Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01
Bronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01
Uploaded by
Peshala Nishadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views1 pageThe document discusses ionic equilibria according to Bronsted-Lowry theory. It asks the reader to identify species that can act as acids or bases, identify the acid in several chemical reactions, identify acid-base conjugate pairs in reactions, and rewrite equations identifying the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.
Original Description:
Original Title
bronsted-lowry_theory worksheet 01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses ionic equilibria according to Bronsted-Lowry theory. It asks the reader to identify species that can act as acids or bases, identify the acid in several chemical reactions, identify acid-base conjugate pairs in reactions, and rewrite equations identifying the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views1 pageBronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01
Bronsted-Lowry - Theory Worksheet 01
Uploaded by
Peshala NishadiThe document discusses ionic equilibria according to Bronsted-Lowry theory. It asks the reader to identify species that can act as acids or bases, identify the acid in several chemical reactions, identify acid-base conjugate pairs in reactions, and rewrite equations identifying the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
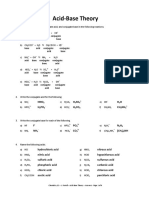
Ionic Equilibrium – Bronsted Lowry theory Worksheet
1. State whether the following species can behave as an acid, as a base, or both and explain its function:
a) NH4+ e) CO32- i) HSO4-
b) NH3 f) NO3- j) HNO3
c) H3O+ g) CH3CH2OH k) HCl
d) HClO4 h) CH3COOH l) C6H5COOH
2. In each of the following reactants, one of the reactants acts as an acid. Identify it:
a) H2O(l) + NH3(aq) == NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
b) CH3COOH(aq) + HClO4(aq) == CH3COOH2+(aq) + ClO4-(aq)
c) HCO3-(aq) + HSO4-(aq) == H2O(l) + CO2(g) + SO42-(aq)
d) H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) == 2H2O(l)
3. Identify the acid-base conjugate pairs in the following reactions:
a) HCO3-(aq) + H2O(l) == CO32-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
b) HCO3-(aq) + H3O+(aq) == CO2(g) + H2O(l) + H2O(l)
c) H2SO4(aq) + HNO3(aq) == HSO4-(aq) + NO2+(aq) + H2O(l)
d) HSO4-(aq) + OH-(aq) == SO42-(aq) + H2O(l)
4. Rewrite each equation. Identify the acid, the base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate
base in each of the equations.
You might also like
- Acid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Document24 pagesAcid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Sara MolinaroNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pageTopic 12 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShanmugam UdhayaNo ratings yet
- Ques1 67abe1mcDocument8 pagesQues1 67abe1mcKerimberdiNo ratings yet
- SAT ABS Bronsted LowryDocument7 pagesSAT ABS Bronsted LowryCatherine Galano PradoNo ratings yet
- ATAR Chemistry Year 12 Asc 2017 Sols (WA)Document12 pagesATAR Chemistry Year 12 Asc 2017 Sols (WA)Raghav GanaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Review W KeyDocument19 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Review W KeyJosephine Charles HoNo ratings yet
- AP Ch. 14-15 Acids & Bases Review AnswersDocument44 pagesAP Ch. 14-15 Acids & Bases Review AnswershksonnganNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equ. (LDA) NMDocument18 pagesIonic Equ. (LDA) NMkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- WORK SHEET - Ionic & Acid-Base ReactionsDocument5 pagesWORK SHEET - Ionic & Acid-Base ReactionsAndrej ZafirovikjNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium WSDocument20 pagesIonic Equilibrium WSVishal MNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Theory AnswersDocument3 pagesAcid Base Theory Answersvinaybharadwajbs0% (1)
- Chemactivity 42 KeyDocument1 pageChemactivity 42 KeyQueenQiNo ratings yet
- Analytic Chem Mitdterm QDocument14 pagesAnalytic Chem Mitdterm Qayshhaa.kNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesAcid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedDaniel Monclear CatiloNo ratings yet
- 2015 BiotechDocument74 pages2015 BiotechRosa DemlieNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Theory AnswersDocument4 pagesAcid Base Theory AnswersPasha TanNo ratings yet
- Neutralization Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pagesNeutralization Reactions Worksheetsamar alassadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet - Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet - Redox Reactionsaryaaayush2006No ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry QuizDocument4 pagesHonors Chemistry QuizmariaNo ratings yet
- Testbank3 Syror Baser+svar PDFDocument10 pagesTestbank3 Syror Baser+svar PDFSandileVilaneNo ratings yet
- Neutralization Reactions Worksheet: A) Csoh + H Co + B) HF + MG (Oh) + C) Hno + Al (Oh) + D) HCL + Koh + E) Hbro + LiohDocument2 pagesNeutralization Reactions Worksheet: A) Csoh + H Co + B) HF + MG (Oh) + C) Hno + Al (Oh) + D) HCL + Koh + E) Hbro + LiohShammany AlsuwaidiiNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium (4 Marks)Document7 pagesIonic Equilibrium (4 Marks)Nagesh NangiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base QuizDocument4 pagesAcid Base QuizHendrix Antonni AmanteNo ratings yet
- Worksheets RRDocument4 pagesWorksheets RRHrithik JerathNo ratings yet
- Neutralization reactions worksheetDocument4 pagesNeutralization reactions worksheetAndrea MontalvanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMay LanieNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Worksheet: © 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights ReservedMiasco Joy AnnNo ratings yet
- Acid Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid Base WorksheetIyanaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetJoseph ZhangNo ratings yet
- Acid Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid Base WorksheetKirsten TroupeNo ratings yet
- APChemDocument8 pagesAPChemMacie CareyNo ratings yet
- 2 Co (G) 2 CO (G) + O (G) H 514 Kj/molDocument3 pages2 Co (G) 2 CO (G) + O (G) H 514 Kj/molShenna Mae Bumanlag DecoroNo ratings yet
- 51 HMW Solutions Ch14Document43 pages51 HMW Solutions Ch14Cbn NoonNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Study GuideDocument4 pagesCH 14 Study Guide4b00d1No ratings yet
- 1c Worksheet Acids Bases With AnswersDocument4 pages1c Worksheet Acids Bases With Answersapi-369690183100% (1)
- Acid Base Theory WorksheetDocument3 pagesAcid Base Theory WorksheetKepala SMA Kusuma BangsaNo ratings yet
- Guia Redox Iv LSCDocument1 pageGuia Redox Iv LSCConstanza HillsNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMDocument3 pagesActivity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMClarise CanANo ratings yet
- NS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesDocument5 pagesNS1Lec - Module 5 - NacionalesWindere Marie NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium Lecture 9 (1st January 2023) Handout and HomeworkDocument402 pagesIonic Equilibrium Lecture 9 (1st January 2023) Handout and Homeworktanishq yadavNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsSaskia Fiestika BerlianaNo ratings yet
- 03 Neutralization Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pages03 Neutralization Reactions Worksheetapi-298247873No ratings yet
- 03 Neutralization Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pages03 Neutralization Reactions Worksheetapi-298247873No ratings yet
- Bronst Acid Base QsDocument8 pagesBronst Acid Base QsIsta EgbetoNo ratings yet
- Calculations Involving FormulaeDocument65 pagesCalculations Involving FormulaeZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Methodist College Kuala Lumpur Assignment 1 Unit 4: Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument1 pageMethodist College Kuala Lumpur Assignment 1 Unit 4: Acid-Base EquilibriaskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- WS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Document4 pagesWS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Yuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Acids BasesDocument3 pagesAssessment Acids BasesJuju ZenemijNo ratings yet
- Bronsted Lowry+WorksheetDocument4 pagesBronsted Lowry+WorksheetHo Hsiao JiunNo ratings yet
- Silberberg 3 e ISMChapter 18Document35 pagesSilberberg 3 e ISMChapter 18henry aguilaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test-IXDocument5 pagesChemistry Test-IXRishiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Acids and Bases SLDocument34 pagesUnit 8 - Acids and Bases SLellhamnasserNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ConceptDocument20 pagesAcid Base Conceptyadavamlesh045No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet