Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Fractions Lesson
Introduction To Fractions Lesson
Uploaded by
Dimple SoodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Fractions Lesson
Introduction To Fractions Lesson
Uploaded by
Dimple SoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Fractions
𝑎 Where 𝑎 and 𝑏 are integers and 𝑏 ≠ 0. In a fraction, 𝑎 is
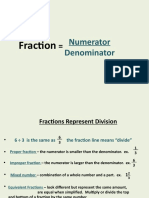
A fraction is written as
called the numerator and 𝑏 is called the denominator.
𝑏
A fraction is a way to represent parts of a whole. The denominator represents the number
of equal parts the whole has been divided into, and the numerator represents how many parts
are included. The denominator cannot equal zero because division by zero is undefined.
Suppose you want to share a pizza equally with three friends.
How much pizza do you each get?
There is one whole pizza, divided into four equal parts. Each person
1
gets one of the four equal parts, so you each get of the pizza.
4
What fraction does the shaded area of each shape represent?
The circle is divided into three equal parts, and two of them are shaded.
2
Therefore, the fraction of the circle that is shaded is .
3
This is called a proper fraction because the numerator is smaller than the
denominator.
The circle is divided into five equal parts, and all five of them are shaded.
Therefore, the whole circle is shaded, so the fraction of the circle that is
5
shaded is = 1.
5
Any fraction that has the same numerator and denominator is one because
any number, except zero, divided by itself is one.
The rectangle is divided into five equal parts, and zero parts are shaded.
0
Therefore, the fraction of the rectangle that is shaded is 5 = 0.
Any fraction that has a numerator of zero equals zero because zero divided
by any number, except zero, is zero.
Source: "Prealgebra" by Lynn Marecek & Mary Anne Anthony-Smith is licensed under CC BY 4.0 / A
derivative from the original work
You might also like
- Geometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemFrom EverandGeometry Snacks: Bite Size Problems and How to Solve ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- FractionsDocument50 pagesFractions1oftheliving100% (9)
- Fractionslesson1 Introduction 151106194602 Lva1 App6892Document19 pagesFractionslesson1 Introduction 151106194602 Lva1 App6892exelligentphmusikahanNo ratings yet
- Fraction Power PointDocument29 pagesFraction Power Pointlunok mariitNo ratings yet
- 2.0 FRACTION - Math 100Document59 pages2.0 FRACTION - Math 100ShanayaNo ratings yet
- Buksis-2.1 Revisi AkhirDocument22 pagesBuksis-2.1 Revisi AkhirF X AGUS SISWANTONo ratings yet
- Fraction 1Document22 pagesFraction 1Aime RoswellNo ratings yet
- Maths Module 2: Working With FractionsDocument15 pagesMaths Module 2: Working With FractionsGemalyn Raymundo GacayanNo ratings yet
- Fractions Grade 4Document108 pagesFractions Grade 4Lorelie VenturaNo ratings yet
- Fractions LessonDocument16 pagesFractions Lessonapi-449501968No ratings yet
- Proper Improper Mixed Number FractionsDocument21 pagesProper Improper Mixed Number FractionsLorenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fractions Lesson 1 The Concept of FractionDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Fractions Lesson 1 The Concept of FractionLeonessa CortesNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Unit 1 NotesDocument29 pagesGrade 9 - Unit 1 Notesapi-2889220720% (1)
- Maths Refresher Workbook 1 3Document1 pageMaths Refresher Workbook 1 3Ivan MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Addition of FractionsDocument10 pagesAddition of Fractionsyoy fajardoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1dawnoundeNo ratings yet
- Math VocabDocument65 pagesMath VocabSajjad LordNo ratings yet
- Fractions and Decimals Made Easy PDFDocument50 pagesFractions and Decimals Made Easy PDFSherShah100% (3)
- 7 FractionsDocument23 pages7 Fractionsdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Mathematics For Nursing and Midwifery 8 - 9 - 2020Document33 pagesMathematics For Nursing and Midwifery 8 - 9 - 2020HasnainNo ratings yet
- Fractions 120213071428 Phpapp01Document40 pagesFractions 120213071428 Phpapp01Christian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Halves and Quarters (Notes)Document3 pagesHalves and Quarters (Notes)TR Vijay PrasadNo ratings yet
- Math 1 FractionDocument6 pagesMath 1 FractionSyrusNo ratings yet
- UK Junior Mathematical Olympiad 2017 SolutionsDocument7 pagesUK Junior Mathematical Olympiad 2017 SolutionsHerwansyahNo ratings yet
- Maths - Grade 3 - Understand Fractions As Numbers - Session 2 - Study Material-USADocument8 pagesMaths - Grade 3 - Understand Fractions As Numbers - Session 2 - Study Material-USAPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- Ee2 Mini LessonDocument12 pagesEe2 Mini Lessonapi-325782732No ratings yet
- Jmo 2017 SDocument7 pagesJmo 2017 Sraman192021No ratings yet
- Factions KuDocument7 pagesFactions KukesodNo ratings yet
- Division of Decimals and Multi-Step Word ProblemsDocument30 pagesDivision of Decimals and Multi-Step Word ProblemsMay CNo ratings yet
- Fractions 5 Class NotesDocument8 pagesFractions 5 Class NotesviswanathNo ratings yet
- Having Fun With FractionsDocument9 pagesHaving Fun With FractionsPrienderen MoodleyNo ratings yet
- PAscals TriangleDocument24 pagesPAscals TriangleChtiba RedaNo ratings yet
- Halves and Quarters (Notes)Document3 pagesHalves and Quarters (Notes)TR Vijay PrasadNo ratings yet
- Grade-05 Maths Fractions and Decimals AUSDocument16 pagesGrade-05 Maths Fractions and Decimals AUSChaitra RNo ratings yet
- Concept of Fraction: - Jaybi Reyes and Krizia Mae GumabonDocument43 pagesConcept of Fraction: - Jaybi Reyes and Krizia Mae GumabonJoshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Fraction To Decimal To PercentDocument7 pagesConversion of Fraction To Decimal To PercentAngelo Rey NavaNo ratings yet
- Fractions Decimals PercentageDocument91 pagesFractions Decimals PercentageDaniel PendonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 Handout 1.1Document8 pagesMathematics 6 Handout 1.1RasiiLNo ratings yet
- Funmath Module 2 - Fractions and PercentagesDocument29 pagesFunmath Module 2 - Fractions and PercentagesRonelle San buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Fractions NotesDocument10 pagesFractions NotesJohn Wilbert R. AretanoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson in MATH 4Document5 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson in MATH 4milafer dabanNo ratings yet
- Bba Iba Math Lecture 01-08Document37 pagesBba Iba Math Lecture 01-08xiaomirealme46No ratings yet
- Types and Nature of NumbersDocument8 pagesTypes and Nature of NumbersAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Fractions H: Learning ÖbjectivesDocument22 pagesFractions H: Learning ÖbjectivesRanjan YadavNo ratings yet
- Fraction NotesDocument51 pagesFraction NoteskushiNo ratings yet
- Fractions Definition of Fractions: Numerator Denominator Fraction Line or Devision BarDocument4 pagesFractions Definition of Fractions: Numerator Denominator Fraction Line or Devision BarMeLatii ApriLiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: FractionsDocument15 pagesUnit 7: FractionsRaulNo ratings yet
- Maths Hints Revision Cards: SymmetryDocument5 pagesMaths Hints Revision Cards: SymmetryaeizatulNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document23 pagesChap 9pasanNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS Business Math 12 Week 1 Comp 1a - 2Document7 pagesQ1 LAS Business Math 12 Week 1 Comp 1a - 2Devilz GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1SANTO WIJAYANo ratings yet
- Maths - Grade 3 - Understand Fractions As Numbers - Session 1 - Study material-USADocument8 pagesMaths - Grade 3 - Understand Fractions As Numbers - Session 1 - Study material-USAPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- Module 2 FractionsDocument36 pagesModule 2 FractionsMa Ronielyn Umantod Mayol100% (1)
- Grade 5 FractionspptDocument46 pagesGrade 5 FractionspptRonaldo ManaoatNo ratings yet
- 5ta. SESION DIAGNOSTICADocument65 pages5ta. SESION DIAGNOSTICADALIA LETICIA CASTILLO SOTONo ratings yet
- The Number Detective: 100 Number Puzzles to Test Your Logical ThinkingFrom EverandThe Number Detective: 100 Number Puzzles to Test Your Logical ThinkingNo ratings yet
- 140823-Sco 7 Select ListDocument3 pages140823-Sco 7 Select ListDimple SoodNo ratings yet
- POD23S1C11310687Document2 pagesPOD23S1C11310687Dimple SoodNo ratings yet
- CBCS SyllabusDocument4 pagesCBCS SyllabusDimple SoodNo ratings yet
- Week3 CS1 391Document3 pagesWeek3 CS1 391Dimple SoodNo ratings yet
- Ey Salary Survey Leaflet Uzbekistan 2020 EngDocument2 pagesEy Salary Survey Leaflet Uzbekistan 2020 EngDimple SoodNo ratings yet
- Wipro Limited Remuneration PolicyDocument3 pagesWipro Limited Remuneration PolicyDimple SoodNo ratings yet