Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Non & Pharmacologic Gout
Non & Pharmacologic Gout
Uploaded by
Ralph Aubrey CulhiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Non & Pharmacologic Gout
Non & Pharmacologic Gout
Uploaded by
Ralph Aubrey CulhiCopyright:
Available Formats
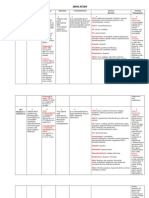
Pharmacologic
The goal of treatment during an acute gout attack is suppression of inflammation and control of
pain.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) PO
o Ibuprofen 800 mg three to four times daily or Indomethacin 25 to 50 mg four
times daily; 5 to 10 days or until symptoms resolve
Colchicine PO
o 30 to 35 mg prednisolone PO for 5 days
Corticosteroids PO
o Low-dose therapy: 2 × 0.5 mg initially, then single administration 0.5 mg after 1
hour
Chronic gout treatment should aim to prevent gout progression and further gout flares, to
eliminate any urate deposits, and to reverse tophus formation.
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor: Allopurinol
o Initially 50 to 100 mg/day; increase to max. 800 mg/day
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor: Febuxostat
o Initially 80 mg/day, increase to 120 mg/day if necessary
Uricosuric agent: Probenecid
o Probenecid can be combined with allopurinol if allopurinol alone is insufficiently
effective
Engel, B., Just, J., Bleckwenn, M., & Weckbecker, K. (2017). Treatment Options for
Gout. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 114(13), 215–222.
https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0215
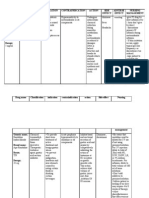
Non-Pharmacologic
Choose healthier beverages
Avoid foods high in purines
Exercise regularly and lose weight
Vitamin C intake above 500 mg/day
Líška D. (2021). Non-pharmacological treatment of gout. Nefarmakologická liečba dny. Vnitrni
lekarstvi, 67(E-2), 25–28.
You might also like
- Basic Concepts About Matter: Test BankDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts About Matter: Test BankRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Drugs NclexDocument30 pagesDrugs Nclexawuahboh100% (1)
- PREDNISONEDocument4 pagesPREDNISONECay SevillaNo ratings yet
- TreatmentDocument1 pageTreatmentMohamad IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Cholecystitis: Narciso A. CañibanDocument10 pagesMedical Management of Cholecystitis: Narciso A. Cañibanalexandrajane2007No ratings yet
- Autacoids and Related DrugsDocument17 pagesAutacoids and Related DrugsmidhunNo ratings yet
- EpicotilDocument2 pagesEpicotilmahgadNo ratings yet
- NSAIDDocument15 pagesNSAIDMaria KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ibuprofen Brand Name: Advil, Ibutab, Midol Classification: AnalgesicsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Ibuprofen Brand Name: Advil, Ibutab, Midol Classification: AnalgesicsSheryll Anne MolartoNo ratings yet
- ISONIAZIDDocument2 pagesISONIAZIDXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesIbuprofen DRUG STUDYKyle Hannah93% (15)
- Treatment of Tuberculosis .2Document59 pagesTreatment of Tuberculosis .2Alexander Santiago Parel0% (1)
- Allopurinal: Aleve (Naproxen)Document7 pagesAllopurinal: Aleve (Naproxen)Zaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- CompositionDocument3 pagesCompositionJai KumarNo ratings yet
- Analgesiainratsandmice2 11Document2 pagesAnalgesiainratsandmice2 11Ciong TanNo ratings yet
- Pharcomology of Oral ContraceptionDocument22 pagesPharcomology of Oral Contraceptioncana geel 2018No ratings yet
- Treatment of SyphilisDocument20 pagesTreatment of SyphilisABDALRAHMAN ABDALLAH KASEMNo ratings yet
- NociceptionDocument8 pagesNociceptionfootballjeinNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology: NTA Level 4 Semester 2Document16 pagesBasic Pharmacology: NTA Level 4 Semester 2MabusiNo ratings yet
- AntifungalDrugsdr - Saad 5443518073990534552Document43 pagesAntifungalDrugsdr - Saad 5443518073990534552okjishnuanandanNo ratings yet
- Betnesol InjectionDocument7 pagesBetnesol Injectionhiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Med Cards Starting With A PDFDocument7 pagesMed Cards Starting With A PDFDonn Patrick AlegreNo ratings yet
- Over The CounterDocument5 pagesOver The CounterJoanna MalizaNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Gout, Reumathoid Athritis Dan OsteoathritisDocument59 pagesFarmakoterapi Gout, Reumathoid Athritis Dan OsteoathritisMuhammadTaufiqHidayatNo ratings yet
- Pharmacolgy Study Guide AdaDocument238 pagesPharmacolgy Study Guide Adamikechur-aNo ratings yet
- Isotretinoin in Acne: Presented By:-Dr Rekha SirviDocument28 pagesIsotretinoin in Acne: Presented By:-Dr Rekha SirviAnurag AnupamNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument5 pagesKidneyAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug AdvilDocument1 pageDrug AdvilDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol - Drug Information - UpToDate-1Document5 pagesHaloperidol - Drug Information - UpToDate-1Vh TRNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidVaibhav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Gastro EnteristisDocument2 pagesDrug Study Gastro Enteristisimeejen100% (1)
- DRUGS1Document7 pagesDRUGS1Maria Frances Antoniette PerezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- Bulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- Loperamide - Pharma Online UstadDocument1 pageLoperamide - Pharma Online UstadF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 pagesDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- INF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringDocument4 pagesINF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringEem Khaye YamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HydrocodoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study - HydrocodoneTarquin Tomada86% (7)
- Anti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsDocument13 pagesAnti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsGabriel KidagayoNo ratings yet
- IbuprofenDocument1 pageIbuprofenDherick RosasNo ratings yet
- Dispepsia 1Document12 pagesDispepsia 1Iwa PrinandiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyALYSSA PACHECONo ratings yet
- Romeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeDocument8 pagesRomeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic: Anticholinergics: Generic and Brand NamesDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic: Anticholinergics: Generic and Brand NamesSaffery Gly LayuganNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Overview and Recommendations: BackgroundDocument46 pagesOverview and Recommendations: BackgroundRubén Casas BenítezNo ratings yet
- IbuprofenDocument3 pagesIbuprofenapi-3797941100% (1)
- Cervical Spondylosis MedicationDocument3 pagesCervical Spondylosis MedicationhendrayatiranyNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Orthodontics - 1Document43 pagesDrugs in Orthodontics - 1Sushma Rayal SANo ratings yet
- Case Diabetes Week 6Document5 pagesCase Diabetes Week 6skyemacdonald23No ratings yet
- Budesonide Drug CardDocument3 pagesBudesonide Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Wepik Ibuprofen Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Applications 2024041118511280imDocument10 pagesWepik Ibuprofen Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Applications 2024041118511280imMeet KoshiyaNo ratings yet
- Pycnogenol Consumer/Patient Information SheetDocument1 pagePycnogenol Consumer/Patient Information SheetDeboraNainggolanNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic: Classification Generic Name Brand NameKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PrescriptionsDocument41 pagesEndocrine PrescriptionsStock CheckNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJason AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2 - Drug Information SourcesDocument2 pagesLab Activity 2 - Drug Information SourcesRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab. 2-Moisture and Determination (Gravimetric Method)Document5 pagesLab. 2-Moisture and Determination (Gravimetric Method)Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Adenosine Triphosphate in The MetabolicDocument1 pageThe Importance of Adenosine Triphosphate in The MetabolicRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Med 1 Lec - Assignment No. 1Document2 pagesPharm Med 1 Lec - Assignment No. 1Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab. 1-Background of The Plant, Preparation of Crude Drug and Official SamplingDocument7 pagesLab. 1-Background of The Plant, Preparation of Crude Drug and Official SamplingRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical SuppositoriesDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical SuppositoriesRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 (I) As in Bit TriviaDocument5 pagesLesson 2 (I) As in Bit TriviaRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- CULHI - 5087 - Evolution of Pharmacy EssayDocument2 pagesCULHI - 5087 - Evolution of Pharmacy EssayRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Pharm InfoDocument2 pagesLab 1 - Pharm InfoRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument1 pagePerdevRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- CFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermDocument1 pageCFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentDocument2 pagesSaint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- 1O Reasons Why Physical Fitness Is ImportantDocument1 page1O Reasons Why Physical Fitness Is ImportantRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Class SchedDocument1 pageClass SchedRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresRalph Aubrey Culhi0% (1)
- PD EssayDocument1 pagePD EssayRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet