Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 31 - Thrombosis
Lecture 31 - Thrombosis
Uploaded by
Hasan Shahzad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesVenous and arterial thrombosis can occur due to slow blood flow, injury to blood vessels, and hypercoagulable states. Venous thrombosis includes deep vein thrombosis (DVTs) and pulmonary embolisms (PEs) which are caused by blood clots in the deep veins or lungs. Arterial thrombosis is caused by atherosclerosis and risk factors like smoking and diabetes, leading to blood clots in arteries like coronary or carotid arteries causing heart attacks or strokes. Both are treated with anticoagulants like heparin or vitamin K antagonists to reduce clotting, while fibrinolytics may break up existing clots.
Original Description:
thROMBOSIS LECTURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVenous and arterial thrombosis can occur due to slow blood flow, injury to blood vessels, and hypercoagulable states. Venous thrombosis includes deep vein thrombosis (DVTs) and pulmonary embolisms (PEs) which are caused by blood clots in the deep veins or lungs. Arterial thrombosis is caused by atherosclerosis and risk factors like smoking and diabetes, leading to blood clots in arteries like coronary or carotid arteries causing heart attacks or strokes. Both are treated with anticoagulants like heparin or vitamin K antagonists to reduce clotting, while fibrinolytics may break up existing clots.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesLecture 31 - Thrombosis
Lecture 31 - Thrombosis
Uploaded by
Hasan ShahzadVenous and arterial thrombosis can occur due to slow blood flow, injury to blood vessels, and hypercoagulable states. Venous thrombosis includes deep vein thrombosis (DVTs) and pulmonary embolisms (PEs) which are caused by blood clots in the deep veins or lungs. Arterial thrombosis is caused by atherosclerosis and risk factors like smoking and diabetes, leading to blood clots in arteries like coronary or carotid arteries causing heart attacks or strokes. Both are treated with anticoagulants like heparin or vitamin K antagonists to reduce clotting, while fibrinolytics may break up existing clots.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
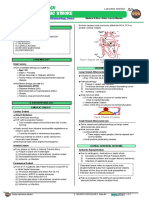
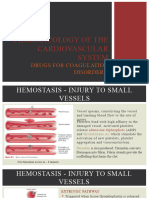
Thrombosis - formation of blood clot in vessel Risk Factors Divided into 3 Main Categories
Causes ischaemia (low blood flow to (Virchows Triad)
organ) 1. Circulatory Stasis - slow blood flow
2. Endothelial Injury (injury to
Thrombotic Disorders: endothelium)
1. Venous Thrombosis 3. Hypercoagulable State - tendency to
DVT - in legs form excess clots
PE - blocked supply to lungs
2. Arterial Thrombosis Note - THROMBOPHILIA = excess abnormal
Myocardial infarction clot formation
Atrial fibrillation
Peripheral vascular disease Thrombosis - caused by procoagulant and
Stroke anti-fibrinolytic mechanisms
Bleeding - caused by anticoagulant +
profibrinolytic mechanisms
VTE (venous thromboembolism) - includes Note - Myocardial infarction (heart attack) =
DVT and PE blocked coronary arteries
1. DVT - can lead to Pulmonary
Embolism (PE) Natural Coagulation Inhibitors in Blood:
Blood clot around valves in DEEP 1. Antithrombin (AT)
VEINS (around legs/arms) Inhibits thrombin, 9a and 10a
Blood clot made of thrombus (fibrin 3. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI)
and erythrocyte rich) Direct inhibitor of 7a/TF and 10a
4. Activated Protein C (aPC)
2. Pulmonary embolism (PE) - part of Proteolytically cleaves 5a and 8a for
DVT thrombus called embolus breaks deactivation
off and travels to heart then lungs and 5. Protein S (PS)
blocks the arteries in the lungs = Cofactor of aPC - helps inactivate 5a
causes low blood supply to tissues and 8a
PE always caused by DVT Deficiency in Coagulation Inhibitors:
Broken off DVT = embolus Idiopathy - no clear triggering factor
D-Dimer - chemical released from 50% of idiopathic patients with
fibrin clots (high in PE patients) thrombosis have APC resistance (like
FVL)
Risk Factors for VTE:
Surgery and cancer can cause high TF Factor 5 Leiden (FVL) - mutation in F5 gene
= more clotting (ARGININE 506 to GLUTAMINE 506)
Immobilisation Common cause of venous thrombosis
Genetic risk factors - Factor 5 Leiden
Mutation + Coagulation inhibitor Normally Activated Protein C (APC) cleaves 3
deficiency peptide bonds in F5 = INACTIVATION = low
coagulation
Factor 5 Leiden mutation = mutation in factor mutation in FVL gene = F5 resistance
5 to APC cleavage = more coagulation)
Treatment of Venous Thrombosis: (like DVT Atherosclerosis causes narrowing of
and PE) coronary arteries
Heparin (ANTITHROMBIN and ANTI
10) - Unfractionated Heparin or Low Carotid artery - supplies blood to brain, neck
Molecular Weight Heparin and face
(LMWH/Timaparin) - low molecular
weight heparin cleaves ONLY FACTOR Effects of arterial thrombosis:
10 Coronary artery thrombosis =
VKA (vitamin K antagonist) - inhibits myocardial infarction
vitamin K (vitamin K dependent Carotid artery = stroke
factors don’t work)
NOACs (non-vitamin K anticoagulants) Drugs used to treat arterial thrombosis:
- antithrombin 1. Anti-platelets
Aspirin - inhibits COX-1 and
Arterial Thrombosis: (caused by thromboxane production
atherosclerosis) Anti A2B3 receptor (fibrinogen and
Inflammation of vessel wall VWF binding)
(macrophages become FOAM CELLS + Anti P2Y receptor (for ADP induced
LDL fat) creates an atherosclerotic platelet aggregation)
plaque around tunica intima which 2. Fibrinolytics - TPA (TISSUE
narrows artery) PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR) and UPA
Plaque rupture causes myocardial
infarction or ischaemic stroke
Anti A2B3:
Note - thrombus (blood clot) are platelet rich ABCIXIMAB
TIROFIBAN
Arterial Thrombosis Risk Factors:
Smoking Anti P2Y
Diabetes CLOPIDOGREL
Hypertension TICAGRELOR
High cholesterol PRASUGREL
Fibrinolysis - break down of fibrin clot PREVENTION of Stroke in atrial fibrillation:
VKA (vitamin K antagonists)
Plaque rupture causes clot to develop which NOACS (either inhibit thrombin or
causes myocardial infarction or ischaemic factor 10a) - named with either XA in
stroke word for anti 10 or 'TRAN' at the end
for anti thrombin
Plaques are made of lots of TF and Collagen
and LPA TRAN - ANTI THROMBIN + Argatroban
Big plaques rupture causes TF and
Collagen leak which activates clotting Heparin - helps NOACs inhibit thrombin and
factors which causes a thrombus 10a
blockage (ARTERIAL THROMBOSIS) +
ischaemia Problem with anticoagulant drugs:
Heparin can be impure - can cause
Collagen - activates platelets via GP6 receptor thrombocytopenia
TF expressed by FOAM CELLS - binds factor 7 - Warfarin - needs close monitoring
activates coagulation Too much anticoagulant = bleeding
Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) activates
platelets via P2Y receptor
You might also like
- Chemistry OCR A - A Level DefinitionsDocument3 pagesChemistry OCR A - A Level DefinitionsHasan Shahzad100% (1)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Thrombosis and Antithrombotic TherapyDocument3 pagesThrombosis and Antithrombotic TherapyAdham TarekNo ratings yet
- 2020 Therapeutic Strategies For Thrombosis - New Targets and ApproachesDocument20 pages2020 Therapeutic Strategies For Thrombosis - New Targets and ApproachesVladimir BasurtoNo ratings yet
- Patho - Platelets AtfDocument19 pagesPatho - Platelets AtfGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- ThrombosisDocument13 pagesThrombosisAbigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Influence CoagulationDocument2 pagesDrugs That Influence CoagulationRy AnneNo ratings yet
- Stroke and HemorrhagesDocument12 pagesStroke and Hemorrhagespbffdnw7xfNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Case StudyDocument4 pagesGroup 7 Case StudyROSE GARETH SEGYEPNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentDocument7 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelets & AnticoagulantsDocument10 pagesAntiplatelets & AnticoagulantsJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Handout - Hemodynamic DisordersDocument114 pagesHandout - Hemodynamic DisorderslydNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke - Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, Treatment AtfDocument7 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke - Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, Treatment AtfArnoldNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladDocument82 pagesHemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladLoly SinagaNo ratings yet
- Hematology - BNBDocument4 pagesHematology - BNBAndleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis and Embolism: by Dr. Maha M. AbuhashimDocument34 pagesThrombosis and Embolism: by Dr. Maha M. AbuhashimRaja EllysyaNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument9 pagesCardiomyopathyMinh Nguyễn Phương HồngNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis AND Disorders OF HemostasisDocument73 pagesThrombosis AND Disorders OF HemostasisAdel mohammadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Document6 pagesCardiovascular Dysfunction: (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)Jc MacujaNo ratings yet
- Platelet: Muhammad Nazarudin, S.STDocument15 pagesPlatelet: Muhammad Nazarudin, S.STFafha FafhaNo ratings yet
- PATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)Document13 pagesPATH - Ischaemic Heart Disease (13p)vikashchahal1987No ratings yet
- DivitiDocument36 pagesDivitiMarLeniRNNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisorderDocument90 pagesBleeding DisorderAnooda MazenNo ratings yet
- P EmbolismDocument29 pagesP EmbolismCommandoCitotz100% (2)
- منار كمDocument61 pagesمنار كمFemale calmNo ratings yet
- Trombosis: DR - Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocument49 pagesTrombosis: DR - Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimLailatul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant/Thrombolytic 1. Anticoagulant: Parenteral AnticoagulantsDocument4 pagesAnticoagulant/Thrombolytic 1. Anticoagulant: Parenteral AnticoagulantsHannaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Blood Drugs Lp1Document32 pagesPharmacology of Blood Drugs Lp1Vittorio CarlinoNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation Disorders 2023Document26 pagesDrugs For Coagulation Disorders 2023aguilarjanicaNo ratings yet
- Prometric High-Yield NOTES PDFDocument135 pagesPrometric High-Yield NOTES PDFDr-Jahanzaib Gondal100% (3)
- Coagulation Disorders in Obstetrics MD5Document51 pagesCoagulation Disorders in Obstetrics MD5gloriashirima8No ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument8 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseJustine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Usmle CK StepDocument74 pagesUsmle CK StepIrfan Majeed100% (1)
- Hematology FA - 1Document78 pagesHematology FA - 1JaankiNo ratings yet
- Fibrinolitiktrombolitik, Antikoagulan Dan AntiplateletDocument31 pagesFibrinolitiktrombolitik, Antikoagulan Dan AntiplateletAnggra OlgabellaNo ratings yet
- Ninja NerdDocument3 pagesNinja NerdSalsabila HMNo ratings yet
- Acute Pulmonary EmbolismDocument7 pagesAcute Pulmonary EmbolismSami Chemais100% (1)
- Path 548 Coag Disorders 20150323Document38 pagesPath 548 Coag Disorders 20150323Bakul DalalNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Dr. Fidha Rahmayani, M.SC, SP.S Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Lampung RS Abdul MulukDocument45 pagesStroke: Dr. Fidha Rahmayani, M.SC, SP.S Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Lampung RS Abdul Mulukdhea nadhiaNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis: Pgi Ricky G. JalecoDocument34 pagesThrombosis: Pgi Ricky G. JalecoRicky JalecoNo ratings yet
- Name: Pardillo, Melody Jane B. Section: Bmls 10-3CDocument8 pagesName: Pardillo, Melody Jane B. Section: Bmls 10-3CJohnpaul FedericoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseA-sHakour AadenNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesDocument3 pagesHeart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (3)
- Pathology RCR1 CardioDocument6 pagesPathology RCR1 CardioeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- 2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyDocument24 pages2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- TROMBOSISDocument49 pagesTROMBOSISAgung WistaraNo ratings yet
- CCHDDocument69 pagesCCHDchebetnaomi945No ratings yet
- Apixaban Cme SlidesDocument26 pagesApixaban Cme SlidesBharat GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Hemodynamic Disorders PDFDocument69 pages6 - Hemodynamic Disorders PDFJames Chua0% (1)
- Lecture - Platelet, Haemostasis - 2Document19 pagesLecture - Platelet, Haemostasis - 2eman el saeedNo ratings yet
- PT1Document4 pagesPT1Roh UANo ratings yet
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 pagesTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction/ Heart AttackDocument2 pagesMyocardial Infarction/ Heart AttackJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Athero 2 Dr. Raquid 2021Document93 pagesAthero 2 Dr. Raquid 2021oreaNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Hemodinamik, Thromboemboli Dan SyokDocument82 pagesKelainan Hemodinamik, Thromboemboli Dan SyokwulanNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy: DR D M KillingoDocument24 pagesCardiomyopathy: DR D M KillingoMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: A guide for practitioners 2/edFrom EverandDeep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: A guide for practitioners 2/edRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsFrom EverandPharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsNo ratings yet
- Hand MusclesDocument5 pagesHand MusclesHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Viral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Document1 pageViral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Hasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- GI Hormone SummaryDocument1 pageGI Hormone SummaryHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- AS Obscure MarksDocument3 pagesAS Obscure MarksHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- GCSE Photosynthesis PowerpointDocument14 pagesGCSE Photosynthesis PowerpointHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- OCR A Biology 2019 Question PaperDocument36 pagesOCR A Biology 2019 Question PaperHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- OCR A Biology 2019 Mark SchemeDocument27 pagesOCR A Biology 2019 Mark SchemeHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology: Functional Classes of DrugsDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology: Functional Classes of DrugsNightingblade The FirstNo ratings yet
- EMT Static and Dynamic Posture LectureDocument9 pagesEMT Static and Dynamic Posture LectureBennat RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture Bee Hives and Their Description, Bee Pasturage, Bee Foraging, Behaviour and CommunicationDocument19 pagesLecture Bee Hives and Their Description, Bee Pasturage, Bee Foraging, Behaviour and CommunicationVIVEK SUTARNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument55 pagesObstetricsKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- 1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IJulliene DadoleNo ratings yet
- Personal Development: Third Grading Summative Test No. 3Document2 pagesPersonal Development: Third Grading Summative Test No. 3MarinaM.CubiaNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument35 pagesHuman Body SystemsSir Rannie Espanto100% (1)
- Download Drug Delivery Aspects Expectations And Realities Of Multifunctional Drug Delivery Systems Volume 4 Expectations And Realities Of Multifunctional Drug Delivery Systems 1St Edition Ranjita Shegokar full chapterDocument68 pagesDownload Drug Delivery Aspects Expectations And Realities Of Multifunctional Drug Delivery Systems Volume 4 Expectations And Realities Of Multifunctional Drug Delivery Systems 1St Edition Ranjita Shegokar full chapterjesse.yardley161100% (12)
- Structure Cells and Function Cells of Coleus AromaticusDocument5 pagesStructure Cells and Function Cells of Coleus AromaticusKath ErineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Life Processes For Class 10 BiologyDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Life Processes For Class 10 BiologyKhushi RochwaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Mechanics in Cardiovascular DevelopmentDocument15 pagesBlood Flow Mechanics in Cardiovascular Developmentromane gaston bretonNo ratings yet
- Strength For WarfightersDocument12 pagesStrength For Warfightersbeltran230111No ratings yet
- Kidney PowerPoint Presentation TemplateDocument14 pagesKidney PowerPoint Presentation TemplateMedicinePPT100% (1)
- Canine Lymphoma A ReviewDocument30 pagesCanine Lymphoma A Reviewbogdan TanasieNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen FixationDocument6 pagesNitrogen FixationSaziya QuadriNo ratings yet
- Autophagy Provides A Conceptual Therapeutic Framework For Bone Metastasis From Prostate CancerDocument8 pagesAutophagy Provides A Conceptual Therapeutic Framework For Bone Metastasis From Prostate CancerAnnisa RahmaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Ultrasound Imaging ProtocolDocument152 pagesCardiac Ultrasound Imaging Protocolbashir019100% (1)
- Ability To Overcome Initial Impulses To Motivational Stimuli Evidenced by Prefrontal Cortex ActivityDocument27 pagesAbility To Overcome Initial Impulses To Motivational Stimuli Evidenced by Prefrontal Cortex ActivityCassie SunNo ratings yet
- AP Catalase Enzyme LabDocument4 pagesAP Catalase Enzyme LabAesthetic LoverNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Raynauds Phenomenon Schematic DiagramDocument6 pagesPathophysiology Raynauds Phenomenon Schematic DiagramEerie Era0% (1)
- Anatomy Question BankDocument13 pagesAnatomy Question BankMahnaz MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5Document20 pages1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5rodriguezruajavierNo ratings yet
- Test Planner For Two Year Medical Phase-02 - AY 2021-2022Document10 pagesTest Planner For Two Year Medical Phase-02 - AY 2021-2022Rishi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- (ANAPHY) Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pages(ANAPHY) Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyPearl FllominNo ratings yet
- BACT Week 2Document21 pagesBACT Week 2FelicityNo ratings yet
- Reference Range and Normal ValuesDocument13 pagesReference Range and Normal ValuesMs Tahniat RehmanNo ratings yet
- Electroencephalogram Recording in Humans: Julia W. Y. Kam and Todd C. HandyDocument18 pagesElectroencephalogram Recording in Humans: Julia W. Y. Kam and Todd C. HandyGemma EINo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Membrane LipidsDocument28 pagesBiosynthesis of Membrane Lipidsangela marie abadillaNo ratings yet
- Proteins As Drug Targets: ReceptorsDocument25 pagesProteins As Drug Targets: ReceptorsAns JavidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PharynxDocument34 pagesAnatomy of PharynxNasr HudaNo ratings yet