Professional Documents
Culture Documents
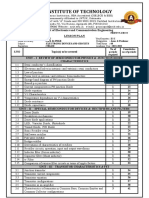
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
Uploaded by
Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Streetmacro 6701 Spec SheetDocument32 pagesStreetmacro 6701 Spec SheetFARHAD SADIQ100% (5)
- Dgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERDocument5 pagesDgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERJagbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Sushma NageshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electromagnetic CompatibilityFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic CompatibilityRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Yamaha Ex5 Adventures in FDSP Water - Brian CowellDocument12 pagesYamaha Ex5 Adventures in FDSP Water - Brian CowelljboltnzNo ratings yet
- Programmers Guide BraumatDocument48 pagesProgrammers Guide BraumatMiroslav Jovanović100% (1)
- Document 2Document15 pagesDocument 2Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Module 4 PDFDocument2 pagesEasa Part 66 Module 4 PDFPRASADNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Electronic Fundamentals Mod b1Document5 pagesSyllabus Electronic Fundamentals Mod b1rakaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus1 PDFDocument3 pagesSyllabus1 PDFdnes9999No ratings yet
- B2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDFDocument1 pageB2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDFИлларион ПанасенкоNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Module 5 PDFDocument3 pagesEasa Part 66 Module 5 PDFPRASADNo ratings yet
- Module 05 SyllabusDocument3 pagesModule 05 Syllabussultansiddiqui609No ratings yet
- Module 05 SyllabusDocument3 pagesModule 05 SyllabusChetan JambukiyaNo ratings yet
- Program Mod 5 PDFDocument3 pagesProgram Mod 5 PDFvalerio freyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Digital Techniques-Eis PDFDocument3 pagesModule 5 - Digital Techniques-Eis PDFRishi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Part66 Module4Document2 pagesPart66 Module4K M Mosheur RahmanNo ratings yet
- DTEIS Syllabus B2Document2 pagesDTEIS Syllabus B2syedhades solNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusDocument23 pagesPolytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusSudhakar MishraNo ratings yet
- Nria20 Edc Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNria20 Edc Lesson PlanD. Ravi ShankarNo ratings yet
- EASA Module 4 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEASA Module 4 SyllabusPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Bamel Holder Syllabus b1Document5 pagesBamel Holder Syllabus b1Anonymous QqSHIKX6bDNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ElectronicsDocument12 pagesSyllabus ElectronicsShubhra Kanti GopeNo ratings yet
- Ipslba 1Document11 pagesIpslba 1Raul FelicianoNo ratings yet
- LDICA Digital NotesDocument263 pagesLDICA Digital NotesAbhishek Reddy Garlapati80% (5)
- Electronic & Pneumatic InstrumentationDocument2 pagesElectronic & Pneumatic InstrumentationMahavirsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- BE2101 - Basic Electronics: (1 Semester - CS, IT) Credits: 3 Contact Hours: 3Document3 pagesBE2101 - Basic Electronics: (1 Semester - CS, IT) Credits: 3 Contact Hours: 3Minimol RajNo ratings yet
- Document From PrajwalDocument200 pagesDocument From PrajwalPrajwal KunderNo ratings yet
- Tradesman - Electronics TED - 1Document4 pagesTradesman - Electronics TED - 1sampreethpNo ratings yet
- Proddocspdf 2 248 PDFDocument20 pagesProddocspdf 2 248 PDFRaj KrishNo ratings yet
- PWD JeDocument11 pagesPWD JeArjun MeghanathanNo ratings yet
- Basic Instrumentation PDFDocument53 pagesBasic Instrumentation PDFAnonymous PTHwJyinsNo ratings yet
- BE Descriptive Notes PDFDocument199 pagesBE Descriptive Notes PDFBOOMERaNG boomNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fundamentals: Q Semiconductors Q Printed Circuit Boards Q ServomechanismsDocument89 pagesElectronic Fundamentals: Q Semiconductors Q Printed Circuit Boards Q Servomechanismsharshitsaxena12No ratings yet
- PLC CurriculumDocument8 pagesPLC Curriculum2O167O5 MC Ekta IspandeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus OnlyDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus OnlyBISHAL AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Solapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemDocument8 pagesSolapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemJAYASHEEBA.J 19BCC142No ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document25 pagesResearch Paper 1GennyNo ratings yet
- Diploma Ii Year (Electronics Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsDocument25 pagesDiploma Ii Year (Electronics Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsAjay GahlotNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Circuit DiagramsDocument31 pagesSymbols and Circuit DiagramsSourabh SamantaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsDocument3 pagesElectrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsJorge GuerreroNo ratings yet
- DR BR Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharDocument3 pagesDR BR Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharArun BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- LICDocument5 pagesLICsaranyavinothkumarNo ratings yet
- PDC Lecture ScheduleDocument2 pagesPDC Lecture ScheduleNileshIndulkarNo ratings yet
- EE PlansDocument53 pagesEE PlansElyssa SimbulanNo ratings yet
- ND40 Service Manual QUICK START RevdDocument29 pagesND40 Service Manual QUICK START RevdMichael PrzybylskiNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ElectronicsDocument318 pagesAnalog and Digital ElectronicsabrhamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Lic-2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Lic-2sangs_jayaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Question BankDocument2 pagesUnit-4 Question BankYashikaNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Applications: Summing, Integrator, Differentiator, V-I and I-V ConvertersDocument3 pagesOp-Amp Applications: Summing, Integrator, Differentiator, V-I and I-V Convertersadsfasfd123No ratings yet
- EDCunit 1Document55 pagesEDCunit 1Shiva NSNo ratings yet
- Ies Ec New SyllabusDocument2 pagesIes Ec New SyllabusPawan PariharNo ratings yet
- EI5007W1D1Document10 pagesEI5007W1D1PyiAungNo ratings yet
- 18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFDocument125 pages18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFsuhas kumarNo ratings yet
- Civil-I-Basic Electronics EnggDocument94 pagesCivil-I-Basic Electronics EnggBHUVANESWARI ANo ratings yet
- Course Plan - EEE - 3412016-17 - 1Document4 pagesCourse Plan - EEE - 3412016-17 - 1Rudraraju ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- IV Sem Syllabus of Degital Electronics - HamzaDocument11 pagesIV Sem Syllabus of Degital Electronics - Hamzamdhamza3636No ratings yet
- Course Outline - EE-227 Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesCourse Outline - EE-227 Electronics Engineeringjazz iconNo ratings yet
- Beb2023 CurriculumDocument2 pagesBeb2023 CurriculumEmmanuel NwannaNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsFrom EverandSignal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsNo ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- Techteach - No Simview Quality Flow Control IndexDocument3 pagesTechteach - No Simview Quality Flow Control IndexDiabloNo ratings yet
- Automatic COntrol With INteractive ToolsDocument366 pagesAutomatic COntrol With INteractive ToolsGeorge IskanderNo ratings yet
- 2019 Issue-1Document84 pages2019 Issue-1Tao HouNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers: Q1. What Is Electronics?Document7 pagesBasic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers: Q1. What Is Electronics?smydyNo ratings yet
- Feedback? Feedback: What Is Forms ofDocument3 pagesFeedback? Feedback: What Is Forms ofdindaNo ratings yet
- Slva633 PDFDocument14 pagesSlva633 PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument18 pagesElectronicsSrinjay BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic LevitatorDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic LevitatorPramote RodbonNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM Software For Solar P.V. System Give Constant Output Voltage at Different Solar RadiationDocument6 pagesSimulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM Software For Solar P.V. System Give Constant Output Voltage at Different Solar Radiationkk_kamalakkannanNo ratings yet
- Unit # 02 Homeostasis Insta - Husain.z.kmuDocument36 pagesUnit # 02 Homeostasis Insta - Husain.z.kmuMuhammad RiazNo ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio MP7000 Trouble Error CodesDocument35 pagesRicoh Aficio MP7000 Trouble Error CodesNafeesAhmadNo ratings yet
- Tesol101 Document HowToStayInTheTargetLanguageDocument6 pagesTesol101 Document HowToStayInTheTargetLanguageLuisa Irene Rico UreñaNo ratings yet
- Man 8055 Inst PDFDocument732 pagesMan 8055 Inst PDFAl ZanoagaNo ratings yet
- Weiss 1972Document10 pagesWeiss 1972PNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesApgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDhanu NetintiNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifierDocument52 pagesFeedback AmplifierBharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Why Do Amplifiers Sound Different - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio & TV News, Mar 1957)Document3 pagesWhy Do Amplifiers Sound Different - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio & TV News, Mar 1957)jimmy67musicNo ratings yet
- IO Module A9056TDocument2 pagesIO Module A9056T许浩江No ratings yet
- Chapter 10-REDUCTION BLOCK DIAGRAMDocument14 pagesChapter 10-REDUCTION BLOCK DIAGRAMpnroslinda91% (23)
- Basic Information: Axial Piston Pumps Single and TandemDocument36 pagesBasic Information: Axial Piston Pumps Single and TandemDarlan AssinkNo ratings yet
- Johari Window ! PDFDocument8 pagesJohari Window ! PDFs.archanaNo ratings yet
- Audio RealityDocument124 pagesAudio Realityterranohr0% (1)
- Instrumentation GPSA HandbookDocument6 pagesInstrumentation GPSA HandbookmusaveerNo ratings yet
- Robotics MainDocument2 pagesRobotics MainrijuNo ratings yet
- Ec 2251 Electronic Circuits IIDocument1 pageEc 2251 Electronic Circuits IIHenri Dass100% (1)
- Motivation For Analog IC DesignDocument32 pagesMotivation For Analog IC DesignSovan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Epc D 150-30 VV 2.0Document2 pagesEpc D 150-30 VV 2.0antonioldiasNo ratings yet
- GE Industrial SystemsDocument20 pagesGE Industrial Systemsfishzee100% (2)
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
Uploaded by
Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
MODULE 4&5 Syllabus
Uploaded by
Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 4.
ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS
Regulation (EU) 2018/1142
MODULE 4. ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS
A B1 B2
B2L
4.1 Semiconductors
4.1.1 Diodes
(a) Diode symbols; — 2 2
Diode characteristics and properties;
Diodes in series and parallel;
Main characteristics and use of silicon controlled rectifiers
(thyristors), light emitting diode, photo conductive diode,
varistor, rectifier diodes;
Functional testing of diodes.
(b) Materials, electron configuration, electrical properties; — — 2
P and N type materials: effects of impurities on conduction,
majority and minority characters;
PN junction in a semiconductor, development of a potential
across a PN junction in unbiased, forward biased and
reverse biased conditions;
Diode parameters: peak inverse voltage, maximum forward
current, temperature, frequency, leakage current, power
dissipation;
Operation and function of diodes in the following circuits:
clippers, clampers, full and half wave rectifiers, bridge
rectifiers, voltage doublers and triplers;
Detailed operation and characteristics of the following
devices: silicon controlled rectifier (thyristor), light emitting
diode, Schottky diode, photo conductive diode, varactor
diode, varistor, rectifier diodes, Zener diode.
4.1.2 Transistors
(a) Transistor symbols; — 1 2
Component description and orientation;
Transistor characteristics and properties.
(b) Construction and operation of PNP and NPN transistors; — — 2
Base, collector and emitter configurations;
Testing of transistors;
Basic appreciation of other transistor types and their uses;
Application of transistors: classes of amplifier (A, B, C);
Simple circuits including: bias, decoupling, feedback and
stabilisation;
Multistage circuit principles: cascades, push-pull,
oscillators, multivibrators, flip-flop circuits.
4.1.3 Integrated Circuits
(a) Description and operation of logic circuits and linear — 1 —
circuits/operational amplifiers;
(b) Description and operation of logic circuits and linear circuits; — — 2
Introduction to operation and function of an operational
amplifier used as: integrator, differentiator, voltage follower,
comparator;
Operation and amplifier stages connecting methods:
MODULE 4. ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS
A B1 B2
B2L
resistive capacitive, inductive (transformer), inductive
resistive (IR), direct;
Advantages and disadvantages of positive and negative
feedback.
4.2 Printed Circuit Boards — 1 2
Description and use of printed circuit boards.
4.3 Servomechanisms
(a) Understanding of the following terms: Open and closed loop — 1 —
systems, feedback, follow up, analogue transducers;
Principles of operation and use of the following synchro
system components/features: resolvers, differential, control
and torque, transformers, inductance and capacitance
transmitters;
(b) Understanding of the following terms: Open and closed loop, — — 2
follow up, servomechanism, analogue, transducer, null,
damping, feedback, deadband;
Construction operation and use of the following synchro
system components: resolvers, differential, control and
torque, E and I transformers, inductance transmitters,
capacitance transmitters, synchronous transmitters;
Servomechanism defects, reversal of synchro leads, hunting.
MODULE 5. DIGITAL TECHNIQUES/ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS
Regulation (EU) 2018/1142
MODULE 5. DIGITAL TECHNIQUES/ELECTRONIC LEVEL
INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS
A B1.1 B1.2 B2 B3
B1.3 B1.4 B2L
5.1 Electronic Instrument Systems 1 2 2 3 1
Typical systems arrangements and cockpit layout of
electronic instrument systems.
5.2 Numbering Systems — 1 — 2 —
Numbering systems: binary, octal and hexadecimal;
Demonstration of conversions between the decimal and
binary, octal and hexadecimal systems and vice versa.
5.3 Data Conversion — 1 — 2 —
Analogue Data, Digital Data;
Operation and application of analogue to digital, and digital
to analogue converters, inputs and outputs, limitations of
various types.
5.4 Data Buses — 2 — 2 —
Operation of data buses in aircraft systems, including
knowledge of ARINC and other specifications.
MODULE 5. DIGITAL TECHNIQUES/ELECTRONIC LEVEL
INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS
A B1.1 B1.2 B2 B3
B1.3 B1.4 B2L
Aircraft Network/Ethernet.
5.5 Logic Circuits
(a) Identification of common logic gate symbols, tables and — 2 — 2 —
equivalent circuits;
Applications used for aircraft systems, schematic
diagrams.
(b) Interpretation of logic diagrams. — — — 2 —
5.6 Basic Computer Structure
(a) Computer terminology (including bit, byte, software, 1 2 — — —
hardware, CPU, IC, and various memory devices
such as RAM, ROM, PROM);
Computer technology (as applied in aircraft
systems).
(b) Computer related terminology; — — — 2 —
Operation, layout and interface of the major
components in a micro computer including their
associated bus systems;
Information contained in single and multiaddress
instruction words;
Memory associated terms;
Operation of typical memory devices;
Operation, advantages and disadvantages of the
various data storage systems.
5.7 Microprocessors — — — 2 —
Functions performed and overall operation of a
microprocessor;
Basic operation of each of the following microprocessor
elements: control and processing unit, clock, register,
arithmetic logic unit.
5.8 Integrated Circuits — — — 2 —
Operation and use of encoders and decoders;
Function of encoder types;
Uses of medium, large and very large scale integration.
5.9 Multiplexing — — — 2 —
Operation, application and identification in logic diagrams of
multiplexers and demultiplexers.
5.10 Fibre Optics — 1 1 2 —
Advantages and disadvantages of fibre optic data
transmission over electrical wire propagation;
Fibre optic data bus;
Fibre optic related terms;
Terminations;
Couplers, control terminals, remote terminals;
Application of fibre optics in aircraft systems.
MODULE 5. DIGITAL TECHNIQUES/ELECTRONIC LEVEL
INSTRUMENT SYSTEMS
A B1.1 B1.2 B2 B3
B1.3 B1.4 B2L
5.11 Electronic Displays — 2 1 2 1
Principles of operation of common types of displays used in
modern aircraft, including Cathode Ray Tubes, Light
Emitting Diodes and Liquid Crystal Display.
5.12 Electrostatic Sensitive Devices 1 2 2 2 1
Special handling of components sensitive to electrostatic
discharges;
Awareness of risks and possible damage, component and
personnel anti-static protection devices.
5.13 Software Management Control — 2 1 2 1
Awareness of restrictions, airworthiness requirements and
possible catastrophic effects of unapproved changes to
software programmes.
5.14 Electromagnetic Environment — 2 2 2 1
Influence of the following phenomena on maintenance
practices for electronic system:
EMC-Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMI-Electromagnetic Interference
HIRF-High Intensity Radiated Field
Lightning/lightning protection.
5.15 Typical Electronic/Digital Aircraft Systems — 2 2 2 1
General arrangement of typical electronic/digital aircraft
systems and associated BITE (Built In Test Equipment)
such as:
(a) For B1 and B2 only:
ACARS-ARINC Communication and Addressing and
Reporting System
EICAS-Engine Indication and Crew Alerting System
FBW-Fly-by-Wire
FMS-Flight Management System
IRS-Inertial Reference System;
(b) For B1, B2 and B3:
ECAM-Electronic Centralised Aircraft Monitoring
EFIS-Electronic Flight Instrument System
GPS-Global Positioning System
TCAS-Traffic Alert Collision Avoidance System
Integrated Modular Avionics
Cabin Systems
Information Systems.
You might also like
- Streetmacro 6701 Spec SheetDocument32 pagesStreetmacro 6701 Spec SheetFARHAD SADIQ100% (5)
- Dgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERDocument5 pagesDgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERJagbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Sushma NageshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electromagnetic CompatibilityFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic CompatibilityRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Yamaha Ex5 Adventures in FDSP Water - Brian CowellDocument12 pagesYamaha Ex5 Adventures in FDSP Water - Brian CowelljboltnzNo ratings yet
- Programmers Guide BraumatDocument48 pagesProgrammers Guide BraumatMiroslav Jovanović100% (1)
- Document 2Document15 pagesDocument 2Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Module 4 PDFDocument2 pagesEasa Part 66 Module 4 PDFPRASADNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Electronic Fundamentals Mod b1Document5 pagesSyllabus Electronic Fundamentals Mod b1rakaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus1 PDFDocument3 pagesSyllabus1 PDFdnes9999No ratings yet
- B2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDFDocument1 pageB2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDFИлларион ПанасенкоNo ratings yet
- Easa Part 66 Module 5 PDFDocument3 pagesEasa Part 66 Module 5 PDFPRASADNo ratings yet
- Module 05 SyllabusDocument3 pagesModule 05 Syllabussultansiddiqui609No ratings yet
- Module 05 SyllabusDocument3 pagesModule 05 SyllabusChetan JambukiyaNo ratings yet
- Program Mod 5 PDFDocument3 pagesProgram Mod 5 PDFvalerio freyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Digital Techniques-Eis PDFDocument3 pagesModule 5 - Digital Techniques-Eis PDFRishi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Part66 Module4Document2 pagesPart66 Module4K M Mosheur RahmanNo ratings yet
- DTEIS Syllabus B2Document2 pagesDTEIS Syllabus B2syedhades solNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusDocument23 pagesPolytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusSudhakar MishraNo ratings yet
- Nria20 Edc Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNria20 Edc Lesson PlanD. Ravi ShankarNo ratings yet
- EASA Module 4 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEASA Module 4 SyllabusPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Bamel Holder Syllabus b1Document5 pagesBamel Holder Syllabus b1Anonymous QqSHIKX6bDNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ElectronicsDocument12 pagesSyllabus ElectronicsShubhra Kanti GopeNo ratings yet
- Ipslba 1Document11 pagesIpslba 1Raul FelicianoNo ratings yet
- LDICA Digital NotesDocument263 pagesLDICA Digital NotesAbhishek Reddy Garlapati80% (5)
- Electronic & Pneumatic InstrumentationDocument2 pagesElectronic & Pneumatic InstrumentationMahavirsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- BE2101 - Basic Electronics: (1 Semester - CS, IT) Credits: 3 Contact Hours: 3Document3 pagesBE2101 - Basic Electronics: (1 Semester - CS, IT) Credits: 3 Contact Hours: 3Minimol RajNo ratings yet
- Document From PrajwalDocument200 pagesDocument From PrajwalPrajwal KunderNo ratings yet
- Tradesman - Electronics TED - 1Document4 pagesTradesman - Electronics TED - 1sampreethpNo ratings yet
- Proddocspdf 2 248 PDFDocument20 pagesProddocspdf 2 248 PDFRaj KrishNo ratings yet
- PWD JeDocument11 pagesPWD JeArjun MeghanathanNo ratings yet
- Basic Instrumentation PDFDocument53 pagesBasic Instrumentation PDFAnonymous PTHwJyinsNo ratings yet
- BE Descriptive Notes PDFDocument199 pagesBE Descriptive Notes PDFBOOMERaNG boomNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fundamentals: Q Semiconductors Q Printed Circuit Boards Q ServomechanismsDocument89 pagesElectronic Fundamentals: Q Semiconductors Q Printed Circuit Boards Q Servomechanismsharshitsaxena12No ratings yet
- PLC CurriculumDocument8 pagesPLC Curriculum2O167O5 MC Ekta IspandeNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus OnlyDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus OnlyBISHAL AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Solapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemDocument8 pagesSolapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemJAYASHEEBA.J 19BCC142No ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document25 pagesResearch Paper 1GennyNo ratings yet
- Diploma Ii Year (Electronics Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsDocument25 pagesDiploma Ii Year (Electronics Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsAjay GahlotNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Circuit DiagramsDocument31 pagesSymbols and Circuit DiagramsSourabh SamantaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsDocument3 pagesElectrical and Computer - Electronics, Controls, and Communications CBT Exam SpecificationsJorge GuerreroNo ratings yet
- DR BR Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharDocument3 pagesDR BR Ambedkar National Institute of Technology JalandharArun BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- LICDocument5 pagesLICsaranyavinothkumarNo ratings yet
- PDC Lecture ScheduleDocument2 pagesPDC Lecture ScheduleNileshIndulkarNo ratings yet
- EE PlansDocument53 pagesEE PlansElyssa SimbulanNo ratings yet
- ND40 Service Manual QUICK START RevdDocument29 pagesND40 Service Manual QUICK START RevdMichael PrzybylskiNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ElectronicsDocument318 pagesAnalog and Digital ElectronicsabrhamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Lic-2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Lic-2sangs_jayaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Question BankDocument2 pagesUnit-4 Question BankYashikaNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Applications: Summing, Integrator, Differentiator, V-I and I-V ConvertersDocument3 pagesOp-Amp Applications: Summing, Integrator, Differentiator, V-I and I-V Convertersadsfasfd123No ratings yet
- EDCunit 1Document55 pagesEDCunit 1Shiva NSNo ratings yet
- Ies Ec New SyllabusDocument2 pagesIes Ec New SyllabusPawan PariharNo ratings yet
- EI5007W1D1Document10 pagesEI5007W1D1PyiAungNo ratings yet
- 18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFDocument125 pages18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFsuhas kumarNo ratings yet
- Civil-I-Basic Electronics EnggDocument94 pagesCivil-I-Basic Electronics EnggBHUVANESWARI ANo ratings yet
- Course Plan - EEE - 3412016-17 - 1Document4 pagesCourse Plan - EEE - 3412016-17 - 1Rudraraju ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- IV Sem Syllabus of Degital Electronics - HamzaDocument11 pagesIV Sem Syllabus of Degital Electronics - Hamzamdhamza3636No ratings yet
- Course Outline - EE-227 Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesCourse Outline - EE-227 Electronics Engineeringjazz iconNo ratings yet
- Beb2023 CurriculumDocument2 pagesBeb2023 CurriculumEmmanuel NwannaNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsFrom EverandSignal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsNo ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- Techteach - No Simview Quality Flow Control IndexDocument3 pagesTechteach - No Simview Quality Flow Control IndexDiabloNo ratings yet
- Automatic COntrol With INteractive ToolsDocument366 pagesAutomatic COntrol With INteractive ToolsGeorge IskanderNo ratings yet
- 2019 Issue-1Document84 pages2019 Issue-1Tao HouNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers: Q1. What Is Electronics?Document7 pagesBasic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers: Q1. What Is Electronics?smydyNo ratings yet
- Feedback? Feedback: What Is Forms ofDocument3 pagesFeedback? Feedback: What Is Forms ofdindaNo ratings yet
- Slva633 PDFDocument14 pagesSlva633 PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument18 pagesElectronicsSrinjay BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic LevitatorDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic LevitatorPramote RodbonNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM Software For Solar P.V. System Give Constant Output Voltage at Different Solar RadiationDocument6 pagesSimulation of Single Phase Inverter Using PSIM Software For Solar P.V. System Give Constant Output Voltage at Different Solar Radiationkk_kamalakkannanNo ratings yet
- Unit # 02 Homeostasis Insta - Husain.z.kmuDocument36 pagesUnit # 02 Homeostasis Insta - Husain.z.kmuMuhammad RiazNo ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio MP7000 Trouble Error CodesDocument35 pagesRicoh Aficio MP7000 Trouble Error CodesNafeesAhmadNo ratings yet
- Tesol101 Document HowToStayInTheTargetLanguageDocument6 pagesTesol101 Document HowToStayInTheTargetLanguageLuisa Irene Rico UreñaNo ratings yet
- Man 8055 Inst PDFDocument732 pagesMan 8055 Inst PDFAl ZanoagaNo ratings yet
- Weiss 1972Document10 pagesWeiss 1972PNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesApgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDhanu NetintiNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifierDocument52 pagesFeedback AmplifierBharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Why Do Amplifiers Sound Different - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio & TV News, Mar 1957)Document3 pagesWhy Do Amplifiers Sound Different - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio & TV News, Mar 1957)jimmy67musicNo ratings yet
- IO Module A9056TDocument2 pagesIO Module A9056T许浩江No ratings yet
- Chapter 10-REDUCTION BLOCK DIAGRAMDocument14 pagesChapter 10-REDUCTION BLOCK DIAGRAMpnroslinda91% (23)
- Basic Information: Axial Piston Pumps Single and TandemDocument36 pagesBasic Information: Axial Piston Pumps Single and TandemDarlan AssinkNo ratings yet
- Johari Window ! PDFDocument8 pagesJohari Window ! PDFs.archanaNo ratings yet
- Audio RealityDocument124 pagesAudio Realityterranohr0% (1)
- Instrumentation GPSA HandbookDocument6 pagesInstrumentation GPSA HandbookmusaveerNo ratings yet
- Robotics MainDocument2 pagesRobotics MainrijuNo ratings yet
- Ec 2251 Electronic Circuits IIDocument1 pageEc 2251 Electronic Circuits IIHenri Dass100% (1)
- Motivation For Analog IC DesignDocument32 pagesMotivation For Analog IC DesignSovan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Epc D 150-30 VV 2.0Document2 pagesEpc D 150-30 VV 2.0antonioldiasNo ratings yet
- GE Industrial SystemsDocument20 pagesGE Industrial Systemsfishzee100% (2)