Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science
Earth Science
Uploaded by
Jillian Mae Cosejo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document discusses the four major subsystems of Earth - the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. It describes how these subsystems interact in complex ways, with the hydrosphere and atmosphere interacting through evaporation and condensation, the biosphere relying on the atmosphere for oxygen and influencing it through life processes, and the hydrosphere constantly interacting with the lithosphere through erosion, sedimentation, and landform formation. It also notes how the subsystems are interconnected and influence one another.
Original Description:
Original Title
earth science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the four major subsystems of Earth - the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. It describes how these subsystems interact in complex ways, with the hydrosphere and atmosphere interacting through evaporation and condensation, the biosphere relying on the atmosphere for oxygen and influencing it through life processes, and the hydrosphere constantly interacting with the lithosphere through erosion, sedimentation, and landform formation. It also notes how the subsystems are interconnected and influence one another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageEarth Science
Earth Science
Uploaded by
Jillian Mae CosejoThe document discusses the four major subsystems of Earth - the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. It describes how these subsystems interact in complex ways, with the hydrosphere and atmosphere interacting through evaporation and condensation, the biosphere relying on the atmosphere for oxygen and influencing it through life processes, and the hydrosphere constantly interacting with the lithosphere through erosion, sedimentation, and landform formation. It also notes how the subsystems are interconnected and influence one another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
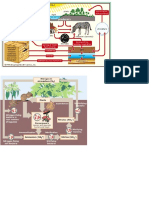
The Earth can be divided into four major subsystems: the litosphere,
hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. These subsystems interact with each
other in complex and interconnected ways, and these interactions play a crucial
role in shaping the Earth's environment and supporting life.
Hydrosphere and Atmosphere interact with each other through
evaporation and condensation as solar energy heats the Earth's surface, causing
water from the hydrosphere (oceans, rivers, lakes) to evaporate into the
atmosphere. Precipitation also helps the atmosphere and hydrosphere to interact
with each other as water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into clouds and falls
back to the Earth's surface that also causes the hydrosphere to replenish.
The biosphere depends on the atmosphere as living things uses oxygen to
live, whereas atmosphere is affected by biosphere as life processes put methane
on it or in short is the exchange of gases through photosynthesis and respiration.
Biosphere interacts with lithosphere or geosphere by influencing soil
formation through the decomposition of organic matter and the creation of
ecosystems, wherein rotting organisms enrich the soil where the plants grow.
Hydrosphere constantly interacts with lithosphere (geosphere) through
erosion, sedimentation, and the formation of landforms like deltas, canyons, and
beaches. The hydrosphere provides the necessary moisture required to weather
and erode the rocks, where in return, the lithosphere (geosphere) allows the ice
to melt and the water bodies flow back into the oceans.
Water is essential for all living organisms, that’s why biosphere relies on
hydrosphere for water and nutrients. Hydrosphere also provides habitat for
aquatic life. The biosphere influences the hydrosphere by regulating nutrient
cycles (e.g., nitrogen and phosphorus cycles) and affecting water quality.
Atmospheric elements like wind, rain, and temperature changes can break
down and erode rocks on the Earth's surface and release minerals contributing to
the geosphere's transformation. The geosphere also influences the atmosphere
by releasing gases through volcanic eruptions and regulating long-term climate
patterns through the carbon cycle.
You might also like
- Global Environment: Water, Air, and Geochemical Cycles - Second EditionFrom EverandGlobal Environment: Water, Air, and Geochemical Cycles - Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Earth's SubsystemsDocument17 pagesThe Earth's SubsystemsAndevie Balili Iguana100% (1)
- SubsystemsDocument3 pagesSubsystemsrzx jnnNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Four Subsystems-The GeoDocument1 pageThe Earth's Four Subsystems-The GeoJohn Edison BrilloNo ratings yet
- Earths Subsystems - Learning MaterialDocument3 pagesEarths Subsystems - Learning MaterialJA Berzabal100% (1)
- Environmental SystemsDocument5 pagesEnvironmental SystemsMehwishNo ratings yet
- Termp Paper-Ensci3110Document8 pagesTermp Paper-Ensci3110Karla CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Geochemical Cycles NotesDocument6 pagesGeochemical Cycles NotesPerlievic TesoroNo ratings yet
- Earth System DefinitionsDocument7 pagesEarth System DefinitionsEhr WinNo ratings yet
- The Ocean and Sea IceDocument5 pagesThe Ocean and Sea IceAbdur RaufNo ratings yet
- Earth Major SystemDocument2 pagesEarth Major SystemDwayne Ashley SilveniaNo ratings yet
- MCB 311 Lecture 2Document12 pagesMCB 311 Lecture 2ejohn8340No ratings yet
- Elements MatterDocument15 pagesElements MatterUsama JavaidNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Subsytem of The EarthDocument20 pagesLESSON 2 Subsytem of The EarthKIP AIZA GABAWANo ratings yet
- Spheres of The EarthDocument1 pageSpheres of The EarthnikkidemonyoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science AssignmentDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Science AssignmentShaista RabailNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles-1Document8 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles-1sehrish iqbalNo ratings yet
- EarthSci DraftsDocument7 pagesEarthSci DraftsClarisse PenaredondoNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecology Principles and Concepts: Topic 3: Biogeochemical CyclesDocument11 pagesBasic Ecology Principles and Concepts: Topic 3: Biogeochemical CycleskathNo ratings yet
- 2 The Earths SubsystemsDocument12 pages2 The Earths SubsystemsPsyche Diana OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. THE EARTH'S SUBSYSTEMSDocument41 pagesLesson 3. THE EARTH'S SUBSYSTEMSMarlyn NavalesNo ratings yet
- Ciclos de La NaturalezaDocument3 pagesCiclos de La NaturalezaLeidis RodríguezNo ratings yet
- HydrosphereDocument1 pageHydrosphereJinn Allan LuañaNo ratings yet
- Geo Assign 2022 End YearDocument5 pagesGeo Assign 2022 End YearHankinsNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemsDocument13 pagesEarth SystemsJoshua Sambrano BelandresNo ratings yet
- Env 107-5Document13 pagesEnv 107-5Avishek PaulNo ratings yet
- Earth's Land Makes Up The GeosphereDocument14 pagesEarth's Land Makes Up The GeosphereBriansky HanNo ratings yet
- Home Task Earth System 2Document6 pagesHome Task Earth System 2Maryfel DuamanNo ratings yet
- EarthsystemDocument23 pagesEarthsystemapi-26963416No ratings yet
- ESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaDocument6 pagesESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaThortheGreayNo ratings yet
- Materi 2. Siklus Energi Dan MateriDocument3 pagesMateri 2. Siklus Energi Dan MateriKhanna HadiramaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Weathering Handouts 46 CopiesDocument2 pagesChemical Weathering Handouts 46 CopiesBegginer to Master of script codeNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT - Biogeochemical CycleDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENT - Biogeochemical CyclePranav100% (2)
- Bio Means (Outline)Document9 pagesBio Means (Outline)Sheila Mae VeralNo ratings yet
- Geography EOT PreparationsDocument6 pagesGeography EOT PreparationsannjelemocampbellNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesClimate ChangeHankinsNo ratings yet
- Earth ScieDocument2 pagesEarth ScieAngelo Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Earth SubsystemDocument26 pagesEarth SubsystemVivi LutherNo ratings yet
- Composition of Biosphere and Natural Composition of Air, Water, and SoilDocument5 pagesComposition of Biosphere and Natural Composition of Air, Water, and SoilPauline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesWater Cycle Lesson PlanExcel Joy MarticioNo ratings yet
- What Is GeologyDocument5 pagesWhat Is GeologyJacqui JuanNo ratings yet
- Earth Hand OutsDocument4 pagesEarth Hand OutsJen AntonioNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Earth Science 2021 2022Document3 pagesModule 2 Earth Science 2021 2022Razen SisonNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & BeyondDocument8 pagesFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument7 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesMARK JUN M. BALTAZARNo ratings yet
- SCHA4004Document87 pagesSCHA4004suwaranapandav59No ratings yet
- Chemistry of SoilDocument11 pagesChemistry of SoilFrancia BalondoNo ratings yet
- Basic Scientific ConceptDocument7 pagesBasic Scientific ConceptRobert Lee DemandanteNo ratings yet
- Four Spheres - The Foundation of Our PlanetDocument4 pagesFour Spheres - The Foundation of Our PlanetAmna GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Cycles and FlowsDocument28 pagesCycles and FlowsRogers Talemwa WakefieldNo ratings yet
- Subsytems of EarthDocument52 pagesSubsytems of EarthHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemDocument6 pagesEarth SystemDwayne Ashley SilveniaNo ratings yet
- Esdm 231Document30 pagesEsdm 231Priyanka Mestri100% (1)
- The Earth's SubsystemsDocument18 pagesThe Earth's Subsystemsthe witcherNo ratings yet
- Earths SubsystemDocument31 pagesEarths SubsystemSeanneira Lacson100% (1)
- Review Well Hehe Kaya Natin 2 Earth and Earth Subsystems: Earth: The Living PlanetDocument29 pagesReview Well Hehe Kaya Natin 2 Earth and Earth Subsystems: Earth: The Living PlanetColeen CalalangNo ratings yet
- Soil Formation: Cavite State UniversityDocument8 pagesSoil Formation: Cavite State UniversityJoshua ZunigaNo ratings yet
- The Fragile Balance: Understanding Earth and Environmental ScienceFrom EverandThe Fragile Balance: Understanding Earth and Environmental ScienceNo ratings yet
- Saving the World 1x1: Nature Conservation, Environmental Protection & Climate Protection for Beginners: How to Recognize the Problems of Today’s World and Gradually Improve Them in Small StepsFrom EverandSaving the World 1x1: Nature Conservation, Environmental Protection & Climate Protection for Beginners: How to Recognize the Problems of Today’s World and Gradually Improve Them in Small StepsNo ratings yet