Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluids and Electrolytes
Fluids and Electrolytes
Uploaded by
Timothy LascoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluids and Electrolytes
Fluids and Electrolytes
Uploaded by
Timothy LascoCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluids
60 % of an adult's
body weight
-
70kg adult male 60 % x 70: =
42L
General Functions
I .
to maintain homeostasis
. to ensure adequate tissue perfusion
3 .
helps transport nutrients gases and wastes , ,
4 to have normal function of cells and the body as a whole
5 . to help maintain body temperature
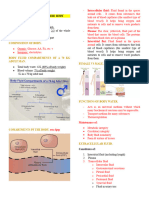
Fluid Distribution
42 L
Extracellular Fluid Intracellular Fluid
Y of total body weight 213 of total body weight
14L 28
Interstitial Fluid 3/4 Plasmally Transcellular Fluid
10 52
.
3 54 .
-
CSF
Tears
Arterial 2% Venous 3%
-
synovial
-
Intraocular
Babies more water 80 %: water M 60% water
=
Adult lesser water
=
F
=
58 % water
·
Both are prone to fluid imbalances
Muscular =
↑ water
Fat ↓ water bec fats ·
repell water
Transport Mechanism
fluids from different
-
compartments move from one
compartment to the other to maintain fluid balance
A Passive .
Transport Process -x
-movement from higher to lower
-without
energy input
Types :
I .
Diffusion-t
-
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration
to an area of lower concentration
2 . Filtration -
↓
-
movement of molecules from an area of higher pressure
to area of lower
an
pressure
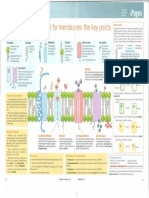
. Active
B Transport Process
-
cell moves substances across a membrane
through ATP
because:
they may be too large
·
Unable to dissolve in the fat core
move uphill against their concentration gradient
G
Types
1.Osmosis ↓ -Y
-
movement of solvent from an area of lower
concentration to an area of concentration
higher
You might also like
- Fluid Balance Monitoring PosterDocument1 pageFluid Balance Monitoring PosterSania oktaNo ratings yet
- Partners in Reduce, Reuse and RecycleDocument27 pagesPartners in Reduce, Reuse and RecycleRana RashidNo ratings yet
- EFSET (B2 Upper Intermediate)Document3 pagesEFSET (B2 Upper Intermediate)chandran_witts100% (1)
- Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMidterm 1 Cheat SheetSharisseNo ratings yet
- 01-06-Viscous ResistanceDocument35 pages01-06-Viscous Resistancerahmahmed200kNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Fluid Balance v14 PDFDocument1 pageICU One Pager Fluid Balance v14 PDFabobader2No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology: Body Water ContentDocument11 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology: Body Water ContentAhmad WardimanNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes HandoutDocument16 pagesFluids & Electrolytes Handoutapi-3722454100% (3)
- IV Fluids Cheat Sheet Copyright BNDocument2 pagesIV Fluids Cheat Sheet Copyright BNJeshan Yanong BeltranNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Part 1) - Fluid Flow in Closed ConduitsDocument3 pagesModule 3 (Part 1) - Fluid Flow in Closed Conduitstoriopeter350No ratings yet
- MS ReviewerDocument3 pagesMS Reviewersherlyn galvanNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesyanNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument4 pagesCell TransportKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 1998 GIRAUD L., D'HUMIERES D., LALLEMAND P. A Lattice Boltzmann Model For Jeffreys Viscoelastic Fluid. Europhysics Letters 42 (June 1998)Document7 pages1998 GIRAUD L., D'HUMIERES D., LALLEMAND P. A Lattice Boltzmann Model For Jeffreys Viscoelastic Fluid. Europhysics Letters 42 (June 1998)10_DAVID_10No ratings yet
- Transport in plants (1)Document50 pagesTransport in plants (1)mr.vedic123No ratings yet
- 2.visualisation of The Flow PatternsDocument7 pages2.visualisation of The Flow PatternsAhmed FarazNo ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument38 pagesViscosityShihabudheenNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsGladi RosinNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsGladi Rosin0% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolytes 3rd Yr 1st SemDocument12 pagesFluid and Electrolytes 3rd Yr 1st SemzashileighNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument2 pagesTransport in Plantsakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Tor ElekDocument9 pagesTor ElekChaori NurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Other Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesOther Properties of Fluidsmicklier baduriaNo ratings yet
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- M.H. Ghatee, H. Ghazipour, Fluid Phase Equilib. 377 (2014) 76-81Document6 pagesM.H. Ghatee, H. Ghazipour, Fluid Phase Equilib. 377 (2014) 76-81PaulaGF88No ratings yet
- Module 1Document18 pagesModule 1andrewmerafuentesNo ratings yet
- NCP1 ErDocument6 pagesNCP1 ErShewit AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Year 1Document11 pagesYear 1fran.nunez2305No ratings yet
- Blood & Body Fluid Tortora 15TH EditionDocument20 pagesBlood & Body Fluid Tortora 15TH Edition334scisyb2020rishabhsingalNo ratings yet
- 1 Parcial Ingles CientificoDocument7 pages1 Parcial Ingles Cientificobelemleyva03No ratings yet
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13Document10 pages11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- 11 Transport in PlantsDocument7 pages11 Transport in PlantsDe DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid MAchinery - March 11,2023Document23 pagesIntroduction To Fluid MAchinery - March 11,2023MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Advance Fluid Mechanics Lectures 1-2Document9 pagesAdvance Fluid Mechanics Lectures 1-2XhaMii RajputNo ratings yet
- 11 Transport in Plants-NotesDocument6 pages11 Transport in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport PDFDocument17 pagesCell Transport PDFWeee BooaaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes 1Document9 pagesFluids and Electrolytes 1Mariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument4 pagesChapter - 7 - Fundamentals of Fluid FlowEstera ShawnNo ratings yet
- Polymer ViscoelasticityDocument32 pagesPolymer ViscoelasticityMAURICIO NICARAGUA MENDEZNo ratings yet
- © by SIAM. Unauthorized Reproduction of This Article Is ProhibitedDocument24 pages© by SIAM. Unauthorized Reproduction of This Article Is ProhibitedМаксим ГалочкінNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction Properties of FluidsDocument24 pagesLecture 1 Introduction Properties of FluidsJaaa ReeedNo ratings yet
- (Exercise) : Chapter 3 - TransportDocument8 pages(Exercise) : Chapter 3 - TransportChloe WongNo ratings yet
- 9 - Fundamentals of FLuid Flow (Bernoulli's Principle) PDFDocument22 pages9 - Fundamentals of FLuid Flow (Bernoulli's Principle) PDFAnn loraine BanzonNo ratings yet
- CE04 Fluid Mechanics Properties of FluidsDocument3 pagesCE04 Fluid Mechanics Properties of Fluidspeter bruceNo ratings yet
- Viscosity and Poiseuille EquationDocument14 pagesViscosity and Poiseuille EquationShivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 2Document7 pagesHE Lecture 2presidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 2 PDFDocument7 pagesHE Lecture 2 PDFpresidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- Session 2 PraDocument3 pagesSession 2 PraHema SalamNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument12 pagesFluidsGolda Meyer Vidal100% (1)
- 4.fluid DynamicsDocument73 pages4.fluid Dynamicskrueg3rNo ratings yet
- The Fluid Mosaic Model For Membr The Key Points: AnesDocument1 pageThe Fluid Mosaic Model For Membr The Key Points: AnesSalmuel SmithNo ratings yet
- Topics 2 and 3 HBDocument16 pagesTopics 2 and 3 HBazankha1990No ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- RenalDocument13 pagesRenalJubilee Christiene AngNo ratings yet
- ورقة عمل لمادة تحليلات اختبارات الابار (خليفه سعد) 26537Document4 pagesورقة عمل لمادة تحليلات اختبارات الابار (خليفه سعد) 26537khalifasaadNo ratings yet
- NCP'.' Cor JesuDocument1 pageNCP'.' Cor JesuAna LanticseNo ratings yet
- Slides 03 Reabsorption1 UrinarySystemDocument19 pagesSlides 03 Reabsorption1 UrinarySystemJonathan BabuyaNo ratings yet
- PHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 10Document11 pagesPHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 10yassin mashalyNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow ppt3Document16 pagesLaminar Flow ppt3Renuja LakviduNo ratings yet
- Transactional AnalysisDocument15 pagesTransactional Analysisshital_vyas1987No ratings yet
- Stress Concentrations at Holes in Thin Rotating Discs: ANG L. TANDocument3 pagesStress Concentrations at Holes in Thin Rotating Discs: ANG L. TANKris SmaczekNo ratings yet
- Tube ClampDocument113 pagesTube ClampAmitava SilNo ratings yet
- DSI Valves: Forged Steel Carbon, Stainless and Alloy Gate, Globe and Check ValvesDocument32 pagesDSI Valves: Forged Steel Carbon, Stainless and Alloy Gate, Globe and Check ValvesJordan Magaña MoralesNo ratings yet
- Software Architecture: An: Vanilson BurégioDocument44 pagesSoftware Architecture: An: Vanilson BurégioAsim RazaNo ratings yet
- Xenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFDocument4 pagesXenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFshiksha torooNo ratings yet
- Metaverse Tourism Conceptual Framework and Research PropositionsDocument8 pagesMetaverse Tourism Conceptual Framework and Research PropositionsMarc MonerNo ratings yet
- G752VSK Rev2.0 PDFDocument83 pagesG752VSK Rev2.0 PDFAlexandru FloricicăNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Power ToolsDocument6 pagesReading Comprehension Power ToolsCarlos Alberto Lopez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Conduction 1Document3 pagesConduction 1Mohamad AlqaruteeNo ratings yet
- PCNE WorkbookDocument83 pagesPCNE WorkbookDaniel N Sherine FooNo ratings yet
- Hippias Major PlatonDocument4 pagesHippias Major PlatonLaura LapoviţăNo ratings yet
- Docit - Tips - Individual Performance Commitment and Review Ipcr Form PDFDocument2 pagesDocit - Tips - Individual Performance Commitment and Review Ipcr Form PDFEdelyn Lindero Ambos50% (2)
- Negor q3 Genbio2 Slkweek3 V2.finalDocument22 pagesNegor q3 Genbio2 Slkweek3 V2.finaljenicahazelmagahisNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Hazards AwarenessDocument27 pagesConfined Space Hazards AwarenessNoor Fadilah Printis100% (1)
- E45 Laboratory4Document7 pagesE45 Laboratory4nickNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 SeriesDocument4 pagesBio 1 SerieskisesarevNo ratings yet
- Nisbet Idea of Progress PDFDocument31 pagesNisbet Idea of Progress PDFHernan Cuevas ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Glyburide (Glibenclamide) : Drug Information: Brand Names: USDocument17 pagesGlyburide (Glibenclamide) : Drug Information: Brand Names: USAnonymous wmF9p2ejNo ratings yet
- Jordan's LemmaDocument3 pagesJordan's LemmaSergey LiflandskyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Questions and Answers - Laplace Transform by Properties - 1Document9 pagesEngineering Mathematics Questions and Answers - Laplace Transform by Properties - 1RAHUL SOLANKENo ratings yet
- NAA ItemNumber391518Document203 pagesNAA ItemNumber391518Jonathan ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Synchronous MachinespptDocument53 pagesChapter 2 Synchronous MachinespptraygharNo ratings yet
- Artificial Retina: Presented byDocument6 pagesArtificial Retina: Presented bySai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 3374 PDFDocument10 pages3374 PDFCornel DumitruNo ratings yet
- Priinciples of Statistics PDFDocument62 pagesPriinciples of Statistics PDFkaroNo ratings yet
- FICS PresentationDocument13 pagesFICS PresentationShujat AliNo ratings yet