Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
45 viewsHow Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
How Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
Uploaded by
Maine PerezThe key steps to prepare for ISO 17025 certification are:
1. Understand the standard's requirements through reading and gap analysis.
2. Develop a quality manual and implement a quality management system with procedures for document control, record keeping, audits, and management reviews.
3. Train personnel, conduct internal audits, and participate in proficiency testing to demonstrate technical competence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- DO 22 S 2017 - QMS Manual PDFDocument154 pagesDO 22 S 2017 - QMS Manual PDFBien_Garcia_II_184175% (8)
- API Spec Q1 9th Edition Training Slides-R1Document88 pagesAPI Spec Q1 9th Edition Training Slides-R1Teeva Battumalai100% (3)
- IATF - 16949 - 2016 Awareness TrainingDocument58 pagesIATF - 16949 - 2016 Awareness Trainingharish pu0% (3)
- FlowchartDocument142 pagesFlowchartAnup Pathak100% (2)
- Guide For Conducting Factory Capability Assessment For Power TransformersDocument103 pagesGuide For Conducting Factory Capability Assessment For Power Transformersme_vahabi100% (2)
- Basic Requirements of A Quality Manual ASQ PublicationDocument12 pagesBasic Requirements of A Quality Manual ASQ PublicationRuchir BhomiaNo ratings yet
- Calibration and Calibration Verification: Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)Document5 pagesCalibration and Calibration Verification: Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)Ricky BatehNo ratings yet
- PEFCR PetFood FinalPEFCRs 2018-05-09Document98 pagesPEFCR PetFood FinalPEFCRs 2018-05-09sachin thakurNo ratings yet
- 1040 Method Development and EvaluationDocument4 pages1040 Method Development and EvaluationRaposo IreneNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper: When Recognition MattersDocument10 pagesWhitepaper: When Recognition MattersLuân Nguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- D M K 4 0 52 Quality Assurance of Oil and Fat: By: Rusyidah Binti Mat Zin Boestami JTKMDocument27 pagesD M K 4 0 52 Quality Assurance of Oil and Fat: By: Rusyidah Binti Mat Zin Boestami JTKMnityaNo ratings yet
- Laboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025Document30 pagesLaboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025nirmal_gcetNo ratings yet
- A2 LaDocument10 pagesA2 LaAri DhamayantiNo ratings yet
- Calibration Requirements For Determining Particle Size Distribution Using Light Interaction MethodsDocument6 pagesCalibration Requirements For Determining Particle Size Distribution Using Light Interaction Methodstuhintahmid1093No ratings yet
- GMP 11 Calibration Intervals 20180131Document9 pagesGMP 11 Calibration Intervals 20180131acanis1016No ratings yet
- Agilent-Introduction ISO 17025 & AccreditationDocument27 pagesAgilent-Introduction ISO 17025 & AccreditationediwskiNo ratings yet
- Requirement of Lab AccreditationDocument4 pagesRequirement of Lab AccreditationGajaNand MallickNo ratings yet
- Content: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of Class I and Class II Biological Safety CabinetsDocument15 pagesContent: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of Class I and Class II Biological Safety CabinetsRoderick BalceNo ratings yet
- Sop For Using Micro-Pipet in Lab.Document3 pagesSop For Using Micro-Pipet in Lab.Shafquat AasifiNo ratings yet
- LAF and BSC Maintenance PDFDocument68 pagesLAF and BSC Maintenance PDFMuchlas AkbarNo ratings yet
- 〈645〉 WATER CONDUCTIVITYDocument4 pages〈645〉 WATER CONDUCTIVITYliêmNo ratings yet
- ISO-NABL Awareness PresentationDocument19 pagesISO-NABL Awareness PresentationvgvpplNo ratings yet
- Environmental Monitoring and Risk Assessment of CLDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Monitoring and Risk Assessment of CLkim_jamjungNo ratings yet
- Form Q-15 Icc-Es Nonaccredited Laboratory Assessment ChecklistDocument5 pagesForm Q-15 Icc-Es Nonaccredited Laboratory Assessment ChecklistShaun HolderNo ratings yet
- Calibration and Metrology PDFDocument10 pagesCalibration and Metrology PDFMano NegraNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityDocument27 pagesDifference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityAmit NainNo ratings yet
- Technical Management - We Dont Need No Technical ManagementDocument7 pagesTechnical Management - We Dont Need No Technical Managementmhk665No ratings yet
- Some Basic Qa QC Concepts: Quality Assurance (QA) Refers To The Overall ManagementDocument8 pagesSome Basic Qa QC Concepts: Quality Assurance (QA) Refers To The Overall ManagementUltrichNo ratings yet
- Implementation of ISO/IEC 17025:2017Document15 pagesImplementation of ISO/IEC 17025:2017Carlos Roque67% (3)
- Guidance Notes For Applying For UKAS AccreditationDocument3 pagesGuidance Notes For Applying For UKAS AccreditationJem ChiltonNo ratings yet
- A New Product - ISO 17025 Audit Checklist Is Launched byDocument2 pagesA New Product - ISO 17025 Audit Checklist Is Launched byahmedNo ratings yet
- A2LA Expalnations For ISO 17025 RequirementsDocument27 pagesA2LA Expalnations For ISO 17025 RequirementsgiamilliaNo ratings yet
- QC 05 06Document17 pagesQC 05 06Ibnu Hufail100% (1)
- ISO 15189 ProceduresDocument63 pagesISO 15189 ProcedureskiransaraiNo ratings yet
- New ISO 17025 and Decision RuleDocument4 pagesNew ISO 17025 and Decision Rulesujud100% (1)
- NABL 160 Quality Manual GuideDocument61 pagesNABL 160 Quality Manual Guidesudhasesh200067% (3)
- Decision Rule 17025Document10 pagesDecision Rule 17025Mostafa AfifyNo ratings yet
- Method Validation PDFDocument63 pagesMethod Validation PDFAhmad Atsari SujudNo ratings yet
- Lab Workflow - ChartDocument1 pageLab Workflow - ChartR.S.SankarasubramanianNo ratings yet
- What Is ValidationDocument6 pagesWhat Is ValidationVishal VakilNo ratings yet
- Quality ManualDocument114 pagesQuality ManualPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- 5 - Decision Rule Associated To The Measurement UncertaintyDocument38 pages5 - Decision Rule Associated To The Measurement UncertaintyMoldoveanu Aliona100% (1)
- Content: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A FreezerDocument7 pagesContent: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A FreezerPrincess PiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 15189 Manual DocumentsDocument10 pagesIso 15189 Manual DocumentsLisyaNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure To Learn How To Behave in Quality Control Laboratory in PharmaceuticalsDocument38 pagesStandard Operating Procedure To Learn How To Behave in Quality Control Laboratory in PharmaceuticalsYulis AdrianaNo ratings yet
- 41 (1) In-Process Revision - 1790 - Visual Inspection of InjectionsDocument10 pages41 (1) In-Process Revision - 1790 - Visual Inspection of InjectionsBudy WijiyantoNo ratings yet
- LAGD 01 Accreditation ProcessDocument10 pagesLAGD 01 Accreditation ProcessAnonymous TVdKmkNo ratings yet
- Steps To Evaluating Measurement UncertaintyDocument14 pagesSteps To Evaluating Measurement UncertaintyAjit K GNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ChecklistDocument22 pagesSelf Assessment ChecklistjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Section 8.5 of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Risks and OpportunitiesDocument3 pagesSection 8.5 of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Risks and OpportunitiesVasaNo ratings yet
- HPLC Analytical Method Development ValidationDocument4 pagesHPLC Analytical Method Development ValidationJoshua CastilloNo ratings yet
- EA-4-02 Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationDocument78 pagesEA-4-02 Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationYesid Javier Pineda LizarazoNo ratings yet
- PG-HDB Automatic Pipette Verification (ENG)Document15 pagesPG-HDB Automatic Pipette Verification (ENG)Simone GiacomelliNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Temp SopDocument8 pagesRefrigerator Temp SopdeshankarunarathneNo ratings yet
- LASR01 2015 Supplementary Requirements For Accreditation of Chemical TestingDocument13 pagesLASR01 2015 Supplementary Requirements For Accreditation of Chemical TestingfelicityNo ratings yet
- Equipment Calibration/Maintenance: APPENDIX D - USFWS QA Program (5/04)Document5 pagesEquipment Calibration/Maintenance: APPENDIX D - USFWS QA Program (5/04)Defry Farhandinata100% (1)
- Sls-Mic 032Document7 pagesSls-Mic 032vpnarashimmanNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandQuality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC 17025: 2005: General Requirements For The Competence of Testing and Calibration LaboratoriesDocument53 pagesISO/IEC 17025: 2005: General Requirements For The Competence of Testing and Calibration LaboratoriesbaxterNo ratings yet
- Overview On GLP, Dr. Anne Bridges, Technical Director, AACC International - 5Document50 pagesOverview On GLP, Dr. Anne Bridges, Technical Director, AACC International - 5mangala jesudossNo ratings yet
- BMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesDocument183 pagesBMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesYogesh AnapNo ratings yet
- Transmille Training - 17025 Quality SystemDocument34 pagesTransmille Training - 17025 Quality SystemSaiful RizamNo ratings yet
- ISO 17025 2017 Training Course and ChangesDocument48 pagesISO 17025 2017 Training Course and Changessadbad6100% (5)
- ISO 17025:2005 TrainingDocument38 pagesISO 17025:2005 TrainingStudent Foreign100% (2)
- Css Result 2022Document1 pageCss Result 2022Maine PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document18 pagesLesson 1Maine PerezNo ratings yet
- Bulacan Agricultural State CollegeDocument21 pagesBulacan Agricultural State CollegeMaine PerezNo ratings yet
- BSE 3B Language and ColorismDocument16 pagesBSE 3B Language and ColorismMaine PerezNo ratings yet
- QSP 7.1-02. Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources (Preview)Document4 pagesQSP 7.1-02. Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources (Preview)Centauri Business Group Inc.100% (1)
- Software ValidationDocument36 pagesSoftware ValidationHilario AlinabonNo ratings yet
- Gs Operation ManualDocument324 pagesGs Operation ManualMohammad Ainuddin100% (3)
- ISO - Proposal - Lala Chcocolate L.L.C.Document4 pagesISO - Proposal - Lala Chcocolate L.L.C.RasnaNo ratings yet
- BMG-F-8Q Stage 1 ReportDocument7 pagesBMG-F-8Q Stage 1 ReportremeshsankarNo ratings yet
- 5R12 Volume 2 Specifications PDFDocument349 pages5R12 Volume 2 Specifications PDFPalade SanduNo ratings yet
- Iatf 16949 PPT Training Awareness - PDF - Quality Management System - Iso 9000Document51 pagesIatf 16949 PPT Training Awareness - PDF - Quality Management System - Iso 9000wadot43402No ratings yet
- SMFBPO101 005 BPO-Operations-Management Slide-Deck 01062013 012-VerDocument54 pagesSMFBPO101 005 BPO-Operations-Management Slide-Deck 01062013 012-VerYumi ChangNo ratings yet
- Ez03 CW06 Alco Civ PRQ 000013 - 3Document176 pagesEz03 CW06 Alco Civ PRQ 000013 - 3Jason RazatlabNo ratings yet
- ANTOLIN - Supplier Quality Manual Rev.03 (English)Document26 pagesANTOLIN - Supplier Quality Manual Rev.03 (English)l.hernandezNo ratings yet
- ISCC 102 Governance 3.0Document32 pagesISCC 102 Governance 3.0Adi PuspitoNo ratings yet
- Fssai NOTES MRINALDocument19 pagesFssai NOTES MRINALmrinalbohra100% (1)
- Company Profile: An ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedDocument22 pagesCompany Profile: An ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedMechatronics EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Iso 9000-2001Document56 pagesIso 9000-2001Anonymous w63sFQiQNo ratings yet
- TESDA QualityManualRev 01Document48 pagesTESDA QualityManualRev 01Aquino SianiparNo ratings yet
- ALLSAFE The Lifting and Lashing Solutions GuideDocument24 pagesALLSAFE The Lifting and Lashing Solutions GuideAfzaalUmair0% (1)
- Isr Iso 9001 Upgrade Planner Delta ChecklistDocument10 pagesIsr Iso 9001 Upgrade Planner Delta ChecklistDelcio MinossoNo ratings yet
- QSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716Document18 pagesQSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716uday yadavNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System - Construction Procedures PDFDocument46 pagesQuality Management System - Construction Procedures PDFCarl Williams100% (2)
- Documentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2Document19 pagesDocumentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- Guide To Performance and Safety TestingDocument26 pagesGuide To Performance and Safety Testingpaninaro2011No ratings yet
- Basics of Quality ManagementDocument14 pagesBasics of Quality ManagementWiki Waqas100% (1)
- What Is ISO 9001Document5 pagesWhat Is ISO 9001Klaus AlmesNo ratings yet
- Some More Objective Questions With AnswersDocument44 pagesSome More Objective Questions With AnswersPratyush Solanki100% (1)
How Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
How Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
Uploaded by
Maine Perez100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
45 views8 pagesThe key steps to prepare for ISO 17025 certification are:
1. Understand the standard's requirements through reading and gap analysis.
2. Develop a quality manual and implement a quality management system with procedures for document control, record keeping, audits, and management reviews.
3. Train personnel, conduct internal audits, and participate in proficiency testing to demonstrate technical competence.
Original Description:
iso how to
Original Title
How do I prepare for ISO 17025 certification
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe key steps to prepare for ISO 17025 certification are:
1. Understand the standard's requirements through reading and gap analysis.
2. Develop a quality manual and implement a quality management system with procedures for document control, record keeping, audits, and management reviews.
3. Train personnel, conduct internal audits, and participate in proficiency testing to demonstrate technical competence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
45 views8 pagesHow Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
How Do I Prepare For ISO 17025 Certification
Uploaded by
Maine PerezThe key steps to prepare for ISO 17025 certification are:
1. Understand the standard's requirements through reading and gap analysis.
2. Develop a quality manual and implement a quality management system with procedures for document control, record keeping, audits, and management reviews.
3. Train personnel, conduct internal audits, and participate in proficiency testing to demonstrate technical competence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
How do I prepare for ISO 17025 certification?
How do I prepare for ISO 17025 certification?
Preparing for ISO 17025 certification requires a structured and systematic
approach to ensure that the laboratory meets all the requirements of the
standard. The following are some general steps that can be taken to prepare
for ISO 17025 certification:
1. Understand the requirements: Read and understand the requirements
of the ISO 17025 standard. This will help you identify the areas that
need to be addressed to meet the standard's requirements.
2. Conduct a gap analysis: Conduct a gap analysis to identify the gaps
between the laboratory's current practices and the requirements of the
ISO 17025 standard. This will help you identify the areas that need
improvement and develop an action plan.
3. Develop a quality manual: Develop a quality manual that documents the
laboratory's quality policy, objectives, and procedures for meeting the
requirements of the ISO 17025 standard.
4. Implement a quality management system: Implement a quality
management system that includes procedures for document control,
record keeping, internal audits, corrective actions, and management
reviews.
5. Train laboratory personnel: Train laboratory personnel on the
requirements of the ISO 17025 standard, the laboratory's quality
manual, and the laboratory's procedures for meeting the standard's
requirements.
6. Conduct internal audits: Conduct internal audits to verify that the
laboratory's quality management system is effective, and to identify
areas for improvement.
7. Participate in proficiency testing: Participate in proficiency testing
programs to demonstrate the laboratory's technical competence in
conducting testing and calibration activities.
8. Implement corrective actions: Implement corrective actions to address
any non-conformities identified during internal audits and proficiency
testing.
9. Obtain accreditation: Apply for accreditation from a recognized
accreditation body that assesses laboratories against the ISO 17025
standard.
By following these steps, laboratories can prepare for ISO 17025 certification
and demonstrate their technical competence and ability to provide reliable and
accurate test results.
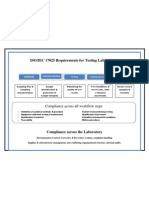
Steps to ISO/IEC 17025 Accreditation
1. Learn about the Standard.
2. Perform a Gap Analysis.
3. Plan your project.
4. Train your organization.
5. Document your Quality Management System.
6. Implement your QMS and conduct business.
7. Audit your QMS.
8. Accreditation Audit.
What are the requirements and guidelines for implementing
a quality management system in accordance with ISO 9001
2015 standards?
ISO 9001 Mandatory Requirements — Documents and Records
Monitoring and measuring equipment calibration records.
Records of training, skills, experience and qualifications.
Product/service requirements review records.
Record about design and development outputs review.
Record about design and development inputs
What is the objective of implementation of the ISO 17025 standard
and the main technological and managerial requirements?
ISO 17025 provides the “General requirements for the competence of
testing and calibration laboratories”. This standard can be applied in
all laboratories and it specifies the requirements of their practices
to raise confidence in their ability to provide reliable and valid testing,
calibration and sampling results.
What is the ISO 17025 quality management process?
ISO 17025 is an international standard that specifies the general
requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories.
The ISO 17025 quality management process is a set of procedures and
practices that laboratories must implement to meet the requirements of the
standard. The following are the key elements of the ISO 17025 quality
management process:
1. Management requirements: This section specifies the laboratory's
organizational structure, management system, policies, and
objectives.
2. Resource requirements: This section specifies the requirements for
personnel, facilities, equipment, and reference materials needed to
ensure the competence of the laboratory.
3. Process requirements: This section specifies the requirements for all
laboratory processes, including sampling, handling of test items,
calibration and testing methods, and reporting of results.
4. Measurement traceability: This section requires the laboratory to
ensure that all measurements are traceable to national or
international standards.
5. Calibration and testing methods: This section requires the laboratory
to select, validate, and implement appropriate calibration and testing
methods.
6. Uncertainty of measurement: This section requires the laboratory to
estimate and report the uncertainty of measurement for all results.
7. Reporting of results: This section specifies the requirements for
reporting test and calibration results, including the content, format,
and timing of reports.
8. Management of non-conformities: This section requires the laboratory
to implement procedures for identifying, documenting, and correcting
non-conformities.
9. Internal audits: This section requires the laboratory to conduct
internal audits of its quality management system to ensure
compliance with the ISO 17025 standard.
By implementing the ISO 17025 quality management process, laboratories
can ensure the competence of their testing and calibration activities, meet
customer requirements, and comply with regulatory and industry standards.
What is the ISO 17025 quality management process
ISO 17025 is an international standard that specifies the general requirements for
the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. The standard outlines the
guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving a
laboratory's quality management system.
The ISO 17025 quality management process involves several key steps, including:
1. Management requirements: This includes establishing a quality policy and
objectives, implementing a quality management system, ensuring the
availability of resources, and conducting regular management reviews.
2. Technical requirements: This includes ensuring the validity and reliability of
testing and calibration methods, maintaining accurate records, and ensuring
the competence of laboratory personnel.
3. Quality control: This involves the use of quality control measures to monitor
the accuracy and precision of laboratory measurements.
4. Proficiency testing: This involves participating in proficiency testing
programs to demonstrate the laboratory's competence in conducting testing
and calibration activities.
5. Traceability of measurements: This involves ensuring that all measurements
are traceable to recognized standards or measurement systems.
6. Continuous improvement: This involves identifying areas for improvement
and implementing actions to continually improve the laboratory's quality
management system.
Overall, the ISO 17025 quality management process is designed to ensure that
testing and calibration laboratories operate in a consistent, reliable, and competent
manner, and that their results are trustworthy and accepted by their customers and
stakeholders.
What is the importance of accreditation in ISO 17025?
Accreditation is an important aspect of ISO 17025 because it provides formal
recognition that a laboratory is competent to perform specific testing and
calibration activities. Accreditation is the process of evaluating a laboratory's
quality management system, technical competence, and performance against
recognized standards and criteria, and granting formal recognition to those that
meet or exceed these requirements.
The importance of accreditation in ISO 17025 can be summarized as follows:
1. Ensures credibility and trustworthiness: Accreditation provides assurance to
customers and stakeholders that a laboratory's test results are accurate,
reliable, and traceable to internationally recognized standards. Accreditation
demonstrates that the laboratory has undergone a rigorous evaluation process
and has demonstrated its technical competence and capability to perform
specific tests and calibrations.
2. Facilitates acceptance of results: Accreditation enhances the acceptance of
test results across national and international borders. Accredited laboratories
are recognized as being competent to provide reliable test results that meet
the needs of their customers and stakeholders.
3. Improves quality and efficiency: Accreditation provides a framework for
continuous improvement of a laboratory's quality management system,
technical competence, and performance. Accredited laboratories are required
to participate in proficiency testing programs, maintain accurate records, and
implement corrective actions to address any identified non-conformities.
This results in improved quality and efficiency of testing and calibration
activities.
4. Increases competitiveness: Accreditation can improve a laboratory's
competitiveness in the marketplace. Accreditation demonstrates to customers
and stakeholders that the laboratory is committed to providing high-quality
services and has the technical competence and capability to meet their needs.
Overall, accreditation is an important aspect of ISO 17025 because it provides
formal recognition of a laboratory's technical competence, enhances the acceptance
of test results, improves quality and efficiency, and increases competitiveness.
What are the steps required to implement quality management systems?
Implementing a quality management system (QMS) requires a structured and
systematic approach to ensure that all the necessary steps are taken to achieve the
desired outcomes. The following are the general steps required to implement
quality management systems:
1. Define the scope and objectives: Define the scope and objectives of the
QMS and identify the relevant regulatory, customer and stakeholder
requirements that need to be met.
2. Develop a QMS framework: Develop a QMS framework that is appropriate
for the organization, including policies, procedures, work instructions, and
documentation.
3. Assign roles and responsibilities: Define roles and responsibilities for all
employees involved in the QMS, including management representatives,
quality coordinators, and other relevant personnel.
4. Train employees: Ensure that all employees are trained on the QMS, its
objectives, and their roles and responsibilities.
5. Develop and implement procedures: Develop and implement procedures for
all relevant activities, including design and development, purchasing,
production, testing, and calibration.
6. Establish performance indicators: Establish performance indicators to
monitor the effectiveness of the QMS and identify areas for improvement.
7. Conduct internal audits: Conduct internal audits to verify compliance with
the QMS and identify areas for improvement.
8. Implement corrective actions: Implement corrective actions to address non-
conformities identified during internal audits and other quality control
processes.
9. Establish a document control system: Establish a document control system
to ensure that all documentation is controlled, including version control,
distribution, and archival.
10.Continual improvement: Implement continual improvement processes to
ensure that the QMS remains effective and efficient over time.
These steps can be adapted to the specific needs of the organization and should be
implemented in a phased and systematic manner, with regular reviews to ensure
that the QMS remains relevant and effective.
What is the purpose of ISO standards created for quality
management systems?
The purpose of ISO standards created for quality management systems (QMS) is to
provide a framework for organizations to consistently deliver products and services
that meet customer requirements and comply with applicable regulations and
standards.
ISO standards for QMS, such as ISO 9001, provide a set of requirements and
guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving
a QMS. These standards focus on the organization's ability to meet customer needs
and expectations, improve internal processes, and demonstrate compliance with
regulatory requirements.
The ISO standards for QMS are designed to help organizations:
1. Improve customer satisfaction: By focusing on meeting customer needs and
expectations, organizations can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Enhance internal processes: By adopting a process-based approach to quality
management, organizations can identify and eliminate inefficiencies and
improve the effectiveness of their processes.
3. Increase efficiency and reduce costs: By streamlining processes and
reducing waste, organizations can increase efficiency and reduce costs.
4. Demonstrate compliance: By implementing a QMS that complies with ISO
standards, organizations can demonstrate their ability to meet regulatory
requirements and industry standards.
5. Continually improve: By adopting a culture of continual improvement,
organizations can identify and address areas for improvement and stay ahead
of the competition.
Overall, ISO standards for QMS provide a framework for organizations to improve their
operations, increase customer satisfaction, and achieve their business objectives.
What is the importance of ISO certification in the success of an
organization?
ISO certification is important for the success of an organization for several reasons:
1. Enhances credibility: ISO certification provides an external validation that
an organization has met the international standards for quality management.
This enhances the credibility of the organization with its customers,
suppliers, and other stakeholders.
2. Improves customer satisfaction: ISO certification requires organizations to
focus on meeting customer needs and expectations, resulting in improved
customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Increases market access: ISO certification is often a requirement for doing
business with certain customers, especially in government and international
markets. Certification can provide a competitive advantage by demonstrating
compliance with international standards.
4. Reduces costs and improves efficiency: ISO certification requires
organizations to implement efficient and effective processes, resulting in
reduced costs and improved efficiency.
5. Facilitates continuous improvement: ISO certification requires organizations
to continually monitor and improve their quality management system,
leading to continuous improvement in their operations and
products/services.
6. Enhances employee engagement: ISO certification requires the involvement
of employees in the development, implementation, and improvement of the
quality management system. This can enhance employee engagement and
motivation.
Overall, ISO certification can provide significant benefits to an organization,
including improved credibility, customer satisfaction, market access, efficiency,
and continuous improvement. These benefits can contribute to the long-term
success and sustainability of the organization.
You might also like
- DO 22 S 2017 - QMS Manual PDFDocument154 pagesDO 22 S 2017 - QMS Manual PDFBien_Garcia_II_184175% (8)
- API Spec Q1 9th Edition Training Slides-R1Document88 pagesAPI Spec Q1 9th Edition Training Slides-R1Teeva Battumalai100% (3)
- IATF - 16949 - 2016 Awareness TrainingDocument58 pagesIATF - 16949 - 2016 Awareness Trainingharish pu0% (3)
- FlowchartDocument142 pagesFlowchartAnup Pathak100% (2)
- Guide For Conducting Factory Capability Assessment For Power TransformersDocument103 pagesGuide For Conducting Factory Capability Assessment For Power Transformersme_vahabi100% (2)
- Basic Requirements of A Quality Manual ASQ PublicationDocument12 pagesBasic Requirements of A Quality Manual ASQ PublicationRuchir BhomiaNo ratings yet
- Calibration and Calibration Verification: Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)Document5 pagesCalibration and Calibration Verification: Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA)Ricky BatehNo ratings yet
- PEFCR PetFood FinalPEFCRs 2018-05-09Document98 pagesPEFCR PetFood FinalPEFCRs 2018-05-09sachin thakurNo ratings yet
- 1040 Method Development and EvaluationDocument4 pages1040 Method Development and EvaluationRaposo IreneNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper: When Recognition MattersDocument10 pagesWhitepaper: When Recognition MattersLuân Nguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- D M K 4 0 52 Quality Assurance of Oil and Fat: By: Rusyidah Binti Mat Zin Boestami JTKMDocument27 pagesD M K 4 0 52 Quality Assurance of Oil and Fat: By: Rusyidah Binti Mat Zin Boestami JTKMnityaNo ratings yet
- Laboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025Document30 pagesLaboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025nirmal_gcetNo ratings yet
- A2 LaDocument10 pagesA2 LaAri DhamayantiNo ratings yet
- Calibration Requirements For Determining Particle Size Distribution Using Light Interaction MethodsDocument6 pagesCalibration Requirements For Determining Particle Size Distribution Using Light Interaction Methodstuhintahmid1093No ratings yet
- GMP 11 Calibration Intervals 20180131Document9 pagesGMP 11 Calibration Intervals 20180131acanis1016No ratings yet
- Agilent-Introduction ISO 17025 & AccreditationDocument27 pagesAgilent-Introduction ISO 17025 & AccreditationediwskiNo ratings yet
- Requirement of Lab AccreditationDocument4 pagesRequirement of Lab AccreditationGajaNand MallickNo ratings yet
- Content: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of Class I and Class II Biological Safety CabinetsDocument15 pagesContent: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of Class I and Class II Biological Safety CabinetsRoderick BalceNo ratings yet
- Sop For Using Micro-Pipet in Lab.Document3 pagesSop For Using Micro-Pipet in Lab.Shafquat AasifiNo ratings yet
- LAF and BSC Maintenance PDFDocument68 pagesLAF and BSC Maintenance PDFMuchlas AkbarNo ratings yet
- 〈645〉 WATER CONDUCTIVITYDocument4 pages〈645〉 WATER CONDUCTIVITYliêmNo ratings yet
- ISO-NABL Awareness PresentationDocument19 pagesISO-NABL Awareness PresentationvgvpplNo ratings yet
- Environmental Monitoring and Risk Assessment of CLDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Monitoring and Risk Assessment of CLkim_jamjungNo ratings yet
- Form Q-15 Icc-Es Nonaccredited Laboratory Assessment ChecklistDocument5 pagesForm Q-15 Icc-Es Nonaccredited Laboratory Assessment ChecklistShaun HolderNo ratings yet
- Calibration and Metrology PDFDocument10 pagesCalibration and Metrology PDFMano NegraNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityDocument27 pagesDifference Between Calibration, Testing and Validation: Accuracy, Precision, Resolution & SensitivityAmit NainNo ratings yet
- Technical Management - We Dont Need No Technical ManagementDocument7 pagesTechnical Management - We Dont Need No Technical Managementmhk665No ratings yet
- Some Basic Qa QC Concepts: Quality Assurance (QA) Refers To The Overall ManagementDocument8 pagesSome Basic Qa QC Concepts: Quality Assurance (QA) Refers To The Overall ManagementUltrichNo ratings yet
- Implementation of ISO/IEC 17025:2017Document15 pagesImplementation of ISO/IEC 17025:2017Carlos Roque67% (3)
- Guidance Notes For Applying For UKAS AccreditationDocument3 pagesGuidance Notes For Applying For UKAS AccreditationJem ChiltonNo ratings yet
- A New Product - ISO 17025 Audit Checklist Is Launched byDocument2 pagesA New Product - ISO 17025 Audit Checklist Is Launched byahmedNo ratings yet
- A2LA Expalnations For ISO 17025 RequirementsDocument27 pagesA2LA Expalnations For ISO 17025 RequirementsgiamilliaNo ratings yet
- QC 05 06Document17 pagesQC 05 06Ibnu Hufail100% (1)
- ISO 15189 ProceduresDocument63 pagesISO 15189 ProcedureskiransaraiNo ratings yet
- New ISO 17025 and Decision RuleDocument4 pagesNew ISO 17025 and Decision Rulesujud100% (1)
- NABL 160 Quality Manual GuideDocument61 pagesNABL 160 Quality Manual Guidesudhasesh200067% (3)
- Decision Rule 17025Document10 pagesDecision Rule 17025Mostafa AfifyNo ratings yet
- Method Validation PDFDocument63 pagesMethod Validation PDFAhmad Atsari SujudNo ratings yet
- Lab Workflow - ChartDocument1 pageLab Workflow - ChartR.S.SankarasubramanianNo ratings yet
- What Is ValidationDocument6 pagesWhat Is ValidationVishal VakilNo ratings yet
- Quality ManualDocument114 pagesQuality ManualPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- 5 - Decision Rule Associated To The Measurement UncertaintyDocument38 pages5 - Decision Rule Associated To The Measurement UncertaintyMoldoveanu Aliona100% (1)
- Content: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A FreezerDocument7 pagesContent: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Use and Maintenance of A FreezerPrincess PiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 15189 Manual DocumentsDocument10 pagesIso 15189 Manual DocumentsLisyaNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure To Learn How To Behave in Quality Control Laboratory in PharmaceuticalsDocument38 pagesStandard Operating Procedure To Learn How To Behave in Quality Control Laboratory in PharmaceuticalsYulis AdrianaNo ratings yet
- 41 (1) In-Process Revision - 1790 - Visual Inspection of InjectionsDocument10 pages41 (1) In-Process Revision - 1790 - Visual Inspection of InjectionsBudy WijiyantoNo ratings yet
- LAGD 01 Accreditation ProcessDocument10 pagesLAGD 01 Accreditation ProcessAnonymous TVdKmkNo ratings yet
- Steps To Evaluating Measurement UncertaintyDocument14 pagesSteps To Evaluating Measurement UncertaintyAjit K GNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ChecklistDocument22 pagesSelf Assessment ChecklistjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Section 8.5 of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Risks and OpportunitiesDocument3 pagesSection 8.5 of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Risks and OpportunitiesVasaNo ratings yet
- HPLC Analytical Method Development ValidationDocument4 pagesHPLC Analytical Method Development ValidationJoshua CastilloNo ratings yet
- EA-4-02 Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationDocument78 pagesEA-4-02 Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationYesid Javier Pineda LizarazoNo ratings yet
- PG-HDB Automatic Pipette Verification (ENG)Document15 pagesPG-HDB Automatic Pipette Verification (ENG)Simone GiacomelliNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Temp SopDocument8 pagesRefrigerator Temp SopdeshankarunarathneNo ratings yet
- LASR01 2015 Supplementary Requirements For Accreditation of Chemical TestingDocument13 pagesLASR01 2015 Supplementary Requirements For Accreditation of Chemical TestingfelicityNo ratings yet
- Equipment Calibration/Maintenance: APPENDIX D - USFWS QA Program (5/04)Document5 pagesEquipment Calibration/Maintenance: APPENDIX D - USFWS QA Program (5/04)Defry Farhandinata100% (1)
- Sls-Mic 032Document7 pagesSls-Mic 032vpnarashimmanNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandQuality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC 17025: 2005: General Requirements For The Competence of Testing and Calibration LaboratoriesDocument53 pagesISO/IEC 17025: 2005: General Requirements For The Competence of Testing and Calibration LaboratoriesbaxterNo ratings yet
- Overview On GLP, Dr. Anne Bridges, Technical Director, AACC International - 5Document50 pagesOverview On GLP, Dr. Anne Bridges, Technical Director, AACC International - 5mangala jesudossNo ratings yet
- BMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesDocument183 pagesBMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesYogesh AnapNo ratings yet
- Transmille Training - 17025 Quality SystemDocument34 pagesTransmille Training - 17025 Quality SystemSaiful RizamNo ratings yet
- ISO 17025 2017 Training Course and ChangesDocument48 pagesISO 17025 2017 Training Course and Changessadbad6100% (5)
- ISO 17025:2005 TrainingDocument38 pagesISO 17025:2005 TrainingStudent Foreign100% (2)
- Css Result 2022Document1 pageCss Result 2022Maine PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document18 pagesLesson 1Maine PerezNo ratings yet
- Bulacan Agricultural State CollegeDocument21 pagesBulacan Agricultural State CollegeMaine PerezNo ratings yet
- BSE 3B Language and ColorismDocument16 pagesBSE 3B Language and ColorismMaine PerezNo ratings yet
- QSP 7.1-02. Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources (Preview)Document4 pagesQSP 7.1-02. Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources (Preview)Centauri Business Group Inc.100% (1)
- Software ValidationDocument36 pagesSoftware ValidationHilario AlinabonNo ratings yet
- Gs Operation ManualDocument324 pagesGs Operation ManualMohammad Ainuddin100% (3)
- ISO - Proposal - Lala Chcocolate L.L.C.Document4 pagesISO - Proposal - Lala Chcocolate L.L.C.RasnaNo ratings yet
- BMG-F-8Q Stage 1 ReportDocument7 pagesBMG-F-8Q Stage 1 ReportremeshsankarNo ratings yet
- 5R12 Volume 2 Specifications PDFDocument349 pages5R12 Volume 2 Specifications PDFPalade SanduNo ratings yet
- Iatf 16949 PPT Training Awareness - PDF - Quality Management System - Iso 9000Document51 pagesIatf 16949 PPT Training Awareness - PDF - Quality Management System - Iso 9000wadot43402No ratings yet
- SMFBPO101 005 BPO-Operations-Management Slide-Deck 01062013 012-VerDocument54 pagesSMFBPO101 005 BPO-Operations-Management Slide-Deck 01062013 012-VerYumi ChangNo ratings yet
- Ez03 CW06 Alco Civ PRQ 000013 - 3Document176 pagesEz03 CW06 Alco Civ PRQ 000013 - 3Jason RazatlabNo ratings yet
- ANTOLIN - Supplier Quality Manual Rev.03 (English)Document26 pagesANTOLIN - Supplier Quality Manual Rev.03 (English)l.hernandezNo ratings yet
- ISCC 102 Governance 3.0Document32 pagesISCC 102 Governance 3.0Adi PuspitoNo ratings yet
- Fssai NOTES MRINALDocument19 pagesFssai NOTES MRINALmrinalbohra100% (1)
- Company Profile: An ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedDocument22 pagesCompany Profile: An ISO 9001:2015 CertifiedMechatronics EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Iso 9000-2001Document56 pagesIso 9000-2001Anonymous w63sFQiQNo ratings yet
- TESDA QualityManualRev 01Document48 pagesTESDA QualityManualRev 01Aquino SianiparNo ratings yet
- ALLSAFE The Lifting and Lashing Solutions GuideDocument24 pagesALLSAFE The Lifting and Lashing Solutions GuideAfzaalUmair0% (1)
- Isr Iso 9001 Upgrade Planner Delta ChecklistDocument10 pagesIsr Iso 9001 Upgrade Planner Delta ChecklistDelcio MinossoNo ratings yet
- QSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716Document18 pagesQSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716uday yadavNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System - Construction Procedures PDFDocument46 pagesQuality Management System - Construction Procedures PDFCarl Williams100% (2)
- Documentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2Document19 pagesDocumentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- Guide To Performance and Safety TestingDocument26 pagesGuide To Performance and Safety Testingpaninaro2011No ratings yet
- Basics of Quality ManagementDocument14 pagesBasics of Quality ManagementWiki Waqas100% (1)
- What Is ISO 9001Document5 pagesWhat Is ISO 9001Klaus AlmesNo ratings yet
- Some More Objective Questions With AnswersDocument44 pagesSome More Objective Questions With AnswersPratyush Solanki100% (1)