Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Digital Marketing AssignmentDocument40 pagesDigital Marketing AssignmentSUDIP100% (2)
- Sad 2 Group 4 - Revised Version by Mam RitzDocument22 pagesSad 2 Group 4 - Revised Version by Mam RitzRyan Danila GalloNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument27 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundCamille CasugaNo ratings yet
- Arjay Coronel Topic Proposal TemplateDocument4 pagesArjay Coronel Topic Proposal TemplateAndanteNo ratings yet
- (IJIT-V3I2P2) : Tarek H.Ahmed, L. Abdul Kadhar Sheriff, A.ShameemFathimaDocument6 pages(IJIT-V3I2P2) : Tarek H.Ahmed, L. Abdul Kadhar Sheriff, A.ShameemFathimaIJITJournalsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Preference Level of Education-Based Mobile Application Reference To Engineering College StudentsDocument9 pagesA Study On Preference Level of Education-Based Mobile Application Reference To Engineering College StudentsMiddle East Journal of Applied Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Students' Perceptions of Mobile Apps A Needs Analysis of EFL LearnersDocument14 pagesStudents' Perceptions of Mobile Apps A Needs Analysis of EFL LearnersNaveed AnvarNo ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument5 pagesMobile PhoneFizza ChNo ratings yet
- Chap 12345 Without ReferencesDocument35 pagesChap 12345 Without ReferencesChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Computers & Education: Janet Mannheimer Zydney, Zachary WarnerDocument17 pagesComputers & Education: Janet Mannheimer Zydney, Zachary WarnerIvanzieo V SNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Application Among Grade 10 StudentsDocument21 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Application Among Grade 10 StudentsAira Jean OcopNo ratings yet
- Literature Review For Android Mobile ApplicationDocument6 pagesLiterature Review For Android Mobile Applicationgw0gbrwe100% (1)
- The Level of Ict Integration Using Samr Model of Kananga Senior High School LearnersDocument15 pagesThe Level of Ict Integration Using Samr Model of Kananga Senior High School LearnersClariess SoronoNo ratings yet
- Kearney & Burke & Schuck (2019) The iPAC ScaleDocument14 pagesKearney & Burke & Schuck (2019) The iPAC Scalemaria.diazvalencia.goetheNo ratings yet
- Smartphone Usability Framework Towards Self-Directed Learning in University of Dar Es SalaamDocument7 pagesSmartphone Usability Framework Towards Self-Directed Learning in University of Dar Es SalaamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- St2da Group 1 Research Chapter 1 2 3 4 5 Andres Carpela Castillo Claro Grefaldon Ibanez Mella Ortega PoliquitDocument19 pagesSt2da Group 1 Research Chapter 1 2 3 4 5 Andres Carpela Castillo Claro Grefaldon Ibanez Mella Ortega PoliquitNhyl Vinzie PesidasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877042814057784 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1877042814057784 MainStem EducationNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Effectiveness of MobDocument10 pagesAn Investigation of Effectiveness of MobJennie ManobanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningDocument15 pagesA Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningAkagami TVNo ratings yet
- Impact of Smartphones Usage On The LearnDocument20 pagesImpact of Smartphones Usage On The LearnAldrin GarciaNo ratings yet
- 645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Document4 pages645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Mobile Learning ApplicationDocument10 pagesDesign and Development of Mobile Learning Applicationradinal fadliNo ratings yet
- The Development of Android-Based Smartphone Learning Application On Teaching Reading ComprehensionDocument8 pagesThe Development of Android-Based Smartphone Learning Application On Teaching Reading ComprehensionLaser RomiosNo ratings yet
- Students Readiness To Engage With Mobile AppsDocument18 pagesStudents Readiness To Engage With Mobile AppsJulia TokarenkoNo ratings yet
- Kroook KrookDocument40 pagesKroook KrookAl ShokoNo ratings yet
- STEM12 CAPSTONE GROUP10 Checked 1 With PosterDocument30 pagesSTEM12 CAPSTONE GROUP10 Checked 1 With PostershennaNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Mobile-Assisted Vocabulary Learning ResearchDocument17 pagesA Systematic Review of Mobile-Assisted Vocabulary Learning ResearchNaveed AnvarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Pangan SanpedroDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Pangan SanpedroSophia San PedroNo ratings yet
- Presentation Imc651Document18 pagesPresentation Imc651Dysoxylon Far Daey HalimNo ratings yet
- Investigation of University Students SmaDocument17 pagesInvestigation of University Students SmaLuisa PuyoNo ratings yet
- Designing Pre-Test Questions As Phone Notifications - Studying TheDocument7 pagesDesigning Pre-Test Questions As Phone Notifications - Studying ThelstaanaNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Effectiveness of MobDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of Effectiveness of MobGayatri GurunathNo ratings yet
- Final Tempate AutorecoveredDocument32 pagesFinal Tempate AutorecoveredRenson CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Critical Thinking Skills in ChemistryDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Critical Thinking Skills in ChemistryRizki AdityawanNo ratings yet
- Development of The Smartphone and Learning Inventory: Measuring Self-Regulated UseDocument17 pagesDevelopment of The Smartphone and Learning Inventory: Measuring Self-Regulated UseMinh Hong NguyenNo ratings yet
- PR2 G12Document19 pagesPR2 G12hazieldc10No ratings yet
- Mobile Applications' Impact On Student Performance and SatisfactionDocument11 pagesMobile Applications' Impact On Student Performance and SatisfactionSacamichi XdNo ratings yet
- Paper-Students' Attitudes Towards Mobile LearningDocument12 pagesPaper-Students' Attitudes Towards Mobile LearningShinya Hilal YamanakaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 1 3Document50 pagesFinal Chapter 1 3Johnly RebitoNo ratings yet
- Mine's ResearchDocument12 pagesMine's Researchearl9rivera-830280No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3 ThesisDocument26 pagesChapter 1 3 ThesisShane Khezia BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Review On Use of Mobile Apps For Language Learning: Ramya GangaiamaranDocument10 pagesReview On Use of Mobile Apps For Language Learning: Ramya GangaiamaranDylan TylNo ratings yet
- A Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningDocument16 pagesA Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningAhmad Zaki IsmailNo ratings yet
- Robayo-Pinzon ET AL. (2021) - Does Excessive Use of Smartphones and Apps Make Us More ImpulsiveDocument10 pagesRobayo-Pinzon ET AL. (2021) - Does Excessive Use of Smartphones and Apps Make Us More ImpulsiveSamuel FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesMobile Literature Reviewgw32pesz100% (1)
- Smartphones and Students Academic PerforDocument39 pagesSmartphones and Students Academic PerforEhra Jiang KangraejoonNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Effects of Mobile Learning 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Effects of Mobile Learning 1api-301114110No ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Phone To Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students in San Pedro Relocation National High School S. Y. 2021-2022Document5 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Phone To Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students in San Pedro Relocation National High School S. Y. 2021-2022Markvince BaliliNo ratings yet
- Tugas TPI Kelas 2C-42518059Document5 pagesTugas TPI Kelas 2C-42518059aurelia rusliNo ratings yet
- Article 2 PDFDocument11 pagesArticle 2 PDFjessamaekempisNo ratings yet
- Local Media3568009793508657403Document16 pagesLocal Media3568009793508657403Azyr SampeloNo ratings yet
- Framework To Evaluate M-Learning Systems: A Technological and Pedagogical ApproachDocument8 pagesFramework To Evaluate M-Learning Systems: A Technological and Pedagogical ApproachPercy QuispeNo ratings yet
- Iconic2022Paper 22 PDFDocument13 pagesIconic2022Paper 22 PDFBenLyn ZaideNo ratings yet
- Mexico GoalDigger ResearchPaper-1Document14 pagesMexico GoalDigger ResearchPaper-1Jarius MacalaguingNo ratings yet
- Mobile Applications Within Education PDFDocument13 pagesMobile Applications Within Education PDFpantelios21No ratings yet
- 944 Me00003Document4 pages944 Me00003eren akarsuNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Mobile Application Usage AmDocument14 pagesFactors That Influence Mobile Application Usage AmNgoc ThuyNo ratings yet
- 3414 Ijite 01Document16 pages3414 Ijite 01ijiteNo ratings yet
- Understanding M-Learning: AbstrackDocument6 pagesUnderstanding M-Learning: AbstrackMohan LalNo ratings yet
- Study Materials Providers ApplicationDocument9 pagesStudy Materials Providers ApplicationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- How To Get Smartphones Into Classes: a guide for teachersFrom EverandHow To Get Smartphones Into Classes: a guide for teachersNo ratings yet
- Post-Pandemic Performance in Content Mastery and Cognitive Skills of Junior High School Students in ChemistryDocument7 pagesPost-Pandemic Performance in Content Mastery and Cognitive Skills of Junior High School Students in ChemistryPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalDocument11 pagesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Leadership Style of The School Heads As Correlates To The Level of Efficiency of Management Practices: Inputs For Professional Development PlanDocument15 pagesLeadership Style of The School Heads As Correlates To The Level of Efficiency of Management Practices: Inputs For Professional Development PlanPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Self-Concept and Level of Career Interest of Grade 9 Students at San Roque National High SchoolDocument10 pagesSelf-Concept and Level of Career Interest of Grade 9 Students at San Roque National High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Opportunities: The Key To Successful Destigmatization of Ex-OffendersDocument11 pagesUnlocking Opportunities: The Key To Successful Destigmatization of Ex-OffendersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Improving Mastery Level in Understanding Typhoon and Earthquake Preparedness Through STEM ModulesDocument12 pagesImproving Mastery Level in Understanding Typhoon and Earthquake Preparedness Through STEM ModulesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyDocument9 pagesThe Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Approach in Teaching Science Grade 7Document10 pagesMultimedia Approach in Teaching Science Grade 7Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Pet Loss: A Study On The Relationship Between Attachment Styles and Cognitive-Emotion Regulation Strategy Among Elderly Pet Owners in Quezon CityDocument12 pagesPet Loss: A Study On The Relationship Between Attachment Styles and Cognitive-Emotion Regulation Strategy Among Elderly Pet Owners in Quezon CityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Experiences of The Lebakeño Grade XI Students On Learning Mathematics in The Modular Approach: Basis For Learning FrameworkDocument34 pagesThe Experiences of The Lebakeño Grade XI Students On Learning Mathematics in The Modular Approach: Basis For Learning FrameworkPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Digital Orientation and Cyber-Victimization of College Students As Mediated by Their Attitude Toward CrimeDocument12 pagesDigital Orientation and Cyber-Victimization of College Students As Mediated by Their Attitude Toward CrimePsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Phonological Awareness of Kindergarten TeachersDocument14 pagesPhonological Awareness of Kindergarten TeachersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal100% (1)
- Influence of Teacher's Personality and Behavior On Students Character BuildingDocument8 pagesInfluence of Teacher's Personality and Behavior On Students Character BuildingPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Empowerment, Organizational Commitment, and Management Performance of Secondary School Heads in The New Normal in The Division of PalawanDocument16 pagesEmpowerment, Organizational Commitment, and Management Performance of Secondary School Heads in The New Normal in The Division of PalawanPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Game-Based and Project-Based Approaches: Their Effects On Grade 10 Learners' Performance in BiologyDocument9 pagesGame-Based and Project-Based Approaches: Their Effects On Grade 10 Learners' Performance in BiologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Exploring Factors Influencing The Non-Completion of Theses Among Teachers Pursuing A Master's Degree: A Case Study AnalysisDocument10 pagesExploring Factors Influencing The Non-Completion of Theses Among Teachers Pursuing A Master's Degree: A Case Study AnalysisPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Four Dimensions of Personnel Relational Work in Multi-Settings: Deriving Sociograms For Work Dynamism and DynamicsDocument17 pagesFour Dimensions of Personnel Relational Work in Multi-Settings: Deriving Sociograms For Work Dynamism and DynamicsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Love Corner: Enhancing Students' English VocabularyDocument10 pagesLove Corner: Enhancing Students' English VocabularyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Digital Marketing Strategies On Customer's Purchase Intention of Selected Fast-Food RestaurantsDocument14 pagesThe Influence of Digital Marketing Strategies On Customer's Purchase Intention of Selected Fast-Food RestaurantsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Gamification Strategy in Increasing The Grade 10 Student's Academic MotivationDocument9 pagesEffectiveness of Gamification Strategy in Increasing The Grade 10 Student's Academic MotivationPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ICT Students' Mastery Level in Setting Up Computer Networks Instructed Using CSS DroidDocument5 pagesGrade 11 ICT Students' Mastery Level in Setting Up Computer Networks Instructed Using CSS DroidPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Development and Comprehension Skills Through Word Games Among Grade 4 LearnersDocument11 pagesVocabulary Development and Comprehension Skills Through Word Games Among Grade 4 LearnersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Watching Movies With English Subtitles and Vocabulary Performance of SPA LearnersDocument12 pagesWatching Movies With English Subtitles and Vocabulary Performance of SPA LearnersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Career Pathways of Technical, Vocational and Livelihood Senior High School Graduates in Pililla National High SchoolDocument10 pagesCareer Pathways of Technical, Vocational and Livelihood Senior High School Graduates in Pililla National High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of T Math Modules To The Numeracy Level of Grade 6 Learners of Patabog Elementary SchoolDocument12 pagesEffect of T Math Modules To The Numeracy Level of Grade 6 Learners of Patabog Elementary SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- SQP2RS Strategy in Teaching Reading Using Different Text Types Among Grade 9 Learners: An Experimental InquiryDocument13 pagesSQP2RS Strategy in Teaching Reading Using Different Text Types Among Grade 9 Learners: An Experimental InquiryPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- School Operations in The Implementation of K-12 Curriculum and Performance of School Heads in CALABARZON: Basis For Curriculum Management FrameworkDocument8 pagesSchool Operations in The Implementation of K-12 Curriculum and Performance of School Heads in CALABARZON: Basis For Curriculum Management FrameworkPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Skills Among Teachers in The Division of Lanao Del NorteDocument14 pagesInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) Skills Among Teachers in The Division of Lanao Del NortePsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management Practices of Teachers and Academic Performance of Grade 3 Learners Across All Learning AreasDocument10 pagesClassroom Management Practices of Teachers and Academic Performance of Grade 3 Learners Across All Learning AreasPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Attitudes of College Students Toward Statistics and Research CoursesDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Attitudes of College Students Toward Statistics and Research CoursesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Inspection at LC Gate: S.No Items Checked Observations/Irregularities Action To Be Taken byDocument3 pagesInspection at LC Gate: S.No Items Checked Observations/Irregularities Action To Be Taken byMadhav PrasadNo ratings yet
- Practice6 CSDocument12 pagesPractice6 CS87shf2xx2jNo ratings yet
- U3D - Archicad U 3D PDFDocument1 pageU3D - Archicad U 3D PDFBojan TokićNo ratings yet
- Lab9 IAA202Document4 pagesLab9 IAA202Đào Mạnh CôngNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking AssignmentDocument4 pagesPublic Speaking AssignmentSiti NursyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Monthly Service Bulletin: FEI Customer Service April 29, 2009Document14 pagesMonthly Service Bulletin: FEI Customer Service April 29, 2009Emad BNo ratings yet
- Telephone Directory July 2008Document112 pagesTelephone Directory July 2008manit SangwanNo ratings yet
- RHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance GuideDocument22 pagesRHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance Guideapiruck sukjingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionDocument39 pagesLecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionAshish JainNo ratings yet
- Publications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleDocument63 pagesPublications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- PPB3033 Assignment Individual InstructionDocument3 pagesPPB3033 Assignment Individual InstructionKkaebsong hoonieNo ratings yet
- ABC Hospital - SolutionDocument12 pagesABC Hospital - SolutionMayank Patel100% (1)
- CGT 163 F20 Syllabus v20Document10 pagesCGT 163 F20 Syllabus v20brinda mehtaNo ratings yet
- Third Product Theme Blutooth Dual SIM AdapterDocument7 pagesThird Product Theme Blutooth Dual SIM Adapterabbasarslan221No ratings yet
- Tur Bulat or WebDocument13 pagesTur Bulat or WebBakkiyarajNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx XC7K160T-2FBG484i FpgaDocument13 pagesWhat Is Xilinx XC7K160T-2FBG484i FpgajackNo ratings yet
- Rns Institute of Technology: Text BooksDocument52 pagesRns Institute of Technology: Text Booksanu radhaNo ratings yet
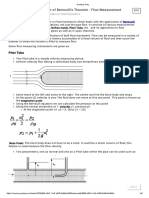
- Application of Bernoulli's TheoremDocument8 pagesApplication of Bernoulli's Theoremram kumarNo ratings yet
- How To Temperature Map Cold Chain Equipment and Storage AreasDocument82 pagesHow To Temperature Map Cold Chain Equipment and Storage AreasramajayamNo ratings yet
- Ecosys M3860idn Ds (En)Document2 pagesEcosys M3860idn Ds (En)Sirajudin ahmad (udin)No ratings yet
- Cullen v. Zoom Video Communications, Inc., Case 5:20-cv-02155-SVK (Northern District of California)Document23 pagesCullen v. Zoom Video Communications, Inc., Case 5:20-cv-02155-SVK (Northern District of California)Law&CrimeNo ratings yet
- Snowflake Is Building A Marketplace For Retail Media DataDocument5 pagesSnowflake Is Building A Marketplace For Retail Media DataPaolo Caviedes SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Liquid Rotor Resistance Starter Conventional LrsDocument3 pagesLiquid Rotor Resistance Starter Conventional Lrsmayur3dhandeNo ratings yet
- LIEBHERR L586 - G6.0 D - 1815 SM PreviewDocument41 pagesLIEBHERR L586 - G6.0 D - 1815 SM PreviewGovanny MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Design of A Heat Exchanger Using HTRIDocument4 pagesDesign of A Heat Exchanger Using HTRIcenter010% (1)
- Brochure GT-Series PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure GT-Series PDFmaxbigosNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Automatic Schedule Generator and Managemant SystemDocument4 pagesReview Paper On Automatic Schedule Generator and Managemant SystemVaidehi LohiyaNo ratings yet
- Huawei ETP4830Document68 pagesHuawei ETP4830x00No ratings yet
- Text 5 - The Modern Age (Electricity)Document2 pagesText 5 - The Modern Age (Electricity)Cofe CodingNo ratings yet
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Reading Mobile Applications On Students' Critical Thinking Skills: A Linear Analysis
Copyright:
Available Formats
READING MOBILE APPLICATIONS ON
STUDENTS’ CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS:
A LINEAR ANALYSIS
PSYCHOLOGY AND EDUCATION: A MULTIDISCIPLINARY JOURNAL
2023
Volume: 11
Pages: 1017-1029
Document ID: 2023PEMJ1032
DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.8229487
Manuscript Accepted: 2023-9-8
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
Reading Mobile Applications on Students’ Critical Thinking Skills:
A Linear Analysis
Sheniel L. Laurente*, Jamaira D. Diva, Adrian M. Abarquez, Rhino Rienz L. Casas,
Airis Kim M. Codiñera, Jomarie Alex A. Guinita
For affiliations and correspondence, see the last page.
Abstract
Reading mobile applications, more generally known as an “applications,” are a category of
application software created specifically to run on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
Critical thinking is the process of actively and successfully conceiving, applying, analyzing,
synthesizing, and evaluating knowledge as a basis for belief and action. This study assessed the
relationship of using reading mobile applications in developing the students’ critical thinking skills. A
correlational design was used in this study to assess whether two different variables have a
relationship. There were 125 grade 10 respondents utilized by the researchers. The research was
carried out at Maguikay High School in G.K. Sudlon, Maguikay, Mandaue City, Cebu, Philippines,
6014. Two-page standardized questionnaires were used in this study, which was calculated using the
Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Every questionnaire fundamentally plays a role in the study to
effectively know the correlation of each variable. The finding showed that there is a significant
relationship between reading mobile applications and critical thinking skills. Therefore, reading
mobile applications can help students gain knowledge, improve their reading skills, and develop their
critical thinking skills.
Keywords: reading mobile applications, critical thinking, correlation, linear analysis
Introduction Maguikay High School students are interested in
adopting mobile applications for reading. Mobile
reading software for students has both benefits and
Reading mobile applications are a class of software drawbacks. Some people use reading apps on their
designed especially for portable devices like mobile devices for academic purposes. Others, though,
smartphones and tablets, more commonly referred to are merely amusing themselves with it. Because this
as “applications.” Libby, eBook, and Scribd are a few study significantly impacts how students use reading
examples of reading-related mobile applications. With mobile applications to develop critical thinking, the
these mobile reading programs, students can look up researchers must continue this investigation.
information for educational purposes at any time and
location that they enjoy reading, which help them stay Internationally, a study by Ismail et al. (2016) in
current even in the modern era. Mobile applications Malaysia entitled “Promoting Students’ Critical
that closely resemble those found on personal Thinking in a Mobile Learning Environment”
computers are commonly accessible to consumers. demonstrates that mobile technology’s advantages and
Applications are frequently distinct, small-sized rapid development enhance education. Nationally, a
software components with limited functionality. The study in Cagayan de Oro, Philippines by Limbaco et
terms iPhone app, smartphone app, web app, and the al. (2021) on “The Use and Perceptions of Students of
online app can all be used to refer to mobile reading Mobile Applications as a Classroom Response
applications (Demir & Akpinar, 2018). It is enjoyable System,” revealed that mobile applications are utilized
for everyone to use mobile applications. We can read as a Classroom Response System by students in a
and study using mobile applications whenever and diverse range of disciplines and educational levels.
wherever we choose. Such applications and handheld devices involve
students, cultivate learning, and develop learning
Critical thinking involves using developed, applied, activities. Further, in Cebu, Etcuban and Pantinople’s
analyzed, synthesized, and effectively evaluated (2018) quasi-experimental study on “Effects of Mobile
knowledge as a basis for belief and action. This mode Applications in Teaching High School Mathematics,”
of thinking requires intellectual discipline and the concluded that using the mobile application to teach
ability to assess facts, data, evidence, observations, math to grade 8 students had improved students’
and circumstances to conclude (Wallman & Hoover, achievement and learning. Additionally, a quasi-
2012). An essential educational objective is critical experimental study on “Mobile Pronunciation
thinking, which is reasonable, reflective thinking Applications for Oral Communication” conducted in
concerned with choosing what to believe or do. Many Cebu, Philippines, by Abarquez (2021) revealed that
Laurente et al. 1017/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
the best way for English teachers to develop outcomes. This review intends to contribute to a better
pronunciation skills in today’s young, tech-savvy understanding of how mobile applications may affect
students is by utilizing the most well-liked mobile reading practices and improve learning experiences for
applications. learners of all ages by conducting an in-depth analysis
of the available studies.
The researchers discovered a research gap in using
reading mobile applications to develop students’ Regarding mobility, location awareness, and the
critical thinking abilities. Previous studies focused on usability of different mobile devices and their apps
mobile apps but did not develop students’ critical owing to the variations between them and other
thinking abilities. A study from earlier research aimed computer system are distinct (Abran et al., 2012).
to use mobile learning technology to help students Mobile devices and their applications offer
develop their critical thinking skills. In contrast, this considerable advantages for their uses. Mobile apps
study aimed to assess the relationship on the various are installed by users from various sources or
reading mobile applications on the critical thinking incorporated into phones during production venues for
skills of junior high school students.Thus, this research action. The software requirements for mobile devices,
determined how using mobile applications for reading such as PDAs and mobile phones, impact the creation
correlates students’ critical thinking skills. Students of mobile applications. Because they are less
must be aware of the significance of reading mobile computer-focused, they are more user-friendly.
applications. The ability to evaluate, comprehend, and
communicate arguments is all improved by reading Speaking of reading applications for mobile devices,
frequently. an electronic book (sometimes referred to as an "e-
book") is a digital publication that can include both
Research Questions text and image content. An electronic book can be read
on a computer using specialized software or on a
This study assessed the relationship of reading mobile proprietary digital device called an e-reader (Rouse,
applications and critical thinking skills among grade 2016).According to Wang et al. (2013), mobile
10 junior high school students of one of the secondary application (APP) is a new, developing mobile
schools in Mandaue City, S. Y. 2022-2023, third technology that has been widely used. This new
quarter. The results of this study were the basis for mobile artifact threatens the existing economic
recommendations.Specifically, this answered the paradigm of mobile business. It opens up new
following recommendations: opportunities for the market, making it more critical
than ever to match consumer demand and launch a
1. What is the weighted mean of the respondents’
product fast and successfully.
reading mobile applications usage?
2. What is the weighted mean of respondents’ critical Mobile technologies enable novel modes of
thinking skills? information and communication access. However,
3. Is there a significant relationship between reading despite these advancements, these technologies must
mobile applications and critical thinking skills? still uphold and defend the values of their users.
4. Based on the findings, what recommendations may Research suggests a significant discrepancy between
be proposed? user values, like privacy, and how mobile technologies
address these values (Martin & Shilton, 2015).
Literature Review Encouraging corporate social responsibility and ethical
considerations among tech companies and developers
remains a persistent and unresolved challenge that
Utilizing Mobile Applications for Reading as a needs to be addressed.
Learning Tool
According to Can (2016), players in the education
In an era where mobile devices have become a sector are looking for the best ways to encourage
fundamental part of our daily lives, their potential as parents' participation in school activities because
effective teaching tools cannot be emphasized. Among parent-teacher collaboration is essential for students'
the numerous programs available, those specialized for achievement. For children to succeed, parents and
reading have acquired enormous momentum as useful teachers must work together. The stakeholders in the
learning tools. This review of related literature education sector are looking for the most effective
attempts to investigate the wide variety of mobile informational notice to encourage parental
reading applications and their impact on learning involvement in academic activities.Moreover,
Laurente et al. 1018/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
according to Phongtraychak and Dolgaya (2018), a today’s requirements. Therefore, problem-based
mobile application is a software program that runs on learning environments should be valuable tools for
portable electronics like smartphones and tablets. It is fostering creativity and critical thinking
a result of recent technological developments. Mobile skills.Furthermore, critical thinking is a commonly
applications result from the convergence of media, acknowledged educational objective, (Hitchcock,
information technology, the internet, and cutting-edge 2018). There is disagreement over the exact definition
technologies. This overview of the literature discusses of the term. However, the differing interpretations can
reading mobile applications. It talks about the be understood as different perspectives of the same
advantages and disadvantages of mobile application core concept: a purposeful and comprehensive
reading for students. For social and educational goals, examination.
students could find reading mobile applications
helpful. In conclusion, reading mobile apps is a Lastly, according to Heard et al. (2020), critical
learning tool that students employ. thinking aims to create a new information,
understanding, hypotheses, and beliefs that are reliable
The Benefits of Critical Thinking for Students’ and insightful. Critical thinking entails assessing and
Learning evaluating facts, arguments, and circumstances by
applying proper criteria. Critical thinking pertains to
In a dynamic environment that requires flexible and an individual’s ability to comprehend decision-making
analytical individuals, critical thinking has emerged as and skillful problem-solving.The above review of
an essential skill set for students of all disciplines. The relevant literature focuses entirely on critical thinking.
ability to critically analyze information, evaluate Students will benefit from having critical thinking
arguments, and make reasoned judgements is essential abilities to succeed. It enables individuals to increase
not only for academic success, but also for personal the effectiveness of their decision making and
growth and professional development. The following problem-solving. Increasing the pupils’ capacity for
review of related literature seeks to provide an critical thought may result in better comprehension,
overview into the wide body of research surrounding hypotheses, and beliefs. As a result, using mobile
the benefits of critical thinking in students' learning applications can help pupils’ critical thinking abilities.
experiences. This review tries to identify the various
benefits of critical thinking by reviewing the existing Mobile Applications that Support Students’
literature. Learning
According to Bezanilla (2019), critical thinking is a In recent years, the widespread usage of mobile
skill students must have to excel in their personal and devices and the development of mobile technology
professional lives. Therefore, it must be a priority for have altered the field of education and created new
universities to incorporate it into their programs, opportunities for supporting students' learning
courses, and extracurricular activities. There is still processes. Particularly, mobile applications have
work to be done since the capacity has to be defined drawn a lot of interest as developing technologies that
clearly, and new active techniques for developing it can enhance the teaching and learning process by
must be improved. Moreover, developing speaking providing access to a wide range of educational
skills through diverse real-word activities can be used resources at any time and from any location. This
in the classroom to help pupils improve their critical review of related studies aims to provide readers with
thinking skills (Muhammadiyeva et al., 2020).Critical an overview of existing studies on mobile educational
thinking (C. T.) is one of the most in-demand abilities resources that support students in a variety of
for a pharmacy graduate (Persky et al.,2019). Some of academic fields.
the many barriers to critical thinking are students’
views, inadequate metacognitive abilities, a fixed A study by Henry and Mohamad (2021) entitled “The
perspective, a nonautomated skillset, heuristic, biases, Use of Mobile tech Technology in Enhancing the
and the fact that thinking is time-consuming. Critical Reading Skills of Pre-University ESL
Students” found that one of the most sought-after
Additionally, Birgili (2015) notes that the capacities qualifications for studies and employment in the 21st
for critical and creative thinking are sometimes used century, critical thinking abilities have been impacted
interchangeably in definitions. They employ various by the industrial revolution, which altered the nature of
constructions because human acts have different effect work, lifestyle, and education. The leading cause of
on different people. People must be able to handle the county’s high unemployment rate is graduates’
everyday situations with both competencies at one of need for critical thinking skills, which are gained
Laurente et al. 1019/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
through critical reading, which calls for complex Additionally, a study by Basal et al. (2016) entitled
thought. The ability to explain one’s own opinions and "Effectiveness of mobile applications in vocabulary
ideas while analyzing, synthesizing, and assessing teaching” indicated that teaching vocabulary through
information from a variety of sources is improved mobile applications can reveal that the latter is a more
through developing critical reading skills. effective tool when compared to traditional paper-
based activities. Smartphones are becoming a more
Moreover, a study by Hasan et al. (2018) entitled, significant part of our daily life. Applications for these
"Development of Interactive E-book on Energy gadgets’ enormous capacity are numerous. Utilizing
Resources to Enhance Student’s Critical Thinking these tools in language learning has opened up new
Ability," concluded that the creation of an interactive avenues for the opportunity and revolutionized how
e-book based on the Learning Content Development teachers and students learn and impart knowledge. The
System (LCDS) has been validated as a teaching article offers recommendations for teaching
resource on the subject of energy resources using a vocabulary with mobile applications.
scientific method to improve students' critical thinking
abilities. It is advised to constantly enhance user Moreover, Hasan et al. (2018), in their study entitled
interface and user experience for the convenience of “Development of an Interactive E-Book on Energy
students, keeping up with technological innovation. Resources to Enhance Student’s Critical Thinking
Ability,” stated that the objective of this research was
Furthermore, Yahaya et al. (2017) explored students’ to produce a trustworthy interactive e-book using the
opinions of using smartphone applications about Learning Content Development System (LCDS) and a
motivation, curiosity, and confidence in a study titled scientific approach to energy resources in order to
“Effectiveness of mobile learning application in enhance students’ critical thinking abilities as well as
enhancing reading skills in the Chinese Language and to assess the readability and usability of the created e-
towards post-attitudes.” Additionally, it looked into book. It employs a process of study and development.
how smartphone apps affected people’s ability to read The created e-book includes essay questions, an
Chinese. Quantitative information was gathered using interactive test, simulations, animations, and a learning
a 4-point Likert scale questionnaire and oral pre-and video. The e-content books and design have undergone
post-tests. The results of this study, which involved 53 verification, and the conclusions are “quite
pupils, showed that test scores rose after receiving appropriate” in terms of quality and “proper to use” as
instruction for four weeks straight. The findings guidance for students researching the topic of energy
resources using a scientific method that fosters critical
showed that students liked and found it easier to use
thinking. The one-on-one test results show that the e-
smartphone applications than conventional methods
book has excellent readability and is very user-
for teaching and learning. Incorporating a smartphone
friendly, scoring 3, 68, and 3, 60, respectively.
application can also increase motivation and interest,
but more assurance is required. Finally, the researchers Moreover, Demir and Akpinar’s (2018) study, entitled
address how this study’s implications might affect “The Influence of Mobile Learning Applications on
mobile learning. Students’ Academic Achievement and Attitudes
Toward Mobile Learning,” concluded a clear
In line with earlier studies, a study by Alqahtani and
correlation between student performance and mobile
Mohammad (2015) entitled “Mobile Applications’
learning. The pupils also appreciated the potential for
Impact on Student Performance and Satisfaction”
mobile learning to increase their motivation
discovered that students’ opinions of their behavior, significantly.Furthermore, a study by Farah and Abu-
performance, and satisfaction with their study of the Dawood (2018) entitled “Using Mobile Phone
Holy Quran are positively correlated with their use of Applications in Teaching and Learning” showed that
the mobile app “Say Quran.” In this study, 118 Al- most students responded favorably to using mobile
Imam Muhammed Bin Saud Islamic University’s applications in teaching and learning. Every student
College of Computer Sciences and Information also owned a smartphone and used various kinds of
Systems students were asked to use the mobile educational software. The research found that most
applications to aid in their study of the Holy Quran. A students preferred using mobile applications for
survey was then distributed to gather information. The teaching and studying. The outcomes also
study provided evidence of a positive relationship demonstrated that the interventions improved student
between students’ reported behavior, performance, and comprehension and learning. This study examined
contentment while studying the Holy Quran using the how Reading Strategy Instruction (RSI) was used in a
mobile app “Say Quran.” reading class to support second language learners in
Laurente et al. 1020/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
developing their critical thinking skills. education. Understanding the benefits of critical
thinking in the context of student learning has gained
In addition, a study entitled “Promoting Students’ greatly in importance as educators attempt to prepare
critical thinking through reading strategy instruction in students for the dynamic demands of the twenty-first
a reading class” by Rani (2016) demonstrated that century. This subsequent review of the relevant studies
incorporating RSI into the reading lesson aided in the seeks to provide useful perspectives on the enormous
participants’ improvement of their critical thinking data of studies on the benefits of critical thinking for
skills. The participants were able to challenge the students' learning experiences.
text’s facts, identify its flaws, and build connections to
the text and the outside world through RSI. They were According to Verburgh and colleagues (2014), a study
also able to develop persuasive arguments and back entitled “Effectiveness of critical thinking instruction
them up with examples from the real world. in higher education.” Discovered that instructional and
student-related variables were significant factors in the
Similarly, a study by Kusmaryani et al. (2019) entitled success of critical thinking (C.T.) education in their
“The Influence of mobile applications on Students’ systematic review of intervention studies. The study
speaking skills and critical thinking in English found that pre-existing student academic performance
language learning” showed how students’ speaking and instructional methods, including C.T. teaching
and critical thinking in English could be improved approaches and methods, had a moderate impact on
using mobile applications as learning aids. Although the success of C.T. in higher education. The findings
their internet connection needed to be addressed, revealed a propensity for C.T. integration within
students were enthused in exploring and using mobile academic areas, but the study did not provide
learning tools, according to the interview. Teachers conclusive evidence linking specific teaching
and students can enhance the quality of teaching and techniques to improved learning outcomes.
learn with the help of technology in the form of mobile
learning applications. Any subject can bene t from Secondly, a study by Popil (2011) entitled “Promotion
selecting pertinent mobile learning applications. of critical thinking by case study as a teaching
method” revealed that this research could be helpful
Lastly, a study by Ismael et al. (2018) entitled “The for other higher education institutions in the more
Effect of Mobile Problem-Based Learning Application amazing Gulf. If the case study method is used, it will
Dic-Science PBL on Students’ Critical Thinking” considerably advance instructors’ knowledge of
discovered that the applications enhanced the students’ leadership and group dynamics in promoting active
critical thinking. The statistics showed that the learning. Additionally, skills for critical thinking,
software enhanced the students’ critical thinking skills. which are essential for building leadership, will
The statistics also showed that the intervention probably be developed.
involved seven phases in fostering students’ critical
thinking. This project adds a mobile problem-based Furthermore, Sarigoz (2012), in his study,
critical thinking paradigm to scientific education. The “Assessment of the high school students’ critical
framework also directs science courses to promote thinking skills,” noted that the critical thinking skills
critical thinking in pupils.The review of related studies of high school students are becoming increasingly
above concerns the effects of reading mobile crucial globally. Particularly, educators are becoming
applications in education. Mobile apps are utilized as more conscious of the importance of students’
teaching tools to help students study more effectively. education. According to the study results, children’s
Students have bene ted from mobile applications in critical thinking skills differ depending on the type of
terms of their academic performance. As a result, even high school they attend, including Anatolian High
if mobile applications have improved our lives and School, Science High School, and Vocational High
made them more accessible, they have also had School.
adverse effects.
Additionally, Duran and Dokme (2016), in their study
The Benefits of Critical Thinking for Students’ entitled “The Impact of an Activity Set Created Using
Learning the Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) Methodology in the
Unit “Particulate Structure of Matter,” stated that the
Critical thinking is widely acknowledged as an study aimed to determine the impact on students’
essential skill that enables students to effectively critical-thinking abilities in science and technology
handle complicated barriers, analyze information, and courses. Ninety-sixth graders from four sixth-grade
make well-informed decisions in the field of secondary school courses took part in the study. The
Laurente et al. 1021/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
researchers developed the guided activity set using the the traditional lecture-based teaching approach in
IBL methodology as part of the study to assess how terms of aiding nursing students in developing their
the IBL approach affected the students’ critical- critical thinking abilities. Participants in the CBL
thinking abilities in science and technology courses. program regularly outperformed those in the didactic
This study included pre- and post-test control group program on the CCTST and its subscales. The study’s
experimental designs. The study’s findings implications for nursing research and nursing
demonstrated how guided learning activities developed education are numerous. The results show that careful
using the IBL technique greatly in influenced students’ case-based training utilizing CBL can improve
capacity for critical thought in science and technology students’ C.T. talents as a substitute for the didactic
courses. lecture-based teaching techniques that have become
extremely popular in school curricula for other
Furthermore, a study by Susilo et al. (2020) entitled disciplines and the training of healthcare professionals.
“Learning Model to enhance student’s critical thinking In order to help students develop the requisite
skills and scientific attitudes,” found that Problem- cognitive skills (C.T.), which could then improve
Based Learning (PBL), Predict, Observe, Explain patient outcomes through nursing care, CBL should be
(POE). With a value of 0.005, their combination encouraged in nursing courses, claims the study.
(PBLPOE) affected the student’s capacity for critical
thought and attitudes toward science in Biology. The Additionally, Hindun et al. (2019), in their study
findings of the LSD test revealed that while PBLPOE entitled “Critical Thinking Skills: The Academic
notably differed from POE and conventional, it did not Ability, Mastering Concepts, and Analytical Skills of
significantly differ from PBL in improving students’ Undergraduate Students,” used the findings of this
critical thinking. The LSD test on students’ attitudes study to pinpoint the characteristics connected to
toward science also showed that PBLPOE significantly students’ critical thinking abilities. Additionally, the
exceeded PBL, POE, and traditional in transforming resu lt s sh o wed th at the th ree p r ed i c to r
students’ attitudes. The post-test result with the highest factors—concept mastery, academic aptitude, and
score came from the PBLPOE class. Therefore, analytical skill—made a substantial impact on
PBLPOE can be used to improve students’ Biology student’s critical thinking abilities at rates of (3.84%),
performance. (32.25%), and, respectively, (54.26%). As a result, the
results of this study could be a crucial reference point
Developing a diagnosis as part of the nursing process for creating a teaching strategy that encourages critical
needs various critical 2 thinking skills, according to thinking in students.
Crossetti et al. (2013) in their study, “Critical thinking
skills in the nursing diagnosis process.” This study Lastly, a study by Sarwanto et al. (2017) entitled
examined how critical thinking skills and the steps of “Development of an e-module combining science
the nursing diagnostic process are related. As a result, process skills and dynamics motion material to
the nursing diagnostic process is used in clinical increase critical thinking skills and improve student
practice and education to inform measures to help learning motivation senior high” showed how science
people acquire critical thinking abilities.Moreover, a process skills were incorporated into the development
study by Shirazi and Heidari (2019) entitled “The of the electronics module in order to boost students’
Relationship Between Critical Thinking Skills and critical thinking skills and motivation. Implementing
Learning Styles and Nursing Students’ Academic electronic scientific modules is a great technique to
Achievement” concluded that students’ critical promote students’ interest in science. According to
thinking skill scores were tolerably low study. As statistical analysis, the control class and the learning
teachers create academic lesson plans, it is imperative motivation grade sample substantially differ by a
to consider expanding critical thinking. As there is a factor of 0.027, which is less than the significance
strong association between learning style and level of 0.05. The data analysis for the study showed
academic success, teachers should consider the that process skills in physics-based science are more
dominant style of each class when designing lessons effective in boosting student motivation than
and use appropriate teaching tactics that take the traditional learning methods.
dominant type into account.
Critical thinking is a proactive and efficient procedure
Similarly, a study by Kadduora (2011) entitled of formulating, utilizing, examining, integrating, and
“Critical thinking skills of nursing students in lecture- scrutinizing knowledge as a framework for belief and
based teaching and case-based learning,” found that action. In conclusion, students place a high value on
the case-based learning strategy had been superior to critical thinking abilities. Reasoning abilities must be
Laurente et al. 1022/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
used when performing critical thinking. It is vital to who used reading mobile applications.
learn rather than absorb information actively. This
essay investigates the impact of critical thinking on The researcher selected the proportional sample at
students’ ability and enthusiasm to learn. Therefore, random. The selection was made with subgroups to
since it is vital for students to think critically today, prevent biases and guarantee that everyone could be
technology and mobile applications used in teaching chosen. Researchers also found that most Maguikay
and learning should also aid in developing these skills. High School students utilize reading apps for their
Mobile applications are becoming increasingly phones, which could improve their capacity for critical
common because of their capacity to simplify daily thought. Due to their high susceptibility to the
tasks. Mobile applications offer more advantages than researcher’s study, junior high school students from
disadvantages. Additionally, using mobile apps could Maguikay High School were chosen to participate.
aid in developing higher-order thinking skills in
children, such as critical thinking. Research Instruments
The researchers employed a survey questionnaire since
Methodology quantitative studies commonly make use of
questionnaires. A 2-page standardized questionnaire
was used in this study. Each questionnaire is necessary
Research Design for the study to understand each variable’s effects
fully. Each factor has a unique questionnaire. Six
This research utilized correlational design under a questions pertain to the first variable, mobile
quantitative approach. Bhandari (2020) defines applications, and eight to the second variable, critical
quantitative research as the process of collecting and thinking.
analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find
patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal The first questionnaire was adapted from Henry and
relationships, and generalize results to wider Mohamad (2021) in their study entitled “The Use of
populations. In a correlational analysis design, mobile technology in Enhancing the Critical Reading
researchers utilized the correlation statistic test to Skills of Pre-University ESL.” The questionnaire was
assess the degree of association between two or more scored using a scale. Respondents can express how
defined and calculated variables or ranking sets, strongly they agree or disagree with the questions on
according to Creswell (2012). utilizing mobile applications using a rating system, a
five- or seven-point scale. The questionnaire includes
The quantitative approach was acceptable because the inquiries on respondents’ use of mobile apps.
researchers collected quantifiable data to generate
accurate and trustworthy results. A correlational The second questionnaire was also adapted from
methodology works well for this study. The Henry and Mohamad (2021) in their study entitled
researchers next assessed how the students’ critical “The Use of mobile technology in Enhancing the
thinking abilities were correlated by reading mobile Critical Reading Skills of Pre-University ESL.” It talks
applications. about how mobile applications impact respondents’
critical thinking abilities.To provide the proper
Research Sample and Sampling Technique answers, respondents must read and understand the
questions. They must check the respective boxes to
There were 181 junior high school students in grade 10 indicate whether they strongly agree, agree, strongly
at Maguikay High School for the academic year 2022– disagree, disagree, or are neutral. This questionnaire is
2023, and the researchers used a sample of 125 included in the study since it perfectly complements
responders through the use of Slovin’s formula. the study’s design and will solicit many respondents
Because they could respond to the survey who will help the researchers collect data. The
questionnaire, the researchers specifically selected researchers used this tool to assess how much reading
junior high school students in grade 10. For this instruction can enhance students’ capacity for critical
survey , the r esearch ers used p r o b ab ility thought.
sampling—more specifically, simple random
sampling. Simkus (2022) defines simple random Data Procedure
sampling as a sampling technique in which there is an
equal chance that every member of a population will When the researchers were given the go-ahead to
be chosen through a fair selection procedure. The conduct the study, they used a two-page questionnaire
survey questionnaires were answered by respondents to distribute the survey to the respondents. The topic of
Laurente et al. 1023/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
the study was then discussed among the researchers. Survey Phase
Data collection involved carefully acquiring the
necessary information to prevent data distortions and The respondents’ permission was sought by the
ensure that the researchers’ analysis is free of researchers in order to conduct the study. After
erroneous assumptions (Sapsford & Jupp, 2006, as reviewing the affidavit of consent’s specifics, the
cited by Parveen & Showkat, 2017). In order to ensure researchers guided the participants through the
the validity of the study, the researchers employed survey’s questions.
proper data collection methods.
Retrieval Phase
At Maguikay High School, information was gathered
from 125 respondents. They responded to a two-page Once the participants had completed the survey and
provided their requests, the researchers examined and
survey form with two major components based on the
collected each questionnaire.
two variables of the study.
Tabulation and Tallying Phase
Phase 1. Approval of the Transmittal Letters and
the Survey Questionnaire Once they had gathered all the required information
and the complete result, the researchers tallied the
The researchers formally reviewed the study. Before findings.
beginning the study, the researchers prepared the
relevant paperwork, such as the transmittal letter, Statistical Treatment of Data
survey questionnaire, and informed consent. The
research professor looked over the survey According to Vishak (2022) stated that the statistical
questionnaires before sending them. The transmittal processing of data is a method used to transform
letter, survey, and final papers were then signed by the uninterrupted raw data into something that can be
research adviser, along with the declaration of understood. The researchers calculated the percentage
permission. Before sending the transmittal letter, the in each table and determined the mean of each
survey, and the affidavit of an agreement to the response using Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient in
principal’s junior high school office for final clearance order to scientifically assess and understand the data
to start the research, the researchers first received needs for the study.
approval from the research coordinator.
According to Laerd Statistics (2020), Pearson’s
Phase 2. Identification of the Research Setting and Correlation Coefficient (r) is a statistical indicator of
the linear relationship between paired data. Xy = is the
Respondents
total of the products of paired stocks, where x = is the
total of the x scores, y = is the total of the y scores, x2
The researchers selected Maguikay High School as the
= is the total of the x scores squared, and y2 = is the
study’s specific location, and Mandaue City was
total of the y scores squared. The aforementioned
chosen as the study’s general study environment.
formula may produce one of three results after
Finally, 125 people answered the researchers’ survey.
measuring the data to be collected. To test the
The respondents were likewise chosen via
significance of r, we need to use the t-test employing
straightforward random selection to gather sufficient
formula. If the t-value is greater than the critical value
data. (taken from the t-table), then reject the null hypothesis
and accept the alternative hypothesis. If the t-value is
Phase 3. Data Collection lesser than the critical value, then accept the null
hypothesis and reject the alternative hypothesis. If the
The respondents’ responses to the questionnaire were null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative
guided by the details in the affidavit of consent. The hypothesis is accepted, meaning there is a significant
respondents completed the questionnaire, and the relationship between to variables, likewise, if the null
researchers then started tallying, recording, and hypothesis is accepted and the alternative hypothesis is
analyzing the results. rejected then there is no significant relationship
between the two variables.
Distribution Phase
Results that are negative show a strong inverse link
Participants first received 125 survey sheets from the between the two variables. If the measurement returns
researchers. a value of zero, the two variables are not related.
Laurente et al. 1024/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
Alternatively, if the measurement returns a value of of the respondents’ usage of reading mobile
zero, the two variables have no relationship. If the applications. The weighted mean of the respondents’
outcome is favorable, it can be said that there is a usage of reading mobile applications shown in the
significant correlation between the two variables. table.
The researchers decided to use a correlational design Table 1. Reading mobile applications are useful in
and were encouraged to use Pearson’s Correlation reading and learning
Coefficient (r) by their research statistician.
Ethical Considerations
Hasan et al. (2021) claim that “ethics in research”
refers to the guidelines for conducting proper research.
It also guides and advises researchers, ensuring they
adhere to a strict code of ethics. The use of ethical
norms was prioritized when performing the study. The
researchers conducted their study with deference,
discretion, candor, and objectivity. The researchers
used these ethical considerations to guarantee an
objective quantitative result that would act as the
foundation for their arguments. After receiving the
respondents' complete agreement before the survey,
consideration was employed. The use of con
confidentiality prevented outcomes that others have
obtained and are working on from being revealed. In
order to guarantee that the data was accurate and had
not been tampered with, transparency was
accomplished by reporting the figures acquired in real
time during this phase.
Social responsibility was upheld by ensuring that
participants in the study would not be forced or placed
in uncomfortable situations. The researchers behaved
impartially, putting aside their own subjective and
individualized viewpoints. The research participants
were kept safe from injury, and awkward, frightful, or
offensive situations were made sure to avoid them.
The goal of the study, the types of information that
would be collected from the respondents, and how that
information would be used were brie y explained by Table 1 shows that the phrase “Reading mobile
the researchers to the respondents. The researchers applications are useful in reading and learning”
made the respondents aware that their full consent appears in the highest weighted mean (4.15).
would be obtained before they took part in the study. Additionally, the lowest mean (3.52) asserts, “Reading
The researchers concluded that these are the best mobile applications requires less effort to become
ethical principles to employ to guarantee the skilled.” This indicates that students use mobile
respondents’ safety and the veracity of the data utilized reading applications to develop their learning and
in this study, which would be factual and unaltered. reading capabilities, primarily due to convenience.
Supporting this notion, a study conducted by Leal et
Results and Discussion al. (2019) indicated that using mobile devices can aid
students in enhancing their critical thinking skills and
applying their learning. According to Yahaya et al.
The weighted average of Reading Mobile (2017), students preferred using smartphone
Applications applications to traditional methods for teaching and
learning, citing ease and convenience as reasons.
With a sample size of 125 displays the weighted mean However, although students find it challenging to learn
Laurente et al. 1025/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
to use them, the same study suggested that students devices are spreading because they make regular tasks
found using smartphone applications during the more accessible. Applications on mobile devices
teaching and learning process more accessible and provide more benefits than drawbacks. Additionally,
enjoyable compared to conventional techniques. mobile apps might help kids learn higher-order
Ultimately, leveraging reading mobile applications is cognitive abilities like critical thinking.
enjoyable and practical and can help students develop
their learning and reading skills. Table 2. Using reading mobile applications improves
my critical reading for English text
The weighted mean of Critical Thinking Skills
The table shows the weighted mean of the critical
thinking skills with the sample (n)=125
Table 2 shows that the statement, “Using reading
mobile applications improves my critical reading for
English text,” has the highest weighted mean of 4.30,
and based on verbal interpretations, students
overwhelmingly concur with doing so. Students agree
that reading mobile applications helps them develop
their critical thinking abilities, as evidenced by the
lowest mean (4.04), which reads, “Reading mobile
applications made it possible for me to accomplish
more critical reading practice that would otherwise be
impossible.” Students concur that using mobile
applications helps them develop their critical thinking
skills. This is followed by the overall mean of variable
one, reading mobile applications, with a mean of
(4.13). This suggests that the respondents concur that
using reading-related mobile applications can aid in
developing their critical thinking abilities and
knowledge and reading abilities. The researchers
evaluate, understand, and offer rational arguments by
using critical thinking. The goal of critical thinking is
to create new knowledge, understandings, hypotheses,
and beliefs that are reliable and perceptive. Critical
thinking entails assessing and evaluating data,
arguments, and circumstances in utilizing suitable
criteria. Critical thinking is the capacity to integrate
and synthesize information to be intelligently applied
to activities for well-informed decision-making and
effective problem-solving (Heard & Co., 2020).
Additionally, critical thinking is a commonly
acknowledged educational objective (Hitchcock,
2018). Its meaning is under dispute, but the conflicting
definitions can be seen as various interpretations of the
same fundamental idea: thorough consideration
directed toward a purpose. Overall, the ability to think
critically will help the student thrive, boosting their
critical thinking. Therefore, employing mobile
applications can develop students’ capacity for critical
thought. However, using technology and mobile
applications in teaching and learning could help
students hone these skills, given that today’s students
are urged to think critically. Applications for mobile
Laurente et al. 1026/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
Relationship between Reading Mobile Applications learning has transformed into an internet-based
and Students’ Critical Thinking Skills learning environment that provides unique
opportunities for students to engage with the subject
Table 3. Relationship between Reading Mobile matter and promote profound learning. Consequently,
Applications and Students’ Critical Thinking Skills mobile reading applications are utilized as
instructional resources to elevate students’ critical
thinking skills.
Students. Students will have a greater understanding of
critical thinking and
Reading on mobile devices. Additionally, instructing
students on using reading mobile applications
Table 3 displays the Pearson-r Correlation that was efficiently can assist students in developing their
utilized to determine the link between two variables, critical thinking abilities.
critical thinking abilities and reading mobile Parents. Parents will thus have a fundamental
applications. A significant positive association understanding of reading mobile applications and
between the two variables is seen in Table 5. It is that r critical thinking. Parents might find this study helpful
= 0.61, indicating a significant positive correlation in understanding why their children utilize reading
between the two variables. When there is a high link, mobile apps. Additionally, it can teach kids how to use
the correlation coefficient is greater than 0. When the mobile apps effectively.
correlation coefficient is 1.0, two variables are entirely Teachers. The teacher could find the study’s
associated. (Nickolas, 2021). Both variables change information and research proposals helpful. They
when one of them changes. While this does not always could assess the student’s proficiency with using
imply that one variable directly affects or modifies the reading mobile applications thanks to the study’s
other, it does suggest that both variables always move findings.
together and are most likely closely related. Reject H0 Researchers. They can learn more about writing
because the t-value (8.52) is greater than the critical research papers from this study. This may also remind
value (1.9794) shows a substantial positive correlation us that a team should conduct group research rather
and indicates that reading mobile applications have a than a single individual.
significant relationship on students’ capacity for Future Researchers. This study can be their guide for
critical thought. This suggests that mobile reading apps generating excellent research output, mainly if they are
are utilized as teaching tools to enhance student’s concerned with reading mobile applications to improve
learning capacities, specifically their critical thinking critical thinking abilities. Additionally, based on the
abilities. According to a study by Leal et al. (2019), knowledge and information gathered for this inquiry,
students’ use of mobile devices can help them apply they could get crucial advice for strengthening their
their learning and develop critical thinking skills. research. The researchers recommend these relevant
Additionally, since it is vital for today’s students to books: (1) The Effect of E-Book Use on Students’
think critically, technology and mobile applications Academic Perception, (2) The Efficiency of E-Book
used in teaching and learning should support students Use in Developing Students’ Critical Thinking Skills,
in strengthening their critical thinking abilities. Thus, (3) The Use of Reading Mobile Applications in
reading mobile applications can aid students in D e v e l o p i n g S t u d e n t s ' E n g li s h R e ad in g
learning new information, improving their reading Comprehension, and (4) The Effect of Reading Mobile
abilities, and sharpening their critical thinking abilities. Applications on Students’ Self-Esteem (5) Mobile
applications’ effects on students’ English-speaking
abilities
Conclusion
References
In contemporary times, it is essential for students to
develop their critical thinking capabilities, and Abarquez, A. M. (2021). Pronunciation Mobile Application for
technology and mobile applications can aid in this Oral Communication. International Journal of English Language
process. Students can make use of reading applications Studies, 3(2), 01- 09.
effortlessly as well. Valconi (2018) argues that mobile
Alqahtani, M., & Mohammad, H. (2015). Mobile applications’
impact on student performance and satisfaction. Turkish Online
Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 14(4), 102-112.
Laurente et al. 1027/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
Basal, A., Yilmaz, S., Tanriverdi, A., & Lutfiye, S. (2016). Technology in Enhancing the Critical Reading Skills of Pre-
Effectiveness of mobile applications in vocabulary teaching. University ESL Students. Creative Education, 12(03), 678.
Contemporary educational technology, 7(1), 47-59.
Hitchcock, D. (2018). Critical thinking.
Bezanilla, M. J., Fernández-Nogueira, D., Poblete, M., & Galindo-
Domínguez, H. (2019). Methodologies for teaching-learning critical Ismail, N. S., Harun, J., Salleh, S., & Zakaria, M. A. Z. M. (2016).
thinking in higher education: The teacher’s view. Thinking skills Supporting students’ critical thinking with a mobile learning
and creativity, 33, 100584. environment: a meta-analysis. In 10th International Technology,
Education and Development Conference [Internet]. Valence, Spain:
Birgili, B. (2015). Creative and critical thinking skills in problem- INTED2016 Proceedings (pp. 3746-55).
based learning environments. Journal of Gifted Education and
Creativity, 2(2), 71-80. Kaddoura, M. A. (2011). Critical Thinking Skills of Nursing
Students in Lecture-Based Teaching and Case-Based Learning.
Bittencourt, G. K. G. D., & Crossetti, M. D. G. O. (2013). Critical International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning,
thinking skills in the nursing diagnosis process. Revista da Escola de 5(2), n2.
Enfermagem da USP, 47, 341-347.
Kusmaryani, W., Musthafa, B., & Purnawarman, P. (2019, April).
Can, M. H. (2016). Use of mobile application: Means of The influence of mobile applications on students’ speaking skill and
communication between parents and class teacher. World Journal on critical thinking in English language learning. In Journal of Physics:
Educational Technology: Current Issues, 8(3), 252-257. Conference Series (Vol. 1193, No. 1, p. 012008). IOP Publishing.
Chee, K. N., Yahaya, N., & Ibrahim, N. H. (2017). Effectiveness of Leal, L. R., Ortega, M. V., & Montes, L. P. (2019, November).
mobile learning application in improving reading skills in Chinese Mobile devices for the development of critical thinking in the
language and towards post-attitudes. International Journal of Mobile learning of differential equations. In Journal of Physics: Conference
Learning and Organisation, 11(3), 210-225. Series (Vol. 1408, No. 1, p. 012015). IOP Publishing.
Crescente, M. L., & Lee, D. (2011). Critical issues of m-learning: Limbaco, J. B., Romerde, K. E. N., Estilo, J. P., Mondelo, B. C., &
design models, adoption processes, and future trends. Journal of the Walag, A. M. P. (2021). Use and Perceptions of Students of a
Chinese institute of industrial engineers, 28(2), 111-123. Mobile Application as a Classroom Response System. Journal of
Innovations in Teaching and Learning, 1(1), 29-35.
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational Research: Planning, Conducting
and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research, 4th ed. Maheshwari (2018) claims that the goal of the causal comparative
Boston, MA: Pearson Education. technique is to establish links between occurrences and
circumstances.
Dawson, C. (2009) Introduction to Research Methods: A Practical
Guide for Anyone Undertaking a Research Project (4th ed.). Oxford:
Martin, K., & Shilton, K. (2016). Putting mobile application privacy
How to Books.
in context: An empirical study of user privacy expectations for
mobile devices. The Information Society, 32(3), 200-216.
Demir, K., & Akpinar, E. (2018). The Effect of Mobile Learning
Applications on Students’. Academic Achievement and Attitudes
Muhammadiyeva, H., Mahkamova, D., Valiyeva, S., & Tojiboyev, I.
toward Mobile Learning. Malaysian Online Journal of Educational
(2020). The role of critical thinking in developing speaking skills.
Technology, 6(2), 48-59
International Journal on Integrated Education, 3(1), 62-64.
Duran, M., & Dökme, I. (2016). The effect of the inquiry-based
Nayebi, F., Desharnais, J. M., & Abran, A. (2012, April). The state
learning approach on student’s critical-thinking skills. Eurasia
of the art of mobile application usability evaluation. In 2012 25th
Journal of Mathematics Science and Technology Education, 12(12).
IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering
Farrah, M., & Abu-Dawood, A. K. (2018). Using mobile phone (CCECE) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
applications in teaching and learning process. International Journal
Perdana, F. A., Sarwanto, S., Sukarmin, S., & Sujadi, I. (2017).
of Research in English Education, 3(2), 48-68.
Development of e-module combining science process skills and
Fitriani, A., Zubaidah, S., Susilo, H., & Al Muhdhar, M. H. I. dynamics motion material to increasing critical thinking skills and
(2020). PBLPOE: A Learning Model to Enhance Students’ Critical improve student learning motivation senior high school. In
Thinking Skills and Scientific Attitudes. International Journal of International Journal of Science and Applied Science: Conference
Instruction, 13(2), 89-106. Series (Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 45-54).
Hasan, N., Rana, R. U., Chowdhury, S., Dola, A. J., & Rony, M. K. Permana, T. I., Hindun, I., Rofi’ah, N. L., & Azizah, A. S. N.
K. (2021). Ethical considerations in research. Journal of Nursing (2019). Critical thinking skills: The academic ability, mastering
Research, Patient Safety and Practise (JNRPSP) 2799-1210, 1(01), concepts, and analytical skill of undergraduate students. JPBI (Jurnal
1-4. Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia), 5(1), 1-8.
Hasan, M. F., Suyatna, A., & Suana, W. (2018). Development of Persky, A. M., Medina, M. S., & Castleberry, A. N. (2019).
interactive e-book on energy resources to enhance student’s critical Developing critical thinking skills in pharmacy students. American
thinking ability. Tadris: Jurnal Keguruan dan Ilmu Tarbiyah, 3(2), journal of pharmaceutical education, 83(2).
109-121.
Phongtraychack, A., & Dolgaya, D. (2018). Evolution of mobile
Henry, C. C., & Mohamad, M. (2021). The Use of Mobile applications. In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 155, p. 01027).
Technology in Enhancing the Critical Reading Skills of Pre- EDP Sciences.
University ESL Students. Creative Education, 12, 678-69.
Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies
Henry, C. C., & Mohamad, M. (2021). The Use of Mobile as teaching method. Nurse education today, 31(2), 204-207.
Laurente et al. 1028/1029
Psych Educ, 2023, 11: 1017-1029, Document ID:2023 PEMJ1032, doi:10.5281/zenodo.8229487, ISSN 2822-4353
Research Article
Rani, K. V. (2016). Promoting students’ critical thinking through Versoza, D. M., De Las Peñas, M., Sarmiento, J. F., Aberin, M. A.
reading strategy instruction in a reading class. Indonesian JELT: Q., Tolentino, M. A. C., & Loyola, M. L. (2021). USING MOBILE
Indonesian Journal of English Language Teaching, 11(2), 133-151. TECHNOLOGY TO PROMOTE HIGHER-ORDER THINKING
SKILLS IN ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS.
Ross, P. T., & Bibler Zaidi, N. L. (2019). Limited by our limitations.
Perspectives on medical education, 8(4), 261-264 Wallmann, H. W., & Hoover, D. L. (2012). Research and critical
thinking: An important link for exercise science students
Rouse, M. (2016). What is an Electronic Book (E-Book)? - transitioning to physical therapy. International journal of exercise
Definition from Techopedia. Techopedia.com. science, 5(2), 1.
Sarigoz, O. (2012). Assessment of the high school students’ critical Affiliations and Corresponding Information
thinking skills. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46,
5315-5319. Sheniel L. Laurente
Maguikay High School
Shirazi, F., & Heidari, S. (2019). The relationship between critical Department of Education – Philippines
thinking skills and learning styles and academic achievement of
nursing students. The journal of nursing research, 27(4), e38. Jamaira D. Diva
Maguikay High School
Showkat, N., & Parveen, H. (2017). Non-probability and probability
sampling. Media and Communications Study, 1-9.
Department of Education - Philippines
Adrian M. Abarquez, EdD (c)
Simkus, J. (2022, January 26). Simple Random Sampling |
Definition, Steps & Examples Simply Psychology. Maguikay High School
Department of Education - Philippines
Theofanidis, D., & Fountouki, A. (2018). Limitations and
delimitations in the research process. Perioperative Nursing- Rhino Rienz L. Casas, LPT
Quarterly scientific, online official journal of GORNA, 7(3 Maguikay High School
September-December 2018), 155-163. Department of Education - Philippines
Tiruneh, D. T., Verburgh, A., & Elen, J. (2014). Effectiveness of Airis Kim Codiñera, PhD (c)
critical thinking instruction in higher education: A systematic review Mandaue City Comprehensive National High School
of intervention studies. Higher Education Studies, 4(1), 1-17.
Department of Education - Philippines
Valconi, R. (2018). Principles and Applications of Mobile Learning
and Technologies. Pressbooks.pub. Jomarie Alex Guinita, MAEd (c)
Catarman Integrated School - Philippines
Laurente et al. 1029/1029
You might also like
- Digital Marketing AssignmentDocument40 pagesDigital Marketing AssignmentSUDIP100% (2)
- Sad 2 Group 4 - Revised Version by Mam RitzDocument22 pagesSad 2 Group 4 - Revised Version by Mam RitzRyan Danila GalloNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument27 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundCamille CasugaNo ratings yet
- Arjay Coronel Topic Proposal TemplateDocument4 pagesArjay Coronel Topic Proposal TemplateAndanteNo ratings yet
- (IJIT-V3I2P2) : Tarek H.Ahmed, L. Abdul Kadhar Sheriff, A.ShameemFathimaDocument6 pages(IJIT-V3I2P2) : Tarek H.Ahmed, L. Abdul Kadhar Sheriff, A.ShameemFathimaIJITJournalsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Preference Level of Education-Based Mobile Application Reference To Engineering College StudentsDocument9 pagesA Study On Preference Level of Education-Based Mobile Application Reference To Engineering College StudentsMiddle East Journal of Applied Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Students' Perceptions of Mobile Apps A Needs Analysis of EFL LearnersDocument14 pagesStudents' Perceptions of Mobile Apps A Needs Analysis of EFL LearnersNaveed AnvarNo ratings yet
- Mobile PhoneDocument5 pagesMobile PhoneFizza ChNo ratings yet
- Chap 12345 Without ReferencesDocument35 pagesChap 12345 Without ReferencesChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Computers & Education: Janet Mannheimer Zydney, Zachary WarnerDocument17 pagesComputers & Education: Janet Mannheimer Zydney, Zachary WarnerIvanzieo V SNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Application Among Grade 10 StudentsDocument21 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Application Among Grade 10 StudentsAira Jean OcopNo ratings yet
- Literature Review For Android Mobile ApplicationDocument6 pagesLiterature Review For Android Mobile Applicationgw0gbrwe100% (1)
- The Level of Ict Integration Using Samr Model of Kananga Senior High School LearnersDocument15 pagesThe Level of Ict Integration Using Samr Model of Kananga Senior High School LearnersClariess SoronoNo ratings yet
- Kearney & Burke & Schuck (2019) The iPAC ScaleDocument14 pagesKearney & Burke & Schuck (2019) The iPAC Scalemaria.diazvalencia.goetheNo ratings yet
- Smartphone Usability Framework Towards Self-Directed Learning in University of Dar Es SalaamDocument7 pagesSmartphone Usability Framework Towards Self-Directed Learning in University of Dar Es SalaamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- St2da Group 1 Research Chapter 1 2 3 4 5 Andres Carpela Castillo Claro Grefaldon Ibanez Mella Ortega PoliquitDocument19 pagesSt2da Group 1 Research Chapter 1 2 3 4 5 Andres Carpela Castillo Claro Grefaldon Ibanez Mella Ortega PoliquitNhyl Vinzie PesidasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877042814057784 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1877042814057784 MainStem EducationNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Effectiveness of MobDocument10 pagesAn Investigation of Effectiveness of MobJennie ManobanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningDocument15 pagesA Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningAkagami TVNo ratings yet
- Impact of Smartphones Usage On The LearnDocument20 pagesImpact of Smartphones Usage On The LearnAldrin GarciaNo ratings yet
- 645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Document4 pages645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Mobile Learning ApplicationDocument10 pagesDesign and Development of Mobile Learning Applicationradinal fadliNo ratings yet
- The Development of Android-Based Smartphone Learning Application On Teaching Reading ComprehensionDocument8 pagesThe Development of Android-Based Smartphone Learning Application On Teaching Reading ComprehensionLaser RomiosNo ratings yet
- Students Readiness To Engage With Mobile AppsDocument18 pagesStudents Readiness To Engage With Mobile AppsJulia TokarenkoNo ratings yet
- Kroook KrookDocument40 pagesKroook KrookAl ShokoNo ratings yet
- STEM12 CAPSTONE GROUP10 Checked 1 With PosterDocument30 pagesSTEM12 CAPSTONE GROUP10 Checked 1 With PostershennaNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Mobile-Assisted Vocabulary Learning ResearchDocument17 pagesA Systematic Review of Mobile-Assisted Vocabulary Learning ResearchNaveed AnvarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Pangan SanpedroDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Pangan SanpedroSophia San PedroNo ratings yet
- Presentation Imc651Document18 pagesPresentation Imc651Dysoxylon Far Daey HalimNo ratings yet
- Investigation of University Students SmaDocument17 pagesInvestigation of University Students SmaLuisa PuyoNo ratings yet
- Designing Pre-Test Questions As Phone Notifications - Studying TheDocument7 pagesDesigning Pre-Test Questions As Phone Notifications - Studying ThelstaanaNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of Effectiveness of MobDocument9 pagesAn Investigation of Effectiveness of MobGayatri GurunathNo ratings yet
- Final Tempate AutorecoveredDocument32 pagesFinal Tempate AutorecoveredRenson CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Critical Thinking Skills in ChemistryDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Critical Thinking Skills in ChemistryRizki AdityawanNo ratings yet
- Development of The Smartphone and Learning Inventory: Measuring Self-Regulated UseDocument17 pagesDevelopment of The Smartphone and Learning Inventory: Measuring Self-Regulated UseMinh Hong NguyenNo ratings yet
- PR2 G12Document19 pagesPR2 G12hazieldc10No ratings yet
- Mobile Applications' Impact On Student Performance and SatisfactionDocument11 pagesMobile Applications' Impact On Student Performance and SatisfactionSacamichi XdNo ratings yet
- Paper-Students' Attitudes Towards Mobile LearningDocument12 pagesPaper-Students' Attitudes Towards Mobile LearningShinya Hilal YamanakaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 1 3Document50 pagesFinal Chapter 1 3Johnly RebitoNo ratings yet
- Mine's ResearchDocument12 pagesMine's Researchearl9rivera-830280No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3 ThesisDocument26 pagesChapter 1 3 ThesisShane Khezia BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Review On Use of Mobile Apps For Language Learning: Ramya GangaiamaranDocument10 pagesReview On Use of Mobile Apps For Language Learning: Ramya GangaiamaranDylan TylNo ratings yet
- A Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningDocument16 pagesA Review of Current Studies of Mobile LearningAhmad Zaki IsmailNo ratings yet
- Robayo-Pinzon ET AL. (2021) - Does Excessive Use of Smartphones and Apps Make Us More ImpulsiveDocument10 pagesRobayo-Pinzon ET AL. (2021) - Does Excessive Use of Smartphones and Apps Make Us More ImpulsiveSamuel FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesMobile Literature Reviewgw32pesz100% (1)
- Smartphones and Students Academic PerforDocument39 pagesSmartphones and Students Academic PerforEhra Jiang KangraejoonNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Effects of Mobile Learning 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Effects of Mobile Learning 1api-301114110No ratings yet
- The Effect of Mobile Phone To Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students in San Pedro Relocation National High School S. Y. 2021-2022Document5 pagesThe Effect of Mobile Phone To Academic Performance of Grade 12 Students in San Pedro Relocation National High School S. Y. 2021-2022Markvince BaliliNo ratings yet
- Tugas TPI Kelas 2C-42518059Document5 pagesTugas TPI Kelas 2C-42518059aurelia rusliNo ratings yet
- Article 2 PDFDocument11 pagesArticle 2 PDFjessamaekempisNo ratings yet
- Local Media3568009793508657403Document16 pagesLocal Media3568009793508657403Azyr SampeloNo ratings yet
- Framework To Evaluate M-Learning Systems: A Technological and Pedagogical ApproachDocument8 pagesFramework To Evaluate M-Learning Systems: A Technological and Pedagogical ApproachPercy QuispeNo ratings yet
- Iconic2022Paper 22 PDFDocument13 pagesIconic2022Paper 22 PDFBenLyn ZaideNo ratings yet
- Mexico GoalDigger ResearchPaper-1Document14 pagesMexico GoalDigger ResearchPaper-1Jarius MacalaguingNo ratings yet
- Mobile Applications Within Education PDFDocument13 pagesMobile Applications Within Education PDFpantelios21No ratings yet
- 944 Me00003Document4 pages944 Me00003eren akarsuNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Mobile Application Usage AmDocument14 pagesFactors That Influence Mobile Application Usage AmNgoc ThuyNo ratings yet
- 3414 Ijite 01Document16 pages3414 Ijite 01ijiteNo ratings yet
- Understanding M-Learning: AbstrackDocument6 pagesUnderstanding M-Learning: AbstrackMohan LalNo ratings yet
- Study Materials Providers ApplicationDocument9 pagesStudy Materials Providers ApplicationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- How To Get Smartphones Into Classes: a guide for teachersFrom EverandHow To Get Smartphones Into Classes: a guide for teachersNo ratings yet
- Post-Pandemic Performance in Content Mastery and Cognitive Skills of Junior High School Students in ChemistryDocument7 pagesPost-Pandemic Performance in Content Mastery and Cognitive Skills of Junior High School Students in ChemistryPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalDocument11 pagesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Leadership Style of The School Heads As Correlates To The Level of Efficiency of Management Practices: Inputs For Professional Development PlanDocument15 pagesLeadership Style of The School Heads As Correlates To The Level of Efficiency of Management Practices: Inputs For Professional Development PlanPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Self-Concept and Level of Career Interest of Grade 9 Students at San Roque National High SchoolDocument10 pagesSelf-Concept and Level of Career Interest of Grade 9 Students at San Roque National High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Opportunities: The Key To Successful Destigmatization of Ex-OffendersDocument11 pagesUnlocking Opportunities: The Key To Successful Destigmatization of Ex-OffendersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Improving Mastery Level in Understanding Typhoon and Earthquake Preparedness Through STEM ModulesDocument12 pagesImproving Mastery Level in Understanding Typhoon and Earthquake Preparedness Through STEM ModulesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyDocument9 pagesThe Level of Learners' Performance in Mathematics Through Mind Mapping StrategyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Approach in Teaching Science Grade 7Document10 pagesMultimedia Approach in Teaching Science Grade 7Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Pet Loss: A Study On The Relationship Between Attachment Styles and Cognitive-Emotion Regulation Strategy Among Elderly Pet Owners in Quezon CityDocument12 pagesPet Loss: A Study On The Relationship Between Attachment Styles and Cognitive-Emotion Regulation Strategy Among Elderly Pet Owners in Quezon CityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Experiences of The Lebakeño Grade XI Students On Learning Mathematics in The Modular Approach: Basis For Learning FrameworkDocument34 pagesThe Experiences of The Lebakeño Grade XI Students On Learning Mathematics in The Modular Approach: Basis For Learning FrameworkPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Digital Orientation and Cyber-Victimization of College Students As Mediated by Their Attitude Toward CrimeDocument12 pagesDigital Orientation and Cyber-Victimization of College Students As Mediated by Their Attitude Toward CrimePsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Phonological Awareness of Kindergarten TeachersDocument14 pagesPhonological Awareness of Kindergarten TeachersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal100% (1)
- Influence of Teacher's Personality and Behavior On Students Character BuildingDocument8 pagesInfluence of Teacher's Personality and Behavior On Students Character BuildingPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Empowerment, Organizational Commitment, and Management Performance of Secondary School Heads in The New Normal in The Division of PalawanDocument16 pagesEmpowerment, Organizational Commitment, and Management Performance of Secondary School Heads in The New Normal in The Division of PalawanPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Game-Based and Project-Based Approaches: Their Effects On Grade 10 Learners' Performance in BiologyDocument9 pagesGame-Based and Project-Based Approaches: Their Effects On Grade 10 Learners' Performance in BiologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Exploring Factors Influencing The Non-Completion of Theses Among Teachers Pursuing A Master's Degree: A Case Study AnalysisDocument10 pagesExploring Factors Influencing The Non-Completion of Theses Among Teachers Pursuing A Master's Degree: A Case Study AnalysisPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Four Dimensions of Personnel Relational Work in Multi-Settings: Deriving Sociograms For Work Dynamism and DynamicsDocument17 pagesFour Dimensions of Personnel Relational Work in Multi-Settings: Deriving Sociograms For Work Dynamism and DynamicsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Love Corner: Enhancing Students' English VocabularyDocument10 pagesLove Corner: Enhancing Students' English VocabularyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Digital Marketing Strategies On Customer's Purchase Intention of Selected Fast-Food RestaurantsDocument14 pagesThe Influence of Digital Marketing Strategies On Customer's Purchase Intention of Selected Fast-Food RestaurantsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Gamification Strategy in Increasing The Grade 10 Student's Academic MotivationDocument9 pagesEffectiveness of Gamification Strategy in Increasing The Grade 10 Student's Academic MotivationPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ICT Students' Mastery Level in Setting Up Computer Networks Instructed Using CSS DroidDocument5 pagesGrade 11 ICT Students' Mastery Level in Setting Up Computer Networks Instructed Using CSS DroidPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Development and Comprehension Skills Through Word Games Among Grade 4 LearnersDocument11 pagesVocabulary Development and Comprehension Skills Through Word Games Among Grade 4 LearnersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Watching Movies With English Subtitles and Vocabulary Performance of SPA LearnersDocument12 pagesWatching Movies With English Subtitles and Vocabulary Performance of SPA LearnersPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Career Pathways of Technical, Vocational and Livelihood Senior High School Graduates in Pililla National High SchoolDocument10 pagesCareer Pathways of Technical, Vocational and Livelihood Senior High School Graduates in Pililla National High SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of T Math Modules To The Numeracy Level of Grade 6 Learners of Patabog Elementary SchoolDocument12 pagesEffect of T Math Modules To The Numeracy Level of Grade 6 Learners of Patabog Elementary SchoolPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- SQP2RS Strategy in Teaching Reading Using Different Text Types Among Grade 9 Learners: An Experimental InquiryDocument13 pagesSQP2RS Strategy in Teaching Reading Using Different Text Types Among Grade 9 Learners: An Experimental InquiryPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- School Operations in The Implementation of K-12 Curriculum and Performance of School Heads in CALABARZON: Basis For Curriculum Management FrameworkDocument8 pagesSchool Operations in The Implementation of K-12 Curriculum and Performance of School Heads in CALABARZON: Basis For Curriculum Management FrameworkPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Skills Among Teachers in The Division of Lanao Del NorteDocument14 pagesInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) Skills Among Teachers in The Division of Lanao Del NortePsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management Practices of Teachers and Academic Performance of Grade 3 Learners Across All Learning AreasDocument10 pagesClassroom Management Practices of Teachers and Academic Performance of Grade 3 Learners Across All Learning AreasPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Attitudes of College Students Toward Statistics and Research CoursesDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Attitudes of College Students Toward Statistics and Research CoursesPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Inspection at LC Gate: S.No Items Checked Observations/Irregularities Action To Be Taken byDocument3 pagesInspection at LC Gate: S.No Items Checked Observations/Irregularities Action To Be Taken byMadhav PrasadNo ratings yet
- Practice6 CSDocument12 pagesPractice6 CS87shf2xx2jNo ratings yet
- U3D - Archicad U 3D PDFDocument1 pageU3D - Archicad U 3D PDFBojan TokićNo ratings yet
- Lab9 IAA202Document4 pagesLab9 IAA202Đào Mạnh CôngNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking AssignmentDocument4 pagesPublic Speaking AssignmentSiti NursyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Monthly Service Bulletin: FEI Customer Service April 29, 2009Document14 pagesMonthly Service Bulletin: FEI Customer Service April 29, 2009Emad BNo ratings yet
- Telephone Directory July 2008Document112 pagesTelephone Directory July 2008manit SangwanNo ratings yet
- RHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance GuideDocument22 pagesRHUB3908 Hardware Maintenance Guideapiruck sukjingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionDocument39 pagesLecture 8: Gradient Descent and Logistic RegressionAshish JainNo ratings yet
- Publications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleDocument63 pagesPublications: Year No. Conference Vol. Firm Country Author TitleArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- PPB3033 Assignment Individual InstructionDocument3 pagesPPB3033 Assignment Individual InstructionKkaebsong hoonieNo ratings yet
- ABC Hospital - SolutionDocument12 pagesABC Hospital - SolutionMayank Patel100% (1)
- CGT 163 F20 Syllabus v20Document10 pagesCGT 163 F20 Syllabus v20brinda mehtaNo ratings yet
- Third Product Theme Blutooth Dual SIM AdapterDocument7 pagesThird Product Theme Blutooth Dual SIM Adapterabbasarslan221No ratings yet
- Tur Bulat or WebDocument13 pagesTur Bulat or WebBakkiyarajNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx XC7K160T-2FBG484i FpgaDocument13 pagesWhat Is Xilinx XC7K160T-2FBG484i FpgajackNo ratings yet
- Rns Institute of Technology: Text BooksDocument52 pagesRns Institute of Technology: Text Booksanu radhaNo ratings yet
- Application of Bernoulli's TheoremDocument8 pagesApplication of Bernoulli's Theoremram kumarNo ratings yet
- How To Temperature Map Cold Chain Equipment and Storage AreasDocument82 pagesHow To Temperature Map Cold Chain Equipment and Storage AreasramajayamNo ratings yet
- Ecosys M3860idn Ds (En)Document2 pagesEcosys M3860idn Ds (En)Sirajudin ahmad (udin)No ratings yet
- Cullen v. Zoom Video Communications, Inc., Case 5:20-cv-02155-SVK (Northern District of California)Document23 pagesCullen v. Zoom Video Communications, Inc., Case 5:20-cv-02155-SVK (Northern District of California)Law&CrimeNo ratings yet
- Snowflake Is Building A Marketplace For Retail Media DataDocument5 pagesSnowflake Is Building A Marketplace For Retail Media DataPaolo Caviedes SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Liquid Rotor Resistance Starter Conventional LrsDocument3 pagesLiquid Rotor Resistance Starter Conventional Lrsmayur3dhandeNo ratings yet
- LIEBHERR L586 - G6.0 D - 1815 SM PreviewDocument41 pagesLIEBHERR L586 - G6.0 D - 1815 SM PreviewGovanny MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Design of A Heat Exchanger Using HTRIDocument4 pagesDesign of A Heat Exchanger Using HTRIcenter010% (1)
- Brochure GT-Series PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure GT-Series PDFmaxbigosNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Automatic Schedule Generator and Managemant SystemDocument4 pagesReview Paper On Automatic Schedule Generator and Managemant SystemVaidehi LohiyaNo ratings yet
- Huawei ETP4830Document68 pagesHuawei ETP4830x00No ratings yet
- Text 5 - The Modern Age (Electricity)Document2 pagesText 5 - The Modern Age (Electricity)Cofe CodingNo ratings yet