Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pouring The Alcohol On Gunpowder
Pouring The Alcohol On Gunpowder
Uploaded by
Jessie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
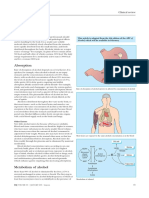
2 views2 pagesThis document summarizes how alcohol is absorbed and metabolized in the body. It notes that alcohol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and diffuses throughout the body. The rate of alcohol absorption depends on factors like food intake, gender, and medications. Once in the bloodstream, 95% of alcohol is metabolized by the liver into carbon dioxide and water by enzymes, while the remaining 5% is excreted by the lungs. However, if alcohol is consumed faster than it can be metabolized, intoxication will occur as alcohol accumulates in the bloodstream.
Original Description:
Original Title
pouring the alcohol on gunpowder
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes how alcohol is absorbed and metabolized in the body. It notes that alcohol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and diffuses throughout the body. The rate of alcohol absorption depends on factors like food intake, gender, and medications. Once in the bloodstream, 95% of alcohol is metabolized by the liver into carbon dioxide and water by enzymes, while the remaining 5% is excreted by the lungs. However, if alcohol is consumed faster than it can be metabolized, intoxication will occur as alcohol accumulates in the bloodstream.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesPouring The Alcohol On Gunpowder
Pouring The Alcohol On Gunpowder
Uploaded by
JessieThis document summarizes how alcohol is absorbed and metabolized in the body. It notes that alcohol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and diffuses throughout the body. The rate of alcohol absorption depends on factors like food intake, gender, and medications. Once in the bloodstream, 95% of alcohol is metabolized by the liver into carbon dioxide and water by enzymes, while the remaining 5% is excreted by the lungs. However, if alcohol is consumed faster than it can be metabolized, intoxication will occur as alcohol accumulates in the bloodstream.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
-pouring the alcohol on gunpowder
-if it’s 50% the gunpowder burns
-if it’s less concentrated, the remaining water content presents the burning
-bioavailability
-how much alcohol is freely available to enter the brain from the blood
-ethyl alcohol readily mixes with water and isn’t high in lipid solubility
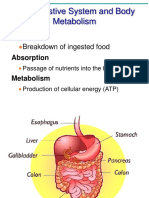
-easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and diffuses throughout the body
-behavioral effects are described on the basis of blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
-not amount ingested
-takes a BAC of 0.04% (40mg of alcohol per 100ml of blood) to produce measurable
behavioral effects
-absorption will occur from the GI tract
-10% from the stomach and 90% from the small intestine
-molecules move by passive diffusion
-higher concentration in GI tract to lower concentration of the blood
-the more alcohol you drink in a short period of time means more rapid movement from
the stomach and intestine to the blood, producing a higher blood level
-presence of food in stomach slows absorption
-delays movement into the small intestine through the pyloric sphincter
-muscle that regulates movement of stuff from stomach to intestine
-milk is really effective in delaying absorption alcohol
-carbonated beverages quicken the absorption of alcohol
-the carbonation speeds the movement of materials from the stomach to
the intestines
-gender differences in the absorption of alcohol
-certain enzymes that are present in gastric fluid are about 60% more active in men than
women
-leaves a higher concentration of alcohol to be absorbed more rapidly in women
-taking aspirin inhibits gastric alcohol dehydrogenase
-to a greater extent in women than men
-cuz women have lower levels of alcohol dehydrogenase to begin with
-ulcer medications also impair gastric metabolism
-increases alcohol concentrations and increases absorption
-once alcohol is in the blood it freely moves via passive diffusion to tissue and other fluid
compartments
-more effective in women too because they have less volume of fluid due to size
-have a higher fat-to-water ratio too
-of the alcohol that reaches the general circulation, ~95% is metabolized by the liver before it’s
excreted as carbon dioxide and water in urine
-remaining 5% is excreted by the lungs
-rate of oxidation is constant over time and doesn’t occur more quickly when the drug is more
concentrated in the blood
-this makes it different from other drugs
-if rate of consumption is faster than rate of metabolism, alcohol accumulates and the
person becomes more intoxicated
-enzymes in the liver
-alcohol dehydrogenase
-found in the stomach
-reduces amount of available alcohol for absorption
-converts alcohol to acetaldehyde
-modified to acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)
-to form acetic acid
-further oxidation yields carbon dioxide, water and energy
-ALDH exists in many forms
-10% Asians have genes that code only for inactive form of the enzyme
-drinking alcohol produces high levels of acetaldehyde
-cau
You might also like
- Zero To Finals MedicineDocument352 pagesZero To Finals MedicinePlay100% (25)
- Lesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On - Essential-NewbornSwati Sharma100% (2)
- Acid Alkaline Acid AlkalineDocument5 pagesAcid Alkaline Acid AlkalineNickHansenNo ratings yet
- Vitros Microslide Assay SummaryDocument10 pagesVitros Microslide Assay SummaryMedLab Şamaxı KlinikasıNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolDocument90 pagesAlcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolNisreen Al-share100% (2)
- AlcoholDocument28 pagesAlcoholpl.wsei.lublinNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Kidney: How Do We Release Urea?Document13 pagesFunctions of The Kidney: How Do We Release Urea?charibel torresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Grouping Work: Bio PresentationDocument36 pagesTutorial Grouping Work: Bio PresentationSharmila BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument5 pagesAcid Base Balancemedha chandNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Chemical DigestionDocument4 pagesMechanical and Chemical Digestionsnehashreemohanty39No ratings yet
- Alcohol in The BodyDocument3 pagesAlcohol in The BodyMarius StancuNo ratings yet
- Bile Salts & It's FunctionsDocument10 pagesBile Salts & It's FunctionsJorge De Vera100% (1)
- 3.2.3. Rehydration-MM-M-v100-enDocument2 pages3.2.3. Rehydration-MM-M-v100-enGratielaNo ratings yet
- Water - HydrationDocument20 pagesWater - HydrationLindiwe RadebeNo ratings yet
- Git Agents Lecture Notes 1Document29 pagesGit Agents Lecture Notes 1Ravi KaushikNo ratings yet
- WATERDocument6 pagesWATERAlthea Aine BalagotNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes A Fast and Easy Way To Understand Acid-Base Balance Without MemorizationDocument195 pagesFluids and Electrolytes A Fast and Easy Way To Understand Acid-Base Balance Without MemorizationNayely MoralesNo ratings yet
- Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument77 pagesAcidosis and Alkalosisnileshwaghmare16No ratings yet
- Digestive System: Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates, Proteins and FatsDocument45 pagesDigestive System: Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates, Proteins and FatshiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesFluid and Electrolytesfelicity tejadaNo ratings yet
- Elimination Through Other Organs BiopharmaceuticalsDocument17 pagesElimination Through Other Organs BiopharmaceuticalsMubammad MursaleenNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument71 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesHarold Castillo OrigenesNo ratings yet
- Glucose-6-Phosphate in Metabolic Processes: ProcessDocument3 pagesGlucose-6-Phosphate in Metabolic Processes: ProcessEL-nina Liebt U VaterNo ratings yet
- 3 7-CatabolismDocument66 pages3 7-CatabolismAlondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- WATERDocument3 pagesWATERKaye Niale BaleteNo ratings yet
- Lec6 Sem4 RENWK4 20140616Document2 pagesLec6 Sem4 RENWK4 20140616Uloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Bio 336 Physio Exam 3 EssaysDocument5 pagesBio 336 Physio Exam 3 Essayssheila100% (3)
- AcidosisDocument2 pagesAcidosismerwe-mariusNo ratings yet
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Document14 pagesHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817No ratings yet
- Document 17Document11 pagesDocument 17ayminqureshi987No ratings yet
- Acid Alkaline 1008Document6 pagesAcid Alkaline 1008api-171980623No ratings yet
- OsmoregulationDocument6 pagesOsmoregulationNIRBHAY_BARDIYANo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis and Fatty LiverDocument2 pagesCirrhosis and Fatty LiverchemismythingNo ratings yet
- Isotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic or Water: Which Sports Drink Is The Best For Athletes? Fluid Facts For WinnersDocument5 pagesIsotonic, Hypertonic, Hypotonic or Water: Which Sports Drink Is The Best For Athletes? Fluid Facts For Winnersnataliatirta100% (1)
- 19 Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance and Nutritional ProblemDocument40 pages19 Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance and Nutritional ProblemPaul EbenezerNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument15 pagesExcretionAisha Ali - 49549/TCHR/EKNNCNo ratings yet
- Responsible Alcohol DrinkingDocument25 pagesResponsible Alcohol DrinkingMary Pauline MuscaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentLec11 RodriguezDocument2 pagesAssignmentLec11 RodriguezRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- What Is Alkaline Water?Document2 pagesWhat Is Alkaline Water?Ely Go AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases Blood and Protein in Urine: FiltrationDocument4 pagesKidney Diseases Blood and Protein in Urine: FiltrationMochichimo TokikutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Excretion in Humans - 2023-2024Document41 pagesChapter 13 Excretion in Humans - 2023-2024buhNo ratings yet
- 146 File 50853Document3 pages146 File 50853solmazbaharyNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismDocument50 pagesAlcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismLeonard BowenNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument4 pagesBiochem NotesJanus ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Kidney AnswersDocument6 pagesKidney Answerssamia islamNo ratings yet
- Secretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionDocument8 pagesSecretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionMarianne Kristelle NonanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM DigestionDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNo ratings yet
- Week 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorDocument4 pagesWeek 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument3 pagesWaterShoaib AhmadNo ratings yet
- Digestion & AbsorptionDocument62 pagesDigestion & AbsorptionArina Windri RivartiNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument37 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Acidosis and AlkolosisDocument4 pagesAcidosis and AlkolosisDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Intake OutputDocument52 pagesIntake Outputkirti thakurNo ratings yet
- Water Balance Calcium (Ca)Document3 pagesWater Balance Calcium (Ca)Remy Martin Guy LesiguesNo ratings yet
- V. AlcoholDocument17 pagesV. AlcoholGeorge TsangNo ratings yet
- BACON B - Bowel EliminationDocument4 pagesBACON B - Bowel EliminationChristian EstevesNo ratings yet
- HangoverDocument3 pagesHangovernajiya hajraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte Acid-Base BalanceDocument17 pagesFluid Electrolyte Acid-Base BalanceBethany HoffmanNo ratings yet
- 3-General Nutrition-Water and Electrolyte-1Document40 pages3-General Nutrition-Water and Electrolyte-1vothithanhyen04No ratings yet
- Alkaline Water Stomach AcidDocument2 pagesAlkaline Water Stomach Acidkausi_2003No ratings yet
- Excretory System: Function and PartsDocument15 pagesExcretory System: Function and PartsVladStoenescuNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SDocument55 pagesShoulder Dislocation: DR Saseendar SPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument12 pagesUlcerative Colitisquidditch07No ratings yet
- Kon Et Al-1969-Journal of PeriodontologyDocument16 pagesKon Et Al-1969-Journal of Periodontologyshir keshalesNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument2 pagesFetal DistressLianne Joie Visitacion ClaroNo ratings yet
- Antiphospholipid Antibody SyndromeDocument78 pagesAntiphospholipid Antibody SyndromeAravindhan Gunasekaran PaediatricianNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures Covid-19 Virus Testing: ObjectiveDocument10 pagesStandard Operating Procedures Covid-19 Virus Testing: ObjectiveShivendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDocument4 pagesDisorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDylan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 and Mental Health-2Document21 pagesCovid-19 and Mental Health-2api-593213381No ratings yet
- 20161024-Fistula Health Education PosterDocument1 page20161024-Fistula Health Education PostergregcolletteNo ratings yet
- UC Care Tier2 Providers Health InsuranceDocument8 pagesUC Care Tier2 Providers Health InsuranceChris NewfieldNo ratings yet
- Kebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Document32 pagesKebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Ilham ApriansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewDocument14 pagesChapter Two: 2. Literuture ReviewAhmedNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Faktor-Faktor Yang Terkait Dengan Kinerja Petugas Dalam Penemuan Kasus Pada Program Tuberkulosis Paru Di Kabupaten GroboganDocument10 pagesGambaran Faktor-Faktor Yang Terkait Dengan Kinerja Petugas Dalam Penemuan Kasus Pada Program Tuberkulosis Paru Di Kabupaten GroboganNurse AdhyNo ratings yet
- Spelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryDocument16 pagesSpelling Mistakes Corrections of Jahangir's Pool of FCPS Part 1 DentistryAisha BanoNo ratings yet
- Medically Important Bacteria Gram Negative - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically.Document104 pagesMedically Important Bacteria Gram Negative - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically.jethreel diosoNo ratings yet
- Conduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDocument2 pagesConduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- RETINOBLASTOMA, DR Claudio Owino, SurgeryDocument30 pagesRETINOBLASTOMA, DR Claudio Owino, SurgeryKaruga NyagahNo ratings yet
- Initial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDocument2 pagesInitial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDalia GomNo ratings yet
- The Emergence and Persistence of C Auris in Western New YorkDocument4 pagesThe Emergence and Persistence of C Auris in Western New YorkLilia JouNo ratings yet
- Coek - Info - Hydrotherapy Principles and PracticeDocument1 pageCoek - Info - Hydrotherapy Principles and PracticeDiegoNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Male Infertility by The World HealthDocument7 pagesPrediction of Male Infertility by The World HealthquickdannyNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017Document16 pagesAntimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017behzad bm0% (1)
- Low Dose Dexamethasone Suppression TestDocument2 pagesLow Dose Dexamethasone Suppression Testsanham100% (1)
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- Muscle Relaxants: Topic OutlineDocument8 pagesMuscle Relaxants: Topic OutlineBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- Micro TeachingDocument6 pagesMicro Teachingkawaljitkang100% (1)
- Naso Gastric Tube Insertion and RemovalDocument5 pagesNaso Gastric Tube Insertion and RemovalPia Mae BuayaNo ratings yet