Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 1
Module 1
Uploaded by
Irene GarderCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- This Is ADHD - Chanelle MoriahDocument12 pagesThis Is ADHD - Chanelle MoriahAllen & Unwin0% (2)
- TEFL AnswerDocument18 pagesTEFL Answerkimberly masangkay100% (1)
- The Child and Adolescent LearnersDocument179 pagesThe Child and Adolescent LearnersMyla Guab100% (1)
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LearnerDocument9 pagesModule 2 LearnerJayson PalmaNo ratings yet
- PED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMDocument43 pagesPED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMMicah Esteban OngpaucoNo ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument106 pagesFacilitating LearningnananaNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Document13 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Rea Jane OrnedoNo ratings yet
- 2prof Ed 02Document17 pages2prof Ed 02airen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Part IDocument17 pagesPart Iairen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching (1) LOUDocument12 pagesModule 2 Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching (1) LOULou Jane YescaNo ratings yet
- The Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceDocument6 pagesThe Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceAbhey Abellera Barcena100% (2)
- Module 2: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Polangui Community CollegeDocument8 pagesModule 2: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Polangui Community CollegeshielaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Week 1: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Document6 pagesModule 1 - Week 1: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Noel Jr MospaNo ratings yet
- Educ 211 Prelim ModuleDocument34 pagesEduc 211 Prelim ModuleRichard RamisNo ratings yet
- PCK 1 Module 2 Week 3 LCPDocument28 pagesPCK 1 Module 2 Week 3 LCPCharlene Mae de leonNo ratings yet
- Almira Abad Btled 2-A Merry Grace Abella Btled 2-A: PreambleDocument5 pagesAlmira Abad Btled 2-A Merry Grace Abella Btled 2-A: PreambleEl Joy BangkilingNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument9 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesCecelien Salgado AntonioNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- PS 5 Module 2 PrelimDocument7 pagesPS 5 Module 2 Prelimblssm AbenesNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Frances Bea Abarado100% (1)
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument3 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesMichael NatividadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mr. RecibeDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Mr. RecibeMoses TamondongNo ratings yet
- PED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2Document4 pagesPED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2YuriNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Introduction Module2 2022Document11 pagesPart 1 Introduction Module2 2022Jodelyn Quirao AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument11 pagesModule-1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesriegocessyNo ratings yet
- Educ 101Document35 pagesEduc 101Cyrell Joshua Salas100% (1)
- LearnerDocument3 pagesLearnerZaira Michaela CamposNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles愛No ratings yet
- Educ 105 3 & 4Document3 pagesEduc 105 3 & 4keana barnajaNo ratings yet
- Week 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesDocument30 pagesWeek 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesTrisha Mae VaguchayNo ratings yet
- M 1 Prof Ed 221Document9 pagesM 1 Prof Ed 221QueencyNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument15 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesShailanie Valle RiveraNo ratings yet
- FLCL Mod 1Document9 pagesFLCL Mod 1Ana Carmela Salazar LaraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument2 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesABADA MARY JANE MALLARINo ratings yet
- 14 PsychologicalPrinciplesDocument23 pages14 PsychologicalPrinciplesJane AgripaNo ratings yet
- 14 Learner Teaching PrincipleDocument4 pages14 Learner Teaching Principlemaela pollen yemaNo ratings yet
- Learners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesAmbita CherylNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaDocument6 pagesModule 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaGeorgie AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Ed 1o1 Modules 1 and 2Document18 pagesEd 1o1 Modules 1 and 2Abdulhamid Baute CodaranganNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Learner Centered PrinciplesDocument7 pages2 3 Learner Centered PrinciplesLeyte Gerodias0% (1)
- 14 PrinciplesDocument33 pages14 PrinciplesTep LeeNo ratings yet
- Ed 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Document3 pagesEd 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Kiara TrozziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document45 pagesLesson 1Ruthche Nova C. PreteNo ratings yet
- Ed1 Module 1 NotesDocument3 pagesEd1 Module 1 NotesChristhie RobleNo ratings yet
- PED05a Module-1 Nagares LucenaDocument11 pagesPED05a Module-1 Nagares LucenaCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Learner-Centered PrinciplesDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Learner-Centered PrinciplesR PadullaNo ratings yet
- Prelim ModuleDocument34 pagesPrelim ModuleKyla Jelinne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument36 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesMariel D. BelandoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Learning PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Learning PrinciplesJohn Mark NovenoNo ratings yet
- Module-Child and Adolescent LearnerDocument85 pagesModule-Child and Adolescent LearnerAira Jane BaliquiaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Metacognitive FactorsDocument4 pagesCognitive and Metacognitive FactorsArlyn ElsiNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument39 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJonathan AysonNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 AssignmentDocument7 pagesEduc 1 AssignmentCloie GadNo ratings yet
- WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document5 pagesWMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)My Home100% (1)
- Learnered Center PriciplesDocument26 pagesLearnered Center PriciplesArselia RubanteNo ratings yet
- FACILITATING LEARNER Module 2Document6 pagesFACILITATING LEARNER Module 2Ivie CastroNo ratings yet
- ED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Document9 pagesED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Yogine M BarongNo ratings yet
- Learning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualFrom EverandLearning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualNo ratings yet
- A Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressDocument7 pagesA Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressHarold TrefforNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Decluttering Your MindDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Decluttering Your MindFabiana Alejandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Laws of LearninDocument2 pagesLaws of LearninDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument27 pagesEmotional IntelligenceSarah ShrisunderNo ratings yet
- Power of LanguageDocument6 pagesPower of Languageapi-660848734No ratings yet
- IVA 2 Detailed ReportDocument5 pagesIVA 2 Detailed ReportmohammadzarekandejaniNo ratings yet
- HẠNH-ĐỀ MINH HOẠ ANH -2023Document6 pagesHẠNH-ĐỀ MINH HOẠ ANH -2023Hoàng PhúcNo ratings yet
- Priming: December 2015Document11 pagesPriming: December 2015Chelsea AsiñeroNo ratings yet
- Gerrits Et Al. - 2020 - Mirrored Brain Organization Statistical Anomaly oDocument9 pagesGerrits Et Al. - 2020 - Mirrored Brain Organization Statistical Anomaly oMaya JacksonNo ratings yet
- Hawaiian Stick Song - SingingDocument4 pagesHawaiian Stick Song - Singingapi-708306698No ratings yet
- MKTG Week 5,6,7 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMKTG Week 5,6,7 ReviewerJelly NomatNo ratings yet
- Variations in Psychological AttributesDocument43 pagesVariations in Psychological Attributesfms7x8b69t100% (1)
- English MapsDocument11 pagesEnglish MapsAshlyn Jade Olleras LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Total Physical Response EssayDocument5 pagesTotal Physical Response EssayTeacher XimenaNo ratings yet
- Cultural and Linguistics Constraints On Mind-1Document29 pagesCultural and Linguistics Constraints On Mind-1Rehan BalochNo ratings yet
- PSY 305 - Chapter 5 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesPSY 305 - Chapter 5 (Reviewer)Ricajoy RicohermosoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual System of World Reflection - 2. Universal MetaphorsDocument23 pagesConceptual System of World Reflection - 2. Universal MetaphorsNazerke AbdrahmanovaNo ratings yet
- YOU MUST BECOME A MASTER OF YOUR MIND (Very Inspirational)Document26 pagesYOU MUST BECOME A MASTER OF YOUR MIND (Very Inspirational)Linh BạchNo ratings yet
- 5 Year Old Boy Case StudyDocument16 pages5 Year Old Boy Case StudyClare LebedaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of PlayDocument1 pageThe Importance of PlayShabree JemmottNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3W1 Day 2Document10 pagesDLP Q3W1 Day 2Marieta SorianoNo ratings yet
- Comb MeritDocument28 pagesComb MeritOmkar BadeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Speaking TasksDocument121 pagesAnalysis of Speaking Tasksrufael disasaNo ratings yet
- Perdev 2Document12 pagesPerdev 2Gwen MigueNo ratings yet
- 177 284 1 PBDocument22 pages177 284 1 PBREZA ALAFARISNo ratings yet
- 04 Mastering Listening PDFDocument8 pages04 Mastering Listening PDFMoshiur Rahman TaneemNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organizational Behavior 12 Edition John R SchermerhornDocument41 pagesTest Bank For Organizational Behavior 12 Edition John R SchermerhornJesseBurnettkemz100% (50)
- Chapter 4 Roles of Educational TechnologyDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Roles of Educational Technology025wilmelNo ratings yet
Module 1
Module 1
Uploaded by
Irene GarderOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 1
Module 1
Uploaded by
Irene GarderCopyright:
Available Formats
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
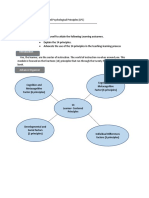
Module 1: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)
The learner the center of instruction. The world of instruction revolves around the learner. This module
introduces you to the fourteen (14) learner-centered principles which shall be used throughout this
module as a guide in determining appropriate pedagogy for learners at different life stages
In this module challenge yourself to:
Explain the 14 principles
Advocate for the use of the 14 principles in the teaching-learning process.
Identify ways on how to apply the 14 principles in instructions as a future
teacher.
Good day! Our lesson for today is about the Learner-Centered Psychological Principles . In this module
you will learn the 14 psychological principles pertain to the learner and the learning process.
The 14 principles have the following aspects:
They focus on psychological factors that are primarily internal to and under the control of the
learner rather than conditioned habits or physiological factors. However, the principles also
attempt to acknowledge external environment or contextual factors that interact with these
internal factors.
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
The principles are intended to deal holistically with learners in the context of real-world learning
situations. Thus, they are best understood as an organized set of principles; no principle should
be viewed in isolation.
The 14 principles are divided into those referring to (1) cognitive and metacognitive, (2)
motivational and affective, (3) developmental and social, and (4) individual difference factors
influencing learners and learning.
Finally, the principles are intended to apply to all learners- from children, to teachers, to
administrators, to parents, and to community members involved in our educational system.
COGNITIVE AND METACOGNITIVE FACTORS
1. Nature of the Learning process
The learning of complex subject matter is most effective when it is an intentional
process of constructing meaning from information and experience.
There are different types of learning processes, for example, habit formation in
motor learning; and learning that involves the generation of knowledge, or
cognitive skills and learning strategies.
Learning in school emphasizes the use of intentional processes that students
can use to construct meaning from information, experiences, and their own
thoughts and beliefs
Successful learners are active, goal-directed, self regulating, and assume
personal responsibility for contributing to their own learning.
2. Goals of the learning process
The successful learner, over time and with support and instructional guidance, can
create meaningful, coherent representations of knowledge
The strategic nature of learning requires students to be goal-directed.
To construct useful representations of knowledge and to acquire the thinking
and learning strategies necessary for continued learning success across the life
span, students must generate and pursue personally relevant goals. Initialy
students’ short-term goals and learning may be sketchy in an area, but over
time their understanding can be refined by filling gaps, resolving inconsistencies,
and deepening their understanding of the subject matter so that they can reach
longer-term goals.
Educators can assist learners in creating meaningful learning goals that are
consistent with both personal and educational aspirations and interests.
3. Construction of knowledge
The successful learner can link new information with existing knowledge in meaningful
ways
Knowledge widens and deepens as students continue to build links between
new information and experiences and their existing knowledge base. The
nature of these links can take a variety of forms, such as adding to, modifying, or
reorganizing existing knowledge or skills. How these links are made or develop
may vary in different subject areas, and among students with varying talents,
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
interests, and abilities. However, unless new knowledge becomes integrated
with the learner’s prior knowledge and understanding, this new knowledge
remains isolated, cannot be used most effectively in new tasks, and does not
transfer readily to new situations.
Educators can assist learners in acquiring and integrating knowledge by a
number of strategies that have been shown to be effective with learners of
varying abilities, such as concept mapping and thematic organization or
categorizing.
4. Strategic thinking
The successful learner can create and use a repertoire of thinking and reasoning
strategies to achieve complex learning goals
Successful learners use strategic thinking in their approach to learning,
reasoning, problem solving, and concept learning
They understand and can use a variety of strategies to help them reach learning
and performance goals, and to apply their knowledge in novel situations.
They also continue to expand their repertoire of strategies by reflecting on the
methods they use to see which work well for them, by receiving guided
instruction and feedback, and by observing or interacting with appropriate
models.
Learning outcomes can enhanced if educators assist learners in developing,
applying, and assessing their strategic learning skills.
5. Thinking about thinking
Higher order strategies for selecting and monitoring mental operations facilitate
creative ad critical thinking
Successful learners can reflect on how they think and learn, set reasonable
learning or performance goals, select potentially appropriate learning strategies
or methods, and monitor their progress toward these goals.
In addition, successful learners know what to do if a problem occurs or if they
are not making sufficient or timely progress toward a goal. They can generate
alternative methods to reach their goal (or reassess the appropriateness and
utility of the goal).
Instructional methods that focus on helping learners develop these higher order
(metacognitive) strategies can enhance student learning and personal
responsibility for learning
6. Context of learning
Learning is influenced by environmental factors, including culture, technology, and
instructional practices.
Learning does not occur in a vacuum. Teachers play a major interactive role
with both the learner and the learning environment.
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
Cultural or group influences on students can impact many educationally
relevant variables, such as motivation, orientation toward learning, and ways of
thinking.
Technologies and instructional practices must be appropriate for learner’s level
of prior knowledge, cognitive abilities and their learning and thinking strategies.
The classroom environment, particularly the degree to which it is nurturing or
not, can also have significant impacts on student learning
MOTIVATIONAL AND AFFECTIVE FACTORS
7. Motivational and emotional influences on learning
What and how much is learned is influenced by the learner’s motivation. Motivation
to learn in turn, is influenced by the individual’s emotional states, beliefs, interests and
goals, and habits of thinking
The rich internal world of thoughts, beliefs, goals, and expectations for success
or failure can enhance or interfere with the learner’s quality of thinking and
information processing.
Students’ belief about themselves as learners and the nature of learning have a
marked influence on motivation. Motivational and emotional and emotional
factors also influence both the quality of thinking and information processing as
well as an individual’s motivation to learn.
Positive emotions, such as curiosity, generally enhance motivation and facilitate
learning and performance by focusing the learner’s attention on a particular
task. However, intense negative emotions (e.g., anxiety, panic, rage, insecurity)
and related thoughts (e.g., worrying about competence, ruminating about
failure, fearing punishment, ridicule, or stigmatizing labels) generally detract
from motivation, interfere with learning, and contribute to low performance.
8. Intrinsic motivation to learn
The learner’s creativity, higher order thinking, and natural curiosity all contribute to
motivation to learn. Intrinsic motivation is stimulated by tasks of optimal novelty and
difficulty; relevant to personal interests, and providing for personal choice and control
Curiosity, flexible and insightful thinking, and creativity are major indicators of
the learners’ intrinsic motivation to learn, which is in large part a function of
meeting basic needs to be competent and to exercise personal control.
Intrinsic motivation is facilitated on tasks that learners perceive as interesting
and personally relevant and meaningful, appropriate in complexity and difficulty
to the learners’ abilities, and on which they believe they can succeed.
Intrinsic motivation is also facilitated on task that are comparable to real-world
situations and meet needs for choice and control.
Educators can encourage and support learners’ natural curiosity and motivation
to learn by attending to individual differences in learner’s perceptions of
optimal novelty and difficulty, relevance, and personal choice and control.
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
9. Effects of motivation on effort
Acquisition of complex knowledge and skills requires extended learner effort and
guided practice. Without learner’s motivation to learn, the willingness to exert this
effort is unlikely without coercion
Effort is another major indicator of motivation to learn. The acquisition of
complex knowledge and skills demands the investment of considerable learner
energy and strategic effort, along with persistence overtime.
Educators need to be concerned with facilitating motivation by strategies that
enhance learner effort and commitment to learning and to achieving high
standards of comprehension and understanding
Effective strategies include purposeful learning activities, guided by practices
that enhance positive emotions and intrinsic motivation to learn, and methods
that increase learner’s perceptions that a task is interesting and personally
relevant.
DEVELOPMENTAL AND SOCIAL FACTORS
10. Developmental influences on learning
As individuals develop, there are different opportunities and constraints for learning.
Learning is most effective when differential development within and across physical,
intellectual, emotional, and social domains is taken into account.
Individuals learn best when material is appropriate to their developmental level
and is presented in an enjoyable and interesting way.
Because individual development varies across intellectual, social, emotional,
and physical domains, achievement in different instructional domains may also
vary
Overemphasis on one type of developmental readiness – such as reading
readiness, for example – may preclude learners from demonstrating that they
are more capable in other areas of performance
The cognitive, emotional, and social development of individual learners and how
they interpret life experiences are affected by prior schooling, home, culture
and community factors.
Early and continuing parental involvement in schooling, and the quality of
language interactions and two-way communications between adults and
children can influence these developmental areas.
Awareness and understanding of developmental differences among children
with and without emotional, physical, or intellectual disabilities, can facilitate
the creation of optimal learning contexts.
11. Social Influences on learning
Learning is influenced by social interactions, interpersonal relations, and
communication with others
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
Learning can be enhanced when the learner has an opportunity to interact and
to collaborative with others on instructional tasks.
Learning settings that allow for social interactions, and that respect diversity,
encourage flexible thinking and social competence.
In interactive and collaborative instructional contexts, individuals have an
opportunity for perspective taking and reflective thinking that may lead to
higher levels of cognitive, social and moral development, as well as self esteem
Quality personal relationships that provide stability, trust, and caring can
increase learner’s sense of belonging, self-respect and self acceptance, and
provide a positive climate for learning
Family influences, positive interpersonal support and instruction in self-
motivation strategies can offset factors that interfere with optimal learning such
as negative beliefs about competence in a particular subject, high levels of test
anxiety, negative sex role expectations, and undue pressure to perform well.
Positive learning climates can also help to establish the context for healthier
levels of thinking, feeling, and behaving. Such contexts help learners feel safe to
share ideas, actively participate in the learning process, and create a learning
community
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES FACTORS
12. Individual differences in learning
Learners have different strategies, approaches, and capabilities for learning that are a
function of prior experience and heredity
Individuals are born with and develop their own capabilities and talents
In addition, through learning and social acculturation, they have acquired their
own preferences for how they like to learn and the pace at which they learn.
However, these preferences are not always useful in helping learners reach their
learning goals.
Educators need to help students examine their learning preferences and expand
or modify them, if necessary.
The interaction between learner differences and curricular and environmental
conditions is another key factor affecting learning outcomes
Educators need to be sensitive to individual differences, in general, They also
need to attend learner perceptions of the degree to which differences are
accepted and adapted to by varying instructional methods and materials
13. Learning and diversity
Learning is most effective when differences in learners’ linguistic, cultural, and social
backgrounds are taken into account
The same basic principles of learning, motivation, and effective instruction apply
to all learners. However, language, ethnicity, race, beliefs, and socioeconomic
status all can influence learning. Careful attention to these factors in the
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
instructional setting enhances the possibilities for designing and implementing
appropriate learning environments
When learners perceive that their individual differences in abilities,
backgrounds, cultures, and experiences are valued, respected, and
accommodated in learning tasks and contexts, levels of motivation and
achievement are enhanced
14. Standards and assessment
Setting appropriately high and challenging standards and assessing the learner as well
as learning progress – including diagnostic, process, and outcome assessment – are
integral parts of the learning process
Assessment provides important information to both the learner and teacher at
all stages of the learning process
Effective learning takes place when learners feel challenged to work towards
appropriately high goals; therefore, appraisal of the learner’s cognitive
strengths and weaknesses, as well as current knowledge and skills, is important
for the selection of instructional materials of an optimal degree of difficulty
Ongoing assessment of the learner’s understanding of the curricular material
can provide valuable feedback to both learners and teachers about progress
toward the learning goals
Standardized assessment of learner progress and outcomes assessment
provides one type of information about achievement levels both within and
across individuals that can inform various types of programmatic decisions
Performance assessments can provide other sources of information about the
attainment of learning outcomes
Self-assessments of learning progress can also improve students self appraisal
skills and enhance motivation and self-directed learning
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
Alexander and Murphy gave a summary of the 14 principles and distilled them
into five areas:
1. The knowledge base – One’s existing knowledge serves as the foundation of all future
learning. The learner’s previous knowledge will influence new learning specially on how he
represents new information, makes associations and filters new experiences
2. Strategic processing and control – Learners can develop skills to reflect and regulate their
thoughts and behaviors in order to learn more effectively (metacognition)
3. Motivation and affect – Factors such as intrinsic motivation (from within), reasons for
wanting to learn, personal goals and enjoyment of learning task all have a crucial role in the
learning process
4. learner has his own unique combination of generic and environmental factors that
influence him
5. Situation or Context – Learning happens in the context of a society as well as within an
individual.
The application of the 14 principles will be done as you explore the succeeding modules. For
now. Keep the 14 principles in mind as you explore the rest of the modules. Always try to relate
these principles to the concepts you will learn. Happy Learning!
REFLECTION
From the Module on Learner-Centered Psychological Principles, I realized
that…..________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
RESEARCH CONNECTION
Read a research or study related to Learner-centered psychological principles (LCP) .
Problem:_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Research
Methodology:_________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Findings:_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Conclusions:___________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Source: (bibliographical entry format)
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
Ed 1 Child and Adolescent Learners and LearningPrinciple
1st Semester, AY 2021-2022
September 1-15, 2021
How are the findings of this research useful to
teachers?_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Brenda B. Corpuz, PhD., et.al “ The Child and Adolescent Learners and
Learning Principles”.,
This material has been prepared and communicated to you by or on behalf of
Palawan State University - CCRD Narra for educational purposes only.
DO NOT REPRODUCE OR COMMUNICATE.
Prepared by: REMEDIOS L. MAGBANUA PSU – CCRD Narra| 1 / 2
You might also like
- This Is ADHD - Chanelle MoriahDocument12 pagesThis Is ADHD - Chanelle MoriahAllen & Unwin0% (2)
- TEFL AnswerDocument18 pagesTEFL Answerkimberly masangkay100% (1)
- The Child and Adolescent LearnersDocument179 pagesThe Child and Adolescent LearnersMyla Guab100% (1)
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LearnerDocument9 pagesModule 2 LearnerJayson PalmaNo ratings yet
- PED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMDocument43 pagesPED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMMicah Esteban OngpaucoNo ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument106 pagesFacilitating LearningnananaNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Document13 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Rea Jane OrnedoNo ratings yet
- 2prof Ed 02Document17 pages2prof Ed 02airen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Part IDocument17 pagesPart Iairen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching (1) LOUDocument12 pagesModule 2 Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching (1) LOULou Jane YescaNo ratings yet
- The Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceDocument6 pagesThe Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceAbhey Abellera Barcena100% (2)
- Module 2: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Polangui Community CollegeDocument8 pagesModule 2: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Polangui Community CollegeshielaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Week 1: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Document6 pagesModule 1 - Week 1: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Noel Jr MospaNo ratings yet
- Educ 211 Prelim ModuleDocument34 pagesEduc 211 Prelim ModuleRichard RamisNo ratings yet
- PCK 1 Module 2 Week 3 LCPDocument28 pagesPCK 1 Module 2 Week 3 LCPCharlene Mae de leonNo ratings yet
- Almira Abad Btled 2-A Merry Grace Abella Btled 2-A: PreambleDocument5 pagesAlmira Abad Btled 2-A Merry Grace Abella Btled 2-A: PreambleEl Joy BangkilingNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument9 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesCecelien Salgado AntonioNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- PS 5 Module 2 PrelimDocument7 pagesPS 5 Module 2 Prelimblssm AbenesNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Frances Bea Abarado100% (1)
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument3 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesMichael NatividadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mr. RecibeDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Mr. RecibeMoses TamondongNo ratings yet
- PED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2Document4 pagesPED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2YuriNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Introduction Module2 2022Document11 pagesPart 1 Introduction Module2 2022Jodelyn Quirao AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument11 pagesModule-1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesriegocessyNo ratings yet
- Educ 101Document35 pagesEduc 101Cyrell Joshua Salas100% (1)
- LearnerDocument3 pagesLearnerZaira Michaela CamposNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles愛No ratings yet
- Educ 105 3 & 4Document3 pagesEduc 105 3 & 4keana barnajaNo ratings yet
- Week 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesDocument30 pagesWeek 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesTrisha Mae VaguchayNo ratings yet
- M 1 Prof Ed 221Document9 pagesM 1 Prof Ed 221QueencyNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument15 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesShailanie Valle RiveraNo ratings yet
- FLCL Mod 1Document9 pagesFLCL Mod 1Ana Carmela Salazar LaraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument2 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesABADA MARY JANE MALLARINo ratings yet
- 14 PsychologicalPrinciplesDocument23 pages14 PsychologicalPrinciplesJane AgripaNo ratings yet
- 14 Learner Teaching PrincipleDocument4 pages14 Learner Teaching Principlemaela pollen yemaNo ratings yet
- Learners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesAmbita CherylNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaDocument6 pagesModule 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaGeorgie AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Ed 1o1 Modules 1 and 2Document18 pagesEd 1o1 Modules 1 and 2Abdulhamid Baute CodaranganNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Learner Centered PrinciplesDocument7 pages2 3 Learner Centered PrinciplesLeyte Gerodias0% (1)
- 14 PrinciplesDocument33 pages14 PrinciplesTep LeeNo ratings yet
- Ed 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Document3 pagesEd 35 Learning Journey 2 Activity 1Kiara TrozziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document45 pagesLesson 1Ruthche Nova C. PreteNo ratings yet
- Ed1 Module 1 NotesDocument3 pagesEd1 Module 1 NotesChristhie RobleNo ratings yet
- PED05a Module-1 Nagares LucenaDocument11 pagesPED05a Module-1 Nagares LucenaCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Learner-Centered PrinciplesDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Learner-Centered PrinciplesR PadullaNo ratings yet
- Prelim ModuleDocument34 pagesPrelim ModuleKyla Jelinne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument36 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesMariel D. BelandoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Learning PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Learning PrinciplesJohn Mark NovenoNo ratings yet
- Module-Child and Adolescent LearnerDocument85 pagesModule-Child and Adolescent LearnerAira Jane BaliquiaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Metacognitive FactorsDocument4 pagesCognitive and Metacognitive FactorsArlyn ElsiNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument39 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJonathan AysonNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 AssignmentDocument7 pagesEduc 1 AssignmentCloie GadNo ratings yet
- WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document5 pagesWMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)My Home100% (1)
- Learnered Center PriciplesDocument26 pagesLearnered Center PriciplesArselia RubanteNo ratings yet
- FACILITATING LEARNER Module 2Document6 pagesFACILITATING LEARNER Module 2Ivie CastroNo ratings yet
- ED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Document9 pagesED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Yogine M BarongNo ratings yet
- Learning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualFrom EverandLearning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualNo ratings yet
- A Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressDocument7 pagesA Study On Understanding The Effectiveness of Audiovisual Aids in Improving English Vocabulary in ESL Classrooms - 2023 - Sciedu PressHarold TrefforNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Decluttering Your MindDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Decluttering Your MindFabiana Alejandra RuizNo ratings yet
- Laws of LearninDocument2 pagesLaws of LearninDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument27 pagesEmotional IntelligenceSarah ShrisunderNo ratings yet
- Power of LanguageDocument6 pagesPower of Languageapi-660848734No ratings yet
- IVA 2 Detailed ReportDocument5 pagesIVA 2 Detailed ReportmohammadzarekandejaniNo ratings yet
- HẠNH-ĐỀ MINH HOẠ ANH -2023Document6 pagesHẠNH-ĐỀ MINH HOẠ ANH -2023Hoàng PhúcNo ratings yet
- Priming: December 2015Document11 pagesPriming: December 2015Chelsea AsiñeroNo ratings yet
- Gerrits Et Al. - 2020 - Mirrored Brain Organization Statistical Anomaly oDocument9 pagesGerrits Et Al. - 2020 - Mirrored Brain Organization Statistical Anomaly oMaya JacksonNo ratings yet
- Hawaiian Stick Song - SingingDocument4 pagesHawaiian Stick Song - Singingapi-708306698No ratings yet
- MKTG Week 5,6,7 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMKTG Week 5,6,7 ReviewerJelly NomatNo ratings yet
- Variations in Psychological AttributesDocument43 pagesVariations in Psychological Attributesfms7x8b69t100% (1)
- English MapsDocument11 pagesEnglish MapsAshlyn Jade Olleras LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Total Physical Response EssayDocument5 pagesTotal Physical Response EssayTeacher XimenaNo ratings yet
- Cultural and Linguistics Constraints On Mind-1Document29 pagesCultural and Linguistics Constraints On Mind-1Rehan BalochNo ratings yet
- PSY 305 - Chapter 5 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesPSY 305 - Chapter 5 (Reviewer)Ricajoy RicohermosoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual System of World Reflection - 2. Universal MetaphorsDocument23 pagesConceptual System of World Reflection - 2. Universal MetaphorsNazerke AbdrahmanovaNo ratings yet
- YOU MUST BECOME A MASTER OF YOUR MIND (Very Inspirational)Document26 pagesYOU MUST BECOME A MASTER OF YOUR MIND (Very Inspirational)Linh BạchNo ratings yet
- 5 Year Old Boy Case StudyDocument16 pages5 Year Old Boy Case StudyClare LebedaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of PlayDocument1 pageThe Importance of PlayShabree JemmottNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3W1 Day 2Document10 pagesDLP Q3W1 Day 2Marieta SorianoNo ratings yet
- Comb MeritDocument28 pagesComb MeritOmkar BadeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Speaking TasksDocument121 pagesAnalysis of Speaking Tasksrufael disasaNo ratings yet
- Perdev 2Document12 pagesPerdev 2Gwen MigueNo ratings yet
- 177 284 1 PBDocument22 pages177 284 1 PBREZA ALAFARISNo ratings yet
- 04 Mastering Listening PDFDocument8 pages04 Mastering Listening PDFMoshiur Rahman TaneemNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organizational Behavior 12 Edition John R SchermerhornDocument41 pagesTest Bank For Organizational Behavior 12 Edition John R SchermerhornJesseBurnettkemz100% (50)
- Chapter 4 Roles of Educational TechnologyDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Roles of Educational Technology025wilmelNo ratings yet