Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 3 Reporting Outline
Group 3 Reporting Outline
Uploaded by
「 」Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 3 Reporting Outline
Group 3 Reporting Outline
Uploaded by
「 」Copyright:
Available Formats
GROUP 3
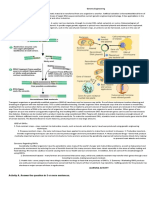
Applications of Genetic Engineering in Animals
Outline:
- Introduction
- Applications of Genetic Engineering in Animals
- Examples of Animals that are genetically modified and description
- Pros and Cons of application of Genetic Engineering in Animals
Examples of Animals that are genetically modified and description.
1. AquAdvantage Salmon
- AquAdvantage Salmon has been genetically engineered so
that it grows faster and reaches an important growth marker
for the aquaculture business more quickly than Atlantic
salmon raised in farms without GE.
- It is engineered to reach market size in 18 months, half the
time of its natural counterpart.
- It does so because it contains an rDNA construct that is composed of the growth hormone gene from
Chinook salmon under the control of a promoter (a sequence of DNA that turns on the expression of a gene)
from another type of fish called an ocean pout.
2. GloFish
- Glofish are one of the first genetically modified animals to
become popular within the pet trade.
- These fish were developed by introducing different
fluorescent proteins into the genome of the fish at the early
stages of development.
- The goal of producing fish that had these fluorescent
proteins was to improve biomedical and environmental
research. It was thought they would be able to detect pollution
within the environment. Now these fish are bred specifically for the ornamental fish pet trade.
3. GM Mosquitos
- A British company called Oxitec created genetically modified
male mosquitoes that carry a “self-limiting gene.” This means
that when they are released into the wild and procreate with
female mosquitoes, their offspring die at a young age.
- GM mosquitos have been successfully used in parts of Brazil,
the Cayman Islands, Panama, and India to control and reduce
Aedis aegypti mosquitoes. (Mosquitoes that spread viruses
including dengue, Zika, and chikungunya)
4. PRRS-resistant pigs
- Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS) causes
significant harm to the welfare of pigs worldwide (extreme
difficulty reproducing, don’t gain weight and have a high
mortality rate), as well as annual revenue losses of £1.8 billion in
the US and Europe.
- In 2018, scientists from the University of Edinburgh’s Roslin
Institute announced they had successfully eradicated the section
of DNA that leaves pigs vulnerable to the porcine reproductive
and respiratory syndrome.
5. GM cows that produce ‘human’ milk
- A team, led by the China Agricultural University, has
successfully introduced human genes into 300 cows to produce
"human" milk which is known to contain high quantities of key
nutrients that can help to boost the immune system of babies and
reduce risk of infections.
- The scientists inserted a human gene into the cows' genetic
information, and the animals' mammary glands now imbue their
milk with large quantities of lysozyme, a protein that is abundant
in human milk, making it much healthier and more nutritious,
according to Ning Li of China's Agricultural University in
Beijing, who led the research.
- Initial research suggests it is indeed safe and may provide significant health benefits, experts say. But
much more testing must be done — and will be done expected within 10 years’ time.
Applications of Genetic Engineering in Animals
Genetic engineering in animals has a wide range of applications, both in research and practical fields Below
are few of the important applications of genetic engineering in animals:
1. Agriculture
Aquaculture - Genetically modified fish can be created to grow more quickly, resist disease, and
adapt to different environments.
Reduced Environmental Impact - By producing less pollution and requiring fewer resources,
genetically modified animals can aid in reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
2. Animal Welfare:
Disease Resistance - Genetic engineering can help create animals that are more resistant to diseases,
reducing the need for antibiotics and improving animal welfare.
Reduced Suffering - Modifications can be made to animals to reduce pain and suffering, such as
hornless cattle or pigs with reduced susceptibility to stress in crowded conditions.
3. Food Production:
Enhanced Nutritional Value - Genetic engineering can be used to create animals that produce meat or
milk with improved nutritional profiles.
It's essential to note that the use of genetic engineering in animals raises ethical, environmental, and
regulatory concerns, and the applications should be carefully evaluated and regulated to ensure their
responsible and ethical use.
Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering
Pros of Genetic Engineering in Animals: Cons of Genetic Engineering in Animals:
1. Health Boost: Scientists can make animals 1. Ethical Concerns: Some people worry that
healthier and more resilient to diseases, which is altering genes might be unfair or harm animals.
great for animal well-being.
2. Environmental Risks: Releasing modified
2. More Food: Genetic engineering helps produce animals into nature could disrupt ecosystems and
more meat, milk, and eggs to meet the demand for create problems.
food.
3. Long-Term Unknowns: We don't always know
3. Nutrient Enrichment: Animal products like what might happen in the future when we tinker
meat can be made healthier by adding essential with genes.
nutrients.
4. Less Animal Variety: Genetic engineering
4. Environmentally Friendly: It can reduce the could lead to fewer diverse animal breeds.
negative impact of animal farming on our
5. Consumer Doubts: Some people might be
environment.
hesitant to eat genetically modified animal
5. Scientific Research: Genetically modified products due to safety or ethical concerns.
animals can be used for studying diseases and
6. Complex Regulations: Making and controlling
developing new medicines.
genetically modified animals is complicated and
requires strict rules.
Sources:
Center. (2023). AquAdvantage Salmon Fact Sheet. U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/aquadvantage-salmon/aquadvantage-salmon-fact-sheet
Perry, S. (2022, August 26). What Are Glofish? Petmd.com; PetMD. https://www.petmd.com/fish/what-are-
glofish
Young, C. (2020, April 28). 11 Real Examples of Genetically Modified Organisms: Marvels or Monsters.
Interestingengineering.com; Interesting Engineering. https://interestingengineering.com/science/11-
real-examples-of-genetically-modified-organisms-marvels-or-monsters
Genetically Engineered Pigs to Fight Disease | Bio-Rad. (2014). Bio-Rad. https://www.bio-rad-
antibodies.com/blog/pigs-to-fight-disease.html#:~:text=CD163%20knockout%20pigs%20are
%20fully,reproductive%20and%20respiratory%20syndrome%20virus.
CDC. (2022, July 25). Genetically Modified Mosquitoes . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/mosquito-control/community/emerging-methods/genetically-
modified-mosquitoes.html
DHNS. (2011, April 3). Now, genetically modified cows that produce “human” milk! Deccan Herald.
https://www.deccanherald.com/archives/now-genetically-modified-cows-produce-2405087
Wolchover, N. (2011, June 10). Cows Make Humanized Milk. But Is It Safe? Livescience.com; Live
Science. https://www.livescience.com/14538-cows-humanized-milk-safe.html
You might also like
- AP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ PreviewDocument30 pagesAP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ Preview(22) Bahar Baturoglu100% (3)
- Role Play On Challenges of Middle AdolescenceDocument4 pagesRole Play On Challenges of Middle Adolescence「 」100% (2)
- Uses of Transgenic AnimalsDocument1 pageUses of Transgenic AnimalsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Scitech Topic 11Document14 pagesScitech Topic 11Merca Rizza SolisNo ratings yet
- STS Chapter 10 - Genetically Modified Organism 2Document20 pagesSTS Chapter 10 - Genetically Modified Organism 2Noreen DelizoNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Disciplines in GeneticsDocument29 pages1.5 Disciplines in GeneticsshrivatsapandeNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismDocument31 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismgoshadabestgrampsNo ratings yet
- 13 Important Genetic Engineering Pros and ConsDocument16 pages13 Important Genetic Engineering Pros and ConsArgel Quilab Larongco100% (1)
- GEC 007 Week 16Document35 pagesGEC 007 Week 16Jheyzel Isano BorresNo ratings yet
- Week 1-4Document6 pagesWeek 1-4jessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- 4Q - Biotechnology - Activity SheetsDocument10 pages4Q - Biotechnology - Activity Sheetsjessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument42 pagesGenetic EngineeringPraveena R. JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Genetically Engineered Animals - An OverviewDocument10 pagesGenetically Engineered Animals - An OverviewronojoysenguptaNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Organisms515Document6 pagesGenetically Modified Organisms515Irvin OngyacoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 10 Techniques of Genetic Engineering TapusDocument10 pagesAssignment # 10 Techniques of Genetic Engineering Tapuskyle james duclanNo ratings yet
- Gmo (STS)Document4 pagesGmo (STS)LA EspirituNo ratings yet
- Food BiotechnologyDocument17 pagesFood BiotechnologyGabriela Vargas González0% (1)
- Animal BioTechnologyDocument2 pagesAnimal BioTechnologyHồ Thanh MaiNo ratings yet
- Animal PharmingDocument6 pagesAnimal PharmingSurajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Double Helix Vol 3 No 1 - April 2024Document8 pagesDouble Helix Vol 3 No 1 - April 2024Ayah SiplonNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Post Qns SolvedDocument4 pagesWeek 9 Post Qns SolvedCA DEEPIKA AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Foods Benefits and Risks PDFDocument12 pagesGenetically Modified Foods Benefits and Risks PDFMacarena OliverioNo ratings yet
- Your Guide To Animal BiotechnologyDocument269 pagesYour Guide To Animal BiotechnologyEzekiel BulusNo ratings yet
- Animal Biotechnology PDFDocument2 pagesAnimal Biotechnology PDFMandapati JanakiramNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and It's ApplicationsDocument19 pagesBiotechnology and It's Applicationssharmakrati762No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument23 pagesGenetic EngineeringAlexander Salas EspaderaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: BiologyDocument18 pagesBiotechnology: BiologyBrij Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1amanuel zeruNo ratings yet
- GM FoodDocument2 pagesGM FoodAnh ThiênNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Organisms (Gmos) and Biotechnology: A. AgricultureDocument4 pagesGenetically Modified Organisms (Gmos) and Biotechnology: A. AgricultureNicole Faye San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Food Technology SummaryDocument40 pagesFood Technology SummaryAnastasia ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Genetically Modified Organisms and NanotechDocument43 pagesModule 7 - Genetically Modified Organisms and Nanotechmaxenesophie.perezNo ratings yet
- TM-08 Ethical Issues in Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) (Gasal 2014-2015)Document38 pagesTM-08 Ethical Issues in Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) (Gasal 2014-2015)himawarumNo ratings yet
- The Biotechnolo Gy Century: Powerpoint Lecture By: Melissa Rowland-Goldsmith Chapman UniversityDocument42 pagesThe Biotechnolo Gy Century: Powerpoint Lecture By: Melissa Rowland-Goldsmith Chapman UniversityMaisha JashimNo ratings yet
- ENVIROPIGDocument5 pagesENVIROPIGdanial.arif301No ratings yet
- Faster Growth Rate Animals and Plants Can Be GeneticallyDocument3 pagesFaster Growth Rate Animals and Plants Can Be GeneticallyIvan NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified CropsDocument45 pagesGenetically Modified Cropsainish rvNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesGenetic EngineeringYih JengNo ratings yet
- Pro or Anti GM FoodsDocument10 pagesPro or Anti GM FoodsTon TonNo ratings yet
- Aya Ahmed Egypt Grand Challenges:: Biology Review byDocument22 pagesAya Ahmed Egypt Grand Challenges:: Biology Review byNabel MohamedNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Gen 1Document11 pagesLaboratory Gen 1donitamaediosanoNo ratings yet
- Genetically Engineered Food Research PaperDocument8 pagesGenetically Engineered Food Research Paperh01zpf0p100% (1)
- Part 5 Unit III Lesson 10 11Document6 pagesPart 5 Unit III Lesson 10 11shashnaepaynagananNo ratings yet
- (Edited and With Comments) STS - Genetic Engineering Assignment - HeavenDocument5 pages(Edited and With Comments) STS - Genetic Engineering Assignment - HeavenArtemio Entendez IINo ratings yet
- Food Processing, Food Spoilage and Their Prevention: An OverviewDocument7 pagesFood Processing, Food Spoilage and Their Prevention: An OverviewSSR-IIJLS Journal100% (1)
- 2.tolerance To HerbicidesDocument3 pages2.tolerance To HerbicidesGeoDith MaganaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering:)Document2 pagesGenetic Engineering:)Annilov MariNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified FoodDocument3 pagesGenetically Modified FoodSarah Don75% (4)
- 12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetically Modified FoodsDocument5 pages12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetically Modified FoodsRaven Kay-Ann Famatigan100% (5)
- The Importance of Agricultural Research: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Agricultural Research: ObjectiveJulianaNo ratings yet
- STS Module 13+finalDocument59 pagesSTS Module 13+finalDesiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- GMO and Gene Therapy Group 8Document10 pagesGMO and Gene Therapy Group 8May Nicole de LeonNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science AB Task: Salote Temu Telopea Park SchoolDocument5 pagesYear 10 Science AB Task: Salote Temu Telopea Park SchoolSalote Olive TemuNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument3 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismsCarlo DiazNo ratings yet
- Advantages 1. Insect Resistance 2. Stronger Crops: Larger Production Decreased Use of PesticidesDocument3 pagesAdvantages 1. Insect Resistance 2. Stronger Crops: Larger Production Decreased Use of PesticidesKaiser SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Food Biotechnology LectureDocument36 pagesFood Biotechnology Lecturezekariyas kuneNo ratings yet
- G-12 BIology PPT-2Document13 pagesG-12 BIology PPT-2mulerman910No ratings yet
- Let's Analyze Act 9 AnswersDocument4 pagesLet's Analyze Act 9 AnswersMikko CuynoNo ratings yet
- Ammar Babar Seminarseminar FillDocument23 pagesAmmar Babar Seminarseminar FillAmmar KhanNo ratings yet
- IndustryDocument4 pagesIndustry「 」No ratings yet
- Communication LetterDocument1 pageCommunication Letter「 」100% (1)
- Existing SolutionsDocument2 pagesExisting Solutions「 」No ratings yet
- Reviewer For DRR Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesReviewer For DRR Quiz Bee「 」100% (1)
- Essay On RocksDocument1 pageEssay On Rocks「 」No ratings yet
- Reporting Earth Sci M11Document5 pagesReporting Earth Sci M11「 」No ratings yet
- MineralsDocument34 pagesMinerals「 」No ratings yet
- Outline Ocean BasinDocument2 pagesOutline Ocean Basin「 」No ratings yet
- Outline Ocean Basin ReportingDocument7 pagesOutline Ocean Basin Reporting「 」No ratings yet
- Assignment Q1 08-31-2022Document1 pageAssignment Q1 08-31-2022「 」No ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivity「 」No ratings yet
- Paaso Short StoryDocument4 pagesPaaso Short Story「 」No ratings yet
- Reporting 21stDocument9 pagesReporting 21st「 」No ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflection「 」No ratings yet
- Medical MarvelsDocument76 pagesMedical MarvelsBenjamin AhambaNo ratings yet
- 223 NotesDocument36 pages223 NotesNing BalderasNo ratings yet
- Network Pharmacology and TCM - Alternative MedicineDocument23 pagesNetwork Pharmacology and TCM - Alternative MedicineyayanicaNo ratings yet
- Peroxynitrite-Mediated SIRT (Sirtuin) - 1 Inactivation Contributes To Nicotine-Induced Arterial Stiffness in MiceDocument13 pagesPeroxynitrite-Mediated SIRT (Sirtuin) - 1 Inactivation Contributes To Nicotine-Induced Arterial Stiffness in MicePretty HiaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument17 pagesChromosomal DisordersJosh Rosenberg100% (1)
- Cordlife Vs LifecellDocument1 pageCordlife Vs Lifecellcdhnalq099No ratings yet
- 9700 w17 QP 11Document16 pages9700 w17 QP 11evaNo ratings yet
- Hema311 Lec - Week 5 - Red Cell Structure, Metabolism, Destruction and FunctionDocument6 pagesHema311 Lec - Week 5 - Red Cell Structure, Metabolism, Destruction and FunctionJayvhie Gulane LayanNo ratings yet
- IFU Gram StainDocument5 pagesIFU Gram StainChandra MohanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 122 Exam 2 February 26, 2009: NAMEDocument7 pagesChemistry 122 Exam 2 February 26, 2009: NAMEjuly4babeNo ratings yet
- Components of Breast MilkDocument2 pagesComponents of Breast MilkAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSSLC Biology (Eng Med) Model Exam 2023 Answer KeyMuhammad SaidiqNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Risk - OSH AnswersDocument5 pagesHazard and Risk - OSH Answersanil73No ratings yet
- M3 WHILE TASK For Lab Exercise 10Document3 pagesM3 WHILE TASK For Lab Exercise 10Michelle LutapNo ratings yet
- GameOver ModRNA en MWGFD OrgDocument2 pagesGameOver ModRNA en MWGFD OrghispalisNo ratings yet
- Theories of Human Aging of Molecules To Society: MOJ ImmunologyDocument10 pagesTheories of Human Aging of Molecules To Society: MOJ ImmunologynmnkjNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biomedical EngineeringDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Biomedical EngineeringAlper Baran SözmenNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Bean PlantDocument10 pagesLife Cycle Bean PlantAntonieta Miroslava Rivadeneira RiveraNo ratings yet
- Transport of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesTransport of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideAiza Ayaz100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Tinea CapitisDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Tinea CapitisKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- (GIT) Hyperacidity With Duodenal Ulcer and GastrinomaDocument3 pages(GIT) Hyperacidity With Duodenal Ulcer and Gastrinomaapi-3769252No ratings yet
- Body Fluids - ForensicDocument12 pagesBody Fluids - ForensicEishani BehlNo ratings yet
- Cancer Chemotherapy - A Critical Analysis of Its 60 Years of HistoryDocument19 pagesCancer Chemotherapy - A Critical Analysis of Its 60 Years of HistoryCarlaValongoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Lsi 2010 UKDocument72 pagesCatalogue Lsi 2010 UKNesak1980No ratings yet
- Onc54. Intradural Extramedullary Spinal TumorsDocument4 pagesOnc54. Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumorsabishek22No ratings yet
- Serves ListDocument34 pagesServes Listgopi100% (1)
- MALDI-ToF Mass SpectrometryDocument1 pageMALDI-ToF Mass SpectrometryTim SandleNo ratings yet
- GlioblastomaDocument10 pagesGlioblastomaapi-451330223No ratings yet
- Case Study The Use of Race and Ethnicity Public SurveillanceDocument7 pagesCase Study The Use of Race and Ethnicity Public SurveillanceM MustafaNo ratings yet