Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet 4
Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet 4
Uploaded by
Waddles EditionCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet 4
Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet 4
Uploaded by
Waddles EditionCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Name: Camille Mcgann
• The 3 particles of the atom are:
• Protons
• Neutrons
• Electrons
Their respective charges are:
• Protons-Positive charge
• Neutron-Neutral charge
• Electron-Negative Charge
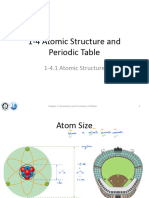
• The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s
Identity , and the number of electrons determines the_Electrical_Charge_of the element.
• The atomic number tells you the number of Protons in one atom of an element. It also
tells you the number of Electrons in aneutral atom of that element. The atomic number
gives the “identity” of an element aswell as its location on the periodic table. No two
different elements will have the
same atomic number.
• The Automic mass of an element is the total number of protons andneutrons in the
mass of the atom.
• In order to calculate the number of neutrons you must subtract the
Mass number from the Atomic Number
• Give the symbol and the number of protons in one atom of:
Lithium Li 3
Calcium Ca 20
Oxygen O 8
Potassium K 9
• Give the symbol of and the number of neutrons in one atom of:
Magnesium Mg =12
Boron B = 639
Chlorine Cl = 18
Carbon___C =6_____________________________
• Write the symbolic notation for the following atoms
12Mg
• 12 electrons, 12 neutrons, 12 protons 24
19K
• 19 protons, 20 neutrons and 19electrons 39
2He
• 2 protons, 2 neutrons and 2 electrons 4
20Ca
• 20 protons, 21 neutrons and 20 electrons 40
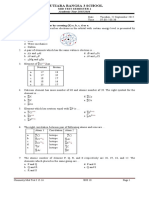
9. Fill in the missing items in the table below.
Name of the Atomic (Z) (A)
element symbol Atomic # Protons Neutrons Electrons Atomic
mass
Boron B 5 5 6 5 11
Sodium Na 11 11 12 11 24
Carbon C 6 6 6 6 12
Nitrogen N 7 7 7 7 14
Helium He 2 2 2 2 4
calcium Ca 20 20 20 20 40
Argon Ar 18 18 22 18 40
Magnesium Mg 12 12 12 12 25
Sulphur S 17 17 18 17 35
You might also like
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice Worksheet For 8th GradeDocument2 pagesProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice Worksheet For 8th GradeDrama Music67% (3)
- Subatomic Particles WsDocument1 pageSubatomic Particles WsYhena ChanNo ratings yet
- Number of Protons WorksheetDocument4 pagesNumber of Protons WorksheetIrene SanchezNo ratings yet
- Kelapa GadingDocument2 pagesKelapa GadingUtari Ika CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Jaeden Reames - Periodic Table Unit Packet PracticeDocument5 pagesKami Export - Jaeden Reames - Periodic Table Unit Packet PracticeJaeden ReamesNo ratings yet
- Lab DrawingsDocument15 pagesLab Drawingschandan naiduNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table - Chem - f2 - V1Document50 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table - Chem - f2 - V1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Scavenger HuntzschallerNo ratings yet
- Cainta Catholic College: Daily Learning Activity SheetDocument2 pagesCainta Catholic College: Daily Learning Activity SheetChynna Alicia B. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Placa de CapDocument1 pagePlaca de CapelenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 HW PacketDocument21 pagesUnit 03 HW Packetanabel mañoNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument13 pages1-4 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table227easonNo ratings yet
- General Science Booklet U 1 - 5Document15 pagesGeneral Science Booklet U 1 - 5amirah1590No ratings yet
- CH 2Document14 pagesCH 2dwarriorsNo ratings yet
- Ion Worksheet KEYDocument1 pageIon Worksheet KEYAna Marie Corales TabunarNo ratings yet
- Notes BasicChemHDocument55 pagesNotes BasicChemHcorygunther6451No ratings yet
- 40 Bench Vice FINALDocument1 page40 Bench Vice FINALadmam jonesNo ratings yet
- Soalan MatricesDocument7 pagesSoalan MatricesLee WSNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Atom Properties and Isotopes: Symbol With AN & MNDocument1 pageAtomic Structure: Atom Properties and Isotopes: Symbol With AN & MNFred EspejoNo ratings yet
- Hany El-Gezawy: HAP Measurements and Density Paper 1Document25 pagesHany El-Gezawy: HAP Measurements and Density Paper 1heteroNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Chap006 - AppDocument10 pagesConsumer Behavior Chap006 - AppAsad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- All About The Periodic Table - Home Laboratory WorksheetDocument4 pagesAll About The Periodic Table - Home Laboratory WorksheetFrank Ed SerranoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Questions 9ZDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Questions 9ZsfjjNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table PDFDocument51 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table PDFKevin NdanyiNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument2 pagesRelative Atomic MassdsanNo ratings yet
- Food Truck The First Revised Design DesignDocument18 pagesFood Truck The First Revised Design Designadugnaw simegnewNo ratings yet
- IMO3 Theory ProblemsDocument20 pagesIMO3 Theory ProblemsPhạm Trung Quốc AnhNo ratings yet
- IMO3 Theory SolutionsDocument21 pagesIMO3 Theory SolutionsPhạm Trung Quốc AnhNo ratings yet
- 4th Olympiad of Metropolises Chemistry: September 4, 2019 Moscow, RussiaDocument23 pages4th Olympiad of Metropolises Chemistry: September 4, 2019 Moscow, Russiamila_a_vaNo ratings yet
- AQA Phys Worksheet4.1.3Document1 pageAQA Phys Worksheet4.1.3CT ONo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table Worksheet WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Periodic Table Worksheet WorksheetsachithNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TablelingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Soal Fusion 360, 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesSoal Fusion 360, 2019 PDFBimo Putra Syaiful HilalNo ratings yet
- FE Quick Review - v0.37Document13 pagesFE Quick Review - v0.37Abdalrahman AntariNo ratings yet
- Basic Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument4 pagesBasic Atomic Structure WorksheetTrisha GolesNo ratings yet
- Stretch SheetDocument2 pagesStretch Sheetjoe bloggNo ratings yet
- Science 8 ReviwerDocument2 pagesScience 8 ReviwerAllynn JunioNo ratings yet
- A4 Periodic TableDocument159 pagesA4 Periodic TableAtharvvaNo ratings yet
- A - 3.1 - Atomic - Structure - and - The - Periodic - Table - QP - Igcse - Cie - Chemistry - Extende - Theory - PaperDocument9 pagesA - 3.1 - Atomic - Structure - and - The - Periodic - Table - QP - Igcse - Cie - Chemistry - Extende - Theory - Paperdeivid floreaNo ratings yet
- FALCON CREST - by Jerry L.Capps, 1/24/2000Document1 pageFALCON CREST - by Jerry L.Capps, 1/24/2000tristanNo ratings yet
- Students File OMC1Document31 pagesStudents File OMC1TechminerNo ratings yet
- Mutiara Bangsa 3 School: Mid Test Semester 1Document3 pagesMutiara Bangsa 3 School: Mid Test Semester 1mianNo ratings yet
- Reading Chemical Symbols ChemistryDocument3 pagesReading Chemical Symbols ChemistryidzienisNo ratings yet
- Screw Bar Vice BodyDocument4 pagesScrew Bar Vice BodyswarajNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Fiche de Données: Symbol Symbole Value Quantité NumériqueDocument1 pageData Sheet Fiche de Données: Symbol Symbole Value Quantité NumériqueSacha Doucet-KimNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Scavenger HuntShawana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Group Activity1Document1 pageGroup Activity1ansalerochNo ratings yet
- Trip Circuit Supervision CircuitDocument1 pageTrip Circuit Supervision CircuitgovindhNo ratings yet
- CHM150 (Practice) (Atomic and Mass Number)Document1 pageCHM150 (Practice) (Atomic and Mass Number)sandraNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test in Mathematics 6Document2 pagesFirst Summative Test in Mathematics 6Paul AquinoNo ratings yet
- 2021 08 25 Atomic Notation Practice WorksheetDocument3 pages2021 08 25 Atomic Notation Practice WorksheetTimothy Urtz (Chicago)No ratings yet
- 1 Grade 11 Review AnswersDocument9 pages1 Grade 11 Review Answersapi-363234558No ratings yet
- Questions: Na Ca He Ne Cu Fe Ar Li AlDocument2 pagesQuestions: Na Ca He Ne Cu Fe Ar Li AlPearly WongNo ratings yet
- LJKDocument1 pageLJKRIDHO NOFIANNo ratings yet
- TK Top Fuel Quickref MY20 Rev2 Feb 22Document9 pagesTK Top Fuel Quickref MY20 Rev2 Feb 22Manu StaffolaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 ISM Chang 14eDocument7 pagesChapter 02 ISM Chang 14elsytb2000No ratings yet
- 12 Volt D.C Relay Data SheetDocument4 pages12 Volt D.C Relay Data SheetcallkalaiNo ratings yet