Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Exam Guide
Biology Exam Guide
Uploaded by
Ke-Deidra DaleyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Frozen Chicken Cuts Price List-OmanDocument3 pagesFrozen Chicken Cuts Price List-Omanlondi m100% (2)
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification Worksheetsarah chuaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocument3 pagesKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- The Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationDocument9 pagesThe Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationliugirmayNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic MicroorganismDocument11 pagesEukaryotic MicroorganismDency Mae AbreNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFDocument25 pagesREVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFizaNo ratings yet
- MCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of BacteriaDocument35 pagesMCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of Bacteriachinecheremstephanie2022No ratings yet
- Science Animal and EcosytemDocument5 pagesScience Animal and EcosytemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument29 pagesBiodiversityGhoulispogNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceCold CoockiesNo ratings yet
- Annelida Written ReportDocument11 pagesAnnelida Written ReportIrish MaireignNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsDocument92 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- ArthropodaDocument56 pagesArthropodamthisis791No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument209 pagesBiologyammugolu07No ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument54 pagesBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- F3biol Revision NotesDocument5 pagesF3biol Revision NotesVinitha MenonNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 7Document6 pagesBio CH 7Madhur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesChapter 2 (Biology)MahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Classifying Living OrganismsDocument54 pagesClassifying Living Organismstiya.bakugo.katsuki01No ratings yet
- (Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Document18 pages(Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Bekele GonfaNo ratings yet
- Arthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesArthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemBello AjetayoNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument16 pagesFungiMaria Christina ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument43 pages1.1 - Introduction To BiologyCj CombisenNo ratings yet
- Oraganism and Its EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesOraganism and Its EnvironmentsKim AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument7 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationArnavNo ratings yet
- Zoology BonDocument118 pagesZoology BonRupkathar Pagol Kra RajkumariNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument26 pagesBIODIVERSITYRea AnsusNo ratings yet
- Charactersitics of Living ThingsDocument69 pagesCharactersitics of Living Thingsrue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Biological Classification NotesDocument7 pagesChapter-2 - Biological Classification NotesAnita TandonNo ratings yet
- The Study of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesThe Study of Living ThingsindahhsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Document7 pagesPre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Maria HwasaNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument3 pagesBab IiiVenty HabibieNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsAmana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Short NotesyusufNo ratings yet
- Carolus LinnaeusDocument5 pagesCarolus LinnaeusMae Jane AguilarNo ratings yet
- Biology: The Cell, Taxonomy and The Human Body SystemsDocument27 pagesBiology: The Cell, Taxonomy and The Human Body SystemsJDR JDRNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PDFDocument67 pagesBiodiversity PDFTanaya BorseNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms ClassifiedDocument24 pagesKingdoms ClassifiedDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationDocument39 pagesHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument90 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingsaisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtistaDocument27 pagesKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- BLG 1502 QuizDocument26 pagesBLG 1502 QuizLisa PretoriusNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz (1st Year)Document26 pagesBiology Quiz (1st Year)Lisa PretoriusNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document31 pagesPresentation 1Soo Ming Huey 明慧No ratings yet
- COL3Document11 pagesCOL3Clefford CorporalNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Class 11 Unit 1Document21 pagesRajkumar Class 11 Unit 1asuhassNo ratings yet
- SZL 201Document182 pagesSZL 201Charity100% (1)
- Biology CSEC PrepDocument43 pagesBiology CSEC PrepMarcellus Lee100% (1)
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio Notes 1Document9 pagesCSEC Bio Notes 1MiaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification WorksheetJhon Vincent GaytaNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsDocument64 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EntomologyDocument43 pagesAquatic EntomologyNagwa SorourNo ratings yet
- Folio Science Aku!!!!Document26 pagesFolio Science Aku!!!!guzer_wan9595% (21)
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Cornbread Say GraceDocument3 pagesHot Water Cornbread Say GraceS.A. KaluNo ratings yet
- Practice Reading TestDocument8 pagesPractice Reading TestBrazilNo ratings yet
- Super Rich Dad Chapter 241-243Document15 pagesSuper Rich Dad Chapter 241-243ElmerNo ratings yet
- Thin-Crust Pizza - King Arthur BakingDocument2 pagesThin-Crust Pizza - King Arthur BakingRonnieNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangeAminaNo ratings yet
- AR19 Final Buhler Annual Report 2019Document147 pagesAR19 Final Buhler Annual Report 2019Phương TrầnNo ratings yet
- Using A Functional Carrot Powder Ingredient To Produce Sausages With High Levels of NutraceuticalsDocument11 pagesUsing A Functional Carrot Powder Ingredient To Produce Sausages With High Levels of NutraceuticalsARROYO MANCILLA ANA ISABELNo ratings yet
- DCP - Back MenuDocument5 pagesDCP - Back MenuJMKNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Food StorageDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Food Storageafmznqfsclmgbe100% (1)
- Investigatory Project Chapter 3Document8 pagesInvestigatory Project Chapter 3Ian Agatha AndresNo ratings yet
- Curso de Ingles UMG 2021Document127 pagesCurso de Ingles UMG 2021KARLA ELIZABETH CASTAÑEDA BATRESNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT B. Inggris K8Document11 pagesSoal PAT B. Inggris K8dellaarienda38No ratings yet
- Production Processing and Utilization of Rosemary in EthiopiaDocument27 pagesProduction Processing and Utilization of Rosemary in EthiopiaOnika BlandinNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes - Module 6Document7 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes - Module 6almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Copper Stone AgeDocument84 pagesCopper Stone AgeclisenbyNo ratings yet
- Galley Steward Knowledge: Free Screening / Interview GuidelineDocument2 pagesGalley Steward Knowledge: Free Screening / Interview GuidelineAgung Mirah Meyliana100% (2)
- Exercise On Unit 6Document11 pagesExercise On Unit 6Thanh ThủyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The EyebrowsDocument10 pagesExercise 1 The EyebrowsJENICA VERTUDESNo ratings yet
- Self-Styling, Popular Culture, and The Construction of Global-Local Identity Among Japanese Food Lovers in PurwokertoDocument20 pagesSelf-Styling, Popular Culture, and The Construction of Global-Local Identity Among Japanese Food Lovers in Purwokertodiana triNo ratings yet
- Food Safety SensorsDocument196 pagesFood Safety SensorsGrigor BadalyanNo ratings yet
- Gulfood 2024 - Space Booking FormDocument2 pagesGulfood 2024 - Space Booking Formsunny.dates.foodsNo ratings yet
- CRM FrameworkDocument9 pagesCRM Frameworkshree dalkeNo ratings yet
- Beans in The GardenDocument3 pagesBeans in The GardenJuan Manuel Herrera NavasNo ratings yet
- X X X X: Contains AllergensDocument4 pagesX X X X: Contains AllergensMa Ana RepeNo ratings yet
- International Sommelier Guild IWC: Welcome!Document65 pagesInternational Sommelier Guild IWC: Welcome!BakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Sarlacc - GM BinderDocument9 pagesSarlacc - GM BinderLuisito Gonzalez0% (1)
- Objective Education: Cheyenne Mountain High SchoolDocument2 pagesObjective Education: Cheyenne Mountain High Schoolapi-665457604No ratings yet
- Munlai Package DetailsDocument8 pagesMunlai Package DetailsNacromancer XFRNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Liquor Price List 2021 PDFDocument41 pagesJharkhand Liquor Price List 2021 PDFRudra RanaNo ratings yet
Biology Exam Guide
Biology Exam Guide
Uploaded by
Ke-Deidra DaleyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Exam Guide
Biology Exam Guide
Uploaded by
Ke-Deidra DaleyCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Exam Guide
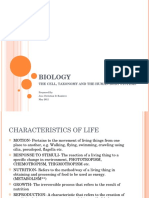
Characteristics
growth
living organisms increase in size and mass
respiration
energy is released to carry out all the life processes
irritability
when living organisms respond to changes to their internal and external environment
movement
plants show growth and animals move from place to place
nutrition
organisms using food as a source of energy. plants get food form photosynthesis while animals
get their food by eating plants and other animals
excretion
living organisms creating waste products that must be removed form the body
reproduction
the production of new organisms
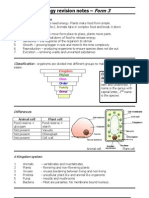
Classifications
Binomial system
a system for naming species with a biological name is called the binomial system
Kingdoms
Prokaryotes
Biology Exam Guide 1
These are commonly called bacteria. They occupy environments such as soil, dust, air, water, and
in or on animals and plants. Some Prokaryotes can be found in hot springs with temperatures
higher than 78 degrees, while some can be found in freezing ice and deep cracks in the ocean
floor. They are the most ancient group of organisms, they have the smallest cellular structure.
Many exist as single cells while others can be found in groups. Their cell structure is simpler
than that of the Eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are decomposers therefore they cause decay to dead
plant and animal material and release the nutrients back into the environment being essential in
the nitrogen cycle. They are important to humans since they cause TB and cholera and are used
in insulin production.
Protoctists
They are unicellular. Algae and Protozoa are two kinds of Protoctists.
Algae live in the sea and freshwater some live on land where the surface is damp. They make
their own food by photosynthesis. Some live as single cells while others are found in colonies or
groups. They can form scum on the surface of rivers, lakes and ponds turning them green. An
example of Algae is seaweed
Protozoa are unicellular and feed on other animals or heterotrophically. They are found in all
environments, especially in the water. Protozoa causes diseases such as malaria and sleeping
sickness. Examples of Protozoa are Amoeba and Paramecium.
Fungi
They range in size and can be unicellular yeasts or large toadstools. They feed heterotrophically
and obtain their food from the environment. However, they do not take in large particles of food.
They digest their food outside the body using enzymes which make it soluble so that they can
absorb the food. They are usually living in or on their food which can be dead or living
organisms. Some are used by humans for medical and dietary purposes, some can cause spoilage
to food, moulds and rusts damage crops. Examples of fungi include mushrooms, yeasts, moulds
and toadstools
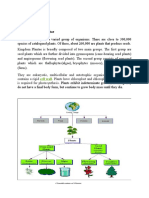
Plant
The plant kingdom includes mosses, liverworts, ferns, conifers, and flowering plants. Many
plants are a source of food for humans and other animals. Some provide a rich a diverse habitat,
some plants can be used as medicine.
Biology Exam Guide 2
Flowering plants are also called angiosperms and are divided into two groups monocotyledons
which have one seed and parallel veins for example corn, cane, and grass, and dicotyledons
which have two seeds and have net-like or branching veins hibiscus, rose, sunflower, and
breadfruit. Angiosperms are the largest group of plants, they include most crop plants,
ornamental plants and plants used as herbs or medicinal plants.
Animals
They contain multicellular heterotrophic organisms and are grouped in phyla.
Cnidaria- jellyfish, sea anemones, coral
Platyhelminthes- flatworms eg. tapeworms
Annelida- roundworm, earthworm, leech
Nematoda- roundworms
Molluscs- conch, snails, slugs, cockles, mussels, octopus, oysters
They have a soft body that is often covered by a shell. Some are used as a source of food,
and farming of molluscs is also practiced.
Chordata- amphibians, mammals, birds, reptiles
They are vertebrates
Humans are in this category
Class
Birds
Have waterproof skin with feathers
Have a beak and no teeth
Forelimbs are modified to form wings
Lay eggs with a hard shell
Are homeothermic
Eg. sparrow, cattle egret, hawk
Biology Exam Guide 3
Reptiles
Have dry waterproof skin with scales
Lay eggs with a rubbery shell on land
Eg. snake, lizard, iguana, turtle
Arthropods
Have waterproof exoskeleton made mainly of chitin
Have a segmented body
Have several pairs of joint legs
Crustaceans
Have two pairs of antennae
Usually have five or seven pairs of legs
Body is divided into head thorax and abdomen
They live in aquatic, damp places
Eg. lobster, shrimp, crab, crayfish, barnacles
Arachnids
Have no antennae
Have four pairs of legs
The body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen
They are mainly terrestrial and carnivorous
Eg. spider, tick, scorpion, mites
Insects
Have one pair of antennae
Have three pairs of legs
The body is divided into had, thorax and abdomen
Biology Exam Guide 4
Have a pair of compound eyes
Most have two pairs of wings
Eg. cockroach, moth, ant, beetles, locusts
Myriapods
Have one pair of antennae
Have many pairs of legs
The body is elongated and divided into many segments
Eg. Millipede Centipede
Characteristics of Classifying Organisms
There are two types of classification Artificial Classification and Natural Classification.
Artificial Classification is based on easily observed physical characteristics for example their
color, shape, number of legs etc. This is an easy way that is designed for a practical purpose.
Natural Classification uses the natural relationships between organisms by using external and
internal characteristics.
Ecological Study
Method to Collect Organisms
Tullgren Funnel
This method is used to extract organisms from the soil. The heat from the bulb dries and warms
the
sample, causing the animals to move downwards and fall through the sieve into the funnel,
which directs them into a collecting dish or tube below. The dish can contain water or alcohol to
prevent the animals from escaping.
Pitfall Trap
Biology Exam Guide 5
This method is used for capturing organisms for example insects. This trap comprises an
appropriately baited vessel (e.g. a
with a bait that is buried so its mouth is at ground level. The mouth is covered by a roof, to
shelter the vessel from rain and prevent larger animals from entering, and raised sufficiently to
allow access for target species.
Pooter
This method is used to collect and transfer small animals. It consists of a jar, sealed by a cover
pierced by two
tubes pointing in opposite directions. The operator sucks on the end of one tube drawing the
organism up the other (open) tube and into the jar.
Plankton Net
This method is used to collect plankton it is generally dragged behind a boat for collection. The
mesh used in a plankton net has holes that are large enough to allow water to pass through but
small enough so that plankton cannot pass through.
Sampling Techniques
Observation
The area should be observed and the common species of plants and animals that are present
should be recorded. Any adaptations that enable the organism to survive should also be noted as
well as the interrelationship between the organisms.
Quadrat
A square frame that is used to study the distribution and abundance of plants and stationary or
slow-moving animals within an ecosystem
Line transects
A measuring tape or string that had marks at regular intervals that is placed in a straight line to
record the species of plants and stationary or slow-moving animals touching the line or touching
the line at each mark
Belt transects
a strip of fixed width made by placing two parallel line transects across an ecosystem and
recording the species found between the lines. Or place a quadrat alongside one of the line
transects and count the number of species found withing its boundaries.
Biology Exam Guide 6
Cycling of Nutrients
Role of fungi and bacteria
Carbon Cycle
Feed on dead organic matter and the carbon would then be incorporated in their bodies
Nitrogen Cycle
Decompose the bodies of plants and animals when they die to make ammonium compounds in
the soil. They decompose the waste for example faeces and urine of the animal
Food Webs, Chains and Feeding Relationships
producers
Producers are autotrophs since they make or produce their own food. They make up the first
level of every food chain. Plants are examples of producers.
consumers
Organisms that consume plants or producers are called consumers.
Herbivores
These are organisms that only feed on plants for example grasshoppers, bees, cows, horses.
Carnivores
These are organisms that only feed on animals, they may hunt and feed animals for food. For
example snakes, lions, dolphins, hawks
Omnivores
They feed on both plants and animals for example pigs and humans
Food chains
Biology Exam Guide 7
A food chain is a simple diagram that shows how the food or nutrients pass from one organism to
another.
The arrows show the movement of energy along the food chain. The leaf is a part of a green
plant that is a producer. The caterpillar eats the leaf to get energy and therefore they are the
consumer. The small bird and hawk are also consumers since they are getting their energy from
other organisms.
Herbivores feed on plants or producers and then the carnivores feed on the herbivores. An
omnivore may feed on the producer or herbivore and in some cases the carnivores.
The trophic level is defined as the position of an organism in the food chain. This can be
determined by the amount of organisms in the food chain.
Predators
These are carnivores that hunt, capture, kill and feed on other animals.
Prey
These are organisms that are hunted and eaten by other animals.
Food webs
A food web is the interlinking of multiple food chains
Biology Exam Guide 8
Decomposers and Detritivores
These two organisms obtain their food or energy by feeding on the remains of dead organisms.
They feed saprophytically. As the decomposers and detritivores feed on the remains of these
organisms it causes the organisms to decay or decompose. They secrete enzymes which break
down dead plants and animals into humus. This helps in the recycling of nutrients.
Special Relationships
Symbiosis
This describes any relationship that exists when different species of organisms live together.
There are three types of symbiosis:
Mutualism
This is any kind of association with two organisms of different species that live closely together
and both benefit.
Examples of mutualism
sea anemones and hermit crabs
the anemone attaches itself to the crab’s shell and obtains scraps of food as the crab feeds. The
crab gains protection from predators by the anemone’s stinging tentacles as well as
camouflaged.
leguminous plants and rhizobium
the rhizobium bacteria live inside the roots of leguminous plants for example peas and beans.
This bacteria will convert nitrogen gas into nitrates which is used directly by the plants for
growth. The rhizobium bacteria benefits since it has a place to live as well as an energy supply
which they get from the plant.
Biology Exam Guide 9
egret and cow
the egret feeds on insects especially ticks which may cause harm to the cow. The egret benefits
by obtaining food and the cow benefits by having the blood-sucking insect removed from its
body.
Commensalism
This is a relationship between two organisms of different species in which one benefits and the
other neither harmed nor benefits.
examples of commensalism
some orchids or ferns on trees
the orchids or ferns are small plants that grow high on trees so that they are able to obtain
sunlight to be able to carry out photosynthesis. The tree in this case neither benefits nor is it
harmed.
shark and remora
the remora attaches itself to the shark and moves around with it and as the shark feeds the remora
will also feed on the scraps of food that are floating around. In this case the shark is neither
harmed nor does it benefit
Parasitism
a parasite is an organism that lives and feeds on or in another organism, which is called the host.
the parasite gains while the host is harmed.
parasites that live on the outer surface of their host is called ectoparasites. for example, ticks,
lice, fleas, and leeches feed on the blood of their hosts such as dogs, humans, cattle and fish.
parasites that live within a host is called endoparasites. an example of an endoparasite is
plasmodium which causes malaria.
Movement of energy through a food chain
In a food chain, there is less energy at each level for the animal in that level than in the level
below. Energy enters a food chain as light energy from the sun and lost from every trophic level
as heat energy to the environment.
Biology Exam Guide 10
The plant gains energy from the sun therefore it would have the most energy. Some of this
energy is lost as heat due to respiration, some of it is stored, some of it is used to carry out life
processes and 10% of the energy is passed on to the primary consumer or herbivore. The
herbivore stores some of the energy in its tissues, some of it is lost as heat due to respiration,
some of it is also lost in urine faeces and then 10% is passed on to the secondary consumer or
carnivore. The same thing happens for the secondary consumer and 10% is passed on to the
tertiary consumer or carnivore.
the amount of organisms present as well as the energy in biomass available at each level also
helps to determine the length of a food chain and the amount of trophic levels.
pyramid of numbers
a pyramid of numbers is like a pyramid of energy but it shows the number of all the organisms at
each tropic level in a food chain at a given area
Definitions
habitat
the place where an organism lives
population
all the members of a particular species living together in a particular habitat
community
all the populations of different species living together in a particular habitat
biotic factors
Biology Exam Guide 11
living components or factors that affect an ecosystem or the organisms living within the
ecosystem. for example preys, predators, decomposers, competitors etc
abiotic factors
non-living components or factors that affect an ecosystem or the organisms that live in an
ecosystem. for example edaphic, climatic and aquatic
edaphic factors
those which are connected to the soil. the soil is a habitat for many organisms and it provides the
organism that is living within it with water, oxygen, nitrogen, and mineral nutrients. other
edaphic factors would include the soil texture, pH, and humus. edaphic factors affect
subterrestrial organisms
climatic factors
these are factors that affect terrestrial organisms this includes:
light
light intensity and duration affects living organisms.
temperature
humidity
humidity can can affect transpiration rate in plants and evaporation rate in some animals
water availability
chemical reactions in cells and most life processes need water in order to take place. It is also
important in photosynthesis
wind
wind is essential for pollination and seed dispersal in many plants, it may also affect migration of
birds. it may affect the transpiration rate in plants and the evaporation rate in animals
atmospheric gases
oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration in almost all living things and carbon dioxide is
essential for photosynthesis. pollutant gases have a negative effect on living organisms.
aquatic factors
anything that affects organisms living in aquatic habitats.
Biology Exam Guide 12
salinity
the concentration of salt in the water. most organisms are adapted to survive in a specific salinity
water movement and wave action
those living in rivers and streams are affected by the constant movement of water, those living
along ocean shorelines are affected by changing water levels as the tide rises and are exposed to
wave action, and those that live in oceans are affected by currents
dissolved oxygen
aquatic organisms use dissolved oxygen for respiration.
plant zonation
Resources
renewable and non-renewable resources
renewable resources
these are resources that can be reused or replaced quickly for example water and soil resources
non-renewable resources
these are resources that are in limited supply and once they are used up, they are gone forever.
for example fuel resources and mineral resources
3 r’s
reuse
waste that can be used again in the same way or in another way. for example tins and jars can be
reused as conatiners
reduce
buying and using only what is needed this will lessen discarded waste and pollution
recycle
Biology Exam Guide 13
collecting materials that are already used and would be considered waste separating and making
them into new products
difficulties of recycling
it can be time-consuming to sort and separate the materials
people who are participating must be educated about how to separate and sort the materials
as well as why this is important
extremely large storage area is needed
expensive- buying containers/bins, transportation, and maintenance of the transportation
consequences of deforestation
soil erosion
increased flooding
destruction of natural resources
soil degradation
destruction of habitats which can result in species destruction
advantages and disadvantages of industrialization
advantage
it generates income for communities and countries
it provides jobs
disadvantages
it causes land, air and water pollution
it causes water shortages
it causes deforestation
Climate Change
effects of climate change
Biology Exam Guide 14
increased drought
rising of ocean levels
more severe storms
hotter temperatures
Population
sigmoid growth curve
The sigmoid growth curve is a common growth curve that illustrates how an organism's
population density rises gradually at first, in a positive acceleration phase, then quickly,
approaching an exponential growth rate before falling in a negative acceleration phase until the
population stabilizes at zero growth rate.
4 phases of growth
phase 1- little growth
phase 2- rapid growth
phase 3- growth slows down
phase 4- no growth, population size is constant
causes of population increase and decrease
increase
few predators or able to avoid predators
good food supply
ability to resist diseases
good water supply
decrease
limited space
many predators present or unable to avoid predators
susceptible to diseases
Biology Exam Guide 15
poor food supply
Biology Exam Guide 16
You might also like
- Frozen Chicken Cuts Price List-OmanDocument3 pagesFrozen Chicken Cuts Price List-Omanlondi m100% (2)
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification Worksheetsarah chuaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocument3 pagesKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- The Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationDocument9 pagesThe Five-Kingdom System of ClassificationliugirmayNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic MicroorganismDocument11 pagesEukaryotic MicroorganismDency Mae AbreNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFDocument25 pagesREVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFizaNo ratings yet
- MCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of BacteriaDocument35 pagesMCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of Bacteriachinecheremstephanie2022No ratings yet
- Science Animal and EcosytemDocument5 pagesScience Animal and EcosytemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument29 pagesBiodiversityGhoulispogNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceCold CoockiesNo ratings yet
- Annelida Written ReportDocument11 pagesAnnelida Written ReportIrish MaireignNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsDocument92 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- ArthropodaDocument56 pagesArthropodamthisis791No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument209 pagesBiologyammugolu07No ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument54 pagesBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- F3biol Revision NotesDocument5 pagesF3biol Revision NotesVinitha MenonNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 7Document6 pagesBio CH 7Madhur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesChapter 2 (Biology)MahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Classifying Living OrganismsDocument54 pagesClassifying Living Organismstiya.bakugo.katsuki01No ratings yet
- (Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Document18 pages(Biol 12) Grade 9 - Unit 5 Notes and MCQ (2016)Bekele GonfaNo ratings yet
- Arthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesArthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemBello AjetayoNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument16 pagesFungiMaria Christina ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument43 pages1.1 - Introduction To BiologyCj CombisenNo ratings yet
- Oraganism and Its EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesOraganism and Its EnvironmentsKim AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument7 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch02 Biological ClassificationArnavNo ratings yet
- Zoology BonDocument118 pagesZoology BonRupkathar Pagol Kra RajkumariNo ratings yet
- Week Two Biology SS1Document12 pagesWeek Two Biology SS1Oseni MuibaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument26 pagesBIODIVERSITYRea AnsusNo ratings yet
- Charactersitics of Living ThingsDocument69 pagesCharactersitics of Living Thingsrue pattinsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Biological Classification NotesDocument7 pagesChapter-2 - Biological Classification NotesAnita TandonNo ratings yet
- The Study of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesThe Study of Living ThingsindahhsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Document7 pagesPre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Maria HwasaNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument3 pagesBab IiiVenty HabibieNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesCharacteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsAmana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Short NotesyusufNo ratings yet
- Carolus LinnaeusDocument5 pagesCarolus LinnaeusMae Jane AguilarNo ratings yet
- Biology: The Cell, Taxonomy and The Human Body SystemsDocument27 pagesBiology: The Cell, Taxonomy and The Human Body SystemsJDR JDRNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PDFDocument67 pagesBiodiversity PDFTanaya BorseNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms ClassifiedDocument24 pagesKingdoms ClassifiedDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationDocument39 pagesHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument90 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingsaisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtistaDocument27 pagesKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- BLG 1502 QuizDocument26 pagesBLG 1502 QuizLisa PretoriusNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz (1st Year)Document26 pagesBiology Quiz (1st Year)Lisa PretoriusNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document31 pagesPresentation 1Soo Ming Huey 明慧No ratings yet
- COL3Document11 pagesCOL3Clefford CorporalNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Class 11 Unit 1Document21 pagesRajkumar Class 11 Unit 1asuhassNo ratings yet
- SZL 201Document182 pagesSZL 201Charity100% (1)
- Biology CSEC PrepDocument43 pagesBiology CSEC PrepMarcellus Lee100% (1)
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio Notes 1Document9 pagesCSEC Bio Notes 1MiaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification WorksheetJhon Vincent GaytaNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsDocument64 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EntomologyDocument43 pagesAquatic EntomologyNagwa SorourNo ratings yet
- Folio Science Aku!!!!Document26 pagesFolio Science Aku!!!!guzer_wan9595% (21)
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Cornbread Say GraceDocument3 pagesHot Water Cornbread Say GraceS.A. KaluNo ratings yet
- Practice Reading TestDocument8 pagesPractice Reading TestBrazilNo ratings yet
- Super Rich Dad Chapter 241-243Document15 pagesSuper Rich Dad Chapter 241-243ElmerNo ratings yet
- Thin-Crust Pizza - King Arthur BakingDocument2 pagesThin-Crust Pizza - King Arthur BakingRonnieNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangeAminaNo ratings yet
- AR19 Final Buhler Annual Report 2019Document147 pagesAR19 Final Buhler Annual Report 2019Phương TrầnNo ratings yet
- Using A Functional Carrot Powder Ingredient To Produce Sausages With High Levels of NutraceuticalsDocument11 pagesUsing A Functional Carrot Powder Ingredient To Produce Sausages With High Levels of NutraceuticalsARROYO MANCILLA ANA ISABELNo ratings yet
- DCP - Back MenuDocument5 pagesDCP - Back MenuJMKNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Food StorageDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Food Storageafmznqfsclmgbe100% (1)
- Investigatory Project Chapter 3Document8 pagesInvestigatory Project Chapter 3Ian Agatha AndresNo ratings yet
- Curso de Ingles UMG 2021Document127 pagesCurso de Ingles UMG 2021KARLA ELIZABETH CASTAÑEDA BATRESNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT B. Inggris K8Document11 pagesSoal PAT B. Inggris K8dellaarienda38No ratings yet
- Production Processing and Utilization of Rosemary in EthiopiaDocument27 pagesProduction Processing and Utilization of Rosemary in EthiopiaOnika BlandinNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes - Module 6Document7 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes - Module 6almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Copper Stone AgeDocument84 pagesCopper Stone AgeclisenbyNo ratings yet
- Galley Steward Knowledge: Free Screening / Interview GuidelineDocument2 pagesGalley Steward Knowledge: Free Screening / Interview GuidelineAgung Mirah Meyliana100% (2)
- Exercise On Unit 6Document11 pagesExercise On Unit 6Thanh ThủyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The EyebrowsDocument10 pagesExercise 1 The EyebrowsJENICA VERTUDESNo ratings yet
- Self-Styling, Popular Culture, and The Construction of Global-Local Identity Among Japanese Food Lovers in PurwokertoDocument20 pagesSelf-Styling, Popular Culture, and The Construction of Global-Local Identity Among Japanese Food Lovers in Purwokertodiana triNo ratings yet
- Food Safety SensorsDocument196 pagesFood Safety SensorsGrigor BadalyanNo ratings yet
- Gulfood 2024 - Space Booking FormDocument2 pagesGulfood 2024 - Space Booking Formsunny.dates.foodsNo ratings yet
- CRM FrameworkDocument9 pagesCRM Frameworkshree dalkeNo ratings yet
- Beans in The GardenDocument3 pagesBeans in The GardenJuan Manuel Herrera NavasNo ratings yet
- X X X X: Contains AllergensDocument4 pagesX X X X: Contains AllergensMa Ana RepeNo ratings yet
- International Sommelier Guild IWC: Welcome!Document65 pagesInternational Sommelier Guild IWC: Welcome!BakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Sarlacc - GM BinderDocument9 pagesSarlacc - GM BinderLuisito Gonzalez0% (1)
- Objective Education: Cheyenne Mountain High SchoolDocument2 pagesObjective Education: Cheyenne Mountain High Schoolapi-665457604No ratings yet
- Munlai Package DetailsDocument8 pagesMunlai Package DetailsNacromancer XFRNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Liquor Price List 2021 PDFDocument41 pagesJharkhand Liquor Price List 2021 PDFRudra RanaNo ratings yet