Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsPermanent Tissue
Permanent Tissue
Uploaded by
TECH CORNERPermanent tissue is formed from meristematic tissue and consists of cells that lose the ability to divide. There are two types: simple permanent tissue composed of only one cell type like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma; and complex permanent tissue composed of more than one cell type like xylem and phloem which form vascular bundles and help transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from the soil to the plant using tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and sclerenchyma, while phloem transports food from leaves to other parts using sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Angiosperms PPT RevisedDocument55 pagesAngiosperms PPT RevisedJohn Philip Neri Besedillas100% (2)
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- BotanyDocument17 pagesBotanyAbdelrhman AmrNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- 1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriDocument27 pages1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriAikay EmmaNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue FinalDocument18 pagesPlant Tissue FinalEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document6 pagesCH 6Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Document31 pagesPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malani100% (1)
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t Ir SectionDocument4 pageshssb2101t Ir Sectionfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Xylem and PhloemDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Xylem and PhloemMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- L2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21Document16 pagesL2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21mvsubtitles276No ratings yet
- Anatomy in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesAnatomy in Flowering PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Tissues: ClassDocument4 pagesTissues: ClassShail KumariNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument15 pagesPlant TissueTaahirahNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPlant PhysiologyJhon BarsaNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- Simple Tissue and Complex TissueDocument4 pagesSimple Tissue and Complex TissueHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- 3.2plant Tissue 36 84Document3 pages3.2plant Tissue 36 84rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemDocument123 pagesPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiology14. Debanjan SahaNo ratings yet
- MF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Document12 pagesMF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Horng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- Bio 2. TissueDocument15 pagesBio 2. TissueRadhika's KitchenNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]No ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument53 pagesPlant TissuesClarissa LaruanNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument9 pagesTISSUEStyrtNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues Noteskapil100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesPlant TissuesKen Torres Paycana100% (1)
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologysakthilogi123No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- TissueDocument11 pagesTissuerizamariyam2010No ratings yet
- Biology Ls 6Document14 pagesBiology Ls 6KhatrasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Document12 pagesDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (8)
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Document17 pagesTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- Plant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesPlant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesSri Nagamani ThumuNo ratings yet
- Ke L-SciDocument5 pagesKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNo ratings yet
- Plant - Tissue NotesDocument3 pagesPlant - Tissue NotesDikshit Rishi JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Meristematic TissuesDocument4 pagesMeristematic TissuesNur Syiffa RosmanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter Tissues-2Document8 pagesNotes - Chapter Tissues-2Meher KodwaniNo ratings yet
- Tissues - YTDocument94 pagesTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- PlanttissuesDocument25 pagesPlanttissuesphuongchi53100% (1)
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Plants and Animal TissueDocument18 pagesPlants and Animal TissueNishikant DesaiNo ratings yet
- Ground TissuesDocument17 pagesGround TissuesHelen Gail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2Document27 pagesTissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2ebrahim hajNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument10 pagesPlant Tissue - Study Notesjjoshin10No ratings yet
- Vascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraDocument22 pagesVascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraGeorgia VasanthaNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument14 pagesLIGHTTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Diet Plan For Weigt GainDocument2 pagesDiet Plan For Weigt GainTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- List of Qualified Candidates For Skill TestDocument100 pagesList of Qualified Candidates For Skill TestTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Science SolutionDocument3 pagesScience SolutionTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document9 pagesPresentation 1Dienha ViyelaNo ratings yet
- Semagn Chapter 1Document21 pagesSemagn Chapter 1alemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- 000 Pharmacognosy Balanophora Fungosa PDFDocument4 pages000 Pharmacognosy Balanophora Fungosa PDFKannan100% (1)
- Penilaian Akhir Semester B.Inggris Kelas 8Document4 pagesPenilaian Akhir Semester B.Inggris Kelas 8Fitriani PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 F5 BiologyDocument37 pagesChap 2 F5 Biologyg-16355677No ratings yet
- Pollination Project New 2Document30 pagesPollination Project New 2SagarNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Subtopic 3.2 Organ For Water and Mineral Salts UptakeDocument16 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 3 Subtopic 3.2 Organ For Water and Mineral Salts UptakeSafwan YusufNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument26 pagesBiology ProjectSaptarsi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Rwi 33Document108 pagesRwi 33NyQ4UNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument8 pagesFlowerAntarnet AntarNo ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 PlantDocument9 pagesLab Report 2 PlantFARALIZA AHMADNo ratings yet
- Sims 3 Nectar RecipesDocument1 pageSims 3 Nectar Recipesgabbychow888No ratings yet
- WGA PDF Plan - Contemporary TV StandDocument7 pagesWGA PDF Plan - Contemporary TV StandSajith ShivashankaranNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t SecquizDocument2 pageshssb2101t Secquizfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Geitonogamy - Transfer of Pollen Grains FromDocument2 pagesGeitonogamy - Transfer of Pollen Grains FromDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hutan Lestari (2019) Vol. 7 (2) : 746 - 751Document6 pagesJurnal Hutan Lestari (2019) Vol. 7 (2) : 746 - 751Oswa PalullunganNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology VocabularyDocument8 pagesPlant Biology Vocabularydevadas panickerNo ratings yet
- Pembuatan Selai Campuran Dami Nangka Dan Sirsak: Duncan's New Multiple Range Test (DNMRT) at Level 5%. The Treatments inDocument15 pagesPembuatan Selai Campuran Dami Nangka Dan Sirsak: Duncan's New Multiple Range Test (DNMRT) at Level 5%. The Treatments inDewi Sri Apriyani HarefaNo ratings yet
- Block-06 GymnospermsDocument82 pagesBlock-06 Gymnospermstamil selviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Revision IV - QuizletDocument14 pagesChapter 8 Revision IV - QuizletChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusDocument17 pagesStructure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Sevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 9Document5 pagesSevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 9Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- American Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyDocument20 pagesAmerican Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyMaikel GaitkoskiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Seed and FruitDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Seed and FruitMonica LumbantobingNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument52 pagesPlant TissuesJessica Evangelista Arcilla100% (1)
- DB 1380 111394271Document34 pagesDB 1380 111394271Andrea Teran CoronelNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure (Flowers) : BOT 1P: Lecture 12Document62 pagesPlant Structure (Flowers) : BOT 1P: Lecture 12Victor TenorioNo ratings yet
- Xamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument31 pagesXamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
Permanent Tissue
Permanent Tissue
Uploaded by
TECH CORNER0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesPermanent tissue is formed from meristematic tissue and consists of cells that lose the ability to divide. There are two types: simple permanent tissue composed of only one cell type like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma; and complex permanent tissue composed of more than one cell type like xylem and phloem which form vascular bundles and help transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from the soil to the plant using tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and sclerenchyma, while phloem transports food from leaves to other parts using sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and
Original Description:
Original Title
PERMANENT TISSUE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPermanent tissue is formed from meristematic tissue and consists of cells that lose the ability to divide. There are two types: simple permanent tissue composed of only one cell type like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma; and complex permanent tissue composed of more than one cell type like xylem and phloem which form vascular bundles and help transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from the soil to the plant using tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and sclerenchyma, while phloem transports food from leaves to other parts using sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesPermanent Tissue
Permanent Tissue
Uploaded by
TECH CORNERPermanent tissue is formed from meristematic tissue and consists of cells that lose the ability to divide. There are two types: simple permanent tissue composed of only one cell type like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma; and complex permanent tissue composed of more than one cell type like xylem and phloem which form vascular bundles and help transport water, minerals, and food throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from the soil to the plant using tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and sclerenchyma, while phloem transports food from leaves to other parts using sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
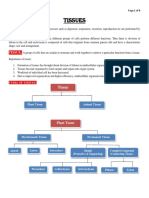
PERMANENT TISSUE
They are formed from meristematic tissue
The cells in the tissue lose the ability to divide and form permanent tissue
Permanent tissue are divided into two types
1. SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE:
Consist of only one type of cells
Simple permanent tissue is of three types
PARENCHYMA
Consists of relatively unspecialized living cells.
Loosely packed thin-walled cells, oval or spherical in structure with
large space between cells.
Cell wall mainly composed of cellulose & pectin.
Large central vacuole for food & water storage.
Primary function is food storage and packing.
Types –
Idioblast:- Some parenchyma involved in storage of excretory substances
such as resin, tannin, gum and oils called as idioblast.
Chlorenchyma:- Chloroplast containing parenchyma tissues are called as
chlorenchyma which perform photosynthesis e.g., mesophyll of leaves.
Aerenchyma:- In hydrophytic plants aerenchyma (a type of parenchyma
containing air spaces) provides buoyancy.
COLLENCHYMA TISSUE
Elongated living cells with thick corners.
Provides flexibility to plant parts & easy bending of various parts of
plant.
Few chloroplasts may be present.
Give mechanical strength elasticity to the growing stems.
They have no or very little intercellular spaces.
SCLERENCHYMA TISSUE
The cells of this tissue are dead, long and narrow.
Walls are thickened due to lignin deposition.
Present in stems, around vascular bundles, in the veins of leaves and
in the hard covering of seeds and nuts
Provides strength to the plant parts and makes plant hard & stiff.
E.g., husk of a coconut
2. COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUE:
Consists of more than one type of cells which together as a unit.
Helps in transportation of organic materials, water and minerals.
Also known as conducting as vascular tissue.
Xylem and phloem together from vascular bundles.
Complex permanent tissue is of two types
1. XYLEM: Help in Transportation of water and minerals from soil to plant.
Types - Xylem consists of four types of cells called as components or
elements:-
Tracheids Vessels Xylem Xylem
parenchyma sclerenchyma
Elongated dead Advance element
cells (primitive (generally found Small & thick- Cells are dead,
elements) mainly in angiosperms) walled thick walled &
involved in flow cylindrical parenchymatous provide
conduction of water tube-like cells designed for mechanical
and minerals in structures placed storage of starch support.
gymnosperms one above the (food).
other end to end Living
to form a
continuous
channel for
efficient
conduction of
water.
2. PHLOEM: It transport (translocation) food from leaves to other parts of
the plant.
Types - Phloem consists of 4 types of components/elements:-
Sieve tubes Companion cells Phloem Phloem
parenchyma sclerenchyma
Sieve tubes are Closely
tubular cells with associated with a Store food dead provide
perforated walls.( element •living mechanical
with pores) support.
You might also like
- Angiosperms PPT RevisedDocument55 pagesAngiosperms PPT RevisedJohn Philip Neri Besedillas100% (2)
- Tissue 9 PDFDocument5 pagesTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument14 pagesTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- BotanyDocument17 pagesBotanyAbdelrhman AmrNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- 1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriDocument27 pages1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriAikay EmmaNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue FinalDocument18 pagesPlant Tissue FinalEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document6 pagesCH 6Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022Document31 pagesPlant Tissues: Class: 7 Board: ICSE Year: 2021-2022shalu malani100% (1)
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t Ir SectionDocument4 pageshssb2101t Ir Sectionfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Xylem and PhloemDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Xylem and PhloemMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- L2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21Document16 pagesL2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21mvsubtitles276No ratings yet
- Anatomy in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesAnatomy in Flowering PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Tissues: ClassDocument4 pagesTissues: ClassShail KumariNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument15 pagesPlant TissueTaahirahNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPlant PhysiologyJhon BarsaNo ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- Simple Tissue and Complex TissueDocument4 pagesSimple Tissue and Complex TissueHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- 3.2plant Tissue 36 84Document3 pages3.2plant Tissue 36 84rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemDocument123 pagesPlant Tissue SystemAnkit Bansal100% (1)
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiology14. Debanjan SahaNo ratings yet
- MF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Document12 pagesMF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Horng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- Bio 2. TissueDocument15 pagesBio 2. TissueRadhika's KitchenNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]No ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument53 pagesPlant TissuesClarissa LaruanNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument9 pagesTISSUEStyrtNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues Noteskapil100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesPlant TissuesKen Torres Paycana100% (1)
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologysakthilogi123No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- TissueDocument11 pagesTissuerizamariyam2010No ratings yet
- Biology Ls 6Document14 pagesBiology Ls 6KhatrasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Document12 pagesDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (8)
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Document17 pagesTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- Plant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesPlant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesSri Nagamani ThumuNo ratings yet
- Ke L-SciDocument5 pagesKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNo ratings yet
- Plant - Tissue NotesDocument3 pagesPlant - Tissue NotesDikshit Rishi JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Meristematic TissuesDocument4 pagesMeristematic TissuesNur Syiffa RosmanNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter Tissues-2Document8 pagesNotes - Chapter Tissues-2Meher KodwaniNo ratings yet
- Tissues - YTDocument94 pagesTissues - YTRaima Sharma100% (3)
- PlanttissuesDocument25 pagesPlanttissuesphuongchi53100% (1)
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Plants and Animal TissueDocument18 pagesPlants and Animal TissueNishikant DesaiNo ratings yet
- Ground TissuesDocument17 pagesGround TissuesHelen Gail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2Document27 pagesTissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2ebrahim hajNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue - Study NotesDocument10 pagesPlant Tissue - Study Notesjjoshin10No ratings yet
- Vascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraDocument22 pagesVascular Tissue and Cork Tissue: Agnes, Handersen, VieraGeorgia VasanthaNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument14 pagesLIGHTTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Diet Plan For Weigt GainDocument2 pagesDiet Plan For Weigt GainTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- List of Qualified Candidates For Skill TestDocument100 pagesList of Qualified Candidates For Skill TestTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Science SolutionDocument3 pagesScience SolutionTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document9 pagesPresentation 1Dienha ViyelaNo ratings yet
- Semagn Chapter 1Document21 pagesSemagn Chapter 1alemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- 000 Pharmacognosy Balanophora Fungosa PDFDocument4 pages000 Pharmacognosy Balanophora Fungosa PDFKannan100% (1)
- Penilaian Akhir Semester B.Inggris Kelas 8Document4 pagesPenilaian Akhir Semester B.Inggris Kelas 8Fitriani PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 F5 BiologyDocument37 pagesChap 2 F5 Biologyg-16355677No ratings yet
- Pollination Project New 2Document30 pagesPollination Project New 2SagarNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Subtopic 3.2 Organ For Water and Mineral Salts UptakeDocument16 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 3 Subtopic 3.2 Organ For Water and Mineral Salts UptakeSafwan YusufNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument26 pagesBiology ProjectSaptarsi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Rwi 33Document108 pagesRwi 33NyQ4UNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument8 pagesFlowerAntarnet AntarNo ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 PlantDocument9 pagesLab Report 2 PlantFARALIZA AHMADNo ratings yet
- Sims 3 Nectar RecipesDocument1 pageSims 3 Nectar Recipesgabbychow888No ratings yet
- WGA PDF Plan - Contemporary TV StandDocument7 pagesWGA PDF Plan - Contemporary TV StandSajith ShivashankaranNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t SecquizDocument2 pageshssb2101t Secquizfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Geitonogamy - Transfer of Pollen Grains FromDocument2 pagesGeitonogamy - Transfer of Pollen Grains FromDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hutan Lestari (2019) Vol. 7 (2) : 746 - 751Document6 pagesJurnal Hutan Lestari (2019) Vol. 7 (2) : 746 - 751Oswa PalullunganNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology VocabularyDocument8 pagesPlant Biology Vocabularydevadas panickerNo ratings yet
- Pembuatan Selai Campuran Dami Nangka Dan Sirsak: Duncan's New Multiple Range Test (DNMRT) at Level 5%. The Treatments inDocument15 pagesPembuatan Selai Campuran Dami Nangka Dan Sirsak: Duncan's New Multiple Range Test (DNMRT) at Level 5%. The Treatments inDewi Sri Apriyani HarefaNo ratings yet
- Block-06 GymnospermsDocument82 pagesBlock-06 Gymnospermstamil selviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Revision IV - QuizletDocument14 pagesChapter 8 Revision IV - QuizletChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusDocument17 pagesStructure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Sevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 9Document5 pagesSevilla, Joyce Anne C - CASNS 1a - Laboratory Module 9Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- American Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyDocument20 pagesAmerican Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyMaikel GaitkoskiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Seed and FruitDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Seed and FruitMonica LumbantobingNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument52 pagesPlant TissuesJessica Evangelista Arcilla100% (1)
- DB 1380 111394271Document34 pagesDB 1380 111394271Andrea Teran CoronelNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure (Flowers) : BOT 1P: Lecture 12Document62 pagesPlant Structure (Flowers) : BOT 1P: Lecture 12Victor TenorioNo ratings yet
- Xamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument31 pagesXamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShireen SuhailNo ratings yet