Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Speed and Velocity - Worksheet
Speed and Velocity - Worksheet
Uploaded by
Marwa ChidiakOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Speed and Velocity - Worksheet
Speed and Velocity - Worksheet
Uploaded by
Marwa ChidiakCopyright:
Available Formats
Motion in One Dimension Name:
Describing Motion Verbally with Speed and Velocity
Read from Lesson 1 of the 1-D Kinematics chapter at The Physics Classroom:
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/1DKin/U1L1d.html
MOP Connection: Kinematic Concepts: sublevels 3 and 6
Review:
1. A _________ quantity is completely described by magnitude alone. A __________ quantity is
completely described by a magnitude with a direction.
a. scalar, vector b. vector, scalar
2. Speed is a __________ quantity and velocity is a __________ quantity.
a. scalar, vector b. vector, scalar
Speed vs. Velocity
Speed and velocity are two quantities in Physics that seem at first glance to have the same meaning.
While related, they have distinctly different definitions. Knowing their definitions is critical to
understanding the difference between them.
Speed is a quantity that describes how fast or how slow an object is moving.
Velocity is a quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object's position changes.
3. Suppose you are considering three different paths (A, B and C) between the same two locations.
Along which path would you have to move with the greatest speed to arrive at the destination in the
same amount of time? __________ Explain.
4. True or False: It is possible for an object to move for 10 seconds at a high speed and end up with an
average velocity of zero.
a. True b. False
5. If the above statement is true, then describe an example of such a motion. If the above statement is
false, then explain why it is false.
6. Suppose that you run for 10 seconds along three different paths.
Rank the three paths from the lowest average speed to the greatest average speed. __________
Rank the three paths from the lowest average velocity to the greatest average velocity. __________
© The Physics Classroom, 2009 Page 1
Calculating Average Speed and Average Velocity
7. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away in 30 minutes. You then
immediately walk home, taking 1 hour on your return trip.
a. What was the average speed (in mi/hr) for the entire trip? _______________
b. What was the average velocity (in mi/hr) for the entire trip? __________ ___
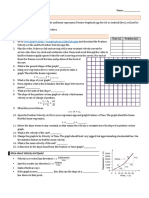
8. A cross-country skier moves from location A to location B to location C to location D. Each leg of the
back-and-forth motion takes 1 minute to complete; the total time is 3 minutes. The unit of length is
meters.
Calculate the average speed (in m/min) and the average velocity (in m/min) of the skier during the
three minutes of recreation. PSYW
Ave. Speed = Ave. Velocity =
© The Physics Classroom, 2009 Page 2
© The Physics Classroom, 2009 Page 3
You might also like
- A Divine Revelation of The Spirit Realm - Mary Baxter (TheGospel - NG)Document166 pagesA Divine Revelation of The Spirit Realm - Mary Baxter (TheGospel - NG)Mufutau Adegoke100% (5)
- Ans 1 Dkin 2Document4 pagesAns 1 Dkin 2Dolores LocañasNo ratings yet
- Nelson Physics 11Document586 pagesNelson Physics 11Jeff An90% (10)
- Answers 1dkinematics PacketDocument28 pagesAnswers 1dkinematics PacketAbdalla MhrzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- Pogil Describing MotionDocument2 pagesPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- High School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsFrom EverandHigh School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Textbook WorkDocument5 pagesTextbook WorkMARIANA ECHEVERRI RESTREPONo ratings yet
- Ipc Describing Motion Verbally With Distance and Displacement Study NotesDocument20 pagesIpc Describing Motion Verbally With Distance and Displacement Study NotesGrantNo ratings yet
- Long Test 1 - Grade 7Document2 pagesLong Test 1 - Grade 7katherine corvera100% (3)
- Hahn y Kleinman - Practica Biomedica (1983) PDFDocument29 pagesHahn y Kleinman - Practica Biomedica (1983) PDFBrenda MogliaNo ratings yet
- Drama ScriptDocument3 pagesDrama ScriptDiana Zaibi57% (7)
- Friedrich Schlegel Emergence of Romantic Philosophy: and TheDocument270 pagesFriedrich Schlegel Emergence of Romantic Philosophy: and TheMiguel Alberti100% (2)
- Speed and Velocity - WorksheetDocument3 pagesSpeed and Velocity - WorksheetMarwa ChidiakNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Direction Part 1Document3 pagesMotion in One Direction Part 1xinned2020No ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument4 pagesSpeed and VelocityMarwa ChidiakNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1Document2 pagesKinematics 1Shalom OhNo ratings yet
- Cactus JackDocument2 pagesCactus JackJacob BeaneNo ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument2 pagesLinear MotionNeha BhagwatNo ratings yet
- 1DKin2 PDFDocument4 pages1DKin2 PDFRane Arielle0% (1)
- CH 3 TestDocument2 pagesCH 3 TestJacob DavisNo ratings yet
- SPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: ReviewDocument6 pagesSPH3U - Kinematics 2: Velocity and Speed: Reviewlim05abcNo ratings yet
- Class: 9 Subject: Physics Date:29.06.2021 LN: Motion Revision Worksheet Learning ObjectiveDocument4 pagesClass: 9 Subject: Physics Date:29.06.2021 LN: Motion Revision Worksheet Learning ObjectiveSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Forces, Motion, and Energy: ScienceDocument39 pagesForces, Motion, and Energy: ScienceElizabeth Inocencio Facundo - SagotNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module5Document17 pagesGrade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module5Krystian BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- General Physics Week 2Document10 pagesGeneral Physics Week 2Velasco, Josiah M.No ratings yet
- MODULE OF INSTRUCTION - : NSCI-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Document7 pagesMODULE OF INSTRUCTION - : NSCI-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Yoo JungNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Physics Holidays Homework (WS)Document12 pagesGrade-9 Physics Holidays Homework (WS)ntreddygreenbagsNo ratings yet
- Finalgeneral-Physics 1 - Module 4Document6 pagesFinalgeneral-Physics 1 - Module 4Julliefe DuranteNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFwade aryanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 ExercisesPauleanne NacarioNo ratings yet
- 5 Module 5 - Q1 - GENERAL PHYSICS 1Document36 pages5 Module 5 - Q1 - GENERAL PHYSICS 1Aika Mae ArakakiNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q4 - Week 3Document23 pagesScience 9 - Q4 - Week 3Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Complete - Quarter 3 - Science 7 - Weeks 1 - 8Document42 pagesComplete - Quarter 3 - Science 7 - Weeks 1 - 8alyzamarie deramos100% (1)
- Specialized 12 GeneralPhysicsI Semi CLAS4 Uniformly-Accelerated-Linear-MotionDocument28 pagesSpecialized 12 GeneralPhysicsI Semi CLAS4 Uniformly-Accelerated-Linear-MotionSheare AlsadNo ratings yet
- 5 Module 5 q1 General Physics 1 1.wordDocument36 pages5 Module 5 q1 General Physics 1 1.wordkazuhaanemo859No ratings yet
- Physics 1e Module 2Document14 pagesPhysics 1e Module 2Rian John PedrosaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Quarter 1 - Week 2 SSLMDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Quarter 1 - Week 2 SSLMCarmina Jane DomantayNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument23 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsErica Bella Magpayo100% (1)
- Forces and Motion TestDocument8 pagesForces and Motion TestFahadImranXhiekhNo ratings yet
- 5 Module 5 q1 General Physics 1Document37 pages5 Module 5 q1 General Physics 1lwitsfadontNo ratings yet
- Seminar Lesson PlanDocument18 pagesSeminar Lesson PlanNo one KnowsNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q4 WW Week 1 4 Master TinDocument5 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q4 WW Week 1 4 Master TineurieanneerviraNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Q1 - Module 2Document28 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Q1 - Module 2Gyeon Dae-HoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Q1 Module 2Document27 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Q1 Module 2elyzadelapena123No ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet
- Case Study Class 9Document4 pagesCase Study Class 9JAYA BALDEV DasNo ratings yet
- Case Study Class 9Document4 pagesCase Study Class 9JAYA BALDEV Das100% (1)
- STRATEGIC INTERVENTION MATERIAL RichDocument15 pagesSTRATEGIC INTERVENTION MATERIAL RichSilver Ritz100% (1)
- Tatabunan Integrated School Talalora Samar THIRD Periodical Examination Science - Grade 7Document2 pagesTatabunan Integrated School Talalora Samar THIRD Periodical Examination Science - Grade 7Tinay Tinay100% (1)
- Physics Notes 1111Document98 pagesPhysics Notes 1111abdul nabiNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse ReadingDocument7 pagesMomentum and Impulse ReadingParvinder Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Motions in One Dimension: Example 1Document3 pagesMotions in One Dimension: Example 1Angelo DumaopNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision TestDocument4 pagesPhysics Revision TestAdvik AeryNo ratings yet
- Physics - Class 11Document16 pagesPhysics - Class 11ameena-11173No ratings yet
- Speed Acceleration VelocityDocument1 pageSpeed Acceleration Velocityabrigojian5No ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13Document18 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13YazaanNo ratings yet
- Balloon LabDocument5 pagesBalloon Labjesussave*No ratings yet
- Test On MOtionDocument2 pagesTest On MOtionSally PocamasNo ratings yet
- What's In: St. Peter'S College of Misamis Oriental, IncDocument14 pagesWhat's In: St. Peter'S College of Misamis Oriental, IncJoan VecillaNo ratings yet
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- HCM Treatment Italy Ammirati2016Document13 pagesHCM Treatment Italy Ammirati2016xy manNo ratings yet
- DBT in ASDDocument9 pagesDBT in ASDCarregan AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Afaq Applied MarketingDocument4 pagesAfaq Applied MarketingSikander JafarNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in MathDocument4 pagesAction Plan in Mathjoanna marie limNo ratings yet
- Proxy FormDocument1 pageProxy FormMarianne OberesNo ratings yet
- Health Care EthicsDocument16 pagesHealth Care EthicsKhenwae Polistico100% (2)
- Unit Assessment MapDocument2 pagesUnit Assessment MapMC Do100% (1)
- Biocon AR2011Document164 pagesBiocon AR2011ruchiwadhawancaNo ratings yet
- Word Study & FluencyDocument16 pagesWord Study & FluencyAmber CastroNo ratings yet
- Laporan AnsysDocument18 pagesLaporan AnsysBoyos HitssNo ratings yet
- Module 1 LO3a & LO3b Prepare Basic Instructional MaterialsDocument15 pagesModule 1 LO3a & LO3b Prepare Basic Instructional Materialsjonellambayan100% (1)
- List The Social Factors Affecting Education and How It Can Support The Development of Education in The Country in General and CommunityDocument4 pagesList The Social Factors Affecting Education and How It Can Support The Development of Education in The Country in General and CommunityJoyce Crystal D. CagadasNo ratings yet
- Ethics 1st Long ExamDocument43 pagesEthics 1st Long ExamPaolo Ervin PerezNo ratings yet
- Eastern Shipping LinesDocument3 pagesEastern Shipping LinessophiaNo ratings yet
- Pitch Error in The Manufacturing of Lead ScrewsDocument9 pagesPitch Error in The Manufacturing of Lead Screwsoyuncu81No ratings yet
- Financial Results For The Year 2019 20Document35 pagesFinancial Results For The Year 2019 20Akshaya SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Part IV: About The AuthorDocument380 pagesPart IV: About The AuthorVale MelgozaNo ratings yet
- Doris Chase DoaneDocument16 pagesDoris Chase DoaneTTamara2950% (2)
- Autism DiagnoseDocument36 pagesAutism DiagnoseAniketh Sam100% (1)
- MunnuDocument8 pagesMunnuPritesh KothariNo ratings yet
- All CLARiiON Disk and FLARE OE MatricesDocument120 pagesAll CLARiiON Disk and FLARE OE MatricesOren ElimelechNo ratings yet
- Wsdot Fop For Waqtc T 168: SignificanceDocument4 pagesWsdot Fop For Waqtc T 168: SignificanceDiegito RecaldeNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care NursesDocument15 pagesIntensive Care NursesUlysses GamayonNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Letter From Teacher Template 15Document6 pagesRecommendation Letter From Teacher Template 15Mohamed MokhtariNo ratings yet
- TNEA 2022 Counselling ProcedureDocument3 pagesTNEA 2022 Counselling ProcedureCTONo ratings yet
- The Disaster Crunch Model: Guidelines For A Gendered ApproachDocument16 pagesThe Disaster Crunch Model: Guidelines For A Gendered ApproachOxfamNo ratings yet