Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question On Pharmacology
Question On Pharmacology
Uploaded by
Vanita MacwanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question On Pharmacology
Question On Pharmacology
Uploaded by
Vanita MacwanCopyright:
Available Formats
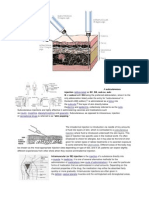
Injection tray;
Formed from high impact polystyrene, injection trays are suitable for storing and
transporting small instruments, hypodermic needles, dressing materials and a variety
of other uses. With a volume of approx 270mL, the tray measures 185mm by 63mm
by 28mm deep.
What is called injection?
An injection is a shot, or a dose of medicine given by way of a syringe and a needle.
The medical kind of injection forces a small amount of a drug under the skin or
directly into a muscle.
What are the 3 types of injections?
The three main routes are intradermal (ID) injection, subcutaneous (SC) injection
and intramuscular (IM) injection. Each type targets a different skin layer:
Subcutaneous injections are administered in the fat layer, underneath the skin.
Intramuscular injections are delivered into the muscle.
What is the classification of injection?
Learn about the 4 types of injection: intradermal, subcutaneous, intravenous and
intramuscular injections, and what they are used for in Singapore.
1. Intravenous (IV) injections. An IV injection is the fastest way to inject a medication
and involves using a syringe to inject a medication directly into a vein. When people
talk about receiving medication via IV, however, they are usually talking about an IV
infusion or drip, which involves using a pump or gravity to infuse the medication into
a vein, rather than a syringe. IV infusions allow a set amount of medication to be
administered in a controlled manner over a period of time.
2. Intramuscular (IM) injections. IM injections are given deep into a muscle where the
medication is then absorbed quickly by surrounding blood vessels.
3. Subcutaneous (SC) injections. SC injections are injected into the innermost layer of
the skin called the subcutis or hypodermis, which is made up of a network of fat and
collagen cells. SC injections are also known as ‘subcut’ or ‘SQ’ injections. These
injections work more slowly than an IV or IM injection because the area does not
have such a rich blood supply.
4. Intradermal (ID) injections. ID injections are given directly into the middle layer of
the skin called the dermis. This type of injection is absorbed more slowly again than
IV, IM or SC injections.
Injection Examples of medications injected via this route
type
IV Certain antimicrobials, anticonvulsants, diuretics, steroids and analgesics
injections
IM Allergy medications, certain antibiotics and contraceptive hormones, other hormones such
injections as testosterone, Botox, steroids, flu shots, Comirnaty (COVID-19 vaccine, mRNA) and other
vaccines, B12 injections and certain antipsychotic drugs
SC Insulin and other medications for diabetes, certain hormone medications such as
injections testosterone, blood thinners, allergy medications, analgesics and arthritis medications
ID Botox, steroids, and the tuberculosis (TB) vaccine. Also used for allergy testing
injections
Other types of injections include:
5. Intra-articular injections - into a joint
6. Peri-articular injections - into the soft tissue close to a joint
7. Intra osseous injections - into the bone marrow
8. Intra detrusor injections - into the muscle in the wall of the bladder
9. Intraocular (intravitreal) injection - into the jelly-like fluid in the eye
10. Intra peritoneal injections - given within the abdominal cavity
11. Intra cardiac injections - into the muscle or ventricles of the heart
12. Intra cavernous injections - into the base of the penis
You might also like
- The Development Manual of JamaicaDocument14 pagesThe Development Manual of JamaicaEverton J. O. SmithNo ratings yet
- Injections SiteDocument10 pagesInjections SiteNora100% (2)
- Ultrasound and clinically guided Injection techniques on the musculoskeletal systemFrom EverandUltrasound and clinically guided Injection techniques on the musculoskeletal systemNo ratings yet
- Drugs and DosagesDocument4 pagesDrugs and DosagesDin-Din Que33% (3)
- 7 - Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction With Pharmacy Franchises - Final PDFDocument10 pages7 - Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction With Pharmacy Franchises - Final PDFWin Yu AungNo ratings yet
- Orange BookDocument18 pagesOrange BookWaseem Mohd0% (1)
- InjectionsDocument18 pagesInjectionsNotInterestedNo ratings yet
- Injection 101: Overview, Types, Common Uses & Risks: What Is An Injection?Document1 pageInjection 101: Overview, Types, Common Uses & Risks: What Is An Injection?Barbara Akua AntwiNo ratings yet
- InjectionsDocument26 pagesInjectionsNotInterested100% (3)
- WeeeeeeeeeDocument1 pageWeeeeeeeeeMarcus Philip GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Types Injection "Intramuscular (Im), Intradermal (Id), Subcutan (SC), and Intravenous (Iv) "Document5 pagesTypes Injection "Intramuscular (Im), Intradermal (Id), Subcutan (SC), and Intravenous (Iv) "Ani SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Whats An InjectionDocument9 pagesWhats An InjectionKaiwan AzadNo ratings yet
- Funda Lab Sas26 Antonette CawalingDocument3 pagesFunda Lab Sas26 Antonette CawalingAntonette CawalingNo ratings yet
- C-15 ParenteralsDocument158 pagesC-15 ParenteralsJennifer Kierstine ChuaNo ratings yet
- #6 Giving Injection (1) TranslationDocument11 pages#6 Giving Injection (1) TranslationSophi RetnaningsihNo ratings yet
- Giving InjectionDocument4 pagesGiving InjectionFatimah Liem SutrisnaNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration: Dr. Shahnaz AyasrahDocument27 pagesMedication Administration: Dr. Shahnaz Ayasrahshahnaz AyasrahNo ratings yet
- What Do You Say As You Are Giving A Shot?Document3 pagesWhat Do You Say As You Are Giving A Shot?Venska TrianaNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug AdministrationDocument4 pagesRoutes of Drug AdministrationJoeyNo ratings yet
- IMI'sDocument6 pagesIMI'sanitha lakshminarayanaNo ratings yet
- Medsitis' Guide To Syringes & NeedlesDocument5 pagesMedsitis' Guide To Syringes & NeedlesNano KaNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument1 pageTutorialIman ArinaNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of NeedleDocument2 pagesDifferent Kinds of NeedleKrycelNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Preparation 01Document18 pagesParenteral Preparation 01monoj5859100% (3)
- IM IV InjectionDocument8 pagesIM IV Injectionmarmar.hussein2001No ratings yet
- Grup 1 Definitions and SOP InjectionDocument8 pagesGrup 1 Definitions and SOP InjectionFina Khotidjah SafinaturrohmahNo ratings yet
- Proper Injection TechniquesDocument5 pagesProper Injection TechniquesAnonymous 0qsVKO0cNNo ratings yet
- Final Pediatrics Procedure FileDocument78 pagesFinal Pediatrics Procedure FileJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris 2Document6 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris 2yuly sukmawatiNo ratings yet
- Demonstrasi InjeksiDocument9 pagesDemonstrasi InjeksiAndar GuswiraNo ratings yet
- Injection by Arnaldio Dan Intan JyyDocument14 pagesInjection by Arnaldio Dan Intan JyyIntan Juita IINo ratings yet
- Parenteral ProductsDocument50 pagesParenteral ProductsMiham SsajnNo ratings yet
- Giving InjectionDocument5 pagesGiving InjectionAlvin W. KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Blood Giving Set Versus Infusion (Iv Giving) SetDocument3 pagesBlood Giving Set Versus Infusion (Iv Giving) SetTiktok- AfricaNo ratings yet
- IM Injuction: Definition of Intramuscular InjectionDocument8 pagesIM Injuction: Definition of Intramuscular InjectiondhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking ExercisesDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking Exercisescarl cosioNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular Injection: Deltoid MuscleDocument2 pagesAdministering Intramuscular Injection: Deltoid MuscleGloredaine BelicarioNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injection (IM) InjectionDocument17 pagesIntramuscular Injection (IM) InjectionArunesh 456100% (1)
- Zulyana Putri (181211468) Iib InjectionDocument5 pagesZulyana Putri (181211468) Iib InjectionZulyana PutriNo ratings yet
- SRM I Year I Basic NursingDocument97 pagesSRM I Year I Basic Nursingmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Giving InjectionDocument21 pagesChapter 7 Giving InjectionZahwaNo ratings yet
- In Medical Terminology Injection Is Referred As A Shot or Jab and Is A Popular Way of Infusing Liquid Medicines in To A PatientDocument10 pagesIn Medical Terminology Injection Is Referred As A Shot or Jab and Is A Popular Way of Infusing Liquid Medicines in To A PatientAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Parental Administration of DrugsDocument15 pagesParental Administration of DrugsShimo AldobbaghNo ratings yet
- Intravena InjectionDocument6 pagesIntravena InjectionEvoLetd'LeenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Procedure ImDocument15 pagesNursing Procedure ImShobha MariaNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injection: 1-DefinitionDocument11 pagesIntramuscular Injection: 1-DefinitionkingNo ratings yet
- P MedicationDocument51 pagesP MedicationMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- SOP: Injections in Dogs and CatsDocument4 pagesSOP: Injections in Dogs and CatsClaritha TaopanNo ratings yet
- Intradermal Injection Injection Into The Dermal Skin LayerDocument2 pagesIntradermal Injection Injection Into The Dermal Skin LayermadhavNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Administration of MedicationsDocument55 pagesParenteral Administration of MedicationsMARIAH ALEXIE GASALNo ratings yet
- Year I Basic NursingDocument99 pagesYear I Basic Nursingmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Adminastration of DrugsDocument2 pagesAdminastration of DrugsЛюбов ВітькоNo ratings yet
- بروسيجرDocument4 pagesبروسيجرnicekiam311No ratings yet
- Aspirate To VaccinateDocument5 pagesAspirate To VaccinateSunil ANo ratings yet
- Update Needle Free Injections PDFDocument10 pagesUpdate Needle Free Injections PDFNithin BattulaNo ratings yet
- Administration of Intramuscular and Sub Cutaneous InjectionsDocument13 pagesAdministration of Intramuscular and Sub Cutaneous InjectionsSundeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Taking Vital Sign (Injection)Document7 pagesBahasa Inggris: Taking Vital Sign (Injection)iyal09No ratings yet
- 2 Skill IntramuscularDocument3 pages2 Skill IntramuscularJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- PARENTERAL MEDICATION Part 1Document8 pagesPARENTERAL MEDICATION Part 1Marielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- GUNA Alfieri Seminar Bucharest 2020 - Compressed PDFDocument248 pagesGUNA Alfieri Seminar Bucharest 2020 - Compressed PDFRobert BotNo ratings yet
- Anatomy csf-1Document16 pagesAnatomy csf-1Private AccountNo ratings yet
- Sterile Dosage Forms Parentals Injections Intravenous RouteDocument3 pagesSterile Dosage Forms Parentals Injections Intravenous RouteChantelle MeaNo ratings yet
- The Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainFrom EverandThe Mindful Spine: A Holistic Approach to Healing Back PainNo ratings yet
- Predatory JournalsDocument9 pagesPredatory JournalsNabeel MuhammadNo ratings yet
- ST Marks Formula Electrolyte Solution - EKPG Information - Jan 2015Document4 pagesST Marks Formula Electrolyte Solution - EKPG Information - Jan 2015mrjsmithsonNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy at Home Nursing Services at HomeDocument2 pagesPhysiotherapy at Home Nursing Services at HomeBhagyesh MasurekarNo ratings yet
- Nueva EtiquetaDocument1 pageNueva EtiquetaAnderson Manuel Marquez NuñezNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Clinical Pharmacy by Joseph T. DiPiroDocument958 pagesEncyclopedia of Clinical Pharmacy by Joseph T. DiPiroAlex Pieces100% (1)
- Stability of Furosemide and Chlorothiazide Stored in SyringesDocument9 pagesStability of Furosemide and Chlorothiazide Stored in SyringesFebye ElizaNo ratings yet
- Office of The Secretary: Republic PhilippinesDocument22 pagesOffice of The Secretary: Republic Philippinesjonathan layaNo ratings yet
- Quality Review Documents Recommendations Expression Strength Name Centrally Authorised Human - enDocument5 pagesQuality Review Documents Recommendations Expression Strength Name Centrally Authorised Human - enJoaquín TodhinNo ratings yet
- FDA Drug Topics: Orange Book: Frequently Asked Questions and AnswersDocument50 pagesFDA Drug Topics: Orange Book: Frequently Asked Questions and AnswersLakshmana Bahrathi SatiyamurthiNo ratings yet
- 1.pinakas Synergazomenon Panepistimion CIVISDocument18 pages1.pinakas Synergazomenon Panepistimion CIVISCourtney YatesNo ratings yet
- Available Medicine at Pharmacy of THQ Hospital Jampur District Rajanpur Date:03.03.2020Document2 pagesAvailable Medicine at Pharmacy of THQ Hospital Jampur District Rajanpur Date:03.03.2020Kashif AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Laboratory of Pharmacokinetics, Dept. of Pharmacy, University of PatrasDocument1 pageThe Laboratory of Pharmacokinetics, Dept. of Pharmacy, University of PatrasnosfarNo ratings yet
- 12 NovDocument5 pages12 NovAnggarita Dwi FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Role of Pharmacist in Health Care SystemDocument4 pagesRole of Pharmacist in Health Care SystemAmanuel TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Implikasi Farmakokinetik KlinisDocument44 pagesImplikasi Farmakokinetik Klinisfauziah qurrota a'yuniNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Principles of PharmacokineticsDocument42 pagesBasic Concepts and Principles of PharmacokineticsSophia AgenyiNo ratings yet
- Review Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDocument6 pagesReview Guide in Pharmacology Prelim ExamDela Cruz, Maria Roanne M.No ratings yet
- Dispensing 1: Unit 3: The Prescription and Medication OrderDocument4 pagesDispensing 1: Unit 3: The Prescription and Medication OrderAllana TapadoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals ListDocument24 pagesPharmaceuticals ListSunny Singh100% (1)
- Clomiphene CitrateDocument1 pageClomiphene Citratehalagur75No ratings yet
- Template of Japan RMP-wordDocument14 pagesTemplate of Japan RMP-wordDina AndiniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic ParametersDocument29 pagesPharmacokinetic Parametersfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- Designing A Computerized Pharmacy Management System With Inventory Stock Alert SystemDocument4 pagesDesigning A Computerized Pharmacy Management System With Inventory Stock Alert SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Pharmacy Informatics in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesImplementation of Pharmacy Informatics in The PhilippinessophiapagaranNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Why Is This Medication Prescribed?Document6 pagesPotassium: Why Is This Medication Prescribed?Anonymous mFvEL96SNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Industry Botanical Drug ProductsDocument52 pagesGuidance For Industry Botanical Drug ProductsJY MarNo ratings yet