Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsBiology Auxin Phototropism
Biology Auxin Phototropism
Uploaded by
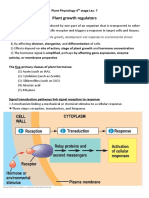
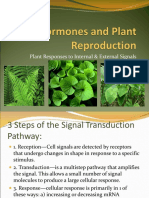
Ab BugarinAuxin is a plant hormone that regulates growth and development. It promotes cell elongation and division, stimulating processes like stem elongation, root formation, flowering and fruit development. Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to light, caused by auxin accumulating on the shaded side and causing those cells to elongate more, bending the plant towards the light source. Too little or too much auxin can harm the plant by inhibiting growth or causing toxicity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Year 10 Biology TestDocument10 pagesYear 10 Biology TestMichael Mc BrienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- PLANT HORMONE - ModuleDocument24 pagesPLANT HORMONE - ModuleMarinel Almencion MagyanoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDocument6 pagesNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- Note PhytohormonesDocument47 pagesNote PhytohormonesAyuni Mokhtar100% (1)
- Bot Lec ReviwerDocument6 pagesBot Lec ReviwerClarence ManlambusNo ratings yet
- AUXINDocument23 pagesAUXINJose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- Pesticides 2 & PGRDocument15 pagesPesticides 2 & PGRmehakfaiz.07No ratings yet
- Plant ResponsesDocument24 pagesPlant Responsesk75544863No ratings yet
- Kuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFDocument38 pagesKuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFRianNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument1 pageQuiz LetAmalia FirdzaNo ratings yet
- O-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYDocument21 pagesO-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYayikoyoroy10No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan Mendiola100% (1)
- Coordination & Response Pt. 2Document22 pagesCoordination & Response Pt. 2Yagna LallNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination in Plants-NotesDocument4 pagesChemical Coordination in Plants-NotesKarishmmNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination in Plants NotesAmna SaleemNo ratings yet
- Auxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyDocument33 pagesAuxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyAyushi MandloiNo ratings yet
- Plant Bio 1Document5 pagesPlant Bio 1Jamaira SamaupanNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: AuxinsDocument8 pagesSlide 1: AuxinsMarawan NoubyNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 4Document24 pagesCropSci101 Module 4Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Crop - Lecture - Growth HormonesDocument9 pagesCrop - Lecture - Growth HormonesCynel DelaNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Growth in Plants 1Document23 pages9.3 Growth in Plants 1ssjqryNo ratings yet
- Plant Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesPlant Control and CoordinationNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 Plant MorphologyDocument3 pagesBIO 2 Plant MorphologyMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 FITOHORMONEDocument23 pagesBab 6 FITOHORMONEnormaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.3: Growth in PlantsDocument17 pagesTopic 9.3: Growth in Plantssalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsDocument4 pagesPlant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsMuhamad MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Topic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerDocument4 pagesTopic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerUrooj UmerNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument6 pagesPlant Hormonesxulunkazimulo083No ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document3 pagesBiology 1Jhon Cusme (jhoncusme)No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Key Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and CompetencesDocument8 pagesKey Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and Competencesnicole mugumbaNo ratings yet
- Plant Response - BB - FinalDocument74 pagesPlant Response - BB - Finaldo hieuNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Plant HormonesDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Plant HormonesJv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- L-2 Control and CoordinationDocument17 pagesL-2 Control and CoordinationdancelikeangelNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants: RadiateDocument14 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants: RadiateTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Auxin and TropismDocument17 pagesAuxin and TropismmarwaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biology TermsDocument120 pagesBiology TermsNiamat UllahNo ratings yet
- Control of Growth and Responses in PlantsDocument4 pagesControl of Growth and Responses in PlantsAlix GrangerNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesControl and CoordinationSuchita JhaNo ratings yet
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BDocument3 pagesSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- BioA4 16 Stimuli Receptors and ResponsesDocument4 pagesBioA4 16 Stimuli Receptors and Responsesthanks btNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsDocument25 pages5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsJharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PLANTDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyIvimina Jack DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewDocument46 pagesBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- Document 20Document24 pagesDocument 202023856678No ratings yet
- BIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesDocument48 pagesBIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesJet DelimaNo ratings yet
- LR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Document19 pagesLR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Kate Jewel CullamatNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth, Development and Life CycleDocument19 pagesPlant Growth, Development and Life CycleCeazar Ian PesimoNo ratings yet
- Growth 1Document35 pagesGrowth 1Gabriella SteeleNo ratings yet
- Study of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.From EverandStudy of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.No ratings yet
- Midterm Syllabus - NurbioLecDocument7 pagesMidterm Syllabus - NurbioLecAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- PLANT NUTRTION and Digestive System - Docx 1Document4 pagesPLANT NUTRTION and Digestive System - Docx 1Ab BugarinNo ratings yet
- Nervous, Excretory System, and HomeostasisDocument3 pagesNervous, Excretory System, and HomeostasisAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Quarter 2 Module 7 Name: - Grade & SectionDocument5 pagesOral Communication in Context Quarter 2 Module 7 Name: - Grade & SectionAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Membrane (CE Bio Structured Questions)Document15 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Membrane (CE Bio Structured Questions)Emily LiNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of OnionDocument23 pagesEffectiveness of OnionRevenlie Galapin0% (2)
- FamilyDocument10 pagesFamilygerrymanderingNo ratings yet
- Cocos NuciferaDocument20 pagesCocos NuciferaRaiza RuizNo ratings yet
- Catalog Planetaverd 2013Document94 pagesCatalog Planetaverd 2013scribullNo ratings yet
- AnthuriumDocument17 pagesAnthuriumdhinglijay100% (2)
- Grain Inspection HandbookDocument28 pagesGrain Inspection HandbookJoan Manuel Tovar CasallasNo ratings yet
- IEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1Document3 pagesIEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1sangdeep waldeNo ratings yet
- TSBIE Bridge Course Q Bank - MQP - Wef 2016-17Document148 pagesTSBIE Bridge Course Q Bank - MQP - Wef 2016-17PRATHYUSH RAJNo ratings yet
- Hawkins and George 1997Document9 pagesHawkins and George 1997vachaspatimishraNo ratings yet
- IGS1.S2 - Science WorkbookDocument114 pagesIGS1.S2 - Science WorkbookjennyhoabcNo ratings yet
- GRE Big Book WordsDocument32 pagesGRE Big Book Wordsapi-3696482100% (1)
- Cut Flower GuideDocument32 pagesCut Flower Guidecapitanmono100% (6)
- HITOIRODocument2 pagesHITOIROapi-3757257100% (1)
- Lake Trevallyn: Blue Green Algal BloomsDocument1 pageLake Trevallyn: Blue Green Algal BloomsThe ExaminerNo ratings yet
- Biology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Document11 pagesBiology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Jashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- CXS - 052e Capsuni Congelate PDFDocument6 pagesCXS - 052e Capsuni Congelate PDFdorinutza280No ratings yet
- Arboles en InglesDocument2 pagesArboles en InglesAzûçenä LčNo ratings yet
- Arise and Shine Like A Light Upon A Hill: SATB VersionDocument3 pagesArise and Shine Like A Light Upon A Hill: SATB VersionnadiaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Meiosis in Tetraploid (4x) Cannabis Sativa (L.) From Lahaul-Spiti (Cold Desert Higher Altitude Himalayas) - A Neglected But Important HerbDocument5 pagesAbnormal Meiosis in Tetraploid (4x) Cannabis Sativa (L.) From Lahaul-Spiti (Cold Desert Higher Altitude Himalayas) - A Neglected But Important HerbD K SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5Document75 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5gerelyn matuteNo ratings yet
- Keys To The Genera of Annonaceae.xDocument10 pagesKeys To The Genera of Annonaceae.xMaikol GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Bgjournal: Ecological Restoration and The Role of Botanic GardensDocument35 pagesBgjournal: Ecological Restoration and The Role of Botanic GardensMynor Morales HerreraNo ratings yet
- Japanese Garden 1Document25 pagesJapanese Garden 1api-37034220% (1)
- AracaceaDocument9 pagesAracaceaBelem AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Trees and Flowering Plants of BangaDocument1 pageTrees and Flowering Plants of BangaKirthika ChithraNo ratings yet
- 2014 1805749Document58 pages2014 1805749S.R hertzNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDocument89 pagesMSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDaguale Melaku AyeleNo ratings yet
- Sayre's Materia Medica FreeDocument84 pagesSayre's Materia Medica Freeakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet
Biology Auxin Phototropism
Biology Auxin Phototropism
Uploaded by
Ab Bugarin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesAuxin is a plant hormone that regulates growth and development. It promotes cell elongation and division, stimulating processes like stem elongation, root formation, flowering and fruit development. Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to light, caused by auxin accumulating on the shaded side and causing those cells to elongate more, bending the plant towards the light source. Too little or too much auxin can harm the plant by inhibiting growth or causing toxicity.
Original Description:
Original Title
BIOLOGY-AUXIN-PHOTOTROPISM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAuxin is a plant hormone that regulates growth and development. It promotes cell elongation and division, stimulating processes like stem elongation, root formation, flowering and fruit development. Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to light, caused by auxin accumulating on the shaded side and causing those cells to elongate more, bending the plant towards the light source. Too little or too much auxin can harm the plant by inhibiting growth or causing toxicity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesBiology Auxin Phototropism
Biology Auxin Phototropism
Uploaded by
Ab BugarinAuxin is a plant hormone that regulates growth and development. It promotes cell elongation and division, stimulating processes like stem elongation, root formation, flowering and fruit development. Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to light, caused by auxin accumulating on the shaded side and causing those cells to elongate more, bending the plant towards the light source. Too little or too much auxin can harm the plant by inhibiting growth or causing toxicity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
the root and shoot elongation and gradually
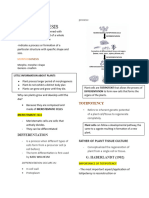
BIOLOGY – AUXXIN & PHOTOTROPISM kills the whole plant
WHAT IS AUXIN PLANT NUTRITION?
AUXIN (Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)) – are a group of
- Plant Growth Regulators. AUXIN is a greek word
naturally occulting and artificially synthesized plant
that means “to increase.” It is a genetic term
hormones. They play an important role in the
for chemicals that typically stimulate cell
regulation of plant growth.
elongation but auxins also influence a wide
- Initially isolated from human urine
range of growth and development response.
- Auxin means to “enlarge” or “increase”
The chemical isolations and characterization
- They induce cell division, differentiation, and
was done by KOGI, et al.
elongation
PHOTOTROPISM – is the growth of an
MAIN FUNCTIONS OF AUXIIN
organism in response to a light stimulus. It is
1. CELL ELONGATION: promotes elongation in
most often observed in plants, but can also
shoots and coleoptiles
occur in other organisms such as fungi.
2. CELL DIVISION AND DIFFERENTIATION:
- “PHOTO” means light, and “TROPISM”
promotes healing
means turning. Phototropism is the
3. CALLUS FORMATION AND MORPHOGENESIS:
phenomenon by which the bending in the
induce callus formation and stimulates
direction of the light.
morphogenesis
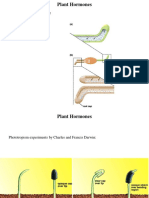
- CHARLES DARWIN detected phototropism
4. SECONDARY GROWTH: promotes secondary
movement (bending of plants towards
growth and induces cell division
light) in the coleoptile of canary grass. He
5. ROOT INITIATION ON CUTTING: NAA is used
observed that there was some influencer at
to initiate root formation in the stem cuttings.
the top of the coleoptile, which was
6. APICAL DOMINANCE: this is used to promote
responsible for the bending towards the
branching
light.
7. PARTHENOCARPY: ovary enlarges and
WHEN DOES PHOTOTROPISM OCCUR?
develops into seedless fruit (unfertilized).
- It occurs as the photoreceptors of a plant
8. FRUIT DEVELOPMENT: produced by seeds and
detect that a light source could be better
it stimulates fruit development.
accessed by the bending plant.
9. FLOWERING: delays the senescence of
- A chemical called AUXIN concentrates on
flowers
the shady side of the plant, causing the
10. HERBICIDES: synthetic auxins are widely used
plant cells to elongate which changes the
to kill weeds
direction of the plant’s growth.
11. PROMOTES TROPISM: auxin induces
WHY DOES PHOTOTROPISM OCCUR AND
phototropism, gravitopism and thigmotropism
WHAT LIGHT CAUSES PHOTOTROPISM?
(I.e. movement in response to light, gravity
- The phototropic response occurs because
and touch, respectively).
greater quantities of auxin are distributed
WHAT WILL HAPPEN TO THE PLANT WHEN IT’S
to the side away from the light than to
LACKING AUXIN?
the side towards it, causing the shaded
- The plant loses its root meristematic activity and
side to elongate more strongly which
the root degenerates since promotes the
changes the direction of the plant’s
growth and development of plants at low
growth
concentrations (0.01-10.0mg/L) and regulates
- When phototropins are activated by blue
numerous developmental processes in plants
light, the hormone auxin accumulates on
including cell expansion, root initiation,
the shaded side of the plant triggering
vascular tissue differentiation, bud and flower
elongation of stem cells and
growth.
phototropism.
WHAT WILL HAPPEN TO THE PLANT IF THE AUXIN
EXAMPLES OF PHOTOTROPISM
IS TOO MUCH?
1. POSITIVE PHOTOTROPISM – it is the
- Its overproduction causes toxicity which kills the
curving of the stem toward sunlight, or
plants. The large concentration of auxin
the growth towards a light source.
stimulates the ethylene. This ethylene inhibits
2. NEGATIVE PHOTOTROPISM – movement
of root away from the light inside the
soil, or growth away from light.
You might also like
- Year 10 Biology TestDocument10 pagesYear 10 Biology TestMichael Mc BrienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- PLANT HORMONE - ModuleDocument24 pagesPLANT HORMONE - ModuleMarinel Almencion MagyanoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDocument6 pagesNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- Note PhytohormonesDocument47 pagesNote PhytohormonesAyuni Mokhtar100% (1)
- Bot Lec ReviwerDocument6 pagesBot Lec ReviwerClarence ManlambusNo ratings yet
- AUXINDocument23 pagesAUXINJose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- Pesticides 2 & PGRDocument15 pagesPesticides 2 & PGRmehakfaiz.07No ratings yet
- Plant ResponsesDocument24 pagesPlant Responsesk75544863No ratings yet
- Kuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFDocument38 pagesKuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFRianNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument1 pageQuiz LetAmalia FirdzaNo ratings yet
- O-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYDocument21 pagesO-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYayikoyoroy10No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan Mendiola100% (1)
- Coordination & Response Pt. 2Document22 pagesCoordination & Response Pt. 2Yagna LallNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination in Plants-NotesDocument4 pagesChemical Coordination in Plants-NotesKarishmmNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination in Plants NotesAmna SaleemNo ratings yet
- Auxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyDocument33 pagesAuxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyAyushi MandloiNo ratings yet
- Plant Bio 1Document5 pagesPlant Bio 1Jamaira SamaupanNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: AuxinsDocument8 pagesSlide 1: AuxinsMarawan NoubyNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 4Document24 pagesCropSci101 Module 4Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Crop - Lecture - Growth HormonesDocument9 pagesCrop - Lecture - Growth HormonesCynel DelaNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Growth in Plants 1Document23 pages9.3 Growth in Plants 1ssjqryNo ratings yet
- Plant Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesPlant Control and CoordinationNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 Plant MorphologyDocument3 pagesBIO 2 Plant MorphologyMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 FITOHORMONEDocument23 pagesBab 6 FITOHORMONEnormaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.3: Growth in PlantsDocument17 pagesTopic 9.3: Growth in Plantssalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsDocument4 pagesPlant Physiology Lec. 7 Growth RegulatorsMuhamad MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Topic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerDocument4 pagesTopic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerUrooj UmerNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument6 pagesPlant Hormonesxulunkazimulo083No ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document3 pagesBiology 1Jhon Cusme (jhoncusme)No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Key Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and CompetencesDocument8 pagesKey Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and Competencesnicole mugumbaNo ratings yet
- Plant Response - BB - FinalDocument74 pagesPlant Response - BB - Finaldo hieuNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Plant HormonesDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Plant HormonesJv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- L-2 Control and CoordinationDocument17 pagesL-2 Control and CoordinationdancelikeangelNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants: RadiateDocument14 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants: RadiateTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Auxin and TropismDocument17 pagesAuxin and TropismmarwaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biology TermsDocument120 pagesBiology TermsNiamat UllahNo ratings yet
- Control of Growth and Responses in PlantsDocument4 pagesControl of Growth and Responses in PlantsAlix GrangerNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesControl and CoordinationSuchita JhaNo ratings yet
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BDocument3 pagesSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- BioA4 16 Stimuli Receptors and ResponsesDocument4 pagesBioA4 16 Stimuli Receptors and Responsesthanks btNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsDocument25 pages5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsJharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PLANTDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyIvimina Jack DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewDocument46 pagesBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- Document 20Document24 pagesDocument 202023856678No ratings yet
- BIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesDocument48 pagesBIO109P Module 4. Plant HormonesJet DelimaNo ratings yet
- LR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Document19 pagesLR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Kate Jewel CullamatNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth, Development and Life CycleDocument19 pagesPlant Growth, Development and Life CycleCeazar Ian PesimoNo ratings yet
- Growth 1Document35 pagesGrowth 1Gabriella SteeleNo ratings yet
- Study of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.From EverandStudy of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.No ratings yet
- Midterm Syllabus - NurbioLecDocument7 pagesMidterm Syllabus - NurbioLecAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- PLANT NUTRTION and Digestive System - Docx 1Document4 pagesPLANT NUTRTION and Digestive System - Docx 1Ab BugarinNo ratings yet
- Nervous, Excretory System, and HomeostasisDocument3 pagesNervous, Excretory System, and HomeostasisAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Quarter 2 Module 7 Name: - Grade & SectionDocument5 pagesOral Communication in Context Quarter 2 Module 7 Name: - Grade & SectionAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Membrane (CE Bio Structured Questions)Document15 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Membrane (CE Bio Structured Questions)Emily LiNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of OnionDocument23 pagesEffectiveness of OnionRevenlie Galapin0% (2)
- FamilyDocument10 pagesFamilygerrymanderingNo ratings yet
- Cocos NuciferaDocument20 pagesCocos NuciferaRaiza RuizNo ratings yet
- Catalog Planetaverd 2013Document94 pagesCatalog Planetaverd 2013scribullNo ratings yet
- AnthuriumDocument17 pagesAnthuriumdhinglijay100% (2)
- Grain Inspection HandbookDocument28 pagesGrain Inspection HandbookJoan Manuel Tovar CasallasNo ratings yet
- IEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1Document3 pagesIEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1sangdeep waldeNo ratings yet
- TSBIE Bridge Course Q Bank - MQP - Wef 2016-17Document148 pagesTSBIE Bridge Course Q Bank - MQP - Wef 2016-17PRATHYUSH RAJNo ratings yet
- Hawkins and George 1997Document9 pagesHawkins and George 1997vachaspatimishraNo ratings yet
- IGS1.S2 - Science WorkbookDocument114 pagesIGS1.S2 - Science WorkbookjennyhoabcNo ratings yet
- GRE Big Book WordsDocument32 pagesGRE Big Book Wordsapi-3696482100% (1)
- Cut Flower GuideDocument32 pagesCut Flower Guidecapitanmono100% (6)
- HITOIRODocument2 pagesHITOIROapi-3757257100% (1)
- Lake Trevallyn: Blue Green Algal BloomsDocument1 pageLake Trevallyn: Blue Green Algal BloomsThe ExaminerNo ratings yet
- Biology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Document11 pagesBiology 1002 Exam 1 Fall 2018Jashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- CXS - 052e Capsuni Congelate PDFDocument6 pagesCXS - 052e Capsuni Congelate PDFdorinutza280No ratings yet
- Arboles en InglesDocument2 pagesArboles en InglesAzûçenä LčNo ratings yet
- Arise and Shine Like A Light Upon A Hill: SATB VersionDocument3 pagesArise and Shine Like A Light Upon A Hill: SATB VersionnadiaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Meiosis in Tetraploid (4x) Cannabis Sativa (L.) From Lahaul-Spiti (Cold Desert Higher Altitude Himalayas) - A Neglected But Important HerbDocument5 pagesAbnormal Meiosis in Tetraploid (4x) Cannabis Sativa (L.) From Lahaul-Spiti (Cold Desert Higher Altitude Himalayas) - A Neglected But Important HerbD K SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5Document75 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5gerelyn matuteNo ratings yet
- Keys To The Genera of Annonaceae.xDocument10 pagesKeys To The Genera of Annonaceae.xMaikol GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Bgjournal: Ecological Restoration and The Role of Botanic GardensDocument35 pagesBgjournal: Ecological Restoration and The Role of Botanic GardensMynor Morales HerreraNo ratings yet
- Japanese Garden 1Document25 pagesJapanese Garden 1api-37034220% (1)
- AracaceaDocument9 pagesAracaceaBelem AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Trees and Flowering Plants of BangaDocument1 pageTrees and Flowering Plants of BangaKirthika ChithraNo ratings yet
- 2014 1805749Document58 pages2014 1805749S.R hertzNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDocument89 pagesMSC Thesis Updated Today PDFDaguale Melaku AyeleNo ratings yet
- Sayre's Materia Medica FreeDocument84 pagesSayre's Materia Medica Freeakbar_rozaaqNo ratings yet