentKimberly Laggui PonayoNo ratings yet
- Module Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesModule Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsIvy ObligadoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKate CamachoNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Lecture Notesyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- Ia ReviewerDocument11 pagesIa Reviewermichelle donaireNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDessa Garong100% (1)
- Notes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument9 pagesNotes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsElaineJrV-IgotNo ratings yet
- Ia1 QualiDocument44 pagesIa1 QualiAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPamela Mae PlatonNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMary Jullianne Caile SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument31 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMark LouieNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Regulatory Counsel in Chicago IL Resume Christell EllisDocument2 pagesHealthcare Regulatory Counsel in Chicago IL Resume Christell EllisChristellEllis1No ratings yet
- Oracle Applications - Inventory Crisp Handout LilDocument20 pagesOracle Applications - Inventory Crisp Handout LilAli xNo ratings yet
- Pexip Infinity Azure Deployment Guide V33.1.aDocument45 pagesPexip Infinity Azure Deployment Guide V33.1.albenharzproNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management PrabhatDocument58 pagesMarketing Management PrabhatParikshit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bob Lite Current Account - Bank of BarodaDocument3 pagesBob Lite Current Account - Bank of Barodasantanusaikia19No ratings yet
- 387 P16mba4ef6 2020051606081212 PDFDocument257 pages387 P16mba4ef6 2020051606081212 PDFParivel ParivelNo ratings yet
- Train TicketDocument6 pagesTrain TicketAnonymous olCc5SiNo ratings yet
- Ekuma, Ojim William CVDocument3 pagesEkuma, Ojim William CVCassandra MeyersNo ratings yet
- Interoperability Report: Alcatel-Lucent OT8118/8128 Motorola Solutions, RFS/NX Controllers AP650/6511/6532/7131Document18 pagesInteroperability Report: Alcatel-Lucent OT8118/8128 Motorola Solutions, RFS/NX Controllers AP650/6511/6532/7131Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6 - Reflective EssayDocument4 pagesWebinar 6 - Reflective Essay뿅아리No ratings yet
- Configuration of Tracking Area Code (TAC) For Paging Optimization in Mobile Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesConfiguration of Tracking Area Code (TAC) For Paging Optimization in Mobile Communication SystemsJose Carlos Mendez PenaNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis of A Radio Over A Fibre SystemDocument13 pagesModelling and Analysis of A Radio Over A Fibre SystemArgentine KazunguNo ratings yet
- Tableau Incoterms 202000Document5 pagesTableau Incoterms 202000souleymane sow100% (6)
- Application For Authority To Establish and Operate As PawnshopDocument38 pagesApplication For Authority To Establish and Operate As PawnshopVenus DuranNo ratings yet
- R Daga & Company: Chartered AccountantsDocument12 pagesR Daga & Company: Chartered AccountantsAdesh NaharNo ratings yet
- ) ) @Ç!!6D!!!!sAPH) & : This Bill $106.48 TotalDocument6 pages) ) @Ç!!6D!!!!sAPH) & : This Bill $106.48 TotalAntonino MontapertoNo ratings yet
- ZujuDocument3 pagesZujuMubarak Ali ShinwariNo ratings yet
- AlibabaDocument19 pagesAlibabaSameer Dubey67% (3)
- Ticket Types: CityxpressDocument4 pagesTicket Types: Cityxpressspati2No ratings yet
- FAR Handout 03 - Trade ReceivablesDocument4 pagesFAR Handout 03 - Trade ReceivablesadieNo ratings yet
- Cecchetti 6e Chapter13 SMDocument8 pagesCecchetti 6e Chapter13 SMyuyu4416No ratings yet
- CBD Smiles PlatinumDocument3 pagesCBD Smiles PlatinumahmedaboziedsubNo ratings yet
- Safe Architecture ToolkitDocument59 pagesSafe Architecture ToolkitSherif SalamaNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Accountingعادل اعظمNo ratings yet
- RocDelhiSTK5 18062018Document502 pagesRocDelhiSTK5 18062018DIVYANI SALDINo ratings yet
- Calim FormDocument2 pagesCalim Formshavi rajput 〰No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Survey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Survey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test Bank PDFfactivesiennesewwz2jj100% (14)
- Assignment CashDocument4 pagesAssignment Cashrj batiyeg100% (1)
- Isbt Requirement ArchitectureDocument17 pagesIsbt Requirement ArchitectureRishabh BhardwajNo ratings yet
NOTESmidterm
NOTESmidterm
Uploaded by
Alexis Jhan Mago0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesThe document defines cash and cash equivalents as highly liquid assets that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash, such as money, bank deposits and short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less. It also discusses the classification, measurement and presentation of cash and cash equivalents in the financial statements, as well as accounting treatments for bank overdrafts, compensating balances, and cash shortages.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines cash and cash equivalents as highly liquid assets that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash, such as money, bank deposits and short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less. It also discusses the classification, measurement and presentation of cash and cash equivalents in the financial statements, as well as accounting treatments for bank overdrafts, compensating balances, and cash shortages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesNOTESmidterm
NOTESmidterm
Uploaded by
Alexis Jhan MagoThe document defines cash and cash equivalents as highly liquid assets that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash, such as money, bank deposits and short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less. It also discusses the classification, measurement and presentation of cash and cash equivalents in the financial statements, as well as accounting treatments for bank overdrafts, compensating balances, and cash shortages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
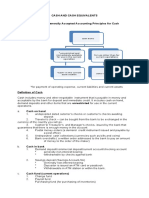
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENT
Chapter 1
- Three-year BSP treasury bill
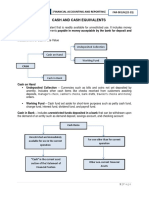
DEFINITION OF CASH
purchased three months before
Cash the date of maturity
Includes money and other - Three months time deposit
negotiable instrument that is - Three month money market
payable in money and acceptable instrument or commercial paper
by the bank for deposit and
Classification of investment of excess
immediate credit
cash
Checks, bank drafts and money
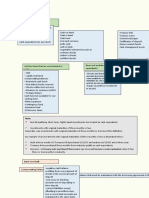
orders a. Three months or Less – cash and
Postdated Check – Not cash cash equivalents
Unrestricted Cash b. Three months with in 1 year –
No specific standards dealing with short term financial asset (CA)
cash c. More than one year – long term
Pas 1 par 66, which provides that investment (NCA)
an entity shall classify an asset as However, if investments
current when asset is cash or cash become due within one year the
equivalent unless it is restricted end of reporting period,
to settle a liability for more than reclassified as current or
twelve months after the end of temporary investment
the reporting period.
Measurement of cash
Cash items included in cash
- Face value
Cash on hand – undeposited cash
- Cash in foreign currency – current
collection and other cash items
exchange rate
awaiting deposit
- If bank or FI holding funds is in
Cash in bank – demand deposit,
bankruptcy – net Realizable value
checking account and saving
if the amount recoverable is
account which are unrestricted as
estimated to be lower than the
to withdrawal
face value
Cash fund – set aside for current
purposes such as petty cash fund, Financial Statement Presentation
payroll fund and dividend fund
Cash and Cash equivalent – first
DEF. OF CASH EQUIVALENTS line item under current asset
Details should be disclosed in the
Examples of Cash equivalents
notes to financial statements
- Three-month BSP treasury bill
Cash fund for a certain purpose balance that must be maintained in
connection with a borrowing arrangement
Long term Investment – Set
with a bank
aside for use in noncurrent
purposes or for payment of Classification of Compensation Balance
noncurrent obligation
- Deposit is not legally restricted as
Examples- sinking fund,
to withdrawal – informal
preference share redemption
compensation balance agreement,
fund, contingent or construction
CASH
of property, plant and equipment
- Legally restricted- formal
Bank Overdraft compensating agreement – “Cash
held as compensating balance”
Overdraft- cash in Bank that has
current assets if related loan is
a credit balance
short term
Results from issuance of checks in
- If loan is long term – noncurrent
excess of deposits
investment
Classified as current liability and
should not be offset against other Undelivered or unreleased check
bank accounts with debit balances.
- One that is merely drawn and
Generally, Overdraft are not
recorded but not given to the
permitted in the Philippines
payee before the end of the
Exception to the rule om overdraft reporting period
- Unreleased checks drawn are
- When an entity maintains two or
included in cash
more accounts in one bank –
allowed to offset Postdated check delivered
- Overdraft can also be offset
- Check drawn, recorded and
against the other bank account if
already given to the payee but it
the amount is not material
bears a date subsequent to the
- Under IFRS, bank overdraft can
end of reporting period
be offset against other bank
- Postdated checks drawn are
account when payable on demand
included in cash
and often fluctuates from positive
- Postdated checks received from
to negative as an integral part of
customers are excluded from cash
cash management
Staled Check
Compensating Balance
- Check not encashed by the payee
Generally takes the form of minimum
within a relatively long period of
checking or demand deposit account
time
BANK RECONCILIATION
Chapter 2
- Reasonable period of time after If no claim – miscellaneous income
issue – depends on entity policy Cash shortage or over 10,000
BANK DEPOSITS
- Staled checks drawn are included Miscellaneous income 10,000
1. Demand Deposits
in cash If found to be the money of cashier –
- current account or checking
- Staled checks received from Payable to cashier
account or commercial deposit
customers are excluded from cash Cash short or over 10,000
where deposits are covered by
Payable to cashier 10,000
Accounting for Cash Shortage deposit slips and where funds are
Petty Cash
withdrawable Fund by
on demand
Where the cash count < balance per book
drawing checks against the bank.
Cash short or over 10,000 - Is money set aside to pay small
- non-interest bearing
Cash 10,000 expenses which cannot paid
- some banks allow as interest
If cashier or cash custodian is held conveniently by means of check
bearing
responsible – due from cashier - Two methods
2. Saving Deposits
Due from cashier 10,000 o Imprest Fund system –
- Depositor is given a passbook upon
Cash short or over 10,000 usually followed
the initial deposit
If fail to disclose the cause of the o Fluctuating fund system –
- Passbook is required when making
shortage – Loss from cash shortage checks drawn to replenish
deposits and withdrawals.
Loss From Cash shortage 10,000 the fund do not necessarily
- Sometimes may require notice of
Cash short or over 10,000 equal the petty cash
withdrawal
disbursements
Accounting for Cash Overage - Interest bearing
3. Time Deposits
Where the cash count > balance per book
- Similar to saving deposits sense
Cash 10,000
that it is interest bearing
Cash short or over 10,000
- Evidenced, however by the formal
agreement embodied in an
instrument called certificate of
deposit
- Preterminated or withdrawn on
demand or after a certain period
of time agreed upon
BANK RECONCILATION
- Necessary only for a demand
deposit or checking account
- To show specimen signatures to be
used in the check
- So that any unfamiliar with a
depositor’s signature can test
authenticity
-
o NSF or no sufficient fund
- If depositor is corporation, will checks / DAIF or drawn
pass a resolution authorizing against insufficient fund
certain officers o Bank service charges –
- It is a statement which brings interest, collection,
into agreement the cash per checkbook, and penalty
balance per book and cash o technically defective
balance per bank checks – absence of sign,
- Prepared monthly erasures not
Bank statement countersigned, mutilated
- Monthly report of the bank to the checks, conflict between
depositor amount in words and figure
- Attached there to the depositor’s o reduction of loans – dep
canceled checks owes to the bank and owes
Canceled checks to the bank and which has
- Issued by the depositor and paid already matured
by the bank during the month Bank reconciling items
- Canceled by stamping or punching c. deposits in transit
to show that they have been paid – collections already recorded by
Reconciling items the depositor as cash receipts but
Book reconciling items not yet reflected on the bank
a. Credit memos statement
- Items not representing deposits o collections already forwarded
- Credit by the bank to the dep. acc to the bank for deposit but
- Not yet recorded by the too late to appear in the BS
depositor as cash receipt o undeposited collections – cash
- Affect of increasing the balance on hand
o Notes receivable d. outstanding checks
o Credited to depositors acc - recorded by the depositor as cash
o Bank loan disbursement but not yet
o Matured time deposits reflected in bank statement
b. Debit memos o checks drawn
- Not representing checks paid by o certified checks
bank Forms of bank reconciliation
- Charge or debited by the bank 1. adjusted balance method
- Not yet recorded by the - book and bank balance are brought
depositor as cash disbursement to a correct cash balance
- Decreasing bank balance - preferred over the other two
2. book to bank
PROOF OF CASH
Chapter 3
- book is reconciled or adjusted to
equal the bank balance; Two-date Bank Reconciliation
3. bank to book method - Literally involves two date
- bank balance is reconciled or - Becomes complicated only when
adjusted to equal the book certain fact or data are omitted
balance Computation of book balance
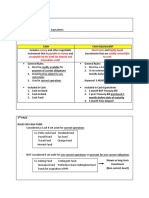
Preforma reconciliation - Bal per Book-beginning add book
Adjusted balance method debit. Less Book credits = BPB end
- BCD, BDO Book debit
- Errors are reconciling items which - Cash receipts or all items debited
committed them to cash in bank acc
- CM always added, DM always Book credit
deducted to/from book balance - Cash disbursement or all items
- DIT always added, OC always credited to the cash in bank acc
deducted to/from bank balance Computation of bank balance
- Book and bank are adjusted to - Bal per bank- beg add bank credit,
equal the correct cash balance less bank debit = BPB-end om
- CM already increased in bank but Bank credits
no effect in book balance - All items credited to the acc of
(understated in relation to depositor which include
correct cash balance) acknowledge by bank Credit memo
- DM decreased in bank but no - Deposits acknowledge by the bank
effect in book balance Bank debits
(overstated in relation to correct - All items debited to the account
cash balance) of the depositor which include
- DIT increased the book but no deposits acknowledge by the bank
effect in bank - Checks paid by the bank
- OC decreased in book but no Computation of deposits in transit
effect in bank DIT – beginning
Book to bank method Add: Cash receipts deposited
- B CO DD B Total deposits to be acknowledge by bank
- Reversed in the adjusted bal. m Less: Deposits acknowledge by bank
- Book balance is adjusted to equal DIT – end of month
the bank Computation of outstanding checks
Bank to book method OC- beginning
- B DD OC B Add: checks drawn by the depositor
- Reversed treatment Total checks to be paid by bank
- Bank balance is adjusted to equal Less: checks paid by bank
the book OC-end of month
Computation of book and bank balance
Balance per book – January
Add: book debits during feb
Total
Less:book credits during feb
Balance per book – February
Balance per bank – January
Add: bank credits during feb
Total
Less: bank debits during feb
Balance per bank - February
Proof of Cash
- Expanded reconciliation in that it
includes proof of receipts and
disbursement
You might also like
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFJade Gomez100% (1)
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- NC Iii Bookkeeping ReviewerDocument18 pagesNC Iii Bookkeeping ReviewerJoseph Dhune Batoctoy100% (2)
- Accounting NotesDocument20 pagesAccounting NotesAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJUST KINGNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lessons - Far 1Document23 pagesCompiled Lessons - Far 1Gwyn OliverNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- C7 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesC7 Lecture NotesJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- 10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pages10 Cash and Cash EquivalentsuncianojhezrhyllemhaeNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsbona jirahNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- and Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashDocument3 pagesand Highly Liquid Investment Readily Convertible Into CashGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Audit of CashDocument6 pagesAudit of Cashannebernadette watanNo ratings yet
- CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerDocument2 pagesCASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS ReviewerhelloangelodavidNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesSummary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMhico Mateo100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentGiyah UsiNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentDarwyn HonaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCamille Joyce Corpuz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- FAR LectureDocument6 pagesFAR Lecturewingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument47 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 - Cash & Cash EquivalentEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument34 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- (Studocu) Int Acc Chapter 1 - Valix, Robles, Empleo, MillanDocument3 pages(Studocu) Int Acc Chapter 1 - Valix, Robles, Empleo, MillanHufana, ShelleyNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheDocument4 pagesCash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheannyeongNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument32 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerMaliha KansiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument32 pagesModule 3 Cash and Cash Equivalentschuchu tv100% (1)
- Cash and ReceivablesDocument25 pagesCash and ReceivablesOjv FgjNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsshe lacks wordsNo ratings yet
- 02 Cash Cash EquivalentDocument5 pages02 Cash Cash EquivalentalteregoNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting NotesDocument7 pagesIntermediate Accounting NotesKyle Angela IlanNo ratings yet
- C and CE NotesDocument4 pagesC and CE NotesFrancine PimentelNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCLEAR MELODY VILLARANNo ratings yet
- Aud 1&2 - CceDocument6 pagesAud 1&2 - Ccecherish melwinNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2Document19 pagesModule 1.2Althea mary kate MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cash Part1Document7 pagesCash Part1cuaresmamonicaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentKimberly Laggui PonayoNo ratings yet
- Module Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesModule Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsIvy ObligadoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKate CamachoNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Lecture Notesyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- Ia ReviewerDocument11 pagesIa Reviewermichelle donaireNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDessa Garong100% (1)
- Notes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument9 pagesNotes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsElaineJrV-IgotNo ratings yet
- Ia1 QualiDocument44 pagesIa1 QualiAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Cash and Cash Equivalent - REVIEWERAiyana AlaniNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPamela Mae PlatonNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMary Jullianne Caile SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument31 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMark LouieNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Regulatory Counsel in Chicago IL Resume Christell EllisDocument2 pagesHealthcare Regulatory Counsel in Chicago IL Resume Christell EllisChristellEllis1No ratings yet
- Oracle Applications - Inventory Crisp Handout LilDocument20 pagesOracle Applications - Inventory Crisp Handout LilAli xNo ratings yet
- Pexip Infinity Azure Deployment Guide V33.1.aDocument45 pagesPexip Infinity Azure Deployment Guide V33.1.albenharzproNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management PrabhatDocument58 pagesMarketing Management PrabhatParikshit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Bob Lite Current Account - Bank of BarodaDocument3 pagesBob Lite Current Account - Bank of Barodasantanusaikia19No ratings yet
- 387 P16mba4ef6 2020051606081212 PDFDocument257 pages387 P16mba4ef6 2020051606081212 PDFParivel ParivelNo ratings yet
- Train TicketDocument6 pagesTrain TicketAnonymous olCc5SiNo ratings yet
- Ekuma, Ojim William CVDocument3 pagesEkuma, Ojim William CVCassandra MeyersNo ratings yet
- Interoperability Report: Alcatel-Lucent OT8118/8128 Motorola Solutions, RFS/NX Controllers AP650/6511/6532/7131Document18 pagesInteroperability Report: Alcatel-Lucent OT8118/8128 Motorola Solutions, RFS/NX Controllers AP650/6511/6532/7131Mohamed SalhiNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6 - Reflective EssayDocument4 pagesWebinar 6 - Reflective Essay뿅아리No ratings yet
- Configuration of Tracking Area Code (TAC) For Paging Optimization in Mobile Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesConfiguration of Tracking Area Code (TAC) For Paging Optimization in Mobile Communication SystemsJose Carlos Mendez PenaNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis of A Radio Over A Fibre SystemDocument13 pagesModelling and Analysis of A Radio Over A Fibre SystemArgentine KazunguNo ratings yet
- Tableau Incoterms 202000Document5 pagesTableau Incoterms 202000souleymane sow100% (6)
- Application For Authority To Establish and Operate As PawnshopDocument38 pagesApplication For Authority To Establish and Operate As PawnshopVenus DuranNo ratings yet
- R Daga & Company: Chartered AccountantsDocument12 pagesR Daga & Company: Chartered AccountantsAdesh NaharNo ratings yet
- ) ) @Ç!!6D!!!!sAPH) & : This Bill $106.48 TotalDocument6 pages) ) @Ç!!6D!!!!sAPH) & : This Bill $106.48 TotalAntonino MontapertoNo ratings yet
- ZujuDocument3 pagesZujuMubarak Ali ShinwariNo ratings yet
- AlibabaDocument19 pagesAlibabaSameer Dubey67% (3)
- Ticket Types: CityxpressDocument4 pagesTicket Types: Cityxpressspati2No ratings yet
- FAR Handout 03 - Trade ReceivablesDocument4 pagesFAR Handout 03 - Trade ReceivablesadieNo ratings yet
- Cecchetti 6e Chapter13 SMDocument8 pagesCecchetti 6e Chapter13 SMyuyu4416No ratings yet
- CBD Smiles PlatinumDocument3 pagesCBD Smiles PlatinumahmedaboziedsubNo ratings yet
- Safe Architecture ToolkitDocument59 pagesSafe Architecture ToolkitSherif SalamaNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Accountingعادل اعظمNo ratings yet
- RocDelhiSTK5 18062018Document502 pagesRocDelhiSTK5 18062018DIVYANI SALDINo ratings yet
- Calim FormDocument2 pagesCalim Formshavi rajput 〰No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Survey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Survey of Accounting 6th Edition Warren Test Bank PDFfactivesiennesewwz2jj100% (14)
- Assignment CashDocument4 pagesAssignment Cashrj batiyeg100% (1)
- Isbt Requirement ArchitectureDocument17 pagesIsbt Requirement ArchitectureRishabh BhardwajNo ratings yet