Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
Uploaded by
Dr. RemedyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2 Renal Tubular FunctionDocument1 page2 Renal Tubular FunctionIts FlorenceNo ratings yet
- L8-Urine Conc.Document15 pagesL8-Urine Conc.Bryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document23 pagesLecture 21sara shloulNo ratings yet
- Renal AnatomyDocument13 pagesRenal AnatomyApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lab OnlineDocument25 pagesUrinary Lab OnlineretterateNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabDocument15 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFDocument11 pagesLect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFBinisha KapadiaNo ratings yet
- KidneyoutlineDocument33 pagesKidneyoutlineapi-273417637No ratings yet
- Renal System 6 1Document30 pagesRenal System 6 1gaurav singhNo ratings yet
- 25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxDocument12 pages25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys: DevelopingDocument18 pagesThe Kidneys: Developingmaria sanchezNo ratings yet
- Bio 11.3Document6 pagesBio 11.3nicholaswzchanNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document7 pagesExcretion 1swinky.dsNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- Concentration and Dilution of UrineDocument26 pagesConcentration and Dilution of UrineHakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Renal 2 and 3Document12 pagesRenal 2 and 3Leugim saveucNo ratings yet
- Parts of Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesParts of Urinary SystemZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- D. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresDocument6 pagesD. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresCatherine BelonioNo ratings yet
- Urinary SysDocument3 pagesUrinary SysMario Antonio CarpioNo ratings yet
- Renal Function: 1 To 1.5 MillionDocument35 pagesRenal Function: 1 To 1.5 MillionUNKNOWN ANGELNo ratings yet
- Activity 36 - Urinary Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument6 pagesActivity 36 - Urinary Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionKaren Joy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Applied Renal PhysiologyDocument18 pagesApplied Renal PhysiologyDamián ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Its EliminationDocument2 pagesExcretory Products and Its Eliminationmariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- Manner: DininDocument6 pagesManner: DininbibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument49 pagesUrinary SystemSalum AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, Nephronlulu.borsikovaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, NephronPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriDocument3 pagesRenal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 1 Lab Report Sedimentation' Water Unit Operations Group 3 Bejarano Moreno Laura, Burgos Lopez Laura, Camacho LinaDocument8 pages1 Lab Report Sedimentation' Water Unit Operations Group 3 Bejarano Moreno Laura, Burgos Lopez Laura, Camacho LinaLaura Bejarano MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDocument49 pagesTubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- 3 - Excretion NotesDocument33 pages3 - Excretion NotesJenny YoonNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument51 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationmadam photonNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemDocument3 pagesAbsorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemNUR'AIN BINTI AZHAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation - Human Excretory SystemDocument13 pagesUrine Formation - Human Excretory SystemRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- L5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationDocument21 pagesL5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationBryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Osmotic Power Generation and Reverse Osmosis Desalination Hybrid SystemDocument4 pagesOsmotic Power Generation and Reverse Osmosis Desalination Hybrid SystemHasim BenziniNo ratings yet
- ANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemSin I GangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument2 pagesTransport in Plantsakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Messias MachineDocument5 pagesMessias MachineMANNAJANELAGUNANo ratings yet
- Ugs - 4Document9 pagesUgs - 4Mohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 Urinary SystemDocument49 pagesChap 14 Urinary Systematytayn9No ratings yet
- Biology 2Document1 pageBiology 2Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- Form'n'Function IIDocument9 pagesForm'n'Function IIRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Counter Current MechanismDocument33 pagesCounter Current MechanismPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer67% (3)
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- Review in AUBFDocument37 pagesReview in AUBFMichelle T. MabasaNo ratings yet
- 10.excretory SystemDocument16 pages10.excretory SystemLeena HassaninNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2nd Semestercm - Cs S.F.ADocument52 pagesPhysiology 2nd Semestercm - Cs S.F.AVeronica Nica MaisteriucNo ratings yet
- Excretory System in Humans: OsmoconformerDocument6 pagesExcretory System in Humans: OsmoconformerJeremy Blanquiza PriaNo ratings yet
- 29 GuytonDocument8 pages29 GuytonBianca Louise Chan LimNo ratings yet
- Ncert Explanation Deep With ExamplesDocument10 pagesNcert Explanation Deep With ExamplesasterclixNo ratings yet
- Urinary Test TemarioDocument3 pagesUrinary Test Temariomagno qzNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function - ExcretionDocument15 pagesKidney Function - Excretionznayune82No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesDiabetes MellitusDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Respiratory-System, GITDocument2 pagesLipids, Respiratory-System, GITDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Sedative and HypnoticsDocument2 pagesSedative and HypnoticsDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Intro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDocument2 pagesIntro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDocument2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Bio01 Co2 PPT - Cell CycleDocument120 pagesBio01 Co2 PPT - Cell CycleMarc Ronald de LeonNo ratings yet
- Primary Health Care Systems (Primasys) : Case Study From CameroonDocument16 pagesPrimary Health Care Systems (Primasys) : Case Study From CameroonEyock PierreNo ratings yet
- DU - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDU - Digestive SystemAlexandra MatysováNo ratings yet
- Morinda Species ProfileDocument13 pagesMorinda Species ProfilebahbaguruNo ratings yet
- 11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыDocument6 pages11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыakzharNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Napkin A24eDocument16 pagesSanitary Napkin A24eKate Navarro100% (1)
- Consensus For EGFR Mutation Testing in Non-Small Cell PDFDocument8 pagesConsensus For EGFR Mutation Testing in Non-Small Cell PDFCahrun CarterNo ratings yet
- Contoh Jurnal Case ControlDocument7 pagesContoh Jurnal Case Controlkrisnantara7No ratings yet
- Sars Cov2 Antigen Presentation Process by Immune Cells: Immunology Assignment - 2Document17 pagesSars Cov2 Antigen Presentation Process by Immune Cells: Immunology Assignment - 2azeema fatimaNo ratings yet
- Ipmat Indore 2021 PaperDocument8 pagesIpmat Indore 2021 PaperdivyanshjoshidpsjkpNo ratings yet
- Mtwara Sisters Seminary: Form Three Mid Term Examination-August 2020 CivicsDocument5 pagesMtwara Sisters Seminary: Form Three Mid Term Examination-August 2020 CivicsPrenge PrengeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma of The Jaw A Case ReportDocument4 pagesMultiple Myeloma of The Jaw A Case ReportWanda Dwiayu SahetapyNo ratings yet
- Aimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Document360 pagesAimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Gibran HolmesNo ratings yet
- GK Questions On Animals and Birds 2Document9 pagesGK Questions On Animals and Birds 2Avinash GamitNo ratings yet
- Yellow: The Primary ColoursDocument20 pagesYellow: The Primary ColourstripNo ratings yet
- Gpat Study MaterialDocument28 pagesGpat Study MaterialRamling PatrakarNo ratings yet
- Guidance and Counselling For AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGuidance and Counselling For AdolescentsNalu ChangNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument45 pages3 PDFLilisNo ratings yet
- Abuse and ViolenceDocument39 pagesAbuse and ViolenceTrisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Silver Book Part A Medication Management ID3104Document7 pagesSilver Book Part A Medication Management ID3104Anton BalansagNo ratings yet
- Development of A Nursing Care Protocol For Care of Neonates With Esophageal Atresia/ Tracheo - Esophageal FistulaDocument14 pagesDevelopment of A Nursing Care Protocol For Care of Neonates With Esophageal Atresia/ Tracheo - Esophageal FistulaSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- E1134 The Effect of Logotherapy On Depression in Cancer Patients A Systematic Review StudyDocument6 pagesE1134 The Effect of Logotherapy On Depression in Cancer Patients A Systematic Review StudyfitranoenoeNo ratings yet
- CashewDocument18 pagesCashewAloy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MSDS OrengeDocument8 pagesMSDS OrengeATOMY KESEHATANNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION AND REPORTING:-Concept of An Accident, Reportable and Non ReportableDocument18 pagesUnit 3: ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION AND REPORTING:-Concept of An Accident, Reportable and Non ReportablezombieNo ratings yet
- Compiled Control of Drug Abuse and MisuseDocument76 pagesCompiled Control of Drug Abuse and MisuseMuhammad Ibtsam - PharmDNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Dr. Magda Havas, Ph. DDocument68 pagesDeclaration of Dr. Magda Havas, Ph. DSarah Smile100% (1)
- Stress: and The IndividualDocument9 pagesStress: and The Individualsamon sumulongNo ratings yet
- Pathlab PDFDocument22 pagesPathlab PDFNicole HoNo ratings yet
- Tuberculin PPD RT 23Document10 pagesTuberculin PPD RT 23Irene Olivia SalimNo ratings yet
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
Uploaded by
Dr. RemedyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 1-Renal 1
Uploaded by
Dr. RemedyCopyright:
Available Formats
SGD - 1
RENAL I
Questions:
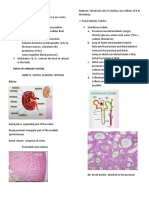
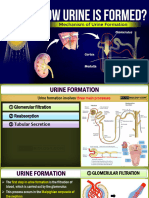
1. Draw a nephron. Label the important parts. Give the function of each part of a
nephron in relation to urine formation.
solutes
i. Renal Corpuscle
responsible for the filtration of fluids and
,
collecting
-
d tubule 2. Proximal Convoluted Tubule itis the first site of water reabsorption and thesite
-
Distal where majority of water 's
,
salt reabsorption takes place
configuredt 3. Loop of Henle -
isa U -
shaped tube consisting of a
descending ascending limb
Renal It transfers fluid from the to the DCT The .
d scending limb is highly
'T
corpuscle permeable to water therefore resulting to reabsorption , while the ascending
limb is impermeable to water but highly permeable to ions .
* Distal Convoluted Tubule is shorter and less convoluted than the PCT Further
- .
reabsorption
and secretion here
/ occurs .
5.co/leotingTubule/ColleotingDuof-lestpartsoflhenephwn.It- collects the urine
✓
" collecting
uninhibited educt
agedeqo.ve#eiat.totherenalpelvisanduretersto
I
of
loop
Henle
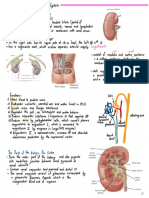
2. Trace the blood flow to and from the kidneys. Discuss the mechanisms that regulate
renal blood flow.
The mechanisms that renal blood
flow are Myogenic mechanism
regulate
and the Tubular glomerular feedback .
•
Myogenic mechanism works if there is high blood volume w/o then results to high blood pressure,this
-
will then stretch the walls release of resulting
particularly the tunica media , there will then be
to smooth muscle contraction andreflex vasoconstriction therefore
decreasing BP .
•
Tubular glomerular Feedback happens when -
blood pressure maybe highorlowwhichwillthen
affect the renal blood flow and
glomerular filtration rate resulting to either high low Na or
filtration This will then be detected by the Macula densawkwillthenalertlheJC.ee/lsto release renin
.
in order to activate RAAS iwkwill normalize the abnormalities .
3. Give the differences between the 2 types of nephron.
The Ztypesof nephron are the Cortical and Juxtemedullangaephwns Their differences are the location .
number of their
length their function and lastly their relation to vascular structures
loops ,
.
.
Cortical Juxta medullary
location Cortex cortex butnear medulla
Number-three
length of loops shorter loops of Henle longer loops ofHenle
Function Dilution of urine Concentration of Urine
Relation to Surrounded by From Peritubular
Peritubular Capillaries upto
vascular structures
capillaries Vasa rect
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
132
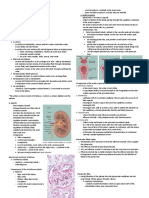
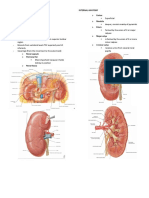
4. Give the composition of the glomerular filtering membrane.
The
glomerularfiltering membrane is composed of the Glomerulus , specifically the
epithelium of the Glomerular capillary next is the Visceral layer of the Bowman 's
,
capsule more importantly the Dodo cy les and lastly is the Basementmembrane wk is
made up of 2 fused 1am in as .
5. Discuss the factors that affect glomerular filtration.
The factors that affect glomerular filtration are the filterability ofthe membrane ,
capillary permeability , capillary surface area which is the Filtration coefficient and the Net filtration
Pressure w Ic is a result ofthe Starling forces ( CHP, COPP I HP, I OPPPP)
,
.
Filtration coefficient is defined as the change in transcapillary fluid exchange induced by a fixed change in trans
capillary
•
•
hydrostatic pressure .
outof the capillary Since filtration
Net Filtration Pressure represents the interaction of the hydrostatic and osmotic pressure driving
.
. ,
is defined as the movement offluid out of the capillary when reabsorption occurs the NFP is a negative number
,
6. Differentiate: Obligatory H2O reabsorption and Facultative H2O reabsorption
Obligatory water when water from the
reabsorption happens
-
plasma filtrate is
returned to the bloodstream Aqua porins presenthere .
are
regardless of the state of hydration .
which resulted
Facultative reabsorption -
happens when water from the plasma filtrate
from the negative feedback control of hydration under the influence
of AD Hor anti diuretic hormone Agua are only present with ADH
porins
.
7. Discuss the following:
A. Counter current multiplier
Is a
single effect process in which small osmotic gradient established at any levelof
10 It is multiplied in to larger Active transport
gradient .
of Na and Chloride
happens
on the thick as water is reabsorbed in the thin descending limb and
c.ending limb
. .
a solute gradient
is then created by the LOH in themedulla
B. Counter current exchanger
of the solvent gradient created
This
process is the maintaining to
by the Lott in the medulla by the vase recta Absorbed water is returned .
slow
circulatory system by the vas are ate then because the blood flow in the capillariesfluidvery
is
the
to into the interstitial wk
diffuse back
solutes thatare reabsorbed into the bloodstream have time
maintains the gradient in the medulla .
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
133
You might also like
- 2 Renal Tubular FunctionDocument1 page2 Renal Tubular FunctionIts FlorenceNo ratings yet
- L8-Urine Conc.Document15 pagesL8-Urine Conc.Bryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document23 pagesLecture 21sara shloulNo ratings yet
- Renal AnatomyDocument13 pagesRenal AnatomyApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lab OnlineDocument25 pagesUrinary Lab OnlineretterateNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabDocument15 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFDocument11 pagesLect-2 Kidneys (RAAS Micturition) PDFBinisha KapadiaNo ratings yet
- KidneyoutlineDocument33 pagesKidneyoutlineapi-273417637No ratings yet
- Renal System 6 1Document30 pagesRenal System 6 1gaurav singhNo ratings yet
- 25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxDocument12 pages25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys: DevelopingDocument18 pagesThe Kidneys: Developingmaria sanchezNo ratings yet
- Bio 11.3Document6 pagesBio 11.3nicholaswzchanNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document7 pagesExcretion 1swinky.dsNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- Concentration and Dilution of UrineDocument26 pagesConcentration and Dilution of UrineHakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Renal 2 and 3Document12 pagesRenal 2 and 3Leugim saveucNo ratings yet
- Parts of Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesParts of Urinary SystemZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- D. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresDocument6 pagesD. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresCatherine BelonioNo ratings yet
- Urinary SysDocument3 pagesUrinary SysMario Antonio CarpioNo ratings yet
- Renal Function: 1 To 1.5 MillionDocument35 pagesRenal Function: 1 To 1.5 MillionUNKNOWN ANGELNo ratings yet
- Activity 36 - Urinary Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument6 pagesActivity 36 - Urinary Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionKaren Joy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Applied Renal PhysiologyDocument18 pagesApplied Renal PhysiologyDamián ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Its EliminationDocument2 pagesExcretory Products and Its Eliminationmariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- Manner: DininDocument6 pagesManner: DininbibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument49 pagesUrinary SystemSalum AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, Nephronlulu.borsikovaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, NephronPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriDocument3 pagesRenal Anatomy and Physiology - Notes - GnvEriEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 1 Lab Report Sedimentation' Water Unit Operations Group 3 Bejarano Moreno Laura, Burgos Lopez Laura, Camacho LinaDocument8 pages1 Lab Report Sedimentation' Water Unit Operations Group 3 Bejarano Moreno Laura, Burgos Lopez Laura, Camacho LinaLaura Bejarano MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDocument49 pagesTubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- 3 - Excretion NotesDocument33 pages3 - Excretion NotesJenny YoonNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument51 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationmadam photonNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemDocument3 pagesAbsorption & Transocation of Water &?? Dissolved Minerals in Plant SystemNUR'AIN BINTI AZHAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation - Human Excretory SystemDocument13 pagesUrine Formation - Human Excretory SystemRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- L5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationDocument21 pagesL5 - 6 - Renal Reabsorbation and SecretationBryn MasvaureNo ratings yet
- Osmotic Power Generation and Reverse Osmosis Desalination Hybrid SystemDocument4 pagesOsmotic Power Generation and Reverse Osmosis Desalination Hybrid SystemHasim BenziniNo ratings yet
- ANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemSin I GangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Urinary System - Class OutlineDocument22 pagesChapter 25 - Urinary System - Class Outlinestupidisg00gleofcourseNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument2 pagesTransport in Plantsakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Messias MachineDocument5 pagesMessias MachineMANNAJANELAGUNANo ratings yet
- Ugs - 4Document9 pagesUgs - 4Mohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 Urinary SystemDocument49 pagesChap 14 Urinary Systematytayn9No ratings yet
- Biology 2Document1 pageBiology 2Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- Form'n'Function IIDocument9 pagesForm'n'Function IIRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Counter Current MechanismDocument33 pagesCounter Current MechanismPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer67% (3)
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- Review in AUBFDocument37 pagesReview in AUBFMichelle T. MabasaNo ratings yet
- 10.excretory SystemDocument16 pages10.excretory SystemLeena HassaninNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2nd Semestercm - Cs S.F.ADocument52 pagesPhysiology 2nd Semestercm - Cs S.F.AVeronica Nica MaisteriucNo ratings yet
- Excretory System in Humans: OsmoconformerDocument6 pagesExcretory System in Humans: OsmoconformerJeremy Blanquiza PriaNo ratings yet
- 29 GuytonDocument8 pages29 GuytonBianca Louise Chan LimNo ratings yet
- Ncert Explanation Deep With ExamplesDocument10 pagesNcert Explanation Deep With ExamplesasterclixNo ratings yet
- Urinary Test TemarioDocument3 pagesUrinary Test Temariomagno qzNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function - ExcretionDocument15 pagesKidney Function - Excretionznayune82No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesDiabetes MellitusDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Respiratory-System, GITDocument2 pagesLipids, Respiratory-System, GITDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Sedative and HypnoticsDocument2 pagesSedative and HypnoticsDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Intro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDocument2 pagesIntro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDocument2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Bio01 Co2 PPT - Cell CycleDocument120 pagesBio01 Co2 PPT - Cell CycleMarc Ronald de LeonNo ratings yet
- Primary Health Care Systems (Primasys) : Case Study From CameroonDocument16 pagesPrimary Health Care Systems (Primasys) : Case Study From CameroonEyock PierreNo ratings yet
- DU - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDU - Digestive SystemAlexandra MatysováNo ratings yet
- Morinda Species ProfileDocument13 pagesMorinda Species ProfilebahbaguruNo ratings yet
- 11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыDocument6 pages11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыakzharNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Napkin A24eDocument16 pagesSanitary Napkin A24eKate Navarro100% (1)
- Consensus For EGFR Mutation Testing in Non-Small Cell PDFDocument8 pagesConsensus For EGFR Mutation Testing in Non-Small Cell PDFCahrun CarterNo ratings yet
- Contoh Jurnal Case ControlDocument7 pagesContoh Jurnal Case Controlkrisnantara7No ratings yet
- Sars Cov2 Antigen Presentation Process by Immune Cells: Immunology Assignment - 2Document17 pagesSars Cov2 Antigen Presentation Process by Immune Cells: Immunology Assignment - 2azeema fatimaNo ratings yet
- Ipmat Indore 2021 PaperDocument8 pagesIpmat Indore 2021 PaperdivyanshjoshidpsjkpNo ratings yet
- Mtwara Sisters Seminary: Form Three Mid Term Examination-August 2020 CivicsDocument5 pagesMtwara Sisters Seminary: Form Three Mid Term Examination-August 2020 CivicsPrenge PrengeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma of The Jaw A Case ReportDocument4 pagesMultiple Myeloma of The Jaw A Case ReportWanda Dwiayu SahetapyNo ratings yet
- Aimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Document360 pagesAimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Gibran HolmesNo ratings yet
- GK Questions On Animals and Birds 2Document9 pagesGK Questions On Animals and Birds 2Avinash GamitNo ratings yet
- Yellow: The Primary ColoursDocument20 pagesYellow: The Primary ColourstripNo ratings yet
- Gpat Study MaterialDocument28 pagesGpat Study MaterialRamling PatrakarNo ratings yet
- Guidance and Counselling For AdolescentsDocument20 pagesGuidance and Counselling For AdolescentsNalu ChangNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument45 pages3 PDFLilisNo ratings yet
- Abuse and ViolenceDocument39 pagesAbuse and ViolenceTrisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Silver Book Part A Medication Management ID3104Document7 pagesSilver Book Part A Medication Management ID3104Anton BalansagNo ratings yet
- Development of A Nursing Care Protocol For Care of Neonates With Esophageal Atresia/ Tracheo - Esophageal FistulaDocument14 pagesDevelopment of A Nursing Care Protocol For Care of Neonates With Esophageal Atresia/ Tracheo - Esophageal FistulaSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- E1134 The Effect of Logotherapy On Depression in Cancer Patients A Systematic Review StudyDocument6 pagesE1134 The Effect of Logotherapy On Depression in Cancer Patients A Systematic Review StudyfitranoenoeNo ratings yet
- CashewDocument18 pagesCashewAloy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MSDS OrengeDocument8 pagesMSDS OrengeATOMY KESEHATANNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION AND REPORTING:-Concept of An Accident, Reportable and Non ReportableDocument18 pagesUnit 3: ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION AND REPORTING:-Concept of An Accident, Reportable and Non ReportablezombieNo ratings yet
- Compiled Control of Drug Abuse and MisuseDocument76 pagesCompiled Control of Drug Abuse and MisuseMuhammad Ibtsam - PharmDNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Dr. Magda Havas, Ph. DDocument68 pagesDeclaration of Dr. Magda Havas, Ph. DSarah Smile100% (1)
- Stress: and The IndividualDocument9 pagesStress: and The Individualsamon sumulongNo ratings yet
- Pathlab PDFDocument22 pagesPathlab PDFNicole HoNo ratings yet
- Tuberculin PPD RT 23Document10 pagesTuberculin PPD RT 23Irene Olivia SalimNo ratings yet