Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometrical Isomerism
Geometrical Isomerism
Uploaded by
AGRPITSEN BROCHAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesGeometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond. It is possible for alkenes containing a C=C double bond with different groups on each carbon. For an alkene to exhibit geometrical isomerism, the groups on each carbon of the double bond must be different. The number of possible geometrical isomers is 2n, where n is the number of carbon-carbon double bonds that can exhibit geometrical isomerism in the molecule.
Original Description:
Original Title
GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGeometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond. It is possible for alkenes containing a C=C double bond with different groups on each carbon. For an alkene to exhibit geometrical isomerism, the groups on each carbon of the double bond must be different. The number of possible geometrical isomers is 2n, where n is the number of carbon-carbon double bonds that can exhibit geometrical isomerism in the molecule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesGeometrical Isomerism
Geometrical Isomerism
Uploaded by
AGRPITSEN BROCHANGeometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation about a carbon-carbon double bond. It is possible for alkenes containing a C=C double bond with different groups on each carbon. For an alkene to exhibit geometrical isomerism, the groups on each carbon of the double bond must be different. The number of possible geometrical isomers is 2n, where n is the number of carbon-carbon double bonds that can exhibit geometrical isomerism in the molecule.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
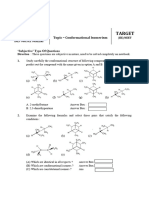
GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM
ICONIC CHEMISTRY CLASSES IITian Sushil Kumar
(B.Tech, IIT Madras)
GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM (M.Tech, IIT Madras)
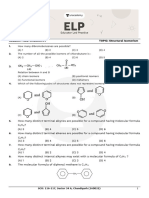
1. Select the correct statement :
(A) Geometrical isomers are configurational isomers
(B) Geometrical isomers arise due to restricted rotation about a bond
(C) Two configurational isomers can be geometrical isomers only if they have different spatial dis-
tances between the atoms or groups
(D) All of these
2. Geometrical isomerism is possible about which of the following multiple bonds?
(A) C=C (B) C=O (C) CC (D) CN
3. Geometrical isomerism is not possible about which of the following multiple bonds?
(A) C=N (B) N=N (C) C=C (D) C=O
4. All alkenes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism. For an alkene to exhibit geometrical isomerism,
which of the following conditions is required?
(A) two atoms or groups bonded with each C of C=C bond should be same
(B) Two atoms or groups bonded with each C of C=C bond should not be same
(C) C=C bond should bear at least three identical groups
(D) C=C bond should bear all four identical atoms or groups
5. Select the incorrect statement about Geometrical isomerism
(A) It can be possible about single bonds in open chain compounds
(B) It can be possible about C=C in a ring if ring size is 8 membered or more
(C) It can be possible in a cycloalkane if ring bears at least two sustituents at different positions
(D) If can be possible about C=N bond in open-chain compounds
6. Which of the following alkenes will not exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) CH3—CH2—CH2—CH=CH2 (B) CH3—CH2—CH=CH—CH3
(C) CH3—CH2—CH=CH—CH2—CH3 (D) CH2=CH—CH=CH—CH=CH2
7. Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) CH2=CH—CH=CH2 (B) CH2= CH—CH=CH—CH3
(C) CH2=CH—CH2—CH=CH2 (D) CH2=CH—CC—CH=CH2
8. Which of these compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
9. Which of these compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
H
(A) (B) (C) (D) All of these
10. Which of the cycloalkenes will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
11. Which of the following will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
12. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) If n is the number of active double bonds in a molecule along which geometrical isomerism is
possible, the number of geometrical isomers must be 2n if molecule is unsymmetrical.
(B) If n is the number of active double bonds in a molecule along which geometrical isomerism is
possible, the number of geometrical isomers must be less than 2n if molecule is symmetrical.
(C) The number of geometrical isomers in CH2=CH—CH=CH—CH=CH2 is 2.
(D) All of these
ICONIC CHEMISTRY CLASSES
Add: Ashoka Tower, 3rd floor ,East Boring Canal Road, Patna-1 Mob: 7903993958,9534286498 (1)
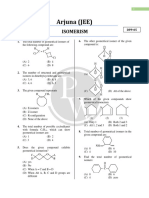
GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM
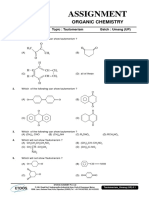
13. Consider the following statements:
(i) The number of geometrical isomers in CH2=CH—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH3 is 4.
(ii) The number of geometrical isomer in CH3—CH2—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH3 is 4.
(iii) The number of geometrical isomer in CH3—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH3 is 4.
(iv) The number of geometrical isomer in CH3—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH=CH—C2H5 is 8.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) (i),(ii),(iii) (B) (i),(ii),(iv) (C) (i),(iii),(iv) (D) (i),(ii),(iii) and (iv)
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) The number of geometrical isomers in CH3—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH=CH—CH3 is 6.
(B) The number of geometrical isomers in is 4.
(C) The number of geometrical isomers in is 3.
(D) All of these
15. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) (No. of G.I. = 2) (B) (No. of G.I. = 2)
(C) (No. of G.I. = 2) (D) (No. of G.I. = 4)
16. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) (No. of G.I. = 2) (B) (No. of G.I. = 2)
(C) (No. of G.I. = 2) (D) (No. of G.I. = 2)
17. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) (No. of G.I. = 2) (B) (No. of G.I. = 2)
(C) (No. of G.I. = 2) (D) (No. of G.I. = 0)
18. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) CH3—CH=C=CH—CH3 (No. of G.I. = 2) (B) CH3—CH=C=C=CH—CH3 (No. of G.I. = 2)
(C) CH3—CH=C=C=CH—C2H5 (No. of G.I. = 2) (D) CH3—CH=C=CH—CH=CH—CH3 (No.of G.I.= 2)
ANSWER
01. (D) 02. (A) 03. (D) 04. (B) 05. (A) 06. (A) 07. (B) 08. (C)
09. (D) 10. (C) 11. (B) 12. (D) 13. (B) 14. (D) 15. (D) 16. (B)
17. (B) 18. (A)
ICONIC CHEMISTRY CLASSES
Add: Ashoka Tower, 3rd floor ,East Boring Canal Road, Patna-1 Mob: 7903993958,9534286498 (2)
You might also like
- ASTM C1218 Standard Test Method For Water-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and ConcreteDocument3 pagesASTM C1218 Standard Test Method For Water-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and ConcreteElbert Contreras R80% (5)
- Organic+Dpps A1-A14 PDFDocument43 pagesOrganic+Dpps A1-A14 PDFAditya ChakraniNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: IsomerismDocument9 pagesFiitjee: IsomerismDhwanit Shah100% (1)
- Isomerism ReviewDocument7 pagesIsomerism Reviewayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Isomerism AssignmentDocument10 pages1.2 Isomerism AssignmentTejas pawarNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismDocument10 pagesPart - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismTejas pawarNo ratings yet
- Byvineet Khatri Sir: Excel Batch DPP. NO.47Document9 pagesByvineet Khatri Sir: Excel Batch DPP. NO.47sarvesh goyalNo ratings yet
- Stereo IsomerismDocument24 pagesStereo IsomerismKrishna ThakurNo ratings yet
- Coformational Isomerism PDFDocument13 pagesCoformational Isomerism PDFJeetNo ratings yet
- CPP3 Isomerism Advan5271813763553783467Document8 pagesCPP3 Isomerism Advan5271813763553783467Pranam ShahNo ratings yet
- Isomerism - DPP 05Document3 pagesIsomerism - DPP 05shishiranand25No ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document96 pagesWa0004.amar vnsNo ratings yet
- 102 IsomerismDocument27 pages102 Isomerismmeme.baker1289No ratings yet
- 01 GOC - (Stability of Resonance, Mesomeric Effect) - OnlineDocument4 pages01 GOC - (Stability of Resonance, Mesomeric Effect) - Onlineventureanime45No ratings yet
- ATP Star 2Document28 pagesATP Star 2Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- PC Copy - DPP-1 (GOC)Document4 pagesPC Copy - DPP-1 (GOC)Dushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- DPP-13 Text Solution 20230717100014Document5 pagesDPP-13 Text Solution 20230717100014ansarinaved8920No ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument21 pagesIsomerismkaransharma690No ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document23 pagesExercise 2Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- Class Test - Structural IsomersDocument3 pagesClass Test - Structural IsomersAlex SamNo ratings yet
- JIPMAT 2023 Original Paper With Answer KeysDocument18 pagesJIPMAT 2023 Original Paper With Answer KeysthedigitalparthNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Optical Isomerism VKP Sir-3706Document3 pagesDPP 1 Optical Isomerism VKP Sir-3706Sanjay Mani TripathiNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument4 pagesIsomerismNaziya KosarNo ratings yet
- Gocdpp 60Document8 pagesGocdpp 60Mrigank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Goc Till Isomerism DPPDocument16 pagesGoc Till Isomerism DPPpranav.padhle6No ratings yet
- DPP 25B Goc Resonance 1684507782845Document4 pagesDPP 25B Goc Resonance 1684507782845Aditya Kumar100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry: by Sy SirDocument21 pagesOrganic Chemistry: by Sy SirambcvcsNo ratings yet
- 13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERDocument23 pages13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERarryan keshanNo ratings yet
- JAM 2020 Chemistry - CyDocument21 pagesJAM 2020 Chemistry - CySubhasish PatraNo ratings yet
- Class Notes 6Document26 pagesClass Notes 6Sudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- Stereo Isomerism 1Document22 pagesStereo Isomerism 1afrin.mtpsNo ratings yet
- Structural IsomerismDocument4 pagesStructural Isomerismujjawaljolly3No ratings yet
- Goal 9-1Document8 pagesGoal 9-1Koleti KoletiNo ratings yet
- Neral Organic Chemistry (62-80)Document19 pagesNeral Organic Chemistry (62-80)udaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Goc QueDocument10 pagesGoc QueMahesh JagtapNo ratings yet
- 12th PCM Gujcet 24Document4 pages12th PCM Gujcet 24sukuna78692No ratings yet
- PACE Final Lap (Organic Chemistry) PDFDocument152 pagesPACE Final Lap (Organic Chemistry) PDFAman AdatiaNo ratings yet
- 6417 Topper 21 129 510 2 8532 Isomerism Up201612091817 1481287659 483 PDFDocument41 pages6417 Topper 21 129 510 2 8532 Isomerism Up201612091817 1481287659 483 PDFMd Waquar SalisNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism Pyqs NsecDocument8 pagesStereoisomerism Pyqs Nsecmanol sahooNo ratings yet
- Goc - 1 (Xii 2022-24) (Ans) 18 06 23Document3 pagesGoc - 1 (Xii 2022-24) (Ans) 18 06 23Piyush Student Acc JEENo ratings yet
- Goc - 1 (Xii 2022-24) (Print) 18 06 23Document3 pagesGoc - 1 (Xii 2022-24) (Print) 18 06 23Piyush Student Acc JEENo ratings yet
- Pieas 07 PlspotDocument4 pagesPieas 07 PlspotTalal zahidNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument4 pagesCoordination CompoundsNUCLEAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument21 pagesAssignment IChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesAssignment: Organic ChemistryWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Isomerism NotesDocument16 pagesIsomerism Notessurendra chowdary Makineni100% (1)
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds SolutionDocument10 pagesCoordination Compounds SolutionNUCLEAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document5 pagesUpload 2k.prarthu0909No ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument12 pagesIsomerismHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- DPP - 02 Stereoisomerism NJ - 247Document3 pagesDPP - 02 Stereoisomerism NJ - 247Ayon BiswasNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFDocument12 pagesCLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Mains2 (Entire 11th)Document7 pagesChemistry - Mains2 (Entire 11th)Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Annual Exam ReappearDocument5 pages11th Chemistry Annual Exam ReappearGPS MAP UpdatesNo ratings yet
- Mat1304 Long Quiz#1Document3 pagesMat1304 Long Quiz#1dkbtqgvhqwNo ratings yet
- Cat 8Document3 pagesCat 8Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Exam-1 Xii 22-24Document10 pagesExam-1 Xii 22-24Swastik DasNo ratings yet
- Cy 2018Document16 pagesCy 2018ArvindNo ratings yet
- Organic JAM PYQ QuestionsDocument61 pagesOrganic JAM PYQ QuestionsSandrapati ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- WinWave Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesWinWave Power Point PresentationpatrizziamarieNo ratings yet
- Polychrome Production of A Romano-Egyptian WorkshopDocument6 pagesPolychrome Production of A Romano-Egyptian WorkshopzttoshaNo ratings yet
- School Level Science Fair Experiments: Standard 4Document25 pagesSchool Level Science Fair Experiments: Standard 4SHAVITHA A/P MADAVAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- FluorineDocument1 pageFluorineAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MMB 417 2Document10 pagesThermodynamics MMB 417 2Kabo BusanangNo ratings yet
- Pharma Week 1-5Document25 pagesPharma Week 1-5Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- RP-HPLC Method Developed For The Estimation of Etodolac and Thiocolchicoside in Bulk and Combined Dosage FormsDocument11 pagesRP-HPLC Method Developed For The Estimation of Etodolac and Thiocolchicoside in Bulk and Combined Dosage FormsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Steel Wire Patenting ProcessDocument3 pagesSteel Wire Patenting Processsmallik3No ratings yet
- 12 Production and Purification of Recombinant Glargine Insulin From Escherichia Coli BL-21 StrainDocument12 pages12 Production and Purification of Recombinant Glargine Insulin From Escherichia Coli BL-21 StrainAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 4 PDFAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Jee Advance 1 Paper 1Document12 pagesJee Advance 1 Paper 1iLearn MathNo ratings yet
- Science UV PPT 1Document20 pagesScience UV PPT 1WISO THE TUTORNo ratings yet
- CHE 503 Lecture 8 - SterilizationDocument21 pagesCHE 503 Lecture 8 - SterilizationZeny NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewDocument24 pagesDistillation Technology and Need of Simultaneous Design and Control A ReviewHesam AhmadianNo ratings yet
- Biomass Pyrolysis Process (Brownsort 2009)Document93 pagesBiomass Pyrolysis Process (Brownsort 2009)iboukisNo ratings yet
- Physics Project XIIDocument14 pagesPhysics Project XIIJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- Steel8 PDFDocument18 pagesSteel8 PDFJon LawheadNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Tutorial 2Document9 pagesEclipse Tutorial 2jefpri simanjuntakNo ratings yet
- EVS Global Warming, Ozone DepletionDocument35 pagesEVS Global Warming, Ozone DepletionYashKhanijoNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityDocument12 pagesBarecuatro - BSN1 11L - Pre Finals ActivityAngelica Claire BarecuatroNo ratings yet
- Transient Flow in Natural Gas PipelineDocument24 pagesTransient Flow in Natural Gas Pipelineaen 010No ratings yet
- Nida OSDocument116 pagesNida OStingnoNo ratings yet
- Technical Data of Vacuum Formed Ceramic Fiber PDFDocument2 pagesTechnical Data of Vacuum Formed Ceramic Fiber PDFba ajinNo ratings yet
- Lebitso Ntini (201700044 (Imb 325) ) - JominyDocument4 pagesLebitso Ntini (201700044 (Imb 325) ) - JominySnr Berel ShepherdNo ratings yet
- 212 - Problem Set 1Document2 pages212 - Problem Set 1everyoneMDNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowDocument2 pagesNutrient Losses Throughout The Blood FlowGwenethVineEscalanteNo ratings yet
- Kollicoat ProtectDocument10 pagesKollicoat ProtectAshok LenkaNo ratings yet
- Sample PDF of STD 12th Science English Medium Perfect Chemistry 1Document27 pagesSample PDF of STD 12th Science English Medium Perfect Chemistry 1Tanisha ShindeNo ratings yet
- REview of Philosophical ChemistryDocument5 pagesREview of Philosophical ChemistryCarlos De Landa AcostaNo ratings yet