Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan 2
Nursing Care Plan 2
Uploaded by
JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NCP Edema (Emdc)Document2 pagesNCP Edema (Emdc)pitchijaneco76% (17)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersDocument42 pagesBiology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersPrasaanth Rock86% (14)
- VedantaDocument3 pagesVedantaSomesh Siddharth100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanDenise Garcia MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaDocument30 pagesNursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalKei Cruz100% (1)
- Assisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingDocument3 pagesAssisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancepsengsonNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument33 pagesPneumothoraxjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document1 pageCourse Task 3Jurielyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions and Rationales: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions and Rationales: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierNo ratings yet
- Maternal Ni SheenaDocument13 pagesMaternal Ni SheenaSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPneumoniaErwin SmithNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternjuanmarcostaglishNo ratings yet
- Intervention Rationale: Provides A Basis For Evaluating Adequacy of VentilationDocument1 pageIntervention Rationale: Provides A Basis For Evaluating Adequacy of VentilationEricka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document2 pagesCourse Task 3Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Oral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningDocument10 pagesOral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Postural DrainageDocument6 pagesPostural DrainageKit Alizon Barredo0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument3 pagesNCP ErPensayo, Stephanie Keith V.No ratings yet
- NebulizationDocument2 pagesNebulizationArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientMG CaballeroNo ratings yet
- School of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityDocument19 pagesSchool of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- NCP SDocument8 pagesNCP SMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care PlansBeng AlontoNo ratings yet
- Course Task CU #3Document1 pageCourse Task CU #3Kel VinNo ratings yet
- Demonstration On Chest Physiotherapy DefinitionDocument3 pagesDemonstration On Chest Physiotherapy Definitiondileep0% (1)
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahDocument61 pagesPulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahNur akilaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarDocument13 pagesAssignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarPawan BatthNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesNursing Intervention RationaleLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Chest PhysiotherapyDocument13 pagesAssignment ON Chest PhysiotherapyGayathri R50% (2)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceNiko Brylle JoverNo ratings yet
- Promoting Oxygenation 2022Document86 pagesPromoting Oxygenation 2022AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions - RespiratoryDocument4 pagesNursing Interventions - Respiratorymanager.intelligentsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- Chap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsDocument13 pagesChap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsElaine Jean UayanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyFrom EverandComprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyNo ratings yet
- Dagdagan Ebp ActivitiesDocument4 pagesDagdagan Ebp ActivitiesJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Family Background - Cardiogenic ShockDocument8 pagesFamily Background - Cardiogenic ShockJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Revised Final Amphetamine SchematicDocument3 pagesRevised Final Amphetamine SchematicJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- References AmphetamineDocument8 pagesReferences AmphetamineJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis-DAGDAGANDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis-DAGDAGANJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Drug ClozapineDocument4 pagesDrug ClozapineJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Impaired Social InteractionDocument3 pagesImpaired Social InteractionJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach 1Document61 pagesBobath Approach 1Senthil Kumar100% (1)
- Unraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureDocument4 pagesUnraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Hope 2Document11 pagesHope 2Trisha Faye Tabuena PlanaNo ratings yet
- Session Guide 1 PDFDocument24 pagesSession Guide 1 PDFMANUEL BACARAC100% (1)
- Exconde Rma Research Topic 1 PDFDocument17 pagesExconde Rma Research Topic 1 PDFMae Gelline ExcondeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistryDocument2 pagesLaboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistrytrialqwNo ratings yet
- 2014 EDAIC II IStanbul 2014 2Document2 pages2014 EDAIC II IStanbul 2014 2igorNo ratings yet
- MS MG GBSDocument1 pageMS MG GBSJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 4Document22 pagesLight Lesson 4rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Ascitic Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesAscitic Fluid AnalysisParsaant SinghNo ratings yet
- Postoperative NCPDocument2 pagesPostoperative NCPFrancis MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Metro Manila Developmental Screening TestDocument6 pagesThe Metro Manila Developmental Screening TestBudoy Washupapi100% (1)
- Acute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsPeter InocandoNo ratings yet
- Main - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonDocument2 pagesMain - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonIndry LabungasaNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The EyeDocument37 pagesTumors of The EyeSyifa PrintingNo ratings yet
- UltraMedicRider Takaful ENG PDFDocument2 pagesUltraMedicRider Takaful ENG PDFDhyra Osem ScienceNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel (Plavix) : in The Management of Unstable Angina / NSTEMI in The Light of Clinical TrialsDocument36 pagesClopidogrel (Plavix) : in The Management of Unstable Angina / NSTEMI in The Light of Clinical TrialsadnanhosenNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Contingency Planning and Emergency Response To Healthcare Waste Spills - FINAL v2Document62 pagesModule 22 Contingency Planning and Emergency Response To Healthcare Waste Spills - FINAL v2ikkaapriliasetiariniNo ratings yet
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Healthy Food Incentive Proposal Policy AnalysisDocument82 pagesDoctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Healthy Food Incentive Proposal Policy AnalysisSandra HurstNo ratings yet
- AIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFDocument2 pagesAIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFVictoria RomeroNo ratings yet
- ATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3Document13 pagesATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3FireAwayNo ratings yet
- Monsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiDocument9 pagesMonsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiSwati Silver DoeNo ratings yet
- RNA Therapy: Rich History, Various Applications and Unlimited Future ProspectsDocument11 pagesRNA Therapy: Rich History, Various Applications and Unlimited Future ProspectsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLarr SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezDocument41 pagesStatistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Policy On Management of The Frenulum inDocument6 pagesPolicy On Management of The Frenulum inLaura Sánchez LoperaNo ratings yet
- Japanese Guidelines For Food AllergyDocument17 pagesJapanese Guidelines For Food AllergyΘεμιστοκλής ΤζατζαΐρηςNo ratings yet
Nursing Care Plan 2
Nursing Care Plan 2
Uploaded by
JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan 2
Nursing Care Plan 2
Uploaded by
JOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANCopyright:
Available Formats
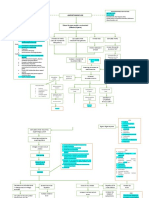
NURSING CARE PLAN
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Airway Clearance related to excessive mucus production secondary to
Community Acquired Pneumonia as evidenced by a respiratory rate of 39, effective cough, use of
accessory muscles when breathing, oxygen saturation of 93%, and a verbalization of “Marigatan nak
mangiruar toy plemak, Maam.”
Nursing Inference: Community Acquired Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma
associated with alveolar edema and congestion. In response to the inflammation, excess mucus is
produced which can block the small airways and reduce respiratory efficiency. Over-production of
mucus leads to frequent coughing, which further irritates the tissues and causes even more mucus
production. Hence, ineffective airway clearance.
Nursing Goals: After 12 hours of rendering effective nursing care, the patient will be able to maintain
a patent airway as evidenced by a respiratory rate between 12-20 cycles per minute, absence of
ineffective cough, does not use the accessory muscles when breathing, oxygen saturation of 98-
100% and a verbalization of, “Mairuruwar ko dagitoy plema kon, Maam.”
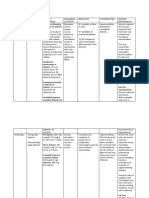
Nursing Interventions and Rationale:
Nursing Interventions Rationale
1. Administer medications such as To alleviate the cough and stops the growth of
antibiotics and bronchodilators, as bacteria.
ordered.
2. Elevate the head of the bed and change To promote chest expansion, aeration of lung
position frequently. segments, mobilization, and expectoration of
secretions.
3. Teach and assist the patient with To facilitate the maximum expansion of the
proper deep-breathing exercises. lungs and smaller airways and improve the
productivity of cough.
4. Teach and assist the patient in proper To help the patient remove most secretions;
splinting of the chest and effective reduce chest discomfort.
coughing while in an upright position.
5. Assist the patient in nebulization To humidify the airway to thin secretions and
therapy and chest physiotherapy. facilitate liquefaction and expectoration of
secretions; to loosen and mobilize secretions in
smaller airways that cannot be removed by
coughing.
6. Provide supplemental oxygen therapy, To prevent hypoxemia.
as ordered.
7. Provide health education about the To aid in the mobilization and expectoration of
importance of increasing fluid intake secretions.
that is warm.
8. Encourage the patient to ambulate as To mobilize secretions and reduce atelectasis.
tolerated.
Nursing Evaluation: After 12 hours of rendering effective nursing care, the patient was able to
maintain a patent airway as evidenced by a respiratory rate between 18 cycles per minute, absence
of ineffective cough, does not use the accessory muscles when breathing, oxygen saturation of 98%
and a verbalization of, “Mairuruwar ko dagitoy plema kon, Maam.”
You might also like
- NCP Edema (Emdc)Document2 pagesNCP Edema (Emdc)pitchijaneco76% (17)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersDocument42 pagesBiology Investigatory Project On Mendelian DisordersPrasaanth Rock86% (14)
- VedantaDocument3 pagesVedantaSomesh Siddharth100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanDenise Garcia MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaDocument30 pagesNursing Diagnosis (1) (1) .Finalgid NiyaReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalKei Cruz100% (1)
- Assisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingDocument3 pagesAssisting A Client With Controlled Coughing and Deep BreathingKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyYuvi Rociandel LUARDONo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancepsengsonNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument33 pagesPneumothoraxjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document1 pageCourse Task 3Jurielyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions and Rationales: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions and Rationales: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierNo ratings yet
- Maternal Ni SheenaDocument13 pagesMaternal Ni SheenaSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPneumoniaErwin SmithNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternjuanmarcostaglishNo ratings yet
- Intervention Rationale: Provides A Basis For Evaluating Adequacy of VentilationDocument1 pageIntervention Rationale: Provides A Basis For Evaluating Adequacy of VentilationEricka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Course Task 3Document2 pagesCourse Task 3Geraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Oral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningDocument10 pagesOral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Postural DrainageDocument6 pagesPostural DrainageKit Alizon Barredo0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument3 pagesNCP ErPensayo, Stephanie Keith V.No ratings yet
- NebulizationDocument2 pagesNebulizationArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment Objective Cues:: Ako," As Verbalized by The ClientMG CaballeroNo ratings yet
- School of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityDocument19 pagesSchool of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- NCP SDocument8 pagesNCP SMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care PlansBeng AlontoNo ratings yet
- Course Task CU #3Document1 pageCourse Task CU #3Kel VinNo ratings yet
- Demonstration On Chest Physiotherapy DefinitionDocument3 pagesDemonstration On Chest Physiotherapy Definitiondileep0% (1)
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahDocument61 pagesPulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahNur akilaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarDocument13 pagesAssignment ON Chest Physiotherapy: Sri Guru Ram Das Nursing Institute Pandher, AmritsarPawan BatthNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention RationaleDocument2 pagesNursing Intervention RationaleLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment ON Chest PhysiotherapyDocument13 pagesAssignment ON Chest PhysiotherapyGayathri R50% (2)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceNiko Brylle JoverNo ratings yet
- Promoting Oxygenation 2022Document86 pagesPromoting Oxygenation 2022AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions - RespiratoryDocument4 pagesNursing Interventions - Respiratorymanager.intelligentsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- Chap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsDocument13 pagesChap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsElaine Jean UayanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyFrom EverandComprehensive Asthma Management: Self-Care, Diet, and HomeopathyNo ratings yet
- Dagdagan Ebp ActivitiesDocument4 pagesDagdagan Ebp ActivitiesJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Family Background - Cardiogenic ShockDocument8 pagesFamily Background - Cardiogenic ShockJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Revised Final Amphetamine SchematicDocument3 pagesRevised Final Amphetamine SchematicJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- References AmphetamineDocument8 pagesReferences AmphetamineJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis-DAGDAGANDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis-DAGDAGANJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Drug ClozapineDocument4 pagesDrug ClozapineJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Impaired Social InteractionDocument3 pagesImpaired Social InteractionJOYCE ANNE SUERTE DAGDAGANNo ratings yet
- Bobath Approach 1Document61 pagesBobath Approach 1Senthil Kumar100% (1)
- Unraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureDocument4 pagesUnraveling The Unprecedented Economic Implications of The COVID-19 Pandemic: Navigating Towards A Resilient and Sustainable FutureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Hope 2Document11 pagesHope 2Trisha Faye Tabuena PlanaNo ratings yet
- Session Guide 1 PDFDocument24 pagesSession Guide 1 PDFMANUEL BACARAC100% (1)
- Exconde Rma Research Topic 1 PDFDocument17 pagesExconde Rma Research Topic 1 PDFMae Gelline ExcondeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistryDocument2 pagesLaboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistrytrialqwNo ratings yet
- 2014 EDAIC II IStanbul 2014 2Document2 pages2014 EDAIC II IStanbul 2014 2igorNo ratings yet
- MS MG GBSDocument1 pageMS MG GBSJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 4Document22 pagesLight Lesson 4rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Ascitic Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesAscitic Fluid AnalysisParsaant SinghNo ratings yet
- Postoperative NCPDocument2 pagesPostoperative NCPFrancis MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Metro Manila Developmental Screening TestDocument6 pagesThe Metro Manila Developmental Screening TestBudoy Washupapi100% (1)
- Acute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsPeter InocandoNo ratings yet
- Main - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonDocument2 pagesMain - Dshs Form Dshs 13 830 Admissions Review Team Checklist Admission To An Icf Iid or Sonf at A Residential Habilitation Center RHC WashingtonIndry LabungasaNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The EyeDocument37 pagesTumors of The EyeSyifa PrintingNo ratings yet
- UltraMedicRider Takaful ENG PDFDocument2 pagesUltraMedicRider Takaful ENG PDFDhyra Osem ScienceNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel (Plavix) : in The Management of Unstable Angina / NSTEMI in The Light of Clinical TrialsDocument36 pagesClopidogrel (Plavix) : in The Management of Unstable Angina / NSTEMI in The Light of Clinical TrialsadnanhosenNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Contingency Planning and Emergency Response To Healthcare Waste Spills - FINAL v2Document62 pagesModule 22 Contingency Planning and Emergency Response To Healthcare Waste Spills - FINAL v2ikkaapriliasetiariniNo ratings yet
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Healthy Food Incentive Proposal Policy AnalysisDocument82 pagesDoctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) Healthy Food Incentive Proposal Policy AnalysisSandra HurstNo ratings yet
- AIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFDocument2 pagesAIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFVictoria RomeroNo ratings yet
- ATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3Document13 pagesATAR Human Biology 12 Units 3FireAwayNo ratings yet
- Monsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiDocument9 pagesMonsoon Advisory 22 - United Way MumbaiSwati Silver DoeNo ratings yet
- RNA Therapy: Rich History, Various Applications and Unlimited Future ProspectsDocument11 pagesRNA Therapy: Rich History, Various Applications and Unlimited Future ProspectsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLarr SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezDocument41 pagesStatistics For Dummies Rachel EnriquezcocopollyNo ratings yet
- Policy On Management of The Frenulum inDocument6 pagesPolicy On Management of The Frenulum inLaura Sánchez LoperaNo ratings yet
- Japanese Guidelines For Food AllergyDocument17 pagesJapanese Guidelines For Food AllergyΘεμιστοκλής ΤζατζαΐρηςNo ratings yet