Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Duplicate For Reviewer
Duplicate For Reviewer
Uploaded by
Virsol Jao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesProbability is the likelihood of an event occurring, when the outcome is unknown. An experiment is an activity with unpredictable results. The possible outcomes make up the sample space, from which a random variable selects outcomes. A random variable assigns a number to each sample space element. It can be discrete, for countable outcomes, or continuous, for measured data ranging over intervals. The mean or expected value of a discrete random variable is the value expected if trials were repeated infinitely.
Original Description:
Original Title
Duplicate for Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProbability is the likelihood of an event occurring, when the outcome is unknown. An experiment is an activity with unpredictable results. The possible outcomes make up the sample space, from which a random variable selects outcomes. A random variable assigns a number to each sample space element. It can be discrete, for countable outcomes, or continuous, for measured data ranging over intervals. The mean or expected value of a discrete random variable is the value expected if trials were repeated infinitely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesDuplicate For Reviewer
Duplicate For Reviewer
Uploaded by
Virsol JaoProbability is the likelihood of an event occurring, when the outcome is unknown. An experiment is an activity with unpredictable results. The possible outcomes make up the sample space, from which a random variable selects outcomes. A random variable assigns a number to each sample space element. It can be discrete, for countable outcomes, or continuous, for measured data ranging over intervals. The mean or expected value of a discrete random variable is the value expected if trials were repeated infinitely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
LESSON 1.
1
PROBABILITY Probability is simply how
likely something is to happen. When we
don't know how an event will turn out, we
can talk about the probabilities of certain
outcomes.
Experiment is an activity in which the
results cannot be predicted with
certainty
Outcome is a result of an experiment
Event is a collection of outcomes
Simple Event is an event with only one
possible outcome
Sample Space is a set S that contains
all the possible outcomes of the
experiment
A random variable is a function that
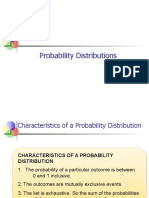
associates a real number to each A Discrete Probability Distribution count
element in the sample space. It is a occurences that have countable or finite
variable whose values are determined outcomes.
by chance. A Mean is the value you expect to get if
A random variable is said to be discrete the trials were repeated infinite number
if its set of possible outcomes is of time.
countable. The mean of a random variable X with a
A random variable is said to be discrete probability distribution is also
continuous if it takes on values from called the expected value of X, denoted
within an interval or disjoint union of by E ( X ). Thus μ = E ( x )
intervals. Often, continuous random
variables represent measured data,
such as heights, weights, and
temperatures.
LESSON 1.2
You might also like
- Class 6 - Statistics - SMT1-2019 - 2020 PDFDocument79 pagesClass 6 - Statistics - SMT1-2019 - 2020 PDFJon SnowNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Probability Distributions and Data ModelingDocument4 pagesAssignment - Probability Distributions and Data Modelingian mercadoNo ratings yet
- Stats and Prob ReviewerDocument7 pagesStats and Prob ReviewerWerNo ratings yet
- Chap5 (Bus Analytics)Document2 pagesChap5 (Bus Analytics)Caila RamosNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionsDocument56 pagesProbability Distributionsveerpatil4372No ratings yet
- Probability Distribution: Question BookletDocument8 pagesProbability Distribution: Question Bookletoliver senNo ratings yet
- Stats Reviewer MemorizeDocument3 pagesStats Reviewer MemorizeMila ANo ratings yet
- ML Unit2-1Document11 pagesML Unit2-1git21ec063-tNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument4 pagesProbability DistributionRabbul HossainNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument50 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributiondaRainNo ratings yet
- Probability: Presented by Eduard Mike Bucad Grace Ann Eroles Chesca Marie Penaranda Xaviera Mae RodriguezDocument2 pagesProbability: Presented by Eduard Mike Bucad Grace Ann Eroles Chesca Marie Penaranda Xaviera Mae RodriguezIanNo ratings yet
- ProbablityDocument37 pagesProbablityEngdaw Asmare GeramiNo ratings yet
- Admas University: Kality Campus Accounting & Finance Department Individual Assignment Basic StatisticsDocument7 pagesAdmas University: Kality Campus Accounting & Finance Department Individual Assignment Basic StatisticsEyob AstatkeNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument15 pagesProbability Distributionpatty444No ratings yet
- STT 206-1-1-1Document64 pagesSTT 206-1-1-1dropNo ratings yet
- 21 Probability PDFDocument11 pages21 Probability PDFreeta ramNo ratings yet
- 3.5.16 Probability Distribution PDFDocument23 pages3.5.16 Probability Distribution PDFGAURAV PARIHARNo ratings yet
- Evidence 2.1 2.3Document10 pagesEvidence 2.1 2.3alan ErivesNo ratings yet
- 04-A Probability ModelsDocument2 pages04-A Probability ModelsanndayoNo ratings yet
- Statistics With R Unit 3Document11 pagesStatistics With R Unit 3Pragatheeswaran shankarNo ratings yet
- Math TRM PPRDocument15 pagesMath TRM PPRsummitzNo ratings yet
- BM TheoryDocument25 pagesBM Theorysharankumarg044No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability KatabasisDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability KatabasisDaniel N Sherine FooNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument25 pagesStatsVenu KumarNo ratings yet
- HL Probability NotesDocument19 pagesHL Probability NotesJoseph AngNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument5 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionsAzimNo ratings yet
- Distribution Theory: Unit IIIDocument70 pagesDistribution Theory: Unit IIITharindu PrabhathNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document45 pagesUnit 4Viji MNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 ProbabilityDocument33 pagesChapter - 15 ProbabilityYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Lesson 1 - Mean of A Discrete Random VariableDocument16 pagesUnit 2 - Lesson 1 - Mean of A Discrete Random VariableJasper A. SANTIAGONo ratings yet
- Bernouli Random VariableDocument3 pagesBernouli Random Variablepi194043No ratings yet
- StatDocument23 pagesStatNoleen Sabatin CuevasNo ratings yet
- Ugc Net Economics English Book 2Document17 pagesUgc Net Economics English Book 2Vidhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Theory of Probability .Document11 pagesTheory of Probability .Harsimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2 - Tarea 3 Juan Nicolas MunevarDocument13 pagesUnidad 2 - Tarea 3 Juan Nicolas MunevarNicolas GarayNo ratings yet
- 1328782338saa Module 2012Document54 pages1328782338saa Module 2012Kudakwashe RuzvidzoNo ratings yet
- Uzair Talpur 1811162 Bba 4B Statistical Inference AssignmentDocument15 pagesUzair Talpur 1811162 Bba 4B Statistical Inference Assignmentuzair talpurNo ratings yet
- Iftikhar Ul HaqDocument2 pagesIftikhar Ul HaqMuhammad GhayoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.1Document12 pagesLecture No.1Shahzad 8bp starNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 Axiom of ProbabilityDocument11 pagesChapter One: 1.1 Axiom of ProbabilityYared SisayNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To ProbabilityDocument2 pages1 - Introduction To ProbabilityYahya AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To StatisticsStephen John NicolasNo ratings yet
- Basic Terms of ProbabilityDocument7 pagesBasic Terms of ProbabilityAbdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics and Statistics BDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics and Statistics BHarawa WonaNo ratings yet
- Enma104 Lessson2 ProbabilityDocument9 pagesEnma104 Lessson2 ProbabilityDJDJDJJDJDJD DJJDJDJDNo ratings yet
- Stats and Prob Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.Document8 pagesStats and Prob Reviewer, Q3 Jess Anch.JessicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Mean Variance of Discrete Random Variables.Document16 pagesLecture 4 Mean Variance of Discrete Random Variables.rigeljoemariealcayraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Cruzzy KaitNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Continuous Random VariableDocument30 pagesGroup 2 Continuous Random VariableJose Miguel MaulionNo ratings yet
- RandomvariablesDocument139 pagesRandomvariablesaaxdhpNo ratings yet
- Classical (Or Theoretical) Probability Is Used When Each Outcome in A Sample Space IsDocument4 pagesClassical (Or Theoretical) Probability Is Used When Each Outcome in A Sample Space Isrosalynmejia1196No ratings yet
- Probability PresentationDocument26 pagesProbability PresentationNada KamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Shimelis TesemaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Probability11 q3 Week2 v4Document10 pagesStatistics Probability11 q3 Week2 v4revamay286No ratings yet
- Two Mark Question and Answers: SRM Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument9 pagesTwo Mark Question and Answers: SRM Institute of Science and TechnologykeerthiiNo ratings yet
- Probability & Statistics Theme 6 Sampling Distribution Random SampleDocument4 pagesProbability & Statistics Theme 6 Sampling Distribution Random Sampleraoulduke88No ratings yet
- Module I. Discrete Random Variables and Continuous Random VariablesDocument5 pagesModule I. Discrete Random Variables and Continuous Random VariablesAnn BisnanNo ratings yet
- Probabilidad TatianavillamizarDocument12 pagesProbabilidad TatianavillamizarTatiana VillamizarNo ratings yet