Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Useful Terminologies
Useful Terminologies
Uploaded by
Hamlyn HolderCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Procedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesDocument28 pagesProcedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesNwokedi Okezie79% (29)
- CAPE BMED Option A Mdraw 2017 U2 P2 PDFDocument10 pagesCAPE BMED Option A Mdraw 2017 U2 P2 PDFLeeanaNo ratings yet
- Standard Plans For Highway Bridges - Concrete Slab BridgesDocument25 pagesStandard Plans For Highway Bridges - Concrete Slab BridgesV Venkata Narayana91% (33)
- Memo For Hand Receipt HoldersDocument10 pagesMemo For Hand Receipt HoldersTerrence StaplesNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesDocument27 pagesProcedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesNwokedi Okezie86% (7)
- Ottawa Air Brakes Service ManualDocument32 pagesOttawa Air Brakes Service ManualcbudkuleyNo ratings yet
- Safety ValvesDocument66 pagesSafety ValvesMuhammad Afiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Cement Mill-1 Girth Gear Alignment Readings Summary Report Girth Gear Axial Runout Girth Gear Radial RunoutDocument4 pagesCement Mill-1 Girth Gear Alignment Readings Summary Report Girth Gear Axial Runout Girth Gear Radial Runoutkaka100% (2)
- Computer Forensics FinalDocument34 pagesComputer Forensics FinalPrathima Prahalad100% (1)
- 13 KEROSENE MEROX PROCEDURE LatestDocument7 pages13 KEROSENE MEROX PROCEDURE LatestMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief SystemsDocument30 pagesPressure Relief SystemsBibek MerNo ratings yet
- PSVDocument13 pagesPSVUMESH GORE100% (1)
- API 576 Study NotesDocument5 pagesAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNo ratings yet
- API 576 Study NotesDocument5 pagesAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNo ratings yet
- Spence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFDocument24 pagesSpence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFJorge DuranNo ratings yet
- PSV Sizing ManualDocument10 pagesPSV Sizing ManualAkshay bhuranNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Kunkle ValveDocument32 pagesCatalogo Kunkle ValveKelvyn RochaNo ratings yet
- Safety Valves and Relief Valves.Document17 pagesSafety Valves and Relief Valves.Shikhar SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualDocument0 pagesTechnical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Plant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationsDocument104 pagesPlant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationskglorstadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety ValveDocument11 pagesPressure Safety ValveamitpallathNo ratings yet
- PSV Data BookDocument16 pagesPSV Data Bookkenoly123No ratings yet
- Pressure Control ValveDocument34 pagesPressure Control ValveHASHEMNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831Document32 pagesPressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831JO100% (1)
- Types of Pressure Relief ValvesDocument22 pagesTypes of Pressure Relief ValvesFaraz MichNo ratings yet
- Procedure PSVDocument24 pagesProcedure PSVAbakar MahamatNo ratings yet
- Terminology: Understanding What The Customer Wants Making It Happen!Document22 pagesTerminology: Understanding What The Customer Wants Making It Happen!Marcelo Kleber FelisbertoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief ValveDocument43 pagesPressure Relief ValveMohammed Hassan B Koraina100% (2)
- Pressure Safety Valve FundamentalsDocument21 pagesPressure Safety Valve Fundamentalsaop10468100% (2)
- API NotesDocument9 pagesAPI Notesking4lifeNo ratings yet
- Types of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not OpenDocument3 pagesTypes of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not Opennafees ahmadNo ratings yet
- Spring Loaded ValvesDocument10 pagesSpring Loaded ValvesKarl NakouziNo ratings yet
- Actuated Valve: Air Distribution Manifold (Instrument Air)Document45 pagesActuated Valve: Air Distribution Manifold (Instrument Air)Suguna moorthyNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation of The Pressure Relief ValvesDocument53 pagesDesign and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valvesghassan hamadNo ratings yet
- Terms FlumachDocument53 pagesTerms FlumachYhuloopz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PRV PetrofacDocument36 pagesPRV PetrofacPradeep MagudeswaranNo ratings yet
- PSVDocument101 pagesPSVEngr Adeel Ahmed Abbasi100% (1)
- Relief Valves PDFDocument14 pagesRelief Valves PDFCarlos Del ToroNo ratings yet
- Writeup On Safety Valve & ErvDocument28 pagesWriteup On Safety Valve & Ervtek_surinder100% (3)
- Design Fundamentals: Materials of ConstructionDocument2 pagesDesign Fundamentals: Materials of ConstructionSusheel WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Testing of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Relieving Devices - 4Document7 pagesInspection & Testing of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Relieving Devices - 4DeepakNo ratings yet
- Axelson 6Document12 pagesAxelson 6Amit MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valves and Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesign and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valves and Rupture Disks Systemghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-IDocument16 pagesPressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-Isabi_shiNo ratings yet
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemKaiwlya BhoyarNo ratings yet
- VALVESDocument3 pagesVALVESSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemULAGANATHAN M100% (1)
- Pressure Relief ValvesDocument12 pagesPressure Relief ValvesyvhtejaswaroopNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas CarriersDocument17 pagesGuidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas Carriers123habib123fikriNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - SV - Part10Document6 pagesMicrosoft Word - SV - Part10aftabulalamNo ratings yet
- Reliability Testing of Pressure Relief Valves: January 2004Document12 pagesReliability Testing of Pressure Relief Valves: January 2004Gama MuktiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief Valve: Definition, Types, Working, Location, Sizing, Codes and StandardsDocument18 pagesPressure Relief Valve: Definition, Types, Working, Location, Sizing, Codes and StandardsMalcolm MooreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Hydraulic PressureDocument47 pagesLecture 5 Hydraulic PressureSAMUEL MAKATANENo ratings yet
- Basic Function of A Spring Loaded Safety ValveDocument3 pagesBasic Function of A Spring Loaded Safety ValveMikelaNo ratings yet
- 331-09-En Hydro Static Pressure TestDocument38 pages331-09-En Hydro Static Pressure TestJose OcañaNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Terminology Ver 1Document14 pagesControl Valve Terminology Ver 1bagastcNo ratings yet
- PSV Back PressureDocument2 pagesPSV Back PressureTon PhichitNo ratings yet
- TypesDocument6 pagesTypesAhmed NagyNo ratings yet
- PSV Back PressureDocument0 pagesPSV Back PressureDana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Testing of Pressure Relief ValveDocument13 pagesTesting of Pressure Relief ValveVishal Abhiman MeshramNo ratings yet
- Relief Valves and Relief SystemsDocument10 pagesRelief Valves and Relief Systemsmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Take Home From Our Facility PSV SizingDocument18 pagesTake Home From Our Facility PSV SizingConnor SailorNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- S4007 0002 10 PDFDocument10 pagesS4007 0002 10 PDFalejoNo ratings yet
- Installation Geo MotionsDocument5 pagesInstallation Geo Motionsoscar morenoNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide en USDocument424 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide en USrpizanaNo ratings yet
- Akumulator Sa HidrogenomDocument6 pagesAkumulator Sa Hidrogenombhstudent_537083349No ratings yet
- An Overview of Electromagnetic and Lightning Induced Voltage TransientsDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Electromagnetic and Lightning Induced Voltage TransientsRavishankar PmNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption Measurement - InstalationDocument32 pagesFuel Consumption Measurement - InstalationadNo ratings yet
- STI Stopper Station SeriesDocument4 pagesSTI Stopper Station SeriesTELNEX SASNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic FBR DesignDocument10 pagesAdiabatic FBR DesignRana UzairNo ratings yet
- MT Catalog 2015-2016Document258 pagesMT Catalog 2015-2016rubitovaleNo ratings yet
- Trilithic Data Sheet Bts 781 GP: 1 1.1 FeaturesDocument17 pagesTrilithic Data Sheet Bts 781 GP: 1 1.1 FeaturesВиктор СабовNo ratings yet
- BTT EB Specification Double Wall 08-07Document13 pagesBTT EB Specification Double Wall 08-07Alonso VillaNo ratings yet
- PG GovernorsDocument4 pagesPG GovernorsPj EastonNo ratings yet
- ME 422 Quiz 1Document3 pagesME 422 Quiz 1Daryl MadejaNo ratings yet
- App CodeDocument1 pageApp Codereyziel barganNo ratings yet
- Naval Ship Concept DesignDocument78 pagesNaval Ship Concept DesignaminNo ratings yet
- Mimaki Engineering Co., LTD.: You Can Also Download The Latest Manual From Our WebsiteDocument148 pagesMimaki Engineering Co., LTD.: You Can Also Download The Latest Manual From Our WebsiteoliveiraNo ratings yet
- Parts of An AircraftDocument29 pagesParts of An Aircrafttsegay100% (1)
- Marathi Shodh Katha, Confession of Thag, by Dhynaneshwar DamaheDocument9 pagesMarathi Shodh Katha, Confession of Thag, by Dhynaneshwar Damaheapi-3777175No ratings yet
- Technical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 934 ' Litronic NEDocument12 pagesTechnical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 934 ' Litronic NELiebherrNo ratings yet
- ICS 29.260.20 ISBN 0-626-17140-7 Edition 1: Warning Should Be Read in Conjunction WithDocument33 pagesICS 29.260.20 ISBN 0-626-17140-7 Edition 1: Warning Should Be Read in Conjunction Withchris541125No ratings yet
- 466 - Hydrology 303 Lecture Notes FinalDocument26 pages466 - Hydrology 303 Lecture Notes Finalanirbanpwd76No ratings yet
- Compresor 1 3HP R134a 110V 1190BTU H Baja Media Alta FFI12HBX EmbracoDocument5 pagesCompresor 1 3HP R134a 110V 1190BTU H Baja Media Alta FFI12HBX EmbracoAntonioNo ratings yet
- CPVC Drainage ProductsDocument11 pagesCPVC Drainage ProductsRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Thermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet
Useful Terminologies
Useful Terminologies
Uploaded by
Hamlyn HolderOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Useful Terminologies
Useful Terminologies
Uploaded by
Hamlyn HolderCopyright:
Available Formats
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVES
Prepared by
USEFUL TERMINOLOGIES
GENERAL
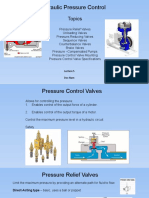
Pressure Relief Devices
A device designed to prevent internal fluid pressure from rising above a predetermined maximum pressure in a pressure vessel exposed to emergency or abnormal conditions
Flow Capacity Testing
Testing of a pressure relief device to determine its operating characteristics including measured relieving capacity
In-Service Testing
Testing of a pressure relief device while protecting the system on which it is installed to determine some or all of its operating characteristics using system pressure solely or other pressure source
or in conjunction with an auxiliary lift device
Bench Testing
Testing of a pressure relief device on a pressurized system to determine set pressure and seat tightness
PARTS OF PRESSURE RELIEF DEVICES
Approach channel
The passage through which the fluid must pass to reach the operating parts of a pressure relief device
Discharge channel
The passage through which the fluid must pass between the operating parts of a pressure relief device and its outlet
Disc
The pressure containing movable element of a pressure relief valve which effects closure
Huddling chamber
The annular pressure chamber located beyond the valve seat for the purpose of generating a popping characteristic
Lifting device -
A device for manually opening a pressure relief valve by the application of external force to lessen the spring loading which holds the valve closed
Nozzle
A pressure containing element which constitutes the inlet flow passage and includes the fixed portion of the seat closure
Pilot valve
An auxiliary valve which actuates a major relieving device
Pressure containing member
A part which is in actual contact with the pressure media in the protected vessel
Pressure retaining member
A part which is stressed due to its function in holding one or more pressure containing members in position
Seat
The pressure containing contact between the fixed and moving portions of the pressure containing elements of a valve
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE DIMENSIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
Actual discharge area
The measured minimum net area which determines the flow through a valve
Bore area
The minimum cross-sectional flow area of a nozzle
Bore diameter
The minimum diameter of a nozzle
Curtain area
The area of the cylindrical or conical discharge opening between the seating surfaces created by the lift of the disc above the seat
Developed lift
The actual travel of the disc from closed position to the position reached when the valve is at flow-rating pressure
Effective discharge area
A nominal or computed area of flow through a pressure relief valve, differing from the actual discharge area, for use in recognized flow formulas to determine the capacity of a pressure relief valve
Inlet size
The nominal pipe size of the inlet of a pressure relief valve, unless otherwise designated
Lift
The actual travel of the disc away from closed position when a valve is relieving
Orifice area
A nominal or computed area of flow through a pressure relief valve, differing from the actual discharge area, for use in recognized flow formulas to determine the capacity of a pressure relief valve
Outlet size
The nominal pipe size of the outlet of a pressure relief valve, unless otherwise designated
Rated lift
The design lift at which a valve attains its rated relieving capacity
Seat angle
The angle between the axis of a valve and the seating surface. A flat-seated valve has a seat angle of 90 degrees
Seat area
The area determined by the seat diameter
Seat diameter
The smallest diameter of contact between the fixed and moving portions of the pressure containing elements of a valve
OPERATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PRESSURE RELIEF VALVES
Back pressure
The static pressure existing at the outlet of a pressure relief device due to pressure in the discharge system
Blowdown
The difference between actual popping pressure of a pressure relief valve and actual reseating pressure expressed as a percentage of set pressure or in pressure units
PRESSURE RELIEF VALVES
Prepared by
USEFUL TERMINOLOGIES
OPERATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PRESSURE RELIEF VALVES (Cont.)
Blowdown pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which no further discharge is detected at the outlet of a pressure relief valve after the valve has been subjected to a pressure equal to or above the popping pressure
Built-up back pressure
Pressure existing at the outlet of a pressure relief device caused by the flow through that particular device into a discharge system
Chatter
Abnormal rapid reciprocating motion of the movable parts of a pressure relief valve in which the disc contacts the seat
Closing pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which the valve disc reestablishes contact with the seat or at which lift becomes zero
Coefficient of discharge
The ratio of the measured relieving capacity to the theoretical relieving capacity
Cold differential test pressure
The inlet static pressure at which a pressure relief valve is adjusted to open on the test stand. This test pressure includes corrections for service conditions of superimposed back pressure
Constant back pressure
A superimposed back pressure which is constant with time
Flow-rating pressure
The inlet static pressure at which the relieving capacity of a pressure relief device is measured
Flutter
Abnormal, rapid reciprocating motion of the movable parts of a pressure relief valve in which the disc does not contact the seat
Leak test pressure
The specified inlet static pressure at which a quantitative seat leakage test is performed in accordance with a standard procedure
Marked pressure
The value or values of pressure marked on a pressure relief device
Measured relieving capacity
The relieving capacity of a pressure relief device measured at the flow-rating pressure, expressed in gravimetric or volumetric units
Opening pressure
The value of increasing inlet static pressure of a pressure relief valve at which there is a measurable lift, or at which the discharge becomes continuous as determined by seeing, feeling, or hearing
Overpressure
A pressure increase over the set pressure of a pressure relief valve, usually expressed as a percentage of set pressure
Popping pressure
The value of increasing inlet static pressure at which the disc moves in the opening direction at a faster rate as compared with corresponding movement at higher or lower pressures. It applies only
to safety or safety relief valves on compressible-fluid service
Primary pressure
The pressure at the inlet in a safety, safety relief, or relief valve
Rated relieving capacity
That portion of the measured relieving capacity permitted by the applicable code or regulation to be used as a basis for the application of a pressure relief device
Reference conditions
Those conditions of a test medium which are specified by either an applicable standard or an agreement between the parties to the test, which may be used for uniform reporting of measured flow test results
Relieving pressure
Set pressure plus overpressure
Resealing pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which no further leakage is detected after closing. The method of detection may be a specified water seal on the outlet or other means appropriate for this application
Reseating pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which the valve disc reestablishes contact with the seat or at which lift becomes zero
Seal-off pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which no further leakage is detected after closing. The method of detection may be a specified water seal on the outlet or other means appropriate for this application
Secondary pressure
The pressure existing in the passage between the actual discharge area and the valve outlet in a safety, safety relief, or relief valve
Set pressure
The value of increasing inlet static pressure at which a pressure relief valve displays one of the operational characteristics as defined under opening pressure, popping pressure, or start-to-leak pressure
Simmer
The audible or visible escape of fluid between the seat and disc at an inlet static pressure below the popping pressure and at no measurable capacity. It applies to safety or safety relief valves on compressiblefluid service
Start-to-discharge pressure
The value of increasing inlet static pressure of a pressure relief valve at which there is a measurable lift, or at which the discharge becomes continuous as determined by seeing, feeling, or hearing
Start-to-leak pressure
The value of increasing inlet static pressure at which the first bubble occurs when a pressure relief valve is tested by means of air under a specified water seal on the outlet
Superimposed back pressure
The static pressure existing at the outlet of a pressure relief device at the time the device is required to operate. It is the result of pressure in the discharge system from other sources
Theoretical relieving capacity
The computed capacity expressed in gravimetric or volumetric units of a theoretically perfect nozzle having a minimum cross-sectional flow area equal to the actual discharge area of a pressure relief valve
or relief area of a non-reclosing pressure relief device
Vapor-tight pressure
The value of decreasing inlet static pressure at which no further leakage is detected after closing. The method of detection may be a specified water seal on the outlet or other means appropriate for this application
Variable back pressure
A superimposed back pressure that will vary with time
You might also like
- Procedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesDocument28 pagesProcedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesNwokedi Okezie79% (29)
- CAPE BMED Option A Mdraw 2017 U2 P2 PDFDocument10 pagesCAPE BMED Option A Mdraw 2017 U2 P2 PDFLeeanaNo ratings yet
- Standard Plans For Highway Bridges - Concrete Slab BridgesDocument25 pagesStandard Plans For Highway Bridges - Concrete Slab BridgesV Venkata Narayana91% (33)
- Memo For Hand Receipt HoldersDocument10 pagesMemo For Hand Receipt HoldersTerrence StaplesNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesDocument27 pagesProcedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesNwokedi Okezie86% (7)
- Ottawa Air Brakes Service ManualDocument32 pagesOttawa Air Brakes Service ManualcbudkuleyNo ratings yet
- Safety ValvesDocument66 pagesSafety ValvesMuhammad Afiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Cement Mill-1 Girth Gear Alignment Readings Summary Report Girth Gear Axial Runout Girth Gear Radial RunoutDocument4 pagesCement Mill-1 Girth Gear Alignment Readings Summary Report Girth Gear Axial Runout Girth Gear Radial Runoutkaka100% (2)
- Computer Forensics FinalDocument34 pagesComputer Forensics FinalPrathima Prahalad100% (1)
- 13 KEROSENE MEROX PROCEDURE LatestDocument7 pages13 KEROSENE MEROX PROCEDURE LatestMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief SystemsDocument30 pagesPressure Relief SystemsBibek MerNo ratings yet
- PSVDocument13 pagesPSVUMESH GORE100% (1)
- API 576 Study NotesDocument5 pagesAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNo ratings yet
- API 576 Study NotesDocument5 pagesAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNo ratings yet
- Spence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFDocument24 pagesSpence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFJorge DuranNo ratings yet
- PSV Sizing ManualDocument10 pagesPSV Sizing ManualAkshay bhuranNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Kunkle ValveDocument32 pagesCatalogo Kunkle ValveKelvyn RochaNo ratings yet
- Safety Valves and Relief Valves.Document17 pagesSafety Valves and Relief Valves.Shikhar SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualDocument0 pagesTechnical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Plant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationsDocument104 pagesPlant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationskglorstadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety ValveDocument11 pagesPressure Safety ValveamitpallathNo ratings yet
- PSV Data BookDocument16 pagesPSV Data Bookkenoly123No ratings yet
- Pressure Control ValveDocument34 pagesPressure Control ValveHASHEMNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831Document32 pagesPressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831JO100% (1)
- Types of Pressure Relief ValvesDocument22 pagesTypes of Pressure Relief ValvesFaraz MichNo ratings yet
- Procedure PSVDocument24 pagesProcedure PSVAbakar MahamatNo ratings yet
- Terminology: Understanding What The Customer Wants Making It Happen!Document22 pagesTerminology: Understanding What The Customer Wants Making It Happen!Marcelo Kleber FelisbertoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief ValveDocument43 pagesPressure Relief ValveMohammed Hassan B Koraina100% (2)
- Pressure Safety Valve FundamentalsDocument21 pagesPressure Safety Valve Fundamentalsaop10468100% (2)
- API NotesDocument9 pagesAPI Notesking4lifeNo ratings yet
- Types of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not OpenDocument3 pagesTypes of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not Opennafees ahmadNo ratings yet
- Spring Loaded ValvesDocument10 pagesSpring Loaded ValvesKarl NakouziNo ratings yet
- Actuated Valve: Air Distribution Manifold (Instrument Air)Document45 pagesActuated Valve: Air Distribution Manifold (Instrument Air)Suguna moorthyNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation of The Pressure Relief ValvesDocument53 pagesDesign and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valvesghassan hamadNo ratings yet
- Terms FlumachDocument53 pagesTerms FlumachYhuloopz AlvarezNo ratings yet
- PRV PetrofacDocument36 pagesPRV PetrofacPradeep MagudeswaranNo ratings yet
- PSVDocument101 pagesPSVEngr Adeel Ahmed Abbasi100% (1)
- Relief Valves PDFDocument14 pagesRelief Valves PDFCarlos Del ToroNo ratings yet
- Writeup On Safety Valve & ErvDocument28 pagesWriteup On Safety Valve & Ervtek_surinder100% (3)
- Design Fundamentals: Materials of ConstructionDocument2 pagesDesign Fundamentals: Materials of ConstructionSusheel WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Testing of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Relieving Devices - 4Document7 pagesInspection & Testing of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Relieving Devices - 4DeepakNo ratings yet
- Axelson 6Document12 pagesAxelson 6Amit MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valves and Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesign and Calculation of The Pressure Relief Valves and Rupture Disks Systemghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-IDocument16 pagesPressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-Isabi_shiNo ratings yet
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemKaiwlya BhoyarNo ratings yet
- VALVESDocument3 pagesVALVESSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Designand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemDocument54 pagesDesignand Calculationofthe Pressure Relief Valvesand Rupture Disks SystemULAGANATHAN M100% (1)
- Pressure Relief ValvesDocument12 pagesPressure Relief ValvesyvhtejaswaroopNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas CarriersDocument17 pagesGuidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas Carriers123habib123fikriNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - SV - Part10Document6 pagesMicrosoft Word - SV - Part10aftabulalamNo ratings yet
- Reliability Testing of Pressure Relief Valves: January 2004Document12 pagesReliability Testing of Pressure Relief Valves: January 2004Gama MuktiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief Valve: Definition, Types, Working, Location, Sizing, Codes and StandardsDocument18 pagesPressure Relief Valve: Definition, Types, Working, Location, Sizing, Codes and StandardsMalcolm MooreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Hydraulic PressureDocument47 pagesLecture 5 Hydraulic PressureSAMUEL MAKATANENo ratings yet
- Basic Function of A Spring Loaded Safety ValveDocument3 pagesBasic Function of A Spring Loaded Safety ValveMikelaNo ratings yet
- 331-09-En Hydro Static Pressure TestDocument38 pages331-09-En Hydro Static Pressure TestJose OcañaNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Terminology Ver 1Document14 pagesControl Valve Terminology Ver 1bagastcNo ratings yet
- PSV Back PressureDocument2 pagesPSV Back PressureTon PhichitNo ratings yet
- TypesDocument6 pagesTypesAhmed NagyNo ratings yet
- PSV Back PressureDocument0 pagesPSV Back PressureDana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Testing of Pressure Relief ValveDocument13 pagesTesting of Pressure Relief ValveVishal Abhiman MeshramNo ratings yet
- Relief Valves and Relief SystemsDocument10 pagesRelief Valves and Relief Systemsmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Take Home From Our Facility PSV SizingDocument18 pagesTake Home From Our Facility PSV SizingConnor SailorNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- S4007 0002 10 PDFDocument10 pagesS4007 0002 10 PDFalejoNo ratings yet
- Installation Geo MotionsDocument5 pagesInstallation Geo Motionsoscar morenoNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide en USDocument424 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide en USrpizanaNo ratings yet
- Akumulator Sa HidrogenomDocument6 pagesAkumulator Sa Hidrogenombhstudent_537083349No ratings yet
- An Overview of Electromagnetic and Lightning Induced Voltage TransientsDocument11 pagesAn Overview of Electromagnetic and Lightning Induced Voltage TransientsRavishankar PmNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption Measurement - InstalationDocument32 pagesFuel Consumption Measurement - InstalationadNo ratings yet
- STI Stopper Station SeriesDocument4 pagesSTI Stopper Station SeriesTELNEX SASNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic FBR DesignDocument10 pagesAdiabatic FBR DesignRana UzairNo ratings yet
- MT Catalog 2015-2016Document258 pagesMT Catalog 2015-2016rubitovaleNo ratings yet
- Trilithic Data Sheet Bts 781 GP: 1 1.1 FeaturesDocument17 pagesTrilithic Data Sheet Bts 781 GP: 1 1.1 FeaturesВиктор СабовNo ratings yet
- BTT EB Specification Double Wall 08-07Document13 pagesBTT EB Specification Double Wall 08-07Alonso VillaNo ratings yet
- PG GovernorsDocument4 pagesPG GovernorsPj EastonNo ratings yet
- ME 422 Quiz 1Document3 pagesME 422 Quiz 1Daryl MadejaNo ratings yet
- App CodeDocument1 pageApp Codereyziel barganNo ratings yet
- Naval Ship Concept DesignDocument78 pagesNaval Ship Concept DesignaminNo ratings yet
- Mimaki Engineering Co., LTD.: You Can Also Download The Latest Manual From Our WebsiteDocument148 pagesMimaki Engineering Co., LTD.: You Can Also Download The Latest Manual From Our WebsiteoliveiraNo ratings yet
- Parts of An AircraftDocument29 pagesParts of An Aircrafttsegay100% (1)
- Marathi Shodh Katha, Confession of Thag, by Dhynaneshwar DamaheDocument9 pagesMarathi Shodh Katha, Confession of Thag, by Dhynaneshwar Damaheapi-3777175No ratings yet
- Technical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 934 ' Litronic NEDocument12 pagesTechnical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 934 ' Litronic NELiebherrNo ratings yet
- ICS 29.260.20 ISBN 0-626-17140-7 Edition 1: Warning Should Be Read in Conjunction WithDocument33 pagesICS 29.260.20 ISBN 0-626-17140-7 Edition 1: Warning Should Be Read in Conjunction Withchris541125No ratings yet
- 466 - Hydrology 303 Lecture Notes FinalDocument26 pages466 - Hydrology 303 Lecture Notes Finalanirbanpwd76No ratings yet
- Compresor 1 3HP R134a 110V 1190BTU H Baja Media Alta FFI12HBX EmbracoDocument5 pagesCompresor 1 3HP R134a 110V 1190BTU H Baja Media Alta FFI12HBX EmbracoAntonioNo ratings yet
- CPVC Drainage ProductsDocument11 pagesCPVC Drainage ProductsRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Thermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelDocument36 pagesThermodyancs Chapter 9 Solution ManuelFarhad MojaverNo ratings yet