Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Uploaded by
Rutchell DologuinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lesson 3: Writing and Deconstruction of Classical TalesDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Writing and Deconstruction of Classical Talesfretzielasala000No ratings yet
- Crisscrossing Through Afro-Asian LiteratureFrom EverandCrisscrossing Through Afro-Asian LiteratureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Morning Sidekick Journal (Fillable & Abridged)Document12 pagesThe Morning Sidekick Journal (Fillable & Abridged)Mel Mourão0% (3)
- Literature Competencies in English K To 12 CurriculumDocument6 pagesLiterature Competencies in English K To 12 CurriculumJoy Erica C. Leo100% (1)
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature of The Philippines and The WorldDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature of The Philippines and The WorldBlue BarridoNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer On The Overview of StylisticsDocument6 pagesGraphic Organizer On The Overview of StylisticsJessa JumawanNo ratings yet
- ARMM - A House Full of DaughtersDocument4 pagesARMM - A House Full of DaughtersMosedeil Herbert Tabios100% (3)
- Interpreting and Evaluating Fictions & Types and Elements of FictionDocument36 pagesInterpreting and Evaluating Fictions & Types and Elements of FictionDixie MhayNo ratings yet
- #2teaching and Assessment of GrammarDocument17 pages#2teaching and Assessment of GrammarDongLei CortezNo ratings yet
- Mythology Module 1 Topic 1 FullDocument6 pagesMythology Module 1 Topic 1 FullLalaine RideraNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Literary Prose and Drama Stylistics: Example of A Poetry Verse vs. The Prose FormDocument43 pagesUnit Ii Literary Prose and Drama Stylistics: Example of A Poetry Verse vs. The Prose FormGenesis Barquilla0% (1)
- Padua, Denotative vs. Connotative, Lex. VS StylisticDocument9 pagesPadua, Denotative vs. Connotative, Lex. VS StylisticLyle Marie Padua100% (2)
- INDONESIAN lITERATUREDocument11 pagesINDONESIAN lITERATURErayhana minalang-limbonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Poem: Valediction Sa Hillcrest Let'S Warm Up!Document7 pagesLesson 2 Poem: Valediction Sa Hillcrest Let'S Warm Up!Angielyn Montibon Jesus0% (1)
- Factors Affecting Interests in Literature-Rayala - 1Document3 pagesFactors Affecting Interests in Literature-Rayala - 1Edward James FellingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To The World of Children and Adolescent LiteratureDocument12 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To The World of Children and Adolescent LiteratureMelo fi6No ratings yet
- Campus Journ ActDocument3 pagesCampus Journ Actlyn calicdanNo ratings yet
- Maestro in Absentia EnglishDocument3 pagesMaestro in Absentia EnglishJff ReyesNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 An Overview of StylisticsDocument53 pagesGROUP 1 An Overview of StylisticsEmyNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 2: Interpreting and Evaluating Fiction: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument8 pagesACTIVITY 2: Interpreting and Evaluating Fiction: Rizal Technological UniversityANGELA MELLINA ADORNo ratings yet
- Module English 26Document42 pagesModule English 26shella mae pormentoNo ratings yet
- New CriticismDocument15 pagesNew CriticismRembrandt GradoNo ratings yet
- Motifs/ Images Mood/ Atmosphere: Silence-A Fable by Edgar Allan PoeDocument2 pagesMotifs/ Images Mood/ Atmosphere: Silence-A Fable by Edgar Allan PoeRegie EstoreonNo ratings yet
- Review of Purposes and Benefits of Literature StudiesDocument8 pagesReview of Purposes and Benefits of Literature StudiesHannah Mae EscasulatanNo ratings yet
- Activity (First Vs Second Language)Document2 pagesActivity (First Vs Second Language)RHEA MARIMLA67% (3)
- Final Demo LPDocument18 pagesFinal Demo LPBob MagcantaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of Afro-Asian LiteratureDocument57 pagesSynopsis of Afro-Asian Literatureمہنور مہتاب100% (2)
- Contemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureDocument11 pagesContemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureRio PendonNo ratings yet
- Hand Out (Like The Molave)Document2 pagesHand Out (Like The Molave)Farrah Mie Felias-Ofilanda100% (1)
- Module in Survey of Philippine Literature (3yr)Document5 pagesModule in Survey of Philippine Literature (3yr)Ferliza Cudiamat PacionNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year BSED EL 118 - MODULE 2 - MID - FINALDocument24 pages3rd Year BSED EL 118 - MODULE 2 - MID - FINALJeiel Collamar Goze100% (1)
- NADELA - Task 1 On Instructional Materials - ACRONYMDocument1 pageNADELA - Task 1 On Instructional Materials - ACRONYMDOROTHY JOY NADELANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan P.PinedaDocument7 pagesLesson Plan P.PinedaMarvinbautistaNo ratings yet
- Saint Vincent de Paul Diocesan College: Read and ExploreDocument5 pagesSaint Vincent de Paul Diocesan College: Read and ExploreTrebligCondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson/Topic: Everybody Has His Burden - An Indonesian Folktale ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson/Topic: Everybody Has His Burden - An Indonesian Folktale Objectivesjenalyn lacaba100% (1)
- Module 1 Intro To EL 112Document11 pagesModule 1 Intro To EL 112Lalaine RideraNo ratings yet
- Poetry: The Ruined City (Figurative Language) : Objectives ResourcesDocument12 pagesPoetry: The Ruined City (Figurative Language) : Objectives ResourcesJoemar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Wk1-5 LessonDocument30 pagesWk1-5 LessonsalditoskriiusyNo ratings yet
- The Transformational AmaranthaDocument6 pagesThe Transformational AmaranthaNoriel Agascon100% (1)
- Case Analysis For The English Language Program For Saharan StudentsDocument5 pagesCase Analysis For The English Language Program For Saharan StudentsNorkhan Macapanton50% (2)
- Literary Criticism MidtermDocument2 pagesLiterary Criticism MidtermWinefredo Quiapo PaghubasanNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN 6 - Campus JournDocument28 pagesDOMAIN 6 - Campus JournJorge Mrose26No ratings yet
- Strategies in Teaching and Assessing PoetryDocument6 pagesStrategies in Teaching and Assessing PoetryRica Mae TabermejoNo ratings yet
- Genres and Branches of LiteratureDocument6 pagesGenres and Branches of LiteratureRENATO JR. RARUGALNo ratings yet
- New Criticism What Is New Criticism?Document6 pagesNew Criticism What Is New Criticism?Shanna Ky Opina100% (1)
- Theories Related To Folk LiteratureDocument6 pagesTheories Related To Folk LiteratureJade Christal Bate100% (1)
- Indian LiteratureDocument13 pagesIndian Literaturerejo12100% (1)
- Intro To Philippine Literature PoetryDocument7 pagesIntro To Philippine Literature PoetryYrrech LaneNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram of Chinese Literature and Hindu LiteratureDocument1 pageVenn Diagram of Chinese Literature and Hindu Literaturekiannatherese andradaNo ratings yet
- Egyptian LiteratureDocument32 pagesEgyptian LiteratureRocio Marie Tejido50% (2)
- JAYARR RONDINA - Literary Analysis-Egyptian Lit.Document2 pagesJAYARR RONDINA - Literary Analysis-Egyptian Lit.JAYARR RONDINA100% (1)
- Chinese Literature Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChinese Literature Test ReviewRashiel Jane Paronia CelizNo ratings yet
- The Restoration and The 18th Century LiteratureDocument29 pagesThe Restoration and The 18th Century LiteraturePrimerose GlnNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism ModuleDocument10 pagesLiterary Criticism ModulePrince Isaiah JacobNo ratings yet
- Acfrogascy-Br Cjcnsy4uqdmfveujkrh4kbg7cwjdhtznrmaz0fqgqbaxq-Jdgww6 Kyxhrrh8adqtcam 5oglf6caow1fqxwthgvs9hzxcaz Uflrne9byvwu-Vlxj8ybc j0d8nvszl Ckb6tDocument18 pagesAcfrogascy-Br Cjcnsy4uqdmfveujkrh4kbg7cwjdhtznrmaz0fqgqbaxq-Jdgww6 Kyxhrrh8adqtcam 5oglf6caow1fqxwthgvs9hzxcaz Uflrne9byvwu-Vlxj8ybc j0d8nvszl Ckb6tJohn Carl AparicioNo ratings yet
- Style As NormDocument26 pagesStyle As NormAnonymous 6rSv4gofk100% (2)
- Linguistic ModeDocument8 pagesLinguistic ModeZorina May AlmadinNo ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishLETDocument30 pagesStructure of EnglishLETAlmarie Fuentes100% (1)
- Developing Materials For Students Listening SkillsDocument25 pagesDeveloping Materials For Students Listening SkillsMikha100% (2)
- Elec 4 ReportDocument2 pagesElec 4 ReportIrishNo ratings yet
- Position of Proverbs in Communicative Activities in EnglishDocument4 pagesPosition of Proverbs in Communicative Activities in EnglishAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- Written Report Denotative vs. Connotative Lexical vs. Stylistics Perodes SongahidDocument6 pagesWritten Report Denotative vs. Connotative Lexical vs. Stylistics Perodes SongahidRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Survey of Prose Authors - Dramatists and Their Unique StylesDocument13 pagesSurvey of Prose Authors - Dramatists and Their Unique StylesRutchell Dologuin100% (1)
- Cover Letter 3Document1 pageCover Letter 3Rutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Apex Construction IncorporatedDocument2 pagesApex Construction IncorporatedRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Set Problem 1 and 2.Document2 pagesSet Problem 1 and 2.Rutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- TQM Semi Final ExamDocument7 pagesTQM Semi Final ExamRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- SemiDocument19 pagesSemiRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q1 - W7Document3 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q1 - W7Sheila Joy Marmol CasinNo ratings yet
- Masako Azuma, Sikh Diaspora in JapanDocument175 pagesMasako Azuma, Sikh Diaspora in JapansinghNo ratings yet
- Robust Vocabulary InstructionDocument4 pagesRobust Vocabulary Instructionmadhu_gopinathanNo ratings yet
- Amanda BaggsDocument7 pagesAmanda Baggsapi-385249708No ratings yet
- Introduction To English AdverbsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To English AdverbsFrankie ArenolliNo ratings yet
- Course FlowDocument12 pagesCourse FlowSheikh MD Sazidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Aprende IdiomasDocument22 pagesAprende IdiomasXimena SánchezNo ratings yet
- Unit08 ExtensionTestDocument3 pagesUnit08 ExtensionTestCarito MoyaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in English 10Document3 pages1st Quarter Exam in English 10Rachelle BobisNo ratings yet
- MUSS: Multilingual Unsupervised Sentence Simplification by Mining ParaphrasesDocument16 pagesMUSS: Multilingual Unsupervised Sentence Simplification by Mining ParaphrasesMustafa GencNo ratings yet
- Incursion Into Wendigo Territory: Jackson Eflin, Ball Sate UniversityDocument11 pagesIncursion Into Wendigo Territory: Jackson Eflin, Ball Sate UniversityZachary GrgichNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Journal Article - TemplateDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Journal Article - TemplateKhaleza ZudiakeNo ratings yet
- Cook-Greuter Construct Aware Stage and The Fool ArchetypeDocument11 pagesCook-Greuter Construct Aware Stage and The Fool ArchetypeRalitza PantchevaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Vocabulary - WorkDocument29 pagesIELTS Vocabulary - WorkStella NguyenNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - English - 2017 - (2nd Ed.)Document8 pagesCourse Outline - English - 2017 - (2nd Ed.)Nuttapong RutamornchaiNo ratings yet
- Noun Types Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesNoun Types Worksheet PDFmoehammadj0% (1)
- To Become: 1. Get To Obtain, To Receive, To Buy 2. Get To Reach, To Arrive 3. Get To BecomeDocument3 pagesTo Become: 1. Get To Obtain, To Receive, To Buy 2. Get To Reach, To Arrive 3. Get To BecomeparulNo ratings yet
- Second Language Urdu: Paper 3248/01 Composition and TranslationDocument7 pagesSecond Language Urdu: Paper 3248/01 Composition and TranslationMahad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Letter FDocument20 pagesLetter FMuhammad HusnainNo ratings yet
- Завдання, 3 курс, 6 семестрDocument11 pagesЗавдання, 3 курс, 6 семестрИльяNo ratings yet
- Adapting and Adopting Learning MaterialsDocument24 pagesAdapting and Adopting Learning Materialsnina so100% (6)
- Speaking Cefr TipsDocument17 pagesSpeaking Cefr TipsPurr MiaowNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument7 pagesRelative ClausesCandelaria LuqueNo ratings yet
- Translation and Mass Communication PDFDocument27 pagesTranslation and Mass Communication PDFrbernabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Countable Uncountable PDFDocument1 pageUnit 7 Countable Uncountable PDFDario AmeriNo ratings yet
- English 2 WorsheetDocument9 pagesEnglish 2 WorsheetNic Hussin MejiaNo ratings yet
- Literacy Progressions K-10Document39 pagesLiteracy Progressions K-10Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Kawi and Kawi MiringDocument553 pagesKawi and Kawi MiringDian KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- A Short Synopsis of The Most Essential Points in Hawaiian Grammar (1864)Document70 pagesA Short Synopsis of The Most Essential Points in Hawaiian Grammar (1864)ursmartinNo ratings yet
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Uploaded by
Rutchell DologuinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context
Uploaded by
Rutchell DologuinCopyright:
Available Formats
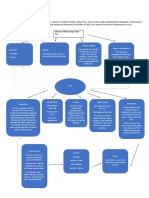
Linguistic vs.
Extralingual Context
Linguistic Context
Extralingual Context
Microcontext
Macrocontext
Megacontext
Language is an essential tool for communication, but it is not the only factor that
affects how people understand each other. Context plays a significant role in
communication, and it can be classified into two types: Linguistic and Extralingual
context.
Linguistic Context
- is the encirclement of a language unit by other language units in speech.
Such encirclement makes the meaning of the unit clear and unambiguous.
It is especially important in case with polysemantic words.
- This includes information about the grammatical structure of a sentence,
the words and phrases that surround a particular word, and the meaning
of those words and phrases in relation to each other.
Examples of Polysemantic Words:
1. “Run”
This word can refer to the act of moving quickly on foot, as in "I
like to run for exercise." However, it can also refer to a tear or snag
in a piece of clothing, as in "I can't wear these pants anymore, and
they have a run in them." Additionally, "run" can mean to manage
or be in charge of something, as in "She runs her own business."
2. "Bat"
This word can refer to a flying mammal, a piece of sporting
equipment used in baseball or cricket, or a swift hit or strike.
EL 115 - STYLISTICS AND DISCOURSE ANALYSIS 1
3. "Crane"
This word can refer to a type of bird, a piece of heavy equipment
used in construction, or a gesture in which one stretches out their
neck to see something better.
4. "Match"
This word can refer to a small stick used to start a fire, a
competition between two teams or individuals, or a pairing of two
people or things that complement each other.
- For example, consider the word "bank". Depending on the context in
which it is used, "bank" could refer to a financial institution, the side of a
river, or the act of tilting or turning something.
1. "I need to go to the bank to deposit a check,"
the word "bank" is clearly referring to a financial institution, as this is the
most likely meaning in this context.
2. "The boat drifted towards the bank of the river,"
the word "bank" is clearly referring to the side of the river.
Extralingual Context
- An extralingual (situational) context is formed by extralingual conditions
in which communication takes place.
- It refers to the non-linguistic factors that influence the meaning and interpretation
of messages.
Two Factors:
1. Physical context - refers to the tangible and observable conditions in
which communication takes place.
2. Abstract context - refers to the intangible and less observable factors
that influence communication. This can include temporal or
chronological context, which refers to the time and sequence in which
events occur. Psychological context is another form of abstract context
EL 115 - STYLISTICS AND DISCOURSE ANALYSIS 2
that refers to the emotional and cognitive state of the participants in the
communication.
TYPES OF LINGUISTIC CONTEXT
1. Microcontext - is the context of a single utterance (sentence).
Example:
Sentence: "I need to change the battery in my watch."
The microcontext of the word "battery" in this sentence is that it refers to a
small, portable power source used to power electronic devices, such as
watches.
2. Macrocontext - is the context of a paragraph in a text. \
Example:
"Despite being a common affliction, anxiety can be incredibly
debilitating for those who experience it. It can lead to a range of
symptoms, including sweating, heart palpitations, and difficulty
concentrating. Furthermore, anxiety can have a significant impact on a
person's quality of life, affecting their ability to work, maintain
relationships, and engage in everyday activities. Fortunately, there are
many effective treatments available for anxiety, such as cognitive-
behavioral therapy and medication."
In this example, the macrocontext would be the larger context of
the entire text that the paragraph is a part of, such as a book, article, or
report. The paragraph is discussing the topic of anxiety, its symptoms,
and its impact on a person's life, and is likely part of a larger discussion
about mental health. The macrocontext is important for understanding the
overall purpose and message of the text as a whole.
EL 115 - STYLISTICS AND DISCOURSE ANALYSIS 3
3. Megacontext - is the context of a book chapter, a story or the whole book.
Example:
The novel "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee.
The megacontext would be the entire novel, which includes various
storylines, characters, and themes. The events that occur in each chapter
build upon each other, and the characters' actions and motivations are
shaped by the events that occur throughout the novel. To fully understand
and appreciate the novel, one must consider the megacontext, which
encompasses the entire narrative and its themes.
Linguistic and extralingual context are both important aspects of communication.
Linguistic context refers to the words and language used to convey a message, while
extralingual context refers to the non-linguistic factors that influence communication,
such as the physical or abstract conditions in which communication takes place. In
order to effectively communicate, it is important to consider both linguistic and
extralingual context. This means paying attention not only to the words being used, but
also to the environment in which communication takes place and the nonverbal cues
being given.
References
Studocu. (n.d). NOTES IN STYLISTIC AND DISCOURSE DEVELOPMENT
Linguistic vs. Extralingual Contexts.
https://www.studocu.com/ph/document/university-of-southern-
mindanao/stylistic-and-discourse-development/linguistic-vs-
extralingual-contexts/31023047
Blanco, A. (Jun 9, 2022). Linguistic vs. Extralingual Context.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KgzC1hlsxZc
Prepared by:
Antiporda, Mylene
Lacumbis, Shaene Mae
Ladrica, Marianne Mae
EL 115 - STYLISTICS AND DISCOURSE ANALYSIS 4
You might also like
- Lesson 3: Writing and Deconstruction of Classical TalesDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Writing and Deconstruction of Classical Talesfretzielasala000No ratings yet
- Crisscrossing Through Afro-Asian LiteratureFrom EverandCrisscrossing Through Afro-Asian LiteratureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Morning Sidekick Journal (Fillable & Abridged)Document12 pagesThe Morning Sidekick Journal (Fillable & Abridged)Mel Mourão0% (3)
- Literature Competencies in English K To 12 CurriculumDocument6 pagesLiterature Competencies in English K To 12 CurriculumJoy Erica C. Leo100% (1)
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature of The Philippines and The WorldDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature of The Philippines and The WorldBlue BarridoNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer On The Overview of StylisticsDocument6 pagesGraphic Organizer On The Overview of StylisticsJessa JumawanNo ratings yet
- ARMM - A House Full of DaughtersDocument4 pagesARMM - A House Full of DaughtersMosedeil Herbert Tabios100% (3)
- Interpreting and Evaluating Fictions & Types and Elements of FictionDocument36 pagesInterpreting and Evaluating Fictions & Types and Elements of FictionDixie MhayNo ratings yet
- #2teaching and Assessment of GrammarDocument17 pages#2teaching and Assessment of GrammarDongLei CortezNo ratings yet
- Mythology Module 1 Topic 1 FullDocument6 pagesMythology Module 1 Topic 1 FullLalaine RideraNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Literary Prose and Drama Stylistics: Example of A Poetry Verse vs. The Prose FormDocument43 pagesUnit Ii Literary Prose and Drama Stylistics: Example of A Poetry Verse vs. The Prose FormGenesis Barquilla0% (1)
- Padua, Denotative vs. Connotative, Lex. VS StylisticDocument9 pagesPadua, Denotative vs. Connotative, Lex. VS StylisticLyle Marie Padua100% (2)
- INDONESIAN lITERATUREDocument11 pagesINDONESIAN lITERATURErayhana minalang-limbonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Poem: Valediction Sa Hillcrest Let'S Warm Up!Document7 pagesLesson 2 Poem: Valediction Sa Hillcrest Let'S Warm Up!Angielyn Montibon Jesus0% (1)
- Factors Affecting Interests in Literature-Rayala - 1Document3 pagesFactors Affecting Interests in Literature-Rayala - 1Edward James FellingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To The World of Children and Adolescent LiteratureDocument12 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To The World of Children and Adolescent LiteratureMelo fi6No ratings yet
- Campus Journ ActDocument3 pagesCampus Journ Actlyn calicdanNo ratings yet
- Maestro in Absentia EnglishDocument3 pagesMaestro in Absentia EnglishJff ReyesNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 An Overview of StylisticsDocument53 pagesGROUP 1 An Overview of StylisticsEmyNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 2: Interpreting and Evaluating Fiction: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument8 pagesACTIVITY 2: Interpreting and Evaluating Fiction: Rizal Technological UniversityANGELA MELLINA ADORNo ratings yet
- Module English 26Document42 pagesModule English 26shella mae pormentoNo ratings yet
- New CriticismDocument15 pagesNew CriticismRembrandt GradoNo ratings yet
- Motifs/ Images Mood/ Atmosphere: Silence-A Fable by Edgar Allan PoeDocument2 pagesMotifs/ Images Mood/ Atmosphere: Silence-A Fable by Edgar Allan PoeRegie EstoreonNo ratings yet
- Review of Purposes and Benefits of Literature StudiesDocument8 pagesReview of Purposes and Benefits of Literature StudiesHannah Mae EscasulatanNo ratings yet
- Activity (First Vs Second Language)Document2 pagesActivity (First Vs Second Language)RHEA MARIMLA67% (3)
- Final Demo LPDocument18 pagesFinal Demo LPBob MagcantaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of Afro-Asian LiteratureDocument57 pagesSynopsis of Afro-Asian Literatureمہنور مہتاب100% (2)
- Contemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureDocument11 pagesContemporary, Popular and Emergent LiteratureRio PendonNo ratings yet
- Hand Out (Like The Molave)Document2 pagesHand Out (Like The Molave)Farrah Mie Felias-Ofilanda100% (1)
- Module in Survey of Philippine Literature (3yr)Document5 pagesModule in Survey of Philippine Literature (3yr)Ferliza Cudiamat PacionNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year BSED EL 118 - MODULE 2 - MID - FINALDocument24 pages3rd Year BSED EL 118 - MODULE 2 - MID - FINALJeiel Collamar Goze100% (1)
- NADELA - Task 1 On Instructional Materials - ACRONYMDocument1 pageNADELA - Task 1 On Instructional Materials - ACRONYMDOROTHY JOY NADELANo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan P.PinedaDocument7 pagesLesson Plan P.PinedaMarvinbautistaNo ratings yet
- Saint Vincent de Paul Diocesan College: Read and ExploreDocument5 pagesSaint Vincent de Paul Diocesan College: Read and ExploreTrebligCondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson/Topic: Everybody Has His Burden - An Indonesian Folktale ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson/Topic: Everybody Has His Burden - An Indonesian Folktale Objectivesjenalyn lacaba100% (1)
- Module 1 Intro To EL 112Document11 pagesModule 1 Intro To EL 112Lalaine RideraNo ratings yet
- Poetry: The Ruined City (Figurative Language) : Objectives ResourcesDocument12 pagesPoetry: The Ruined City (Figurative Language) : Objectives ResourcesJoemar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Wk1-5 LessonDocument30 pagesWk1-5 LessonsalditoskriiusyNo ratings yet
- The Transformational AmaranthaDocument6 pagesThe Transformational AmaranthaNoriel Agascon100% (1)
- Case Analysis For The English Language Program For Saharan StudentsDocument5 pagesCase Analysis For The English Language Program For Saharan StudentsNorkhan Macapanton50% (2)
- Literary Criticism MidtermDocument2 pagesLiterary Criticism MidtermWinefredo Quiapo PaghubasanNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN 6 - Campus JournDocument28 pagesDOMAIN 6 - Campus JournJorge Mrose26No ratings yet
- Strategies in Teaching and Assessing PoetryDocument6 pagesStrategies in Teaching and Assessing PoetryRica Mae TabermejoNo ratings yet
- Genres and Branches of LiteratureDocument6 pagesGenres and Branches of LiteratureRENATO JR. RARUGALNo ratings yet
- New Criticism What Is New Criticism?Document6 pagesNew Criticism What Is New Criticism?Shanna Ky Opina100% (1)
- Theories Related To Folk LiteratureDocument6 pagesTheories Related To Folk LiteratureJade Christal Bate100% (1)
- Indian LiteratureDocument13 pagesIndian Literaturerejo12100% (1)
- Intro To Philippine Literature PoetryDocument7 pagesIntro To Philippine Literature PoetryYrrech LaneNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram of Chinese Literature and Hindu LiteratureDocument1 pageVenn Diagram of Chinese Literature and Hindu Literaturekiannatherese andradaNo ratings yet
- Egyptian LiteratureDocument32 pagesEgyptian LiteratureRocio Marie Tejido50% (2)
- JAYARR RONDINA - Literary Analysis-Egyptian Lit.Document2 pagesJAYARR RONDINA - Literary Analysis-Egyptian Lit.JAYARR RONDINA100% (1)
- Chinese Literature Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChinese Literature Test ReviewRashiel Jane Paronia CelizNo ratings yet
- The Restoration and The 18th Century LiteratureDocument29 pagesThe Restoration and The 18th Century LiteraturePrimerose GlnNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism ModuleDocument10 pagesLiterary Criticism ModulePrince Isaiah JacobNo ratings yet
- Acfrogascy-Br Cjcnsy4uqdmfveujkrh4kbg7cwjdhtznrmaz0fqgqbaxq-Jdgww6 Kyxhrrh8adqtcam 5oglf6caow1fqxwthgvs9hzxcaz Uflrne9byvwu-Vlxj8ybc j0d8nvszl Ckb6tDocument18 pagesAcfrogascy-Br Cjcnsy4uqdmfveujkrh4kbg7cwjdhtznrmaz0fqgqbaxq-Jdgww6 Kyxhrrh8adqtcam 5oglf6caow1fqxwthgvs9hzxcaz Uflrne9byvwu-Vlxj8ybc j0d8nvszl Ckb6tJohn Carl AparicioNo ratings yet
- Style As NormDocument26 pagesStyle As NormAnonymous 6rSv4gofk100% (2)
- Linguistic ModeDocument8 pagesLinguistic ModeZorina May AlmadinNo ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishLETDocument30 pagesStructure of EnglishLETAlmarie Fuentes100% (1)
- Developing Materials For Students Listening SkillsDocument25 pagesDeveloping Materials For Students Listening SkillsMikha100% (2)
- Elec 4 ReportDocument2 pagesElec 4 ReportIrishNo ratings yet
- Position of Proverbs in Communicative Activities in EnglishDocument4 pagesPosition of Proverbs in Communicative Activities in EnglishAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- Written Report Denotative vs. Connotative Lexical vs. Stylistics Perodes SongahidDocument6 pagesWritten Report Denotative vs. Connotative Lexical vs. Stylistics Perodes SongahidRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Survey of Prose Authors - Dramatists and Their Unique StylesDocument13 pagesSurvey of Prose Authors - Dramatists and Their Unique StylesRutchell Dologuin100% (1)
- Cover Letter 3Document1 pageCover Letter 3Rutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Apex Construction IncorporatedDocument2 pagesApex Construction IncorporatedRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- Set Problem 1 and 2.Document2 pagesSet Problem 1 and 2.Rutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- TQM Semi Final ExamDocument7 pagesTQM Semi Final ExamRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- SemiDocument19 pagesSemiRutchell DologuinNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q1 - W7Document3 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q1 - W7Sheila Joy Marmol CasinNo ratings yet
- Masako Azuma, Sikh Diaspora in JapanDocument175 pagesMasako Azuma, Sikh Diaspora in JapansinghNo ratings yet
- Robust Vocabulary InstructionDocument4 pagesRobust Vocabulary Instructionmadhu_gopinathanNo ratings yet
- Amanda BaggsDocument7 pagesAmanda Baggsapi-385249708No ratings yet
- Introduction To English AdverbsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To English AdverbsFrankie ArenolliNo ratings yet
- Course FlowDocument12 pagesCourse FlowSheikh MD Sazidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Aprende IdiomasDocument22 pagesAprende IdiomasXimena SánchezNo ratings yet
- Unit08 ExtensionTestDocument3 pagesUnit08 ExtensionTestCarito MoyaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in English 10Document3 pages1st Quarter Exam in English 10Rachelle BobisNo ratings yet
- MUSS: Multilingual Unsupervised Sentence Simplification by Mining ParaphrasesDocument16 pagesMUSS: Multilingual Unsupervised Sentence Simplification by Mining ParaphrasesMustafa GencNo ratings yet
- Incursion Into Wendigo Territory: Jackson Eflin, Ball Sate UniversityDocument11 pagesIncursion Into Wendigo Territory: Jackson Eflin, Ball Sate UniversityZachary GrgichNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Journal Article - TemplateDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Journal Article - TemplateKhaleza ZudiakeNo ratings yet
- Cook-Greuter Construct Aware Stage and The Fool ArchetypeDocument11 pagesCook-Greuter Construct Aware Stage and The Fool ArchetypeRalitza PantchevaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Vocabulary - WorkDocument29 pagesIELTS Vocabulary - WorkStella NguyenNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - English - 2017 - (2nd Ed.)Document8 pagesCourse Outline - English - 2017 - (2nd Ed.)Nuttapong RutamornchaiNo ratings yet
- Noun Types Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesNoun Types Worksheet PDFmoehammadj0% (1)
- To Become: 1. Get To Obtain, To Receive, To Buy 2. Get To Reach, To Arrive 3. Get To BecomeDocument3 pagesTo Become: 1. Get To Obtain, To Receive, To Buy 2. Get To Reach, To Arrive 3. Get To BecomeparulNo ratings yet
- Second Language Urdu: Paper 3248/01 Composition and TranslationDocument7 pagesSecond Language Urdu: Paper 3248/01 Composition and TranslationMahad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Letter FDocument20 pagesLetter FMuhammad HusnainNo ratings yet
- Завдання, 3 курс, 6 семестрDocument11 pagesЗавдання, 3 курс, 6 семестрИльяNo ratings yet
- Adapting and Adopting Learning MaterialsDocument24 pagesAdapting and Adopting Learning Materialsnina so100% (6)
- Speaking Cefr TipsDocument17 pagesSpeaking Cefr TipsPurr MiaowNo ratings yet
- Relative ClausesDocument7 pagesRelative ClausesCandelaria LuqueNo ratings yet
- Translation and Mass Communication PDFDocument27 pagesTranslation and Mass Communication PDFrbernabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Countable Uncountable PDFDocument1 pageUnit 7 Countable Uncountable PDFDario AmeriNo ratings yet
- English 2 WorsheetDocument9 pagesEnglish 2 WorsheetNic Hussin MejiaNo ratings yet
- Literacy Progressions K-10Document39 pagesLiteracy Progressions K-10Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Kawi and Kawi MiringDocument553 pagesKawi and Kawi MiringDian KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- A Short Synopsis of The Most Essential Points in Hawaiian Grammar (1864)Document70 pagesA Short Synopsis of The Most Essential Points in Hawaiian Grammar (1864)ursmartinNo ratings yet