Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics For Business Topic - Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions
Statistics For Business Topic - Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions
Uploaded by
Trần Lê Thiên VươngOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics For Business Topic - Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions
Statistics For Business Topic - Chapter 6 - Discrete Probability Distributions
Uploaded by
Trần Lê Thiên VươngCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6.
Discrete probability distribution Nguyen Thi Thu Van - October 24, 2022
A random variable is a rule that assigns a numerical value to each outcome in the sample space of a random experiment in
accordance with the following regulation: more than one outcome can be assigned to one numerical value, but two different PDF P(X=x) CDF P(X ≤ x)
Probability distribution
numerical values cannot be represented for the same outcome. for three coin flips 0.875 1.000
1.0 1.0
Possible events X P(X=x) 0.375 0.375 0.500
TTT 0 0.125 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.5 0.125
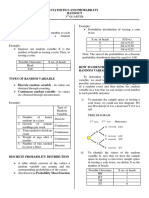
Discrete random variables have a countable number of distinct values. For example, tossing a coin three times, the number
HTT, THT, TTH 1 0.375 0.0
of times that the coin comes up head is a random variable 𝑋 = {0,1,2,3} 0.0
HHT, THH, HTH 2 0.375
Continuous random variables can have any value within an interval and can take on an infinite number of possible HHH 3 0.125
0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3
values (say, X = the average height of a random group of students). 1 Number of heads Number of heads
Expected value of a discrete random variable Variance of a discrete random variable Standard deviation A discrete probability distribution assigns a probability to each value of a discrete variable and can be described either by
𝑁 phương sai 𝑁
𝜎 = √𝜎 2 probability density/mass function (PDF/PMF) that shows the probability of each X–value
𝐸(𝑋) ≡ 𝜇 = ∑ 𝑥𝑖 𝑃(𝑥𝑖 ) 𝑉𝑎𝑟(𝑋) ≡ 𝜎 2 = ∑(𝑥𝑖 − 𝜇)2 𝑃(𝑥𝑖 )
𝑖=1 𝑖=1
độ lệch chuẩn cumulative distribution function (CDF) that shows the cumulative sum of probabilities, adding from the smallest to the largest X–value.
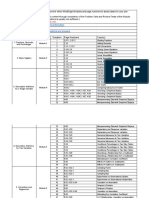
Uniform distribution Binomial distribution Poisson distribution Hypergeometric distribution Geometric distribution
Descriptions Uniform distribution describes a Binomial distribution describes a random variable arising from Poisson distribution [Siméon-Denis Poisson (1781– Hypergeometric distribution is similar Geometric distribution is related to the
random variable with a finite Bernoulli experiments [Jakob Bernoulli (1654–1705)] (a random 1840)] describes the number of events occurring in a to the binomial except that sampling is binomial. It describes the number of
number of equally likely experiment has only two outcomes). In a binomial experiment, we fixed interval of time or space. For the Poisson without replacement from a finite Bernoulli trials until the first success is
consecutive integer values are interested in 𝑋 the number of successes in 𝑛 trials and all trials distribution to apply, the events must occur randomly population of 𝑁 items. observed.
from 𝑎 to 𝑏. are independent, so the binomial random variable 𝑋 is the sum of and independently over a continuum of time or space. Note that it can be approximated by a
s n
𝑛 independent Bernoulli random variables. binomial with π = if < 0.05.
N N
Example The daily 3 lottery has a uniform On average, 20 percent of the emergency room patients at At an outpatient mental health clinic, appointment A statistics textbook chapter contains At Faber University, 15 percent of the
distribution with 1000 equally Greenwood General Hospital lack health insurance. In a random cancellations occur at a mean rate of 1.5 per day on a 60 exercises, 6 of which are essay alumni (the historical percentage) make a
likely outcomes range from 000 sample of four patients, what is the probability that two will be typical Wednesday. What is the probability that no questions. A student is assigned 10 donation or pledge during the annual tele-
through 999: 𝑋 = {000, … , 999}. uninsured? cancellations will occur on a particular Wednesday? problems. What is the probability that fund. What is the probability that the first
𝑋 = the number of uninsured patients, 𝑋 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}. X = the number of cancellations on a particular none of the questions are essay? donation will come within the first 5 calls?
Wednesday, 𝑋 = {0,1,2, … } X = the number of essay questions the 𝑋 = the number of calls make until the first
student receives, 𝑋 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6} success is achieved, 𝑋 = {1,2,3,4, … }
Parameters 𝑎: lower limit and 𝑏: upper limit 𝑛 : number of trials fixed 𝜆: mean arrivals per unit of time or space 𝑁: population size; 𝜋: probability of success
𝜋: probability of success 𝑛 : sample size
𝑠 : number of successes in population
𝑥: number of successes in sample
PDF/PMF 1 𝑛! 𝑥 −𝜆
𝜆 𝑒 𝑠 𝐶𝑥 × 𝑁−𝑠 𝐶𝑛−𝑥 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) = 𝜋(1 − 𝜋)𝑥−1
𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) = 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) = 𝜋 𝑥 (1 − 𝜋)𝑛−𝑥 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) = 𝑃(𝑋 = 𝑥) =
P(X=x) 𝑏−𝑎+1 𝑥! (𝑛 − 𝑥)! 𝑥! 𝑁 𝐶𝑛
Excel /Table 𝐵𝐼𝑁𝑂𝑀. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝑛, 𝜋 ,0) or Table A 𝑃𝑂𝐼𝑆𝑆𝑂𝑁. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝜆, 0) or Table B 𝐻𝑌𝑃𝐺𝐸𝑂𝑀. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝑛, 𝑠, 𝑁, 0) 𝐸𝑋𝑃𝑂𝑁. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝜆 ,0)
CDF 𝑥−𝑎+1 not cumulative 𝑃(𝑋 ≤ 𝑥) = 1 − (1 − 𝜋)𝑥 , 𝑥 ≥ 1
𝑃(𝑋 ≤ 𝑥) = ,𝑎 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 𝑏
P(X<=x) 𝑏−𝑎+1
Excel 𝐵𝐼𝑁𝑂𝑀. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝑛, 𝜋 ,1) cumulative 𝑃𝑂𝐼𝑆𝑆𝑂𝑁. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝜆, 1) 𝐻𝑌𝑃𝐺𝐸𝑂𝑀. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝑛, 𝑠, 𝑁, 1) 𝐸𝑋𝑃𝑂𝑁. 𝐷𝐼𝑆𝑇(𝑥, 𝜆 ,1)
𝑎+𝑏 𝑠 1
Mean 𝜇 = 𝑛𝜋 𝜇= 𝜆 𝜇 = 𝑛𝜋 where 𝜋 =
𝜇= 𝑁 𝜇=
2 𝜋
Standard 𝜎 = √𝑛𝜋(1 − 𝜋) 𝜎 = √𝜆 𝑁−𝑛
[(𝑏 − 𝑎) + 1]2 − 1 𝜎 = √𝑛𝜋(1 − 𝜋) × √ 1−𝜋
deviation 𝜎=√ 𝑁−1 𝜎=√ 2
12 𝜋
𝑠
Shape Symmetric with no mode Skewed right if 𝜋 < 0.5, skewed left if 𝜋 > 0.5 and symmetric if Always right-skewed, but less so for larger 𝜆. Symmetric if = 0.5 Highly skewed
𝑁
𝜋 = 0.5
Characteristics Uniform model is useful as a There are a fixed number of trials 𝑛 An event of interest occurs randomly over time or The trials are not independent. There is at least one trial to obtain the
benchmark and also to generate There are only two outcomes for each trial: success or failure. space. The probability of success is not first success, but the number of trials is
random integers for sampling, or in The probability of success for each trial 𝜋 remains constant. The average arrival rate 𝜆 remains constant. constant from trial to trial. not fixed.
simulation models. For example, The trials are independent of each other. The arrivals are independent of each other.
lotteries are frequently studied to The random variable 𝑋 is the number of successes. The random variable 𝑋 is the number of events
make sure they are truly random. within an observed time interval.
You might also like
- Republican Challenge Against Mail Ballot LawDocument18 pagesRepublican Challenge Against Mail Ballot LawJessica HillNo ratings yet
- Pokémon Unbound Mission List+ v2.1.0Document8 pagesPokémon Unbound Mission List+ v2.1.0Kokot100% (3)
- Class 6 - Statistics - SMT1-2019 - 2020 PDFDocument79 pagesClass 6 - Statistics - SMT1-2019 - 2020 PDFJon SnowNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 6 Discrete Probability DistributionsMichaela QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Lect - 01 Introduction Probability (Part B)Document20 pagesLect - 01 Introduction Probability (Part B)trasakroftNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Probability DistributionsDocument97 pagesCHAPTER 7 Probability DistributionsAyushi Jangpangi100% (1)
- CH01 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCH01 Cheat SheetISLAM KHALED ZSCNo ratings yet
- 1 DiscreteDistribution2018Document75 pages1 DiscreteDistribution2018Anirudh RaghavNo ratings yet
- DDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andDocument3 pagesDDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andLabonnoAkterLabonnoNo ratings yet
- CH01 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCH01 Cheat SheetISLAM KHALED ZSCNo ratings yet
- Stat Prob - Q3-HandoutDocument6 pagesStat Prob - Q3-Handoutmarlonprospero20No ratings yet
- Learning Module - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument123 pagesLearning Module - Statistics and ProbabilityZyrill MachaNo ratings yet
- Bpa12303 Week3 28randomvariables 29Document35 pagesBpa12303 Week3 28randomvariables 29Nur MaishaNo ratings yet
- Random Variables Discrete and Continuous ExplainedDocument3 pagesRandom Variables Discrete and Continuous Explainedmadina.aliyeva.2611No ratings yet
- Chap 1Document4 pagesChap 1RUHDRANo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions FinalDocument23 pagesProbability Distributions FinalTushar Gautam100% (1)
- Lesson 3-Discreet Probability DistributionsDocument13 pagesLesson 3-Discreet Probability Distributionscrisostomo.neniaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability DistributionDocument67 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionElthon Jake BuhayNo ratings yet
- 03 Handout 1Document7 pages03 Handout 1Adrasteia ZachryNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Probability DistributionDocument46 pagesTopic 1 - Probability DistributionnajmiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Probability DistributionsDocument8 pagesLesson 5 - Probability DistributionsEdward NjorogeNo ratings yet
- ch07 DiscreteProbabilityDistributionsDocument6 pagesch07 DiscreteProbabilityDistributionsHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Random Variable and Probability Distribution 115728Document24 pagesChapter 6 Random Variable and Probability Distribution 115728Nati EmruNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2 - Tarea 3 Juan Nicolas MunevarDocument13 pagesUnidad 2 - Tarea 3 Juan Nicolas MunevarNicolas GarayNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Topic 5Document7 pagesRandom Variables and Probability Distributions: Topic 5Sana SiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics Part IV: Statistical Inference: Achim Ahrens Anna Babloyan Erkal ErsoyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Statistics Part IV: Statistical Inference: Achim Ahrens Anna Babloyan Erkal ErsoyJovan SsenkandwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Shimelis TesemaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument23 pagesDiscrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionsSheikh MisbahNo ratings yet
- (MATH 102) SUM OF THREE ReviewersDocument6 pages(MATH 102) SUM OF THREE ReviewersChelsea JacotNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data Analysis Chapter 3 - Discrete Probability DistributionDocument18 pagesEngineering Data Analysis Chapter 3 - Discrete Probability Distributionetdr4444No ratings yet
- LectureDocument15 pagesLecture29k7trcf2gNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document39 pagesChapter 3api-3729261No ratings yet
- Workbook 2Document9 pagesWorkbook 2Lucas JerichoNo ratings yet
- FRM Part 1: DistributionsDocument25 pagesFRM Part 1: DistributionsRa'fat JalladNo ratings yet
- Random VariableDocument15 pagesRandom VariableKhim Aporbo EtchonNo ratings yet
- Probability and Inference: Random VariablesDocument22 pagesProbability and Inference: Random VariablescrutiliNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document37 pagesChap 5K60 Ngô Thị Cẩm NhungNo ratings yet
- 11 - Queing Theory Part 1Document31 pages11 - Queing Theory Part 1sairamNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods in ManagementDocument100 pagesQuantitative Methods in Managementsudheer gottetiNo ratings yet
- PSM 2 Variabel AcakDocument27 pagesPSM 2 Variabel AcakIzza AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Reation Between Exponential Dist and PoissonDocument24 pagesReation Between Exponential Dist and Poissonco21351No ratings yet
- Unit 11 Continuous Probability Distributions: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesUnit 11 Continuous Probability Distributions: ObjectivesRajvi SampatNo ratings yet
- S-11 - Random Variables and Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument24 pagesS-11 - Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions8918.stkabirdinNo ratings yet
- 2 Random Variable 11102020 060347pmDocument19 pages2 Random Variable 11102020 060347pmIrfan AslamNo ratings yet
- Random VariableDocument2 pagesRandom VariableBibhush MaharjanNo ratings yet
- 10 Inferential StatisticsDocument39 pages10 Inferential StatisticsShams QureshiNo ratings yet
- Random VariableDocument4 pagesRandom VariableTehseen ShahNo ratings yet
- Theory of Probability .Document11 pagesTheory of Probability .Harsimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabililityDocument6 pagesStatistics and ProbabililityTricia MendozaNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution II - Normal Distribution & Small Sampling Distribution (Students Notes) MAR 23Document27 pagesProbability Distribution II - Normal Distribution & Small Sampling Distribution (Students Notes) MAR 23halilmohamed830No ratings yet
- Stat Pre-MidtermDocument6 pagesStat Pre-MidtermhjNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument50 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributiondaRainNo ratings yet
- Stat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK1Document12 pagesStat - Prob 11 - Q3 - SLM - WK1rico.odalNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory Review 2Document13 pagesProbability Theory Review 2Erik LampeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document28 pagesLecture 9Luna eukharisNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distribution SVDocument31 pagesContinuous Distribution SVMai Ý NhưNo ratings yet
- STA1007S Lab 10: Confidence Intervals: October 2020Document5 pagesSTA1007S Lab 10: Confidence Intervals: October 2020mlunguNo ratings yet
- SSP Notes PDFDocument125 pagesSSP Notes PDFsandeepdevasriiNo ratings yet
- Basic Probability Reference Sheet: February 27, 2001Document8 pagesBasic Probability Reference Sheet: February 27, 2001Ibrahim TakounaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument81 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityJoh Tayag100% (1)
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Wellness Campus Song LyricsDocument2 pagesWellness Campus Song LyricsIshmael NarioNo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasDocument7 pagesUnit 10: Values: Lesson A Objective: Learn To Talk About Moral DilemmasLiss PeñafielNo ratings yet
- Cross Docking in SAP EWMDocument24 pagesCross Docking in SAP EWMS Banerjee100% (1)
- HMP Openser Sip AnDocument9 pagesHMP Openser Sip Anchingo9252No ratings yet
- Best Way To Eat BiscuitsDocument3 pagesBest Way To Eat BiscuitsChuanyui TehNo ratings yet
- Bec ExaminationDocument2 pagesBec ExaminationHiken D. ChoNo ratings yet
- Sample 1Document26 pagesSample 1Vraizen LagnayoNo ratings yet
- End Term Question Paper Linux For Devices 2021Document2 pagesEnd Term Question Paper Linux For Devices 2021KeshavNo ratings yet
- Importance of IqDocument4 pagesImportance of Iqmark ignacioNo ratings yet
- FidBond Enrolment Form Template Pinaka Bago PassiNHSDocument7 pagesFidBond Enrolment Form Template Pinaka Bago PassiNHSJoji Marie Castro PalecNo ratings yet
- MSC 1-Circ 1164-Rev 26Document6 pagesMSC 1-Circ 1164-Rev 26armanNo ratings yet
- Head and Shoulders by Nausherwan Khan NiaziDocument27 pagesHead and Shoulders by Nausherwan Khan NiaziNausherwan Khan Niazi50% (2)
- Pradeep Kumar: Curriculum-VitaeDocument4 pagesPradeep Kumar: Curriculum-VitaeMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Art 11 Justifying CircumstancesDocument30 pagesArt 11 Justifying CircumstancesJabami YumekoNo ratings yet
- WK 40 - The Dream of Hamzah Bin Habib Al-ZayyatDocument2 pagesWK 40 - The Dream of Hamzah Bin Habib Al-ZayyatE-Tilawah AcademyNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care (ANC)Document77 pagesAntenatal Care (ANC)tareNo ratings yet
- Let's Celebrate Diversity!: Activity 2: Our Abilities Lead inDocument6 pagesLet's Celebrate Diversity!: Activity 2: Our Abilities Lead inSoy Lat GamerNo ratings yet
- Cep CommunicationDocument13 pagesCep CommunicationMUHAMMAD BADAR ASHRAF RANANo ratings yet
- The Worst Day of My LifeDocument6 pagesThe Worst Day of My LifejoannaNo ratings yet
- Rogue's TavernDocument1 pageRogue's TavernautohagNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Short Scene With Literary DevicesDocument1 pageRubric For Short Scene With Literary DevicespaympmnpNo ratings yet
- Mti and Pulsed DopplerDocument33 pagesMti and Pulsed DopplerWaqar Shaikh67% (3)
- In Re Hill Trustees Preliminary Recommendation On Sanctions For Leslie PUIDA and GMM 17 Nov 2010Document9 pagesIn Re Hill Trustees Preliminary Recommendation On Sanctions For Leslie PUIDA and GMM 17 Nov 2010William A. Roper Jr.No ratings yet
- Shiva RatriDocument14 pagesShiva RatriTaoshobuddha100% (1)
- Analysis of Satellite Constellations For The Continuous Coverage of Ground RegionsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Satellite Constellations For The Continuous Coverage of Ground RegionsOksana VoloshenyukNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare in Love ScriptDocument134 pagesShakespeare in Love ScriptbelleNo ratings yet
- C955 Pre-Assessment - MindEdge Alignment Table - Sheet1Document3 pagesC955 Pre-Assessment - MindEdge Alignment Table - Sheet1Robert Allen Rippey0% (1)
- MSDS CavitonDocument9 pagesMSDS CavitonIka KusumawatiNo ratings yet