Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsFull Mock Test Series 02
Full Mock Test Series 02
Uploaded by
Abhilasha CIVILThis mock test for junior engineers covers various subjects related to civil engineering. It contains 20 multiple choice questions to be completed within 2 hours, with negative marking for incorrect answers. Proper instructions are provided regarding conducting the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- KCCQ 12 Scoring InstructionsDocument3 pagesKCCQ 12 Scoring Instructionsping fanNo ratings yet
- Civil Breadth Mor Question 1 Sample PDFDocument7 pagesCivil Breadth Mor Question 1 Sample PDFSharifNo ratings yet
- DM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsDocument3 pagesDM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsMohamed Taha100% (10)
- Community Support Analysis - Darpan ChaudharyDocument6 pagesCommunity Support Analysis - Darpan ChaudharyDarpan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6hrfjbjrfrfNo ratings yet
- Ies 2008 Paper-II CivilDocument15 pagesIes 2008 Paper-II CivilrameshNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For Civil PDFDocument14 pagesDocuments - MX - SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For Civil PDFGene Paul Gamalo SusonNo ratings yet
- Mix Question WBPSC JE Set-03Document4 pagesMix Question WBPSC JE Set-03ghosh_951746604No ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2001 Paper IDocument14 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2001 Paper Itom stuartNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullDocument130 pagesQuestion Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullJayakrishnan VNo ratings yet
- CARTO 1 Cartography - Refresher - 1 - 2021Document3 pagesCARTO 1 Cartography - Refresher - 1 - 2021Loki Balder BaldoviNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 05Document10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 05Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Combined Test-4Document7 pagesCombined Test-4NISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 03 AnswerDocument11 pagesFull Mock Test Series 03 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ch#14&15 MCQSDocument3 pagesch#14&15 MCQSMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Transmission FundamentalsDocument47 pagesTransmission Fundamentalsroel balolong0% (1)
- Design PreboardDocument9 pagesDesign PreboardReinyl Angelo Cruz100% (1)
- Ce352 Comprehensive Exam, July 2021Document6 pagesCe352 Comprehensive Exam, July 2021seldageorge03No ratings yet
- Physics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Document8 pagesPhysics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Inesh0% (1)
- Mix Question WBPSC JE Set-01Document4 pagesMix Question WBPSC JE Set-01ghosh_951746604No ratings yet
- Phy Set 5 PDFDocument6 pagesPhy Set 5 PDFSurbhi and vartika SahuNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CentermateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 3 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 3 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2Document3 pagesCE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2rando12345No ratings yet
- Module 13.8 Module 13Document1 pageModule 13.8 Module 13Pravin HandeNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Surveying2Document9 pagesReviwer Surveying2Row RowNo ratings yet
- 2005 May Prob OkDocument3 pages2005 May Prob OkreynaldmiasisNo ratings yet
- Indiabix 1-4Document18 pagesIndiabix 1-4Row RowNo ratings yet
- Reviwer SurveyingDocument3 pagesReviwer SurveyingRow RowNo ratings yet
- SET-3 (CHANDAN's Guidance)Document16 pagesSET-3 (CHANDAN's Guidance)Debashis RouthNo ratings yet
- Physics Aptitude Test SHM, Waves and Sound: From The Desk of Engr. M. KASHIF ANEESDocument5 pagesPhysics Aptitude Test SHM, Waves and Sound: From The Desk of Engr. M. KASHIF ANEESKomalNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityJaineshNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Document1 pageRefresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Renz Ryan DolorNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoBenjie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ouat 2020 PCBDocument13 pagesOuat 2020 PCBAswini Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Puea Set-1Document10 pagesPuea Set-1NISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Nez A2.1 Ab LSDocument9 pagesNez A2.1 Ab LSRaja KeshavNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Electrical Engineering 2000 Paper IIDocument14 pagesIES OBJ Electrical Engineering 2000 Paper IIjitenNo ratings yet
- Question ADocument2 pagesQuestion AEr. Rajendra AcharayaNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2000 Paper IIDocument15 pagesIES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2000 Paper IIlaxminarayana_2003No ratings yet
- Ass. Sub Engineer 04 04Document3 pagesAss. Sub Engineer 04 04Bipul PoudelNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 2Document2 pagesHyd Ref 2rando12345No ratings yet
- B U Ww:I: RN :.H Fe!!:, F I Ti'i-: :'!"1' 7T-:' ..,.-"'-LDocument17 pagesB U Ww:I: RN :.H Fe!!:, F I Ti'i-: :'!"1' 7T-:' ..,.-"'-LAmbesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Document3 pagesRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Greg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Session Ending 2024Document10 pagesClass Ix Session Ending 2024Shiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mitrc Refresher Course Radiowave Propagation & AntennaDocument5 pagesMitrc Refresher Course Radiowave Propagation & AntennaAlbert AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- EXDocument3 pagesEXsaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 6 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 6 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- TRB Test SeriesDocument12 pagesTRB Test SeriesGokul ParthibanNo ratings yet
- Corre CeDocument29 pagesCorre CeKim VeneracionNo ratings yet
- 06 AntennasDocument7 pages06 AntennasSpencer HayesNo ratings yet
- SecquizDocument3 pagesSecquizdeezm579No ratings yet
- Jamb Physics 1993Document5 pagesJamb Physics 1993aladefawaz72No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Carto RefresherDocument2 pagesCarto RefresherMaridith Corpus SaradiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 23-Jan-2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 23-Jan-2023ankith sNo ratings yet
- Physic Eng Mech StremaDocument9 pagesPhysic Eng Mech StremaAllyssa ErcillaNo ratings yet
- File 1582710448 PDFDocument5 pagesFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- D. Her Mass Moment of Inertia Is Reduced: 1-Point QuestionsDocument21 pagesD. Her Mass Moment of Inertia Is Reduced: 1-Point QuestionsShinNo ratings yet
- 3rd Round - 2015 - Mock Nationa Exit ExamDocument20 pages3rd Round - 2015 - Mock Nationa Exit ExamteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- O C F Q: PEN Hannel LOW UestionsDocument10 pagesO C F Q: PEN Hannel LOW UestionsYashwantNo ratings yet
- Jamb Physics 2004Document4 pagesJamb Physics 2004Oyinlola AyomideNo ratings yet
- Engineers Academy SSC-JE 2018 Main Paper II Test 03Document2 pagesEngineers Academy SSC-JE 2018 Main Paper II Test 03Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - B SolutionDocument12 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - B SolutionAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - A SolutionDocument14 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - A SolutionAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - ADocument12 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - AAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 04 AnswerDocument12 pagesFull Mock Test Series 04 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 01 AnswerDocument10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 01 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 05Document10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 05Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 03 AnswerDocument11 pagesFull Mock Test Series 03 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Varian Chapter28 Game TheoryDocument94 pagesVarian Chapter28 Game TheoryBongani TutaniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Advanced Transformer Testing - IntroductionDocument32 pages1 - Advanced Transformer Testing - IntroductionFederico100% (1)
- CHP 11 Part 2Document24 pagesCHP 11 Part 2Valarmathi SaravananNo ratings yet
- Circuits SolnDocument5 pagesCircuits Solndwaytikitan28No ratings yet
- Space and Geometry - DissertationDocument60 pagesSpace and Geometry - DissertationNeha Syal100% (1)
- Nuclear Physics Type 2 PART 1 OF 2 ENG PDFDocument12 pagesNuclear Physics Type 2 PART 1 OF 2 ENG PDFTanmoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Coincidence or Suppression of The Self-Powering Battery 2Document5 pagesCoincidence or Suppression of The Self-Powering Battery 2wes_aussyNo ratings yet
- CE Overbooking (RAN18.1 - 02)Document96 pagesCE Overbooking (RAN18.1 - 02)Cedric Kouamen DjandaNo ratings yet
- Uhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesDocument33 pagesUhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesBegu CataNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Storage MethodDocument11 pagesSolar Energy Storage MethodĐặng HuyNo ratings yet
- Hanwha QCELLS GMBH Data Sheet QPEAK-G2 2013-01 Rev02 EN PDFDocument2 pagesHanwha QCELLS GMBH Data Sheet QPEAK-G2 2013-01 Rev02 EN PDFZorica SailovićNo ratings yet
- Aisi 1040 Carbon Steel (Uns g10400)Document3 pagesAisi 1040 Carbon Steel (Uns g10400)anishraobNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV 4 DempsterShaferTheoryDocument19 pagesUNIT IV 4 DempsterShaferTheorySravani Srav100% (1)
- ChatGPT What Do Know About TelepathyDocument6 pagesChatGPT What Do Know About TelepathyBruce WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Hydram PDFDocument6 pagesHydram PDFDedi SatriyawanNo ratings yet
- Design of The Low Head Slide GateDocument15 pagesDesign of The Low Head Slide GateAlok Sarkar100% (1)
- The Adjustment Instructions of The Control Parameters of The Fardriver ControllerDocument6 pagesThe Adjustment Instructions of The Control Parameters of The Fardriver ControllerTips Trik TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Route OptimizationDocument9 pagesRoute OptimizationSri Susilawati IslamNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials Lab ManualDocument61 pagesConstruction Materials Lab Manualaugupta2001No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Maria Resureccion MaanNo ratings yet
- HarwellDocument11 pagesHarwellLuis Antonio CNo ratings yet
- P EM 3. Time Varying Electromagnetic FieldsDocument24 pagesP EM 3. Time Varying Electromagnetic FieldsSinshaw BekeleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4, LAS-1-2: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) For Business Mathematics Grade 11Document4 pagesQuarter 4, LAS-1-2: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) For Business Mathematics Grade 11Cristian Dominic Escarlan100% (2)
- Acid Base Equilibria QPDocument28 pagesAcid Base Equilibria QPTrance OscNo ratings yet
- Testmaster 10Document8 pagesTestmaster 10Đức ĐạtNo ratings yet
Full Mock Test Series 02
Full Mock Test Series 02
Uploaded by
Abhilasha CIVIL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views8 pagesThis mock test for junior engineers covers various subjects related to civil engineering. It contains 20 multiple choice questions to be completed within 2 hours, with negative marking for incorrect answers. Proper instructions are provided regarding conducting the exam.
Original Description:
Original Title
FULL MOCK TEST SERIES 02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis mock test for junior engineers covers various subjects related to civil engineering. It contains 20 multiple choice questions to be completed within 2 hours, with negative marking for incorrect answers. Proper instructions are provided regarding conducting the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views8 pagesFull Mock Test Series 02
Full Mock Test Series 02
Uploaded by
Abhilasha CIVILThis mock test for junior engineers covers various subjects related to civil engineering. It contains 20 multiple choice questions to be completed within 2 hours, with negative marking for incorrect answers. Proper instructions are provided regarding conducting the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
JUNIOR ENGINEER EXAM
FULL MOCK TEST SERIES
CIVIL ENGINEERING Test No. 02
Topic
All subjects as per previous syllabus
Duration: 2 hours Total Marks: 200
Read the following instructions carefully
There will be negative marking for wrong answer; 2/3 marks will be deducted
for each wrong answer.
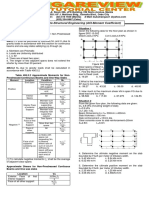
1. The plan of a map was photo copied to a b. 1870
reduced size such that a line originally 100 mm, c. 1900
measures 90 mm. The original scale of the plan d. 1930
was 1: 1000. The revised scale is 4. The method of orientation used, when the plane
a. 1:900 table occupies a position not yet located on the
b. 1:1111 map, is called as
c. 1:1121
d. 1:1221 a. Traversing
b. Radiation
2. The type of surveying in which the curvature of c. Levelling
the earth is taken into account is called d. Resection
a. Geodetic surveying 5. The reduced bearing of a 10m long line is
b. Plane surveying N300E. The departure of the line is
c. Preliminary surveying a. 10.00 m
d. Topographical surveying b. 8.66 m
3. The observed magnetic bearing of a line OE c. 7.52 m
was found to be 1850. It was later discovered d. 5.00 m
that station O had a local attraction of +1.50. 6. While doing levelling in undulating terrain, it is
The true bearing of the line OE, considering a preferable to set the level on
magnetic declination of 3.50E shall be a. the top of summit
a. 1800 b. the bottom of a valley
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 1
c. one side of the slope d. Falling weight deflectometer
d. anywhere 14. Alligator or map cracking is the common type
7. The rise and fall method of levelling provides a of failure in
complete check on a. Concrete pavements
a. back sight and fore sight b. Bituminous surfacing
b. intermediate sight c. Gravel roads
c. back sight and intermediate sight d. WBM construction
d. back sight, intermediate sight and fore 15. Select the strength parameter of concrete used
sight in design of plain joined cement pavement from
8. The combined correction due to curvature and the following choices:
refraction (in m) for distance of 1 km on the a. Tensile strength
surface of Earth is b. Compressive strength
c. Flexural strength
a. 0.0673
d. Shear strength
b. 0.673
16. During a CBR test, the load sustained by a
c. 7.63
remolded soil specimen at 5.0 mm penetration
d. 0.763
is 50 kg. The CBR value of the soil will be
9. If r is the radius of curvature at any point of a a. 10.0 %
transition curve and l is the distance from the b. 5.0 %
beginning of the transition curve to that point, c. 3.6 %
then for ideal transition d. 2.4 %
a. l×r 17. In Marshall testing of bituminous mixes, as the
b. l×r2 bitumen content increases the flow value
c. l×1/r a. Remains constant
d. l×1/r2 b. Decreases first and then increases
10. Anallactic lens provided in a tacheometer is a c. Increases monotonically
a. Concave lens d. Increases first and then decreases
b. Convex lens 18. Aggregate impact value indicates which one of
c. Plano-convex lens the following property of aggregates?
d. Plane lens a. Durability
b. Toughness
11. The magnetic bearing of a line AB is S450E and
c. Hardness
the declination is 50 West. The true bearing of
d. Strength
the line AB is
19. The set-back distance from the centre line of the
a. S450E inner lane is
b. S400E a. 7.93 m
c. S500E b. 8.10 m
d. S500W c. 9.60 m
12. Curvature correction to a staff reading in a d. 9.77 m
different levelling survey is 20. The value of lateral friction or side friction used
in the design of horizontal curve as per Indian
a. Always subtractive Roads Congress guidelines is
b. Always zero a. 0.40
c. Always additive b. 0.35
d. Dependent on latitude c. 0.24
13. Road roughness is measured using d. 0.15
a. Benkelman beam
b. Bump integrator
c. Dynamic cone penetrometer
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 2
21. A 1-hour rainfall of 10 cm has return period of d. Mass curve analysis
50 year. The 1 hour of rainfall 10 cm or more 27. A stable channel is to be designed for a
will occur in each of two successive year is discharge of Q m3/s with silt factor f as per
a. 0.04 Lacey’s method. The mean flow velocity (m/s)
b. 0.2 in the channel is obtained by
c. 0.02 1
Qf 2 6
d. 0.0004 a.
22. The peak discharge of the instantaneous unit 140
1
hydrograph of a basin, when compared to the Qf 2 3
peak discharge of a 4 hour unit hydrograph of b.
140
that basin, would be 1
a. Greater Q2 f 2 6
c.
b. Equal 140
c. Equal or lesser 1
d. Lesser Q 3
d. 0.48
23. Isopleths are line on a map through points f
having equal depth of 28. Sprinkler irrigation system is suitable when
a. Rainfall a. The land gradient is steep and soil is easily
b. Infiltration erodible
c. Evaporation b. The soil is having low permeability
d. Total runoff c. The water table is low
24. A hyetograph is a graph representing d. The crop to be grown have deep roots
a. Rainfall volume with time 29. If duty (D) is 142 hectares/cumec and base
b. Rainfall intensity with time period (B) is 120 days for an irrigated crop, then
c. Rainfall volume with duration delta ( ) in meters is given by
d. Rainfall intensity over an area a. 102.8
25. A weir on a permeable foundation with b. 0.73
downstream sheet pile is shown in the figure c. 1.38
below. The exit gradient as per Khosla’s d. 0.01
method is 30. The water utilizable by plants is available in
soils mainly in the form of
a. gravity water
b. capillary water
c. hygroscopic water
d. chemical water
31. A canal which is aligned at right angles to the
contour us called
a. contour canal
b. watershed canal
a. 1 in 6.0 c. branch canal
b. 1 in 5.0 d. side slope canal
c. 1 in 3.4 32. As per the recommendation of IS, the shape of
d. 1 in 2.5 lined canal is
26. The live storage requirement for a reservoir is a. trapezoidal
to be determined by b. semicircular
a. Topographical survey c. parabolic
b. Annual demand d. elliptic
c. Double mass curve analysis
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 3
33. The most important type of species involved in b. Duration of flooding and ground level
the degradation of organic matter in the case of elevation
activated sludge process is c. Duration of water supply in a city and
a. Autotrophs proportion of area receiving supply
b. Heterotrophs exceeding this duration
c. Prototrophs d. Flow rate and duration of time taken to
d. Photo-autotrophs empty a reservoir at the flow rate
34. The minimum dissolved oxygen content (ppm) 41. Zero hardness of water is achieved by
in a river necessary for the survival of aquatic a. Lime soda process
life is b. Excess lime treatment
a. 0 c. Ion exchange treatment
b. 2 d. Excess alum and lime treatment
c. 4 42. Two samples of water A and B have pH values
d. 8 of 4.4 and 6.4 respectively. Then how many
35. Total Kjeldahl nitrogen is a measure of times sample A is more acidic than sample B?
a. Total organic nitrogen a. 0
b. Total organic and ammonia nitrogen b. 50
c. Total ammonia nitrogen c. 100
d. Total inorganic and ammonia nitrogen d. 200
36. Crown correction in a reinforced concrete 43. Mechanical stabilization requires
sewer is caused by a. Mixing of two or more types of natural
a. H2S soils
b. CO2 b. Addition of chemical to soils
c. CH4 c. Addition of lime to soils
d. NH3 d. Addition of cementing material to soils
37. The relationship between porosity (n), specific 44. The most commonly used sample for obtaining
yield (Y) and specific retention (S) of an a disturbed sample of the soil is
unconfined aquifer is a. Split spoon sampler
a. Y + S = n b. Open drive sampler
b. Y + n = S c. Piston sampler
c. S + n = Y d. Thin wall shell by tube sampler
d. Y + S + n = 1 45. The action of negative skin friction on the pile
38. The following chemical is used for coagulation is to
a. Ammonium Chloride a. Increase the ultimate load on the pile
b. Aluminium Chloride b. Reduce the allowable load on the pile
c. Aluminium Sluphate c. Maintain the working load on the pile
d. Copper Sulphate d. Reduce the settlement of the pile
39. Some of the nontoxic metals normally found in 46. A strip footing is resting on the ground surface
natural water are of a pure clay bed having an undrained
a. Arsenic, lead and mercury cohesion cu. The ultimate bearing capacity of
b. Calcium, sodium and silver the footing is equal to
c. Cadmium, chromium and copper a. 2πcu
d. Iron, manganese and magnesium b. πcu
40. A conventional flow duration curve is a plot c. (π + 1) cu
between d. (π + 2) cu
a. Flow and percentage time flow in 47. Surcharge loading required to be placed on the
exceeded horizontal backfill of a smooth retaining
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 4
vertical wall so as to completely eliminate b. 75 years
tensile crack is c. 80 years
a. 2c d. 85 years
b. 2cKa 54. According to Darcy’s law for flow through
c. 2c√Ka porous media, the velocity is proportional to
d. 2c/√Ka a. Effective stress
48. For a saturated cohesive soil, a triaxial test b. Hydraulic gradient
yields the angle of internal friction (φ) as zero. c. Cohesion
The conducted test is d. Stability number
a. Consolidated drained (CD) test 55. A fine-grained soil is found to be plastic in the
b. Consolidate undrained (CU) test water content range of 26 – 48%. As per Indian
c. Unconfined compression (UC) test Standard Classification System, the soil is
d. Unconsolidated undrained (UU) test classified as
49. A uniformly distributed line load of 500 kN/m a. CL
is acting on the ground surface. Based on b. CH
Boussinesq’a theory, the ratio of vertical stress c. CL-ML
at depth 2 m to that at 4 m, right below the line d. CI
of loading is 56. The liquid limit (LL), plastic limit (PL) and
a. 0.25 shrinkage limit (SL) of a cohesive soil satisfy
b. 0.5 the relation
c. 2.0 a. LL>PL<SL
d. 4.0 b. LL>PL>SL
50. Compaction by vibratory roller is the best c. LL<PL<SL
method of compaction in case of d. LL<PL>SL
a. Moist silty sand 57. A soil sample has a void ratio of 0.5 and its
b. Well graded dry sand porosity will be close to
c. Clay of medium compressibility a. 50%
d. Silt of high compressibility b. 66%
51. Deposit with flocculated structure is formed c. 100%
when d. 33%
a. Clay particles settle on sea bed 58. The shape factor for a rectangular section is
b. Clay particles settle on fresh water lake bed a. 1.00
c. Sand particles settle on river bed b. 1.50
d. Sand particles settle on sea bed c. 2.00
52. The relationship between the specific gravity of d. 2.50
sand (G) and the hydraulic gradient (i) to 59. The square root of the ratio of moment of
initiate quick condition in the sand layer having inertia of the cross section to its cross-sectional
porosity of 30% is area is called
a. G = 0.7i + 1 a. Second moment of area
b. G = 1.43i – 1 b. Slenderness ratio
c. G = 1.43i + 1 c. Section modulus
d. G = 0.7i – 1 d. Radius of gyration
53. The time for a clay layer to achieve 90% 60. The standard size of modular brick is
consolidation is 15 years. The time required to a. 18 cm x 18 cm x 18 cm
achieve 90% consolidation, if the layer were b. 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm
twice as thick, 3 times more permeable and 4 c. 20 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm
times more compressible would be d. 21 cm x 11 cm x 11 cm
a. 70 years
61. Glazing is used to make earthenware
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 5
a. hard 69. Percentage of carbon content in mild steel is
b. soft a. less than 0.25
c. porous
d. impervious b. between 0.25 and 0.7
62. Which of the following metamorphic rocks has c. between 0.7 and 1.5
the most weather resisting characteristics?
d. greater than 1.5
a. marble
b. quartzite 70. The type of Bond provided in brick masonry for
c. slate carrying heavy loads is
d. lime stone a. single Flemish
63. In which of the following directions, the b. double Flemish bond
strength of timber is maximum? c. English bond
a. parallel to grains d. zigzag bond
b. 45° to greams
c. perpendicular to grains 71. The stretcher bond in brick masonry can be
d. same in all direction used only when the thickness of wall is
64. Hydrated lime for making mortars is slaked for a. 90 mm
a. 1 day b. 180 mm
b. 3 days c. 190 mm
c. 7 days d. 280 mm
d. 14 days 72. Minimum thickness of wall ware single
65. The base in a paint is added to Flemish bond can be used is
a. improve the quality of paint
a. half brick thick
b. make smooth surface
b. one brick thick
c. hide the surface to be painted
c. one and half bricks thick
d. all of these
d. two bricks thick
66. For complete hydration of cement, the w/c ratio
needed is 73. The most important tool in brick laying for
lifting and spreading mortar and for forming
a. less than 0.25
joints is
b. more than 0.25 but less than 0.35
a. Trowel
c. more than 0.35 but less than 0.45 b. square
d. more than 0.45 but less than 0.60 c. bolster
d. scotch
67. The fineness of cement is tested by
a. Air- permeability method 74. For good bonding in brick masonry
b. Le- chatelier’s method a. all bricks need not be uniform in size
b. bats must be used in alternate courses only
c. Vicat' s apparatus c. the vertical joints in alternate courses should
d. all of these fall in plumb
d. cement mortar used must have surkhi as
68. A gauged mortar is obtained by adding which
additive
of the following ingredients to cement?
75. Number of independent elastic constants for
a. sand stone
Orthotropic material are
b. sand and surthi a. 2
c. sand and lime b. 3
c. 9
d. surkhi alone
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 6
d. 21 a. E = 2K (1- 2u)
76. The number of independent elastic constants b. E = 3K (1+ u)
for a linear elastic isotropic and homogeneous c. E = 3K (1- 2u)
material is d. E= 2K (1+ u)
a. 4 84. Limiting values of Poisson's ratio are
b. 3 a. -1 and 0.5
c. 2 b. -1 and -0.5
d. 1 c. 1 and -0.5
77. The material that exhibits the same elastic d. 0 and 0.5
properties in all directions at a point is said to 85. The elongation of a conical bar under its own
be weight is equal to
a. homogeneous a. that of a prismatic bar of same length
b. orthotropic b. one half that of a prismatic bar of same
c. viscoelastic length
d. isotropic c. one third that of a prismatic bar of same
78. The symmetry of stress tensor at a point in the length
body under equilibrium is obtained from d. one fourth that of a prismatic bar of a same
a. Conservation of mass length
b. Force equilibrium equations 86. If a material has identical properties in all
c. Moment equilibrium equations directions, it is said to be
d. Conservation of energy a. Homogeneous
79. Limit of proportionality depends upon b. Isotropic
a. area of cross section c. Elastic
b. type of loading d. Orthotropic
c. type of material 87. Two bars of different materials are of the same
d. all of the above size and are subjected to same tensile forces. If
80. Modulus of rigidity is defined as the ratio of the bars have unit elongation in the ratio of 4:
a. longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain 7, then the ratio of moduli of elasticity of the
b. shear stress to shear strain two materials is
c. stress to strain a. 7: 4
d. stress to volumetric strain b. 4: 7
81. If the Young's modulus of elasticity of a c. 4: 17
material is twice its modulus of rigidity, then d. 16: 49
the Poisson's ratio of the material is 88. If φ = nominal diameter of reinforcing bar, fck =
a. -1 compressive stress in the bar and fbd = design
b. -0.5 bond stress of concrete, the anchorage length La
c. 0.5 of straight bar in compression is equal to
d. Zero f
a. La = s
82. If all the dimensions of a prismatic bar are f bd
double, then the maximum stress produced in it fs
under its own weight will b. La =
2 fbd
a. Decrease
fs
b. remain unchanged c. La =
c. increase to two times
fbd
d. increase to four times fs
d. La =
83. The relationship between Young's Modulus of 4 fbd
elasticity E, bulk modulus K and Poisson's ratio 89. Ductility of a flexural member (Reinforced
u is given by concrete) can be increased by
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 7
a. Increasing percentage of tensile b. Preliminary estimate
reinforcement. c. Plinth estimate
b. Decreasing percentage of tensile d. Curb rate estimate
reinforcement. 96. If B is the width of formation, d is the height of
c. Decreasing percentage of compressive the embankment, side slope S:1, for a highway
reinforcement. with no transverse slope, the area of correct
d. Decreasing the shear reinforcement. section is
90. The percentage of HYSD bars in one-way slabs
to cater for shrinkage or temperature, as per a. B+d+Sd
IS:456 is b. Bd+Sd²
a. 1.2% c. B×d-Sd½
b. 1.0% d. 1/2(Bd+Sd²)
c. 0.2% 97. The state of stresses on an element is shown in
d. 0.12% the fig. The values of stresses are σx (=32 Mpa);
91. As per IS 456: 2000 for the design of reinforced σy (=-10 Mpa) and major principal stress σ1
concrete beam, the maximum allowable shear (=40 Mpa).
stress (τcmax) depends on the
a. Grade of concrete and grade of steel
b. Grade of concrete only
c. Grade of steel only
d. Grade of concrete and percentage of
reinforcement
92. A reinforced concrete (RC) beam with width of
250 mm and effective depth of 400 mm is
The minor principal stress’σ2’ is
reinforced with Fe 415 steel. As per the
a. -22 Mpa
provisions of IS 456: 2000, the minimum and
b. -18 Mpa
maximum amount of tensile reinforcement
c. 22 Mpa
(expressed in mm2) for the section are,
d. Indeterminate due to insufficient data
respectively
98. The plane of maximum shear stress has normal
a. 250 and 3500
stress that is
b. 205 and 4000
a. Maximum
c. 270 and 2000
b. Minimum
d. 300 and 2500
c. Zero
93. The basic perfect frame is d. None of the above
a. Triangle 99. Average rate of water consumption per head
b. Rectangle per day as per Indian standard is
c. Square
a. 100 litres
d. Hexagon
94. For determinant pin-joined plain frame the b. 135 litres
relation between the number of joints j and c. 165 litres
member m is given by
d. 200 litres.
b. m = 2j-3
c. m = 3j-6 100. The devices which are installed for drawing
d. m > 2j-3 water from the sources are called
e. m > 3j-6 a. Aquifers
b. Aquiclude
95. The most reliable estimate is
c. Filter
a. Detailed estimate d. Intake
Prepared by: Er. Abhilash Jana, M.E. Jadavpur University, 8100407226 8
You might also like
- KCCQ 12 Scoring InstructionsDocument3 pagesKCCQ 12 Scoring Instructionsping fanNo ratings yet
- Civil Breadth Mor Question 1 Sample PDFDocument7 pagesCivil Breadth Mor Question 1 Sample PDFSharifNo ratings yet
- DM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsDocument3 pagesDM Exam G+Unlimited DEQ QuestionsMohamed Taha100% (10)
- Community Support Analysis - Darpan ChaudharyDocument6 pagesCommunity Support Analysis - Darpan ChaudharyDarpan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6hrfjbjrfrfNo ratings yet
- Ies 2008 Paper-II CivilDocument15 pagesIes 2008 Paper-II CivilrameshNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For Civil PDFDocument14 pagesDocuments - MX - SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For Civil PDFGene Paul Gamalo SusonNo ratings yet
- Mix Question WBPSC JE Set-03Document4 pagesMix Question WBPSC JE Set-03ghosh_951746604No ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2001 Paper IDocument14 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2001 Paper Itom stuartNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullDocument130 pagesQuestion Paper Discussion 22-6-2023 1 To100 FullJayakrishnan VNo ratings yet
- CARTO 1 Cartography - Refresher - 1 - 2021Document3 pagesCARTO 1 Cartography - Refresher - 1 - 2021Loki Balder BaldoviNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 05Document10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 05Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Combined Test-4Document7 pagesCombined Test-4NISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 03 AnswerDocument11 pagesFull Mock Test Series 03 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ch#14&15 MCQSDocument3 pagesch#14&15 MCQSMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Transmission FundamentalsDocument47 pagesTransmission Fundamentalsroel balolong0% (1)
- Design PreboardDocument9 pagesDesign PreboardReinyl Angelo Cruz100% (1)
- Ce352 Comprehensive Exam, July 2021Document6 pagesCe352 Comprehensive Exam, July 2021seldageorge03No ratings yet
- Physics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Document8 pagesPhysics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Inesh0% (1)
- Mix Question WBPSC JE Set-01Document4 pagesMix Question WBPSC JE Set-01ghosh_951746604No ratings yet
- Phy Set 5 PDFDocument6 pagesPhy Set 5 PDFSurbhi and vartika SahuNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CentermateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 3 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 3 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2Document3 pagesCE Refresher Apr 2024 - GEO 2rando12345No ratings yet
- Module 13.8 Module 13Document1 pageModule 13.8 Module 13Pravin HandeNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Surveying2Document9 pagesReviwer Surveying2Row RowNo ratings yet
- 2005 May Prob OkDocument3 pages2005 May Prob OkreynaldmiasisNo ratings yet
- Indiabix 1-4Document18 pagesIndiabix 1-4Row RowNo ratings yet
- Reviwer SurveyingDocument3 pagesReviwer SurveyingRow RowNo ratings yet
- SET-3 (CHANDAN's Guidance)Document16 pagesSET-3 (CHANDAN's Guidance)Debashis RouthNo ratings yet
- Physics Aptitude Test SHM, Waves and Sound: From The Desk of Engr. M. KASHIF ANEESDocument5 pagesPhysics Aptitude Test SHM, Waves and Sound: From The Desk of Engr. M. KASHIF ANEESKomalNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityJaineshNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Document1 pageRefresher Module-Structural Engineering (ACI-Moment Coefficient)Renz Ryan DolorNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Eval Exam by SorianoBenjie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Ouat 2020 PCBDocument13 pagesOuat 2020 PCBAswini Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Puea Set-1Document10 pagesPuea Set-1NISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Nez A2.1 Ab LSDocument9 pagesNez A2.1 Ab LSRaja KeshavNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Electrical Engineering 2000 Paper IIDocument14 pagesIES OBJ Electrical Engineering 2000 Paper IIjitenNo ratings yet
- Question ADocument2 pagesQuestion AEr. Rajendra AcharayaNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2000 Paper IIDocument15 pagesIES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2000 Paper IIlaxminarayana_2003No ratings yet
- Ass. Sub Engineer 04 04Document3 pagesAss. Sub Engineer 04 04Bipul PoudelNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 2Document2 pagesHyd Ref 2rando12345No ratings yet
- B U Ww:I: RN :.H Fe!!:, F I Ti'i-: :'!"1' 7T-:' ..,.-"'-LDocument17 pagesB U Ww:I: RN :.H Fe!!:, F I Ti'i-: :'!"1' 7T-:' ..,.-"'-LAmbesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Document3 pagesRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Greg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Session Ending 2024Document10 pagesClass Ix Session Ending 2024Shiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mitrc Refresher Course Radiowave Propagation & AntennaDocument5 pagesMitrc Refresher Course Radiowave Propagation & AntennaAlbert AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- EXDocument3 pagesEXsaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 6 MsteDocument2 pagesAlejandro 6 MsteBack UpNo ratings yet
- TRB Test SeriesDocument12 pagesTRB Test SeriesGokul ParthibanNo ratings yet
- Corre CeDocument29 pagesCorre CeKim VeneracionNo ratings yet
- 06 AntennasDocument7 pages06 AntennasSpencer HayesNo ratings yet
- SecquizDocument3 pagesSecquizdeezm579No ratings yet
- Jamb Physics 1993Document5 pagesJamb Physics 1993aladefawaz72No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Carto RefresherDocument2 pagesCarto RefresherMaridith Corpus SaradiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 23-Jan-2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 23-Jan-2023ankith sNo ratings yet
- Physic Eng Mech StremaDocument9 pagesPhysic Eng Mech StremaAllyssa ErcillaNo ratings yet
- File 1582710448 PDFDocument5 pagesFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- D. Her Mass Moment of Inertia Is Reduced: 1-Point QuestionsDocument21 pagesD. Her Mass Moment of Inertia Is Reduced: 1-Point QuestionsShinNo ratings yet
- 3rd Round - 2015 - Mock Nationa Exit ExamDocument20 pages3rd Round - 2015 - Mock Nationa Exit ExamteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- O C F Q: PEN Hannel LOW UestionsDocument10 pagesO C F Q: PEN Hannel LOW UestionsYashwantNo ratings yet
- Jamb Physics 2004Document4 pagesJamb Physics 2004Oyinlola AyomideNo ratings yet
- Engineers Academy SSC-JE 2018 Main Paper II Test 03Document2 pagesEngineers Academy SSC-JE 2018 Main Paper II Test 03Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - B SolutionDocument12 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - B SolutionAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - A SolutionDocument14 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - A SolutionAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- ACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - ADocument12 pagesACE ACADEMY GATE Full Length Mock Test - AAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 04 AnswerDocument12 pagesFull Mock Test Series 04 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 01 AnswerDocument10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 01 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 05Document10 pagesFull Mock Test Series 05Abhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Full Mock Test Series 03 AnswerDocument11 pagesFull Mock Test Series 03 AnswerAbhilasha CIVILNo ratings yet
- Varian Chapter28 Game TheoryDocument94 pagesVarian Chapter28 Game TheoryBongani TutaniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Advanced Transformer Testing - IntroductionDocument32 pages1 - Advanced Transformer Testing - IntroductionFederico100% (1)
- CHP 11 Part 2Document24 pagesCHP 11 Part 2Valarmathi SaravananNo ratings yet
- Circuits SolnDocument5 pagesCircuits Solndwaytikitan28No ratings yet
- Space and Geometry - DissertationDocument60 pagesSpace and Geometry - DissertationNeha Syal100% (1)
- Nuclear Physics Type 2 PART 1 OF 2 ENG PDFDocument12 pagesNuclear Physics Type 2 PART 1 OF 2 ENG PDFTanmoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Coincidence or Suppression of The Self-Powering Battery 2Document5 pagesCoincidence or Suppression of The Self-Powering Battery 2wes_aussyNo ratings yet
- CE Overbooking (RAN18.1 - 02)Document96 pagesCE Overbooking (RAN18.1 - 02)Cedric Kouamen DjandaNo ratings yet
- Uhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesDocument33 pagesUhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesBegu CataNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Storage MethodDocument11 pagesSolar Energy Storage MethodĐặng HuyNo ratings yet
- Hanwha QCELLS GMBH Data Sheet QPEAK-G2 2013-01 Rev02 EN PDFDocument2 pagesHanwha QCELLS GMBH Data Sheet QPEAK-G2 2013-01 Rev02 EN PDFZorica SailovićNo ratings yet
- Aisi 1040 Carbon Steel (Uns g10400)Document3 pagesAisi 1040 Carbon Steel (Uns g10400)anishraobNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV 4 DempsterShaferTheoryDocument19 pagesUNIT IV 4 DempsterShaferTheorySravani Srav100% (1)
- ChatGPT What Do Know About TelepathyDocument6 pagesChatGPT What Do Know About TelepathyBruce WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Hydram PDFDocument6 pagesHydram PDFDedi SatriyawanNo ratings yet
- Design of The Low Head Slide GateDocument15 pagesDesign of The Low Head Slide GateAlok Sarkar100% (1)
- The Adjustment Instructions of The Control Parameters of The Fardriver ControllerDocument6 pagesThe Adjustment Instructions of The Control Parameters of The Fardriver ControllerTips Trik TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Route OptimizationDocument9 pagesRoute OptimizationSri Susilawati IslamNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials Lab ManualDocument61 pagesConstruction Materials Lab Manualaugupta2001No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Maria Resureccion MaanNo ratings yet
- HarwellDocument11 pagesHarwellLuis Antonio CNo ratings yet
- P EM 3. Time Varying Electromagnetic FieldsDocument24 pagesP EM 3. Time Varying Electromagnetic FieldsSinshaw BekeleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4, LAS-1-2: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) For Business Mathematics Grade 11Document4 pagesQuarter 4, LAS-1-2: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) For Business Mathematics Grade 11Cristian Dominic Escarlan100% (2)
- Acid Base Equilibria QPDocument28 pagesAcid Base Equilibria QPTrance OscNo ratings yet
- Testmaster 10Document8 pagesTestmaster 10Đức ĐạtNo ratings yet