Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Jason MacatuggalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidDocument8 pagesAnatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidTahir Aziz50% (2)
- Topographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisDocument11 pagesTopographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisJohn NinNo ratings yet
- Drenaj LimfaticDocument71 pagesDrenaj LimfaticGugiu Bogdan Ștefan90% (20)
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesGr10 Endocrine SystemDomuNo ratings yet
- Science 10 The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesScience 10 The Endocrine SystemTO NT ONNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument3 pagesParathyroid GlandsRosita RamosNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their Hormonestomman warmanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Grade 10Document2 pagesReviewer For Grade 10euramaneNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Week5 Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesWeek5 Endocrine SystemHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemcjhundaleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemkatrizmaervillagantolNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- IOE Endocrine System 22-23Document13 pagesIOE Endocrine System 22-23genevievekearney04No ratings yet
- Week 5 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Endocrine SystemJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Q3 1 EndocrineDocument42 pagesQ3 1 Endocrineerlamay.valeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- 10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdateDocument44 pages10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdatehelalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Hormone PairingDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Hormone PairingDóra ImreNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Functions & GlandsDocument11 pagesEndocrine System Functions & Glandssaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemnickbelle05No ratings yet
- Academics - Academic Resources - Academic Coaching Tutoring Center - Endocrine SysDocument3 pagesAcademics - Academic Resources - Academic Coaching Tutoring Center - Endocrine SysTirao, Lizette Luz O.No ratings yet
- q3 Module Edited w1-7Document21 pagesq3 Module Edited w1-7Regine DigamonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument26 pagesEndocrine SystemMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- GlandDocument2 pagesGlandsmith joeNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesThe Endocrine SystemPhea VillarealNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System RevDocument3 pagesEndocrine System RevWena Grace NonanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Activity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Document1 pageActivity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Megan WolvesNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument2 pagesHSBAreefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesEndocrine Systemmarygracenezel13No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocument13 pagesBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionDocument1 pageChemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document22 pagesChapter1 2Thea NatacNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument1 pageEndocrineDiwata DonatoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine Systemfranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesEndocrine SystemGiselle AlindoganNo ratings yet
- To Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleDocument5 pagesTo Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleRimaHimeNo ratings yet
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document15 pagesTask 3maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Jhizy ScienceDocument10 pagesJhizy Scienceacelcaringal10No ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceFrom EverandEndocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida NotesDocument75 pagesOral Revalida NotesStephanie C. Bautista100% (3)
- Lecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral CavityDocument9 pagesLecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral Cavitykasonde bowaNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus Notes11.13Document11 pagesBrachial Plexus Notes11.13cpNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik PPT (3440) - 1Document18 pagesSyok Kardiogenik PPT (3440) - 1Mark YangNo ratings yet
- Positioning ChecklistDocument2 pagesPositioning ChecklistMark Terence Padua AbrenicaNo ratings yet
- Borgstein ENTbookDocument191 pagesBorgstein ENTbookdokhenNo ratings yet
- XERO 1 Below Final PF1Document4 pagesXERO 1 Below Final PF1Damian De la rosaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Regio Colli: Dr. W. Winami Wati Mbiomed Pa Bagian Anatomi FK UkridaDocument6 pagesVascular Regio Colli: Dr. W. Winami Wati Mbiomed Pa Bagian Anatomi FK UkridaFelix RicoNo ratings yet
- Corrective Exercise InfographicDocument1 pageCorrective Exercise Infographicapi-531066194No ratings yet
- Muscle and Bone PalpationDocument9 pagesMuscle and Bone PalpationIzzati WanNo ratings yet
- Medical GK QuestionsDocument7 pagesMedical GK QuestionsParmanand Sharma0% (1)
- Suwwan Ihab Y 200803 Master ThesisDocument192 pagesSuwwan Ihab Y 200803 Master Thesisphan hoangNo ratings yet
- Brioso, Dani Leigh B. (Coa Activity)Document2 pagesBrioso, Dani Leigh B. (Coa Activity)Leigh BriosoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Semifinals NotesDocument20 pagesPhysiology Semifinals NotesIsabille MusongNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Skeletal System and Its FunctionDocument9 pages1 - The Skeletal System and Its Functionh8alfredNo ratings yet
- Judo Self-Taught in PicturesDocument81 pagesJudo Self-Taught in Picturesvmnt100% (1)
- Atg Dense Strenght ProgramDocument11 pagesAtg Dense Strenght Programlonegunman2405No ratings yet
- Airway MXDocument47 pagesAirway MXansuh22No ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test BankDocument15 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test Bankandrewmccoymrpazkcnwi100% (53)
- Endocrine Gland AssignmentDocument1 pageEndocrine Gland Assignmentapi-277668098No ratings yet
- Dimension VerticalDocument5 pagesDimension Verticalitzel lopezNo ratings yet
- Class II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowDocument10 pagesClass II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowNawaf RuwailiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentDocument56 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaNo ratings yet
- Tajweed PPT Lesson 4Document34 pagesTajweed PPT Lesson 4api-243246739No ratings yet
- Radio Imagistica EsofaguluiDocument192 pagesRadio Imagistica EsofaguluimyreadNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Document24 pagesAnatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Warni PutriNo ratings yet
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Jason MacatuggalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Jason MacatuggalCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
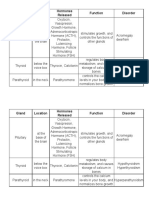
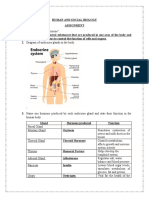
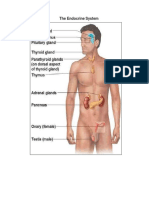
Gland Location Hormones Function
Ex: Pituitary At the base of the brain Oxytocin, Growth, Produces hormones that stimulate
Hormones growth, and controls the functions
of other glands
(GH), Prolactin (PRL),
Luteinizing Hormone (LH),
Follicle Stimulating
Hormone
(FSH),
Adrenocorticotrophic
Hormone (ACTH),
Antidiuretic Hormone
(AH), and Thyroid
Stimulating
Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid posterior to the sternothyroid tetraiodothyronine (T4) and
produces hormones that regulate the
and sternohyoid muscles, triiodothyronine
body's metabolic rate, growth and
wrapping around the cricoid
development
cartilage and tracheal rings.
Endocrine System
Parathyroid on the dorsum of the thyroid at parathyroid hormone regulation of calcium levels in the
each of its four poles. blood
Thymus in the chest, between the lungs thymosin, thymopoietin, and production and maturation of
and behind the breastbone or thymulin immune cells; including small
sternum lymphocytes that protect the body
against foreign antigens
Adrenal one on top of each kidney. adrenaline, noradrenaline, produce hormones that help regulate
cortisol and aldosterone your metabolism, immune system,
blood pressure, response to stress
and other essential functions
Pancreas insulin and glucagon regulate your blood sugar levels and
across the back of the belly, appetite, stimulate stomach acids,
behind the stomach and tell your stomach when to
empty.
Reproductive in the scrotum testosterone sex hormone, and for producing
testes sperm
Ovaries in shallow depressions, called estrogen and progesterone
ovarian fossae, one on each side
of the uterus, in the lateral walls breast development, body shape,
of the pelvic cavity and body hair
You might also like
- Anatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidDocument8 pagesAnatomy: Axial Skeleton MCQS: C SphenoidTahir Aziz50% (2)
- Topographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisDocument11 pagesTopographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisJohn NinNo ratings yet
- Drenaj LimfaticDocument71 pagesDrenaj LimfaticGugiu Bogdan Ștefan90% (20)
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesGr10 Endocrine SystemDomuNo ratings yet
- Science 10 The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesScience 10 The Endocrine SystemTO NT ONNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument3 pagesParathyroid GlandsRosita RamosNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their Hormonestomman warmanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Grade 10Document2 pagesReviewer For Grade 10euramaneNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Week5 Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesWeek5 Endocrine SystemHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemcjhundaleNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemkatrizmaervillagantolNo ratings yet
- Activity Science - TableDocument4 pagesActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- IOE Endocrine System 22-23Document13 pagesIOE Endocrine System 22-23genevievekearney04No ratings yet
- Week 5 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Endocrine SystemJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Q3 1 EndocrineDocument42 pagesQ3 1 Endocrineerlamay.valeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- 10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdateDocument44 pages10-17-2019 Neuroendocrinology in Mental Health An UpdatehelalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Hormone PairingDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Hormone PairingDóra ImreNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Functions & GlandsDocument11 pagesEndocrine System Functions & Glandssaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemnickbelle05No ratings yet
- Academics - Academic Resources - Academic Coaching Tutoring Center - Endocrine SysDocument3 pagesAcademics - Academic Resources - Academic Coaching Tutoring Center - Endocrine SysTirao, Lizette Luz O.No ratings yet
- q3 Module Edited w1-7Document21 pagesq3 Module Edited w1-7Regine DigamonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument26 pagesEndocrine SystemMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- GlandDocument2 pagesGlandsmith joeNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesThe Endocrine SystemPhea VillarealNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System RevDocument3 pagesEndocrine System RevWena Grace NonanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Activity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Document1 pageActivity 3.3 The Endocrine System - 084504Megan WolvesNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument2 pagesHSBAreefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesEndocrine Systemmarygracenezel13No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocument13 pagesBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionDocument1 pageChemical Coordination and Integration: Source Hormone Target ActionNaman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 2Document22 pagesChapter1 2Thea NatacNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument1 pageEndocrineDiwata DonatoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine Systemfranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesEndocrine SystemGiselle AlindoganNo ratings yet
- To Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleDocument5 pagesTo Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleRimaHimeNo ratings yet
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- 4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionsDocument3 pages4a.endocrine Gland Secretions and FunctionssikaboaduaNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document15 pagesTask 3maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Jhizy ScienceDocument10 pagesJhizy Scienceacelcaringal10No ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceFrom EverandEndocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida NotesDocument75 pagesOral Revalida NotesStephanie C. Bautista100% (3)
- Lecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral CavityDocument9 pagesLecture Notes in Anatomy Embryology of The Oral Cavitykasonde bowaNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus Notes11.13Document11 pagesBrachial Plexus Notes11.13cpNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik PPT (3440) - 1Document18 pagesSyok Kardiogenik PPT (3440) - 1Mark YangNo ratings yet
- Positioning ChecklistDocument2 pagesPositioning ChecklistMark Terence Padua AbrenicaNo ratings yet
- Borgstein ENTbookDocument191 pagesBorgstein ENTbookdokhenNo ratings yet
- XERO 1 Below Final PF1Document4 pagesXERO 1 Below Final PF1Damian De la rosaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Regio Colli: Dr. W. Winami Wati Mbiomed Pa Bagian Anatomi FK UkridaDocument6 pagesVascular Regio Colli: Dr. W. Winami Wati Mbiomed Pa Bagian Anatomi FK UkridaFelix RicoNo ratings yet
- Corrective Exercise InfographicDocument1 pageCorrective Exercise Infographicapi-531066194No ratings yet
- Muscle and Bone PalpationDocument9 pagesMuscle and Bone PalpationIzzati WanNo ratings yet
- Medical GK QuestionsDocument7 pagesMedical GK QuestionsParmanand Sharma0% (1)
- Suwwan Ihab Y 200803 Master ThesisDocument192 pagesSuwwan Ihab Y 200803 Master Thesisphan hoangNo ratings yet
- Brioso, Dani Leigh B. (Coa Activity)Document2 pagesBrioso, Dani Leigh B. (Coa Activity)Leigh BriosoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Semifinals NotesDocument20 pagesPhysiology Semifinals NotesIsabille MusongNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Skeletal System and Its FunctionDocument9 pages1 - The Skeletal System and Its Functionh8alfredNo ratings yet
- Judo Self-Taught in PicturesDocument81 pagesJudo Self-Taught in Picturesvmnt100% (1)
- Atg Dense Strenght ProgramDocument11 pagesAtg Dense Strenght Programlonegunman2405No ratings yet
- Airway MXDocument47 pagesAirway MXansuh22No ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test BankDocument15 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test Bankandrewmccoymrpazkcnwi100% (53)
- Endocrine Gland AssignmentDocument1 pageEndocrine Gland Assignmentapi-277668098No ratings yet
- Dimension VerticalDocument5 pagesDimension Verticalitzel lopezNo ratings yet
- Class II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowDocument10 pagesClass II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowNawaf RuwailiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentDocument56 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaNo ratings yet
- Tajweed PPT Lesson 4Document34 pagesTajweed PPT Lesson 4api-243246739No ratings yet
- Radio Imagistica EsofaguluiDocument192 pagesRadio Imagistica EsofaguluimyreadNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Document24 pagesAnatomi Regio Antebrachii Et Manus (Lo 1)Warni PutriNo ratings yet