Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Uploaded by
pattie29Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderDocument32 pagesSage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517Document42 pagesIntroduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517ATIRAH100% (1)
- Vanmeter: Gould'S Pathophysiology For The Health Professions, 5Th EditionDocument1 pageVanmeter: Gould'S Pathophysiology For The Health Professions, 5Th EditionAnne VaughanNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of Immune SystemDocument7 pagesCells and Organs of Immune Systemanumaria2024No ratings yet
- Lymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsDocument14 pagesLymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsEdgar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)Document10 pagesLymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)KarthigaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Nursing Management of PatientDocument30 pagesNursing Management of PatientShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesModule 7 Lymphatic SystemWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadDocument28 pagesImmunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 06 Lymphoid System and Location of The Immune CellsDocument16 pagesLECTURE 06 Lymphoid System and Location of The Immune Cellssamarsamar6000No ratings yet
- Reticulo Endothelial SystemDocument15 pagesReticulo Endothelial Systemssdb14No ratings yet
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Raport 2Document9 pagesRaport 2shko noshaNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical Immunology PDFDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical Immunology PDFAbbass El-Outa100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Immune SystemDocument37 pagesLesson Plan - Immune Systemsonyblank0% (1)
- Imm Lect 2Document22 pagesImm Lect 2samarsamar6000No ratings yet
- Micro B SDLDocument29 pagesMicro B SDLIsraelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemSnehjyoti JhaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic Systemdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Primary or Central 33Document23 pagesPrimary or Central 33Mahesh DevarintiNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Nursing HandoutsDocument22 pagesImmunology - Nursing HandoutsRayePrudente100% (1)
- Unit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Document9 pagesUnit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyElyka Alivan Valdez Polonio100% (1)
- Histology of Lymphoid Organ PDFDocument82 pagesHistology of Lymphoid Organ PDFRionaldy TaminNo ratings yet
- Name: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Document10 pagesName: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Abby YongNo ratings yet
- 12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMDocument20 pages12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument4 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityBlessed May PastranaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemAlyssa Mae AzarconNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To ImmunologyDocument39 pages2.introduction To ImmunologyZakaria MakereNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System For Medical StudentsDocument18 pagesLymphatic System For Medical StudentsTriza JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Immune System and Lymphoid OrgansDocument15 pagesImmune System and Lymphoid Organscatalia fuaresNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic SystemDocument26 pagesWhite Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic Systemislamicmedia188No ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesBio ProjectJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Organs of Immune SystemDocument31 pagesOrgans of Immune Systemspourush100% (2)
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesLymphatic SystemxoxoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 pagesLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Organs and TissuesDocument3 pagesLymphatic Organs and TissuesSaman Bharatha KotigalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical ImmunologyDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical ImmunologyWael AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Lymphoid SystemDocument4 pagesChapter Three: The Lymphoid SystemaiaiNo ratings yet
- 09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Document12 pages09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDocument9 pagesLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- LymphaticDocument3 pagesLymphaticTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- What Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?Document3 pagesWhat Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?yumie dimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Besana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFDocument9 pagesBesana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytes and MonocytesDocument7 pagesLymphocytes and MonocytesSarfraz Hussain MalikNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid OrganDocument23 pagesLymphoid OrganSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Powerlecture: ImmunityDocument107 pagesPowerlecture: Immunitymr. nicartNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document40 pagesLecture 2Emmanuel Thon MadingNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (Anaphy)Document27 pagesLymphatic System (Anaphy)Ryan RanasNo ratings yet
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Uploaded by
pattie29Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Chapter 11 Questions 1
Uploaded by
pattie29Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 Questions 1, 3 and 4
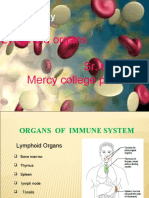
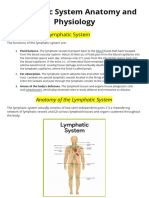
1.The lymph nodes ensure constant filtration and surveillance of body fluids, removing
foreign or dangerous materials. They are essential to the body’s immune response.
The thymus gland is the final site of leucocyte development before birth and is
responsible for the secretion of hormones after birth, which enables lymphocytes to
develop into mature T cells.
Tonsils function as protection against bacterial infections in the area of the openings
between the nasal and oral cavities.
The spleen functions in body defense - macrophages remove microorganisms in the
blood, monocytes and lymphocytes mature in the spleen. Before birth, erythrocytes are
formed in the spleen; old red blood cells and platelets are broken down and recycled in
the spleen; and finally, the spleen serves as a large reservoir for blood, which can be
quickly returned to the circulatory system if needed.
3.Hodgkin’s lymphoma is characterized by T lymphocyte and Reed Sternberg cells and
painless non tender cervical lymph nodes; it spreads to adjacent lymph nodes.
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is characterized by multiple involvement of scattered lymph
nodes.
Multiple myeloma is characterized by plasma cells (B lymphocytes) in the bone marrow,
multiple tumors in vertebrae, skull, ribs, pain, and pathologic fractures.
4.The two types of Castleman disease are unicentric and multicentric. The unicentric type
involves a single lymph node with more local effects and is usually more easily treated
with surgery. The multicentric type involves multiple lymph nodes, displaying more
serious systemic manifestations; surgery is not a practical treatment because multiple sites
are involved.
You might also like
- Sage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderDocument32 pagesSage Glod Brush Stroke Watercolor A4 Blank Page BorderJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517Document42 pagesIntroduction To Immunology 1: Chapter 16 & 17 of Tortora PG 465 - 517ATIRAH100% (1)
- Vanmeter: Gould'S Pathophysiology For The Health Professions, 5Th EditionDocument1 pageVanmeter: Gould'S Pathophysiology For The Health Professions, 5Th EditionAnne VaughanNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of Immune SystemDocument7 pagesCells and Organs of Immune Systemanumaria2024No ratings yet
- Lymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsDocument14 pagesLymphatics - Immunity Lec Notes - With PicsEdgar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)Document10 pagesLymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)KarthigaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Nursing Management of PatientDocument30 pagesNursing Management of PatientShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodeDocument13 pagesLymph NodeNurul Ilma AllauwNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesModule 7 Lymphatic SystemWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadDocument28 pagesImmunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Reticuloendothelial SystemDocument26 pagesReticuloendothelial SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 06 Lymphoid System and Location of The Immune CellsDocument16 pagesLECTURE 06 Lymphoid System and Location of The Immune Cellssamarsamar6000No ratings yet
- Reticulo Endothelial SystemDocument15 pagesReticulo Endothelial Systemssdb14No ratings yet
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Raport 2Document9 pagesRaport 2shko noshaNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical Immunology PDFDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical Immunology PDFAbbass El-Outa100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Immune SystemDocument37 pagesLesson Plan - Immune Systemsonyblank0% (1)
- Imm Lect 2Document22 pagesImm Lect 2samarsamar6000No ratings yet
- Micro B SDLDocument29 pagesMicro B SDLIsraelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Immune System and Lymphatic SystemSnehjyoti JhaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Function of Lymphoid Tissues: Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic Systemdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Primary or Central 33Document23 pagesPrimary or Central 33Mahesh DevarintiNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Nursing HandoutsDocument22 pagesImmunology - Nursing HandoutsRayePrudente100% (1)
- Unit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Document9 pagesUnit-IXLymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology.Rao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLymphatic System Anatomy and PhysiologyElyka Alivan Valdez Polonio100% (1)
- Histology of Lymphoid Organ PDFDocument82 pagesHistology of Lymphoid Organ PDFRionaldy TaminNo ratings yet
- Name: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Document10 pagesName: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Abby YongNo ratings yet
- 12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMDocument20 pages12SUMMARYLYMPHATICSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument4 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityBlessed May PastranaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemAlyssa Mae AzarconNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To ImmunologyDocument39 pages2.introduction To ImmunologyZakaria MakereNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System For Medical StudentsDocument18 pagesLymphatic System For Medical StudentsTriza JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Immune System and Lymphoid OrgansDocument15 pagesImmune System and Lymphoid Organscatalia fuaresNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic SystemDocument26 pagesWhite Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic Systemislamicmedia188No ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesBio ProjectJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Organs of Immune SystemDocument31 pagesOrgans of Immune Systemspourush100% (2)
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument17 pagesLymphatic SystemxoxoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 pagesLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Organs and TissuesDocument3 pagesLymphatic Organs and TissuesSaman Bharatha KotigalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical ImmunologyDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical ImmunologyWael AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Lymphoid SystemDocument4 pagesChapter Three: The Lymphoid SystemaiaiNo ratings yet
- 09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Document12 pages09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDocument9 pagesLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- LymphaticDocument3 pagesLymphaticTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- What Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?Document3 pagesWhat Is/are The Most Abundant Connective Tissue Cells Present in The Stroma?yumie dimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Besana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFDocument9 pagesBesana 121106035558 Phpapp02 PDFAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytes and MonocytesDocument7 pagesLymphocytes and MonocytesSarfraz Hussain MalikNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid OrganDocument23 pagesLymphoid OrganSwetha RameshNo ratings yet
- Powerlecture: ImmunityDocument107 pagesPowerlecture: Immunitymr. nicartNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document40 pagesLecture 2Emmanuel Thon MadingNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (Anaphy)Document27 pagesLymphatic System (Anaphy)Ryan RanasNo ratings yet