Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
api-688514833Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Free DSLR Beginners GuideDocument18 pagesFree DSLR Beginners GuideMichael Zhang56% (18)
- Camera Exposure - Aperture ISO Shutter SpeedDocument5 pagesCamera Exposure - Aperture ISO Shutter SpeedngrakeshNo ratings yet
- Froknowsphoto Guide 1Document11 pagesFroknowsphoto Guide 1Badrul AminNo ratings yet
- Article On Manual ModeDocument80 pagesArticle On Manual ModeSourajit Banerjee100% (1)
- 13 Camera SettingsDocument15 pages13 Camera SettingsRameshKulandaiveluNo ratings yet
- PhotojournalismDocument195 pagesPhotojournalismAthan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ography-Basics/: 1.camera ModesDocument12 pagesOgraphy-Basics/: 1.camera ModesVlad ElisabetaNo ratings yet
- 20 Essential Photography Tips For BeginnersDocument5 pages20 Essential Photography Tips For BeginnersJohn Rey Manolo BaylosisNo ratings yet
- BAJMC Video Production Practical FileDocument27 pagesBAJMC Video Production Practical FileNaman jainNo ratings yet
- Know This: These Terms Are Very, Very Interchangeable in The Photography World. Here's The Sparknotes Version of Them All. You Can Refer To This List Forever To Find AnswersDocument4 pagesKnow This: These Terms Are Very, Very Interchangeable in The Photography World. Here's The Sparknotes Version of Them All. You Can Refer To This List Forever To Find AnswersHemanth ThiruNo ratings yet
- A. Introduction To Digital PhotographyDocument33 pagesA. Introduction To Digital PhotographylalaNo ratings yet
- A Technical Guide To Advance PH - Elizabeth FrasersDocument94 pagesA Technical Guide To Advance PH - Elizabeth FrasersRazvan Scarlat100% (1)
- Eos 3000NDocument6 pagesEos 3000Nignaciogarcia.codeNo ratings yet
- Frs3 Chapter 8Document5 pagesFrs3 Chapter 8Gielhene MinearNo ratings yet
- Abby SugaDocument80 pagesAbby SugaJebun LangaminNo ratings yet
- Camera Modes: Auto ModeDocument4 pagesCamera Modes: Auto ModeZulzamri Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Basicphotography 1217986159022700 9Document28 pagesBasicphotography 1217986159022700 9jbvegaNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Your Photography Skills - Beginner Photographer's Guide - Learn Essential PhotographyDocument17 pagesHow To Improve Your Photography Skills - Beginner Photographer's Guide - Learn Essential PhotographyAditogatorNo ratings yet
- Basic+ Photography Workshop ModuleDocument66 pagesBasic+ Photography Workshop ModuleBobby BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Basics of PhotographyDocument37 pagesBasics of PhotographyAmrut AtreNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Camera ProjectsDocument8 pagesOutdoor Camera ProjectsScribme_tooNo ratings yet
- Photography Class For Beginners - BookletDocument8 pagesPhotography Class For Beginners - Bookletybyouhub123No ratings yet
- 10 Camera ControlsDocument20 pages10 Camera ControlsJulianne Bsc100% (1)
- Photo JournalismDocument41 pagesPhoto JournalismVinit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sharper PicturesDocument4 pagesSharper PicturesScribme_too100% (1)
- Basicphotography 1217986159022700 9Document20 pagesBasicphotography 1217986159022700 9Dumbrava Caius FlorinNo ratings yet
- Canon Picture ZonesDocument10 pagesCanon Picture ZonesScribme_tooNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesDocument59 pagesAn Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesSreemannarayana MusunuriNo ratings yet
- basicphotography-Document20 pagesbasicphotography-mohmad abdullahNo ratings yet
- 12 Essential Facts, Formulas, and Photographic Rules: The OcalDocument1 page12 Essential Facts, Formulas, and Photographic Rules: The Ocalopenid_Ds8hAkazNo ratings yet
- WithLuke Masterclass - Photographers HandbookDocument14 pagesWithLuke Masterclass - Photographers Handbookcurso.rhavienglish100% (1)
- Photography - 101: (101 The Basics)Document27 pagesPhotography - 101: (101 The Basics)sserr436tttNo ratings yet
- Basic Photography TranscriptDocument3 pagesBasic Photography Transcriptvladic3110No ratings yet
- Understand Your Camera - 0Document4 pagesUnderstand Your Camera - 0RoninNo ratings yet
- Indesign Photo ManualDocument10 pagesIndesign Photo Manualapi-344644095No ratings yet
- Canon Eos Guide: Aperture, Shutter, ISODocument3 pagesCanon Eos Guide: Aperture, Shutter, ISOTibzNo ratings yet
- Ebook Pixinfocus 7 Day Intro To PhotographyDocument44 pagesEbook Pixinfocus 7 Day Intro To PhotographyBlanca BlancaNo ratings yet
- Webinarnotes: Getting It Right in CameraDocument7 pagesWebinarnotes: Getting It Right in CameraIulia Florina SimaNo ratings yet
- Digital Photography Techniques - Autumn 2008Document116 pagesDigital Photography Techniques - Autumn 2008Naiyer AlamNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER PhotographyDocument22 pagesCOMPUTER PhotographyKhate VargasNo ratings yet
- Camera FunctionsDocument14 pagesCamera FunctionsmayurinstruNo ratings yet
- En 16Document8 pagesEn 16aptureincNo ratings yet
- Drone Photography NotesDocument11 pagesDrone Photography Notesasfuentealbar4386No ratings yet
- Forensic Photography: Mr. Bhoopesh SharmaDocument6 pagesForensic Photography: Mr. Bhoopesh SharmaPeter SakiwatNo ratings yet
- VCD 151 Manual CameraDocument24 pagesVCD 151 Manual CameraPetrichorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Photography: An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Digital Photography: An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic Techniquessachin_mane88No ratings yet
- Basic Parts of DSLR Camera and Their FunctionsDocument10 pagesBasic Parts of DSLR Camera and Their FunctionsTHIRDVISION STUDIOSNo ratings yet
- Jargon Buster DownloadDocument14 pagesJargon Buster DownloadpatrickNo ratings yet
- Into To PhotographyDocument58 pagesInto To PhotographyKuldeep KuldeepNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Photographer - 12 Essential Rules (Photography) PDFDocument0 pagesOutdoor Photographer - 12 Essential Rules (Photography) PDFcelblackNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To Basic Camera SettingsDocument10 pagesA Beginners Guide To Basic Camera Settingsgraceolajide79No ratings yet
- How To Use DSLR CameraDocument12 pagesHow To Use DSLR CameraatikahNo ratings yet
- Flash Photo2Document40 pagesFlash Photo2shiv patilNo ratings yet
- Basic PhotographyDocument4 pagesBasic Photographyιωαναθαν ρααγασNo ratings yet
- Proper Exposure (Greg Benz)Document9 pagesProper Exposure (Greg Benz)Rafael ManjarrezNo ratings yet
- All About CameraDocument48 pagesAll About CameralizaNo ratings yet
- Dslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)From EverandDslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)No ratings yet
- ASLEHIREDocument3 pagesASLEHIRENik LyonsNo ratings yet
- Live Audio EngineerDocument3 pagesLive Audio EngineerGoran OsmakNo ratings yet
- 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User ManualDocument2 pages16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User ManualArthur BaltharNo ratings yet
- Marshall 1960a enDocument12 pagesMarshall 1960a enaldoNo ratings yet
- MIL REVIEWER For 2nd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesMIL REVIEWER For 2nd Quarter ExamClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- IteDocument20 pagesIteJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- x-t30-2 Manual en S FDocument360 pagesx-t30-2 Manual en S FwalkrogNo ratings yet
- What Is AmbisonicsDocument10 pagesWhat Is AmbisonicsSoham PawarNo ratings yet
- 415-00 Information and Entertainment System - General Information PICKUP JMCDocument3 pages415-00 Information and Entertainment System - General Information PICKUP JMCRusonegroNo ratings yet
- John Opera Presentation - Anthony CicconeDocument25 pagesJohn Opera Presentation - Anthony Cicconeapi-607508930No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: F60 (E) 02.12.27 5:34 PM Page 1Document41 pagesInstruction Manual: F60 (E) 02.12.27 5:34 PM Page 1Mikkel WiederNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital RecordingDocument4 pagesAnalogue and Digital RecordingKavita koNo ratings yet
- CV Colin Paterson Audio 5Document3 pagesCV Colin Paterson Audio 5api-466096632No ratings yet
- V. I ManualDocument8 pagesV. I ManualDirdas HairNo ratings yet
- Compression Fundamentals Course NotesDocument7 pagesCompression Fundamentals Course NotesjoneNo ratings yet
- Mic Techniques DrumsDocument12 pagesMic Techniques DrumsjimpeckhamNo ratings yet
- Akai s3000xlDocument313 pagesAkai s3000xltigerstyle1No ratings yet
- Ipb 331Document1 pageIpb 331Jawad RaoNo ratings yet
- Dee 5103Document4 pagesDee 5103ike979402No ratings yet
- Thomson Chassis Lcd12b 20lb120s4Document18 pagesThomson Chassis Lcd12b 20lb120s4vascoalmNo ratings yet
- DS 2ce16c2t Ir2 PDFDocument1 pageDS 2ce16c2t Ir2 PDFAnderson RamosNo ratings yet
- Camera Sony A7Document19 pagesCamera Sony A7loco lotsoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Fidelity Sound Company 1973Document59 pagesCatalogue Fidelity Sound Company 1973LarcierNo ratings yet
- BEHRINGER - UCA202 P0484 - Product Information Document PDFDocument6 pagesBEHRINGER - UCA202 P0484 - Product Information Document PDFbeeej.bNo ratings yet
- C5 (X7) - D4EA05YZP0 - 8 - 24 - 08 - 2015 - Description - Function - Audio Amplifier (With Hi-Fi Option)Document4 pagesC5 (X7) - D4EA05YZP0 - 8 - 24 - 08 - 2015 - Description - Function - Audio Amplifier (With Hi-Fi Option)francisco javier fernandez talaveronNo ratings yet
- Night Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom RaithbyDocument18 pagesNight Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom Raithbyebi18750No ratings yet
- Daewoo VTB834NET3 (168) Service ManualDocument71 pagesDaewoo VTB834NET3 (168) Service ManualDennis KrizanNo ratings yet
- Spirit King416Document3 pagesSpirit King416Keravnos DramNo ratings yet
- Artica Jelly: User'S ManualDocument36 pagesArtica Jelly: User'S ManualjjtanksNo ratings yet
- Mixing and Mastering Masterclass V3Document22 pagesMixing and Mastering Masterclass V3Nehemias Rivera0% (1)
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
api-688514833Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
api-688514833Copyright:
Available Formats
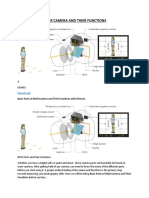
1.
a space through which light passes in an optical or photographic instrument, especially the
variable opening by which light enters a camera. a device that opens and closes to expose
the film in a camera.ISO Sensitivity is a standard set by the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) that represents sensitivity to light as a numerical value.
2. Lower values are great when there is plenty of light to work with. Higher ISO values are
needed for working in low light.
3. your camera will vary the exposure settings depending on the aperture value you set. in the
sense that it gives you complete control over shutter speed while making all the other
settings automatically.
4. One-shot AF, Servo AF and AI Autofocus.You have to use the shutter button.
5. The first mode obviously allows you to shoot one frame at a time. It great for studio work or
when shooting anything you have complete control over. CL is great for portraits when you
have an expressive model and don't want to miss any interesting faces. CH is the shooting
mode for sports, wildlife and anything that moves fast.
6. Wide-angle lenses are a staple in most landscape photographers' kits, popular for their ability
to capture sweeping vistas and starry nights. and the telephoto lens is a longer lens and
gives a narrow point of view. The normal is a 35-50mm lens which is almost like the human
eye.
7. White balance is a camera setting that establishes the true color of white. To balance the
colors in the picture.
8. Depth of field is the area of acceptable sharpness in front of and behind the subject which
the lens is focused on. Shallow depth of field (also called “small” or “narrow”) means that
only a part of the image is in focus. The background and sometimes the foreground is
blurred. Good depth of field is where everything is in field.
9. The first mode obviously allows you to shoot one frame at a time. It great for studio work or
when shooting anything you have complete control over. CL is great for portraits when you
have an expressive model and don't want to miss any interesting faces. CH is the shooting
mode for sports, wildlife and anything that moves fast. There are three metering modes in
most cameras, each with a specific job. They have different names depending on camera
manufacturer, but essentially they behave the same. The best way to master metering
modes is to start by reading the camera manual. After that, photograph the same scene
using all three modes and compare the results.
10. It is a +/- scale that will tell your camera to increase or decrease exposure, depending on
your needs. It works for all semi-automatic modes (P, Av, TV) and will influence exposure in
increments. Be careful not to set it too high or low from the first attempt and instead try to get
to a correct exposure gradually.
You might also like
- Free DSLR Beginners GuideDocument18 pagesFree DSLR Beginners GuideMichael Zhang56% (18)
- Camera Exposure - Aperture ISO Shutter SpeedDocument5 pagesCamera Exposure - Aperture ISO Shutter SpeedngrakeshNo ratings yet
- Froknowsphoto Guide 1Document11 pagesFroknowsphoto Guide 1Badrul AminNo ratings yet
- Article On Manual ModeDocument80 pagesArticle On Manual ModeSourajit Banerjee100% (1)
- 13 Camera SettingsDocument15 pages13 Camera SettingsRameshKulandaiveluNo ratings yet
- PhotojournalismDocument195 pagesPhotojournalismAthan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ography-Basics/: 1.camera ModesDocument12 pagesOgraphy-Basics/: 1.camera ModesVlad ElisabetaNo ratings yet
- 20 Essential Photography Tips For BeginnersDocument5 pages20 Essential Photography Tips For BeginnersJohn Rey Manolo BaylosisNo ratings yet
- BAJMC Video Production Practical FileDocument27 pagesBAJMC Video Production Practical FileNaman jainNo ratings yet
- Know This: These Terms Are Very, Very Interchangeable in The Photography World. Here's The Sparknotes Version of Them All. You Can Refer To This List Forever To Find AnswersDocument4 pagesKnow This: These Terms Are Very, Very Interchangeable in The Photography World. Here's The Sparknotes Version of Them All. You Can Refer To This List Forever To Find AnswersHemanth ThiruNo ratings yet
- A. Introduction To Digital PhotographyDocument33 pagesA. Introduction To Digital PhotographylalaNo ratings yet
- A Technical Guide To Advance PH - Elizabeth FrasersDocument94 pagesA Technical Guide To Advance PH - Elizabeth FrasersRazvan Scarlat100% (1)
- Eos 3000NDocument6 pagesEos 3000Nignaciogarcia.codeNo ratings yet
- Frs3 Chapter 8Document5 pagesFrs3 Chapter 8Gielhene MinearNo ratings yet
- Abby SugaDocument80 pagesAbby SugaJebun LangaminNo ratings yet
- Camera Modes: Auto ModeDocument4 pagesCamera Modes: Auto ModeZulzamri Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Basicphotography 1217986159022700 9Document28 pagesBasicphotography 1217986159022700 9jbvegaNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Your Photography Skills - Beginner Photographer's Guide - Learn Essential PhotographyDocument17 pagesHow To Improve Your Photography Skills - Beginner Photographer's Guide - Learn Essential PhotographyAditogatorNo ratings yet
- Basic+ Photography Workshop ModuleDocument66 pagesBasic+ Photography Workshop ModuleBobby BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Basics of PhotographyDocument37 pagesBasics of PhotographyAmrut AtreNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Camera ProjectsDocument8 pagesOutdoor Camera ProjectsScribme_tooNo ratings yet
- Photography Class For Beginners - BookletDocument8 pagesPhotography Class For Beginners - Bookletybyouhub123No ratings yet
- 10 Camera ControlsDocument20 pages10 Camera ControlsJulianne Bsc100% (1)
- Photo JournalismDocument41 pagesPhoto JournalismVinit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sharper PicturesDocument4 pagesSharper PicturesScribme_too100% (1)
- Basicphotography 1217986159022700 9Document20 pagesBasicphotography 1217986159022700 9Dumbrava Caius FlorinNo ratings yet
- Canon Picture ZonesDocument10 pagesCanon Picture ZonesScribme_tooNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesDocument59 pagesAn Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesSreemannarayana MusunuriNo ratings yet
- basicphotography-Document20 pagesbasicphotography-mohmad abdullahNo ratings yet
- 12 Essential Facts, Formulas, and Photographic Rules: The OcalDocument1 page12 Essential Facts, Formulas, and Photographic Rules: The Ocalopenid_Ds8hAkazNo ratings yet
- WithLuke Masterclass - Photographers HandbookDocument14 pagesWithLuke Masterclass - Photographers Handbookcurso.rhavienglish100% (1)
- Photography - 101: (101 The Basics)Document27 pagesPhotography - 101: (101 The Basics)sserr436tttNo ratings yet
- Basic Photography TranscriptDocument3 pagesBasic Photography Transcriptvladic3110No ratings yet
- Understand Your Camera - 0Document4 pagesUnderstand Your Camera - 0RoninNo ratings yet
- Indesign Photo ManualDocument10 pagesIndesign Photo Manualapi-344644095No ratings yet
- Canon Eos Guide: Aperture, Shutter, ISODocument3 pagesCanon Eos Guide: Aperture, Shutter, ISOTibzNo ratings yet
- Ebook Pixinfocus 7 Day Intro To PhotographyDocument44 pagesEbook Pixinfocus 7 Day Intro To PhotographyBlanca BlancaNo ratings yet
- Webinarnotes: Getting It Right in CameraDocument7 pagesWebinarnotes: Getting It Right in CameraIulia Florina SimaNo ratings yet
- Digital Photography Techniques - Autumn 2008Document116 pagesDigital Photography Techniques - Autumn 2008Naiyer AlamNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER PhotographyDocument22 pagesCOMPUTER PhotographyKhate VargasNo ratings yet
- Camera FunctionsDocument14 pagesCamera FunctionsmayurinstruNo ratings yet
- En 16Document8 pagesEn 16aptureincNo ratings yet
- Drone Photography NotesDocument11 pagesDrone Photography Notesasfuentealbar4386No ratings yet
- Forensic Photography: Mr. Bhoopesh SharmaDocument6 pagesForensic Photography: Mr. Bhoopesh SharmaPeter SakiwatNo ratings yet
- VCD 151 Manual CameraDocument24 pagesVCD 151 Manual CameraPetrichorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Photography: An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic TechniquesDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Digital Photography: An Overview of Digital Camera Technology, Basic Photographic Techniquessachin_mane88No ratings yet
- Basic Parts of DSLR Camera and Their FunctionsDocument10 pagesBasic Parts of DSLR Camera and Their FunctionsTHIRDVISION STUDIOSNo ratings yet
- Jargon Buster DownloadDocument14 pagesJargon Buster DownloadpatrickNo ratings yet
- Into To PhotographyDocument58 pagesInto To PhotographyKuldeep KuldeepNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Photographer - 12 Essential Rules (Photography) PDFDocument0 pagesOutdoor Photographer - 12 Essential Rules (Photography) PDFcelblackNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To Basic Camera SettingsDocument10 pagesA Beginners Guide To Basic Camera Settingsgraceolajide79No ratings yet
- How To Use DSLR CameraDocument12 pagesHow To Use DSLR CameraatikahNo ratings yet
- Flash Photo2Document40 pagesFlash Photo2shiv patilNo ratings yet
- Basic PhotographyDocument4 pagesBasic Photographyιωαναθαν ρααγασNo ratings yet
- Proper Exposure (Greg Benz)Document9 pagesProper Exposure (Greg Benz)Rafael ManjarrezNo ratings yet
- All About CameraDocument48 pagesAll About CameralizaNo ratings yet
- Dslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)From EverandDslr: The Beginners Guide to Master Camera & Improve (Learn How to Master the Art of Dslr Photography)No ratings yet
- ASLEHIREDocument3 pagesASLEHIRENik LyonsNo ratings yet
- Live Audio EngineerDocument3 pagesLive Audio EngineerGoran OsmakNo ratings yet
- 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User ManualDocument2 pages16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User Manual 16, 22, 22MTK User ManualArthur BaltharNo ratings yet
- Marshall 1960a enDocument12 pagesMarshall 1960a enaldoNo ratings yet
- MIL REVIEWER For 2nd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesMIL REVIEWER For 2nd Quarter ExamClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- IteDocument20 pagesIteJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- x-t30-2 Manual en S FDocument360 pagesx-t30-2 Manual en S FwalkrogNo ratings yet
- What Is AmbisonicsDocument10 pagesWhat Is AmbisonicsSoham PawarNo ratings yet
- 415-00 Information and Entertainment System - General Information PICKUP JMCDocument3 pages415-00 Information and Entertainment System - General Information PICKUP JMCRusonegroNo ratings yet
- John Opera Presentation - Anthony CicconeDocument25 pagesJohn Opera Presentation - Anthony Cicconeapi-607508930No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: F60 (E) 02.12.27 5:34 PM Page 1Document41 pagesInstruction Manual: F60 (E) 02.12.27 5:34 PM Page 1Mikkel WiederNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital RecordingDocument4 pagesAnalogue and Digital RecordingKavita koNo ratings yet
- CV Colin Paterson Audio 5Document3 pagesCV Colin Paterson Audio 5api-466096632No ratings yet
- V. I ManualDocument8 pagesV. I ManualDirdas HairNo ratings yet
- Compression Fundamentals Course NotesDocument7 pagesCompression Fundamentals Course NotesjoneNo ratings yet
- Mic Techniques DrumsDocument12 pagesMic Techniques DrumsjimpeckhamNo ratings yet
- Akai s3000xlDocument313 pagesAkai s3000xltigerstyle1No ratings yet
- Ipb 331Document1 pageIpb 331Jawad RaoNo ratings yet
- Dee 5103Document4 pagesDee 5103ike979402No ratings yet
- Thomson Chassis Lcd12b 20lb120s4Document18 pagesThomson Chassis Lcd12b 20lb120s4vascoalmNo ratings yet
- DS 2ce16c2t Ir2 PDFDocument1 pageDS 2ce16c2t Ir2 PDFAnderson RamosNo ratings yet
- Camera Sony A7Document19 pagesCamera Sony A7loco lotsoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Fidelity Sound Company 1973Document59 pagesCatalogue Fidelity Sound Company 1973LarcierNo ratings yet
- BEHRINGER - UCA202 P0484 - Product Information Document PDFDocument6 pagesBEHRINGER - UCA202 P0484 - Product Information Document PDFbeeej.bNo ratings yet
- C5 (X7) - D4EA05YZP0 - 8 - 24 - 08 - 2015 - Description - Function - Audio Amplifier (With Hi-Fi Option)Document4 pagesC5 (X7) - D4EA05YZP0 - 8 - 24 - 08 - 2015 - Description - Function - Audio Amplifier (With Hi-Fi Option)francisco javier fernandez talaveronNo ratings yet
- Night Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom RaithbyDocument18 pagesNight Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom Raithbyebi18750No ratings yet
- Daewoo VTB834NET3 (168) Service ManualDocument71 pagesDaewoo VTB834NET3 (168) Service ManualDennis KrizanNo ratings yet
- Spirit King416Document3 pagesSpirit King416Keravnos DramNo ratings yet
- Artica Jelly: User'S ManualDocument36 pagesArtica Jelly: User'S ManualjjtanksNo ratings yet
- Mixing and Mastering Masterclass V3Document22 pagesMixing and Mastering Masterclass V3Nehemias Rivera0% (1)