Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
Uploaded by
王博瑀Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mastering Physics 2Document12 pagesMastering Physics 2ozilla_26_me80% (5)
- Thermocold AWC PROZONE Tech PDFDocument44 pagesThermocold AWC PROZONE Tech PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 01 CVPM Packet 2013Document12 pagesHPhys Unit 01 CVPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (5)
- High School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsFrom EverandHigh School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Science College Entrance Mock ExamDocument13 pagesScience College Entrance Mock ExamDavid Kim100% (2)
- Gen Physics 1 - Final ExamDocument2 pagesGen Physics 1 - Final ExamArielle Ariane Nacar100% (3)
- The Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document4 pagesThe Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112No ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFDocument14 pagesHPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFjbc929_billsNo ratings yet
- Radar Plotting 2Document14 pagesRadar Plotting 2Sto Cu100% (3)
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1No ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.5 and 1.6Document5 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.5 and 1.6王博瑀No ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.4Document3 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.4王博瑀No ratings yet
- Kinematics and Dynamics WorksheetsDocument49 pagesKinematics and Dynamics Worksheetsknoxphysics100% (1)
- SPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedDocument10 pagesSPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedlarrylynnmailNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument1 pageMIDTERMDatuali UmalNo ratings yet
- Lab-Motion-student GuideDocument6 pagesLab-Motion-student Guidematt --0% (3)
- Answer Scheme For Class 9 CBSE Physics Test PaperDocument3 pagesAnswer Scheme For Class 9 CBSE Physics Test Paperaadit thakralNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Materials in Science 7 Q3Document3 pagesContextualized Materials in Science 7 Q3Christy CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Mid Term 2,3,9Document2 pagesMid Term 2,3,9felicia.wNo ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.3Document3 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.3王博瑀No ratings yet
- Module Kinematics Week 6 To 8Document13 pagesModule Kinematics Week 6 To 8Kriselle Keith NaragNo ratings yet
- Engr102 17S2 - ExamDocument12 pagesEngr102 17S2 - ExamowmferrierNo ratings yet
- 1 Hour: Name: ... Class: Physics April 2013Document17 pages1 Hour: Name: ... Class: Physics April 2013jgd2080No ratings yet
- Q CE 6502 Oct-21Document3 pagesQ CE 6502 Oct-21Md. Shofiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Acceleration LabDocument7 pagesAcceleration Labapi-261954479No ratings yet
- University of Mumbai Institute of Distance Education MCA (Distance Education) ENTRANCE TEST - 2008Document4 pagesUniversity of Mumbai Institute of Distance Education MCA (Distance Education) ENTRANCE TEST - 2008Sushmita JkNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Document17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - 2 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal Exam - 2 PDFSyed Muhammad Moin Ud Din SajjadNo ratings yet
- Shajra AttariaDocument5 pagesShajra AttariaFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 2with AnswersDocument22 pagesUnit Test 2with AnswersPhysicshekNo ratings yet
- University Tenaga National College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesUniversity Tenaga National College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringabdallah baderNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet
- Internal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefDocument8 pagesInternal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Assignment 3 Question PaperDocument3 pagesProblem Based Assignment 3 Question PaperarlandoNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Practice Has As Main Objective To Corroborate A Data That Was Obtained From The TheoryDocument6 pagesAn Experimental Practice Has As Main Objective To Corroborate A Data That Was Obtained From The TheoryAnonymous OP6R1ZSNo ratings yet
- Class 09 Science Motion Sample Test 03Document2 pagesClass 09 Science Motion Sample Test 03Govind ChettyNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Motion Test 03Document2 pages09 Science Motion Test 03Mrigendra MishraNo ratings yet
- (R) MCV4U Final Exam Review OutlineDocument3 pages(R) MCV4U Final Exam Review OutlinelaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- UBGLXP-15-3 January 2016 PDFDocument4 pagesUBGLXP-15-3 January 2016 PDFLibraryNo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument8 pagesSummative Assessmentapi-376643450No ratings yet
- Graphics SyllabusDocument9 pagesGraphics SyllabusAdarsh RNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Practice Test 2015Document3 pagesKinematics Practice Test 2015BassilObeidiNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion Oct 1. 2018Document5 pagesLinear Motion Oct 1. 2018carlierosetalNo ratings yet
- The Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document5 pagesThe Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112No ratings yet
- 2.11.2 Project - Performance Task - The Parallax Problem (Project)Document16 pages2.11.2 Project - Performance Task - The Parallax Problem (Project)8xy2th9rwdNo ratings yet
- SPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedDocument10 pagesSPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedlarrylynnmailNo ratings yet
- General Physics For Engineering I (PHYS191) : L53 CRN: 11728Document7 pagesGeneral Physics For Engineering I (PHYS191) : L53 CRN: 11728Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Rotational DynamicsDocument2 pagesCircular Motion and Rotational DynamicsChasel Jane LaygoNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 WorksheetsDocument9 pagesAs Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 Worksheetsapi-183882946No ratings yet
- LacasseS PH 20 Lesson 3 Self-CheckDocument4 pagesLacasseS PH 20 Lesson 3 Self-Checkfuzzysamurai23No ratings yet
- AP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookDocument401 pagesAP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookGabby Tanaka0% (1)
- Bunda Mulia School (SPK) : GRADEDocument4 pagesBunda Mulia School (SPK) : GRADEScience MS/HSNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Linear Motion 2012Document18 pages2.1 Linear Motion 2012cikgusuriyatiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 SUVAT EquationsDocument8 pagesPart 2 SUVAT Equationsvian.gargNo ratings yet
- Part 2 SUVAT EquationsDocument8 pagesPart 2 SUVAT Equationsvian.gargNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Brill, J. P. and Mukherjee, H. - Multiphase Flow in WellsDocument149 pagesBrill, J. P. and Mukherjee, H. - Multiphase Flow in WellsMisael GarcíaNo ratings yet
- LWT - Food Science and Technology: A B C D ADocument6 pagesLWT - Food Science and Technology: A B C D AVidaluz VanegasNo ratings yet
- A Century of PhysicsDocument8 pagesA Century of PhysicsMohd Afiq AminNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument11 pagesThermal EngineeringParasNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGDocument3 pagesPowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGanon_370743546No ratings yet
- UPS2000-G - 1 kVA-3 kVADocument64 pagesUPS2000-G - 1 kVA-3 kVAsmart studioNo ratings yet
- Gearless Traction Machine Application: 1. General Speed Passenger ElevatorDocument4 pagesGearless Traction Machine Application: 1. General Speed Passenger ElevatorChang ChangNo ratings yet
- CO ECE - Criteria 3 CO PO Mapping 2018 2021Document33 pagesCO ECE - Criteria 3 CO PO Mapping 2018 2021Dr. Subhendu Sekhar Sahoo (EEE Dept)No ratings yet
- VelocityDocument3 pagesVelocityleizl MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)Document59 pagesCivil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)TrevorKetso100% (1)
- 03 Spectrophysics Rick Trebino Modern Physics Wide StudIPDocument35 pages03 Spectrophysics Rick Trebino Modern Physics Wide StudIPhansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4Saravanan MunusamyNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Faculty Name - Prof. Satya Prakash Program - B.Tech IV Batch - 2018-22 Course - Mine EnvironmentDocument8 pagesFaculty Name - Prof. Satya Prakash Program - B.Tech IV Batch - 2018-22 Course - Mine Environmentshivam raiNo ratings yet
- PowerTransmissionCourse2 2Document116 pagesPowerTransmissionCourse2 2Yan Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Document34 pagesScheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Malik HammadNo ratings yet
- Equipment: Unit Identification CardDocument7 pagesEquipment: Unit Identification CardMax Rojas100% (1)
- SIUI General ProbeDocument14 pagesSIUI General ProbeRudy Jaramillo100% (1)
- M&MV Lab Exp 5 Constant Acceleratin CamDocument12 pagesM&MV Lab Exp 5 Constant Acceleratin CamSyeda Sara BatoolNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction Volume 21, Supramolecular Aspects of Solvent Extraction (Bruce A Moyer) (Z-Library)Document290 pagesIon Exchange and Solvent Extraction Volume 21, Supramolecular Aspects of Solvent Extraction (Bruce A Moyer) (Z-Library)Alejandro VillalbaNo ratings yet
- 6 Exam Paper - IB HL - DifferentiationDocument35 pages6 Exam Paper - IB HL - DifferentiationDarshana JainNo ratings yet
- Thermo MCQDocument23 pagesThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Hagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesDocument48 pagesHagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesFarah Taha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ABB-LVP in High AltitudesDocument13 pagesABB-LVP in High AltitudesRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERSDocument79 pagesTRANSDUCERSregi destawanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Apparatus and Devices Laboratory Exercise 1 TransformerDocument17 pagesElectrical Apparatus and Devices Laboratory Exercise 1 TransformerMary Grace CuevaNo ratings yet
- Multistage and Poly Stage ConverterDocument22 pagesMultistage and Poly Stage ConverterkirthikNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids (MRH)Document49 pagesCarboxylic Acids (MRH)Ali Akand AsifNo ratings yet
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
Uploaded by
王博瑀Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
SPH4U Classwork 1.2
Uploaded by
王博瑀Copyright:
Available Formats
SPH4U_Classwork 1.
2
Equations of Motion
Name: Score: /60
Teacher: Date: Time:
Purpose of Assessment: Assessment OF Learning
Method of Assessment: KTCA Four Level +/-
Learning Goals:
● Understand the equations of motion that describe the motion of particles.
● Make predictions of their position, velocity and acceleration.
Overall Expectations
B. Dynamics
B1. analyse technological devices that apply the principles of the dynamics of motion, and assess the
technologies’ social and environmental impact; B2. investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms,
forces involved in uniform circular motion and motion in a plane, and solve related problems;
Specific Expectations
B2.1 use appropriate terminology related to dynamics, including, but not limited to: inertial and non-inertial
frames of reference, components, centripetal, period, frequency, static friction, and kinetic friction [C]
B2.2 solve problems related to motion, including projectile and relative motion, by adding and subtracting
two-dimensional vector quantities, using vector diagrams, vector components, and algebraic methods [PR,
AI, C
Instructions:
1. Make a copy of this document.
2. Answer textbook questions: Page 21 all odd numbers.
K: /20 T: /15 C and A: /25
Knowledge 20
Upon leaving the starting gate, a racehorse accelerates at a constant 4.1 m/s2 [forward] for 5.2 s.
Determine the horse’s (a) displacement (b) final velocity.
Marking Scheme (10 marks)
● 5 marks for presenting correct and complete step-by-step solution.
● 3 marks for calculating the horse’s displacement
● 2 marks for calculating the final velocity
A toy rocket starts from rest on the ground and then accelerates at 39.2 m/s2 [up] for 5.0 s.
(a) Calculate the velocity of the rocket when the engines stop firing after 5.0 s.
(b) Calculate the maximum height of the rocket.
(c) How long will it take the rocket to hit the ground from rest at the maximum height and initial rest?
Marking Scheme (10 marks)
● 4 marks for presenting correct and complete step-by-step solution.
● 2 marks for calculating the velocity
● 2 marks for calculating the height
● 2 marks for calculating the time
Thinking 15
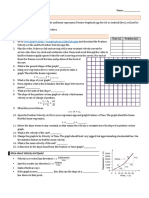
Study the graph in Figure 14.
(a) Determine the average acceleration for the entire trip.
(b) Determine the instantaneous acceleration at 3.0 s, 6.0 s, and 9.0 s.
(c) Sketch a qualitative acceleration–time graph of the motion.
Marking Scheme (15 marks)
● 5 marks for presenting correct and complete step-by-step solutions.
● 3 marks for calculating the average acceleration
● 3 marks for calculating the instantaneous acceleration
● 4 marks for the graph of the motion
Communication and Application 25
A police officer at rest at the side of the highway notices a speeder moving at 62 km/h along a
straight level road near an elementary school. When the speeder passes, the officer accelerates at 3.0
m/s2 in pursuit. The speeder does not notice until the police officer catches up.
(a) How long will it take for the officer to catch the speeder?
(b) How far will they move from the position where the officer was at rest?
(c) Calculate the speed of the police car when the officer catches the speeder. Is this reasonable?
(d) Now assume that the police officer accelerates until the police car is moving 10.0 km/h faster
than the speeder and then moves at a constant velocity until the police officer catches up. How long
will it take to catch the speeder? Is this scenario more reasonable than the scenario in (c)? Explain your
answer.
Marking Scheme (15 marks)
● 5 marks for presenting correct and complete step-by-step solutions.
● 2 marks for determining the time needed for the officer to catch the speeder
● 2 marks for calculating the distance
● 6 marks for presenting and explaining the correct answers
A baseball player throws a ball straight up and then catches it 2.4 s later at the same height from
which he threw it. Determine (a) the initial velocity (b) the maximum height of the ball.
Marking Scheme (10 marks)
● 5 marks for presenting correct and complete step-by-step solution.
● 3 marks for calculating the initial velocity
● 2 marks for calculating the maximum height of the ball
You might also like
- Mastering Physics 2Document12 pagesMastering Physics 2ozilla_26_me80% (5)
- Thermocold AWC PROZONE Tech PDFDocument44 pagesThermocold AWC PROZONE Tech PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 01 CVPM Packet 2013Document12 pagesHPhys Unit 01 CVPM Packet 2013Kelly O'Shea100% (5)
- High School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsFrom EverandHigh School Physics: Questions & Explanations for High School PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Science College Entrance Mock ExamDocument13 pagesScience College Entrance Mock ExamDavid Kim100% (2)
- Gen Physics 1 - Final ExamDocument2 pagesGen Physics 1 - Final ExamArielle Ariane Nacar100% (3)
- The Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document4 pagesThe Moving Man Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112No ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFDocument14 pagesHPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFjbc929_billsNo ratings yet
- Radar Plotting 2Document14 pagesRadar Plotting 2Sto Cu100% (3)
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1No ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.5 and 1.6Document5 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.5 and 1.6王博瑀No ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.4Document3 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.4王博瑀No ratings yet
- Kinematics and Dynamics WorksheetsDocument49 pagesKinematics and Dynamics Worksheetsknoxphysics100% (1)
- SPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedDocument10 pagesSPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedlarrylynnmailNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument1 pageMIDTERMDatuali UmalNo ratings yet
- Lab-Motion-student GuideDocument6 pagesLab-Motion-student Guidematt --0% (3)
- Answer Scheme For Class 9 CBSE Physics Test PaperDocument3 pagesAnswer Scheme For Class 9 CBSE Physics Test Paperaadit thakralNo ratings yet
- Contextualized Materials in Science 7 Q3Document3 pagesContextualized Materials in Science 7 Q3Christy CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- Mid Term 2,3,9Document2 pagesMid Term 2,3,9felicia.wNo ratings yet
- SPH4U Classwork 1.3Document3 pagesSPH4U Classwork 1.3王博瑀No ratings yet
- Module Kinematics Week 6 To 8Document13 pagesModule Kinematics Week 6 To 8Kriselle Keith NaragNo ratings yet
- Engr102 17S2 - ExamDocument12 pagesEngr102 17S2 - ExamowmferrierNo ratings yet
- 1 Hour: Name: ... Class: Physics April 2013Document17 pages1 Hour: Name: ... Class: Physics April 2013jgd2080No ratings yet
- Q CE 6502 Oct-21Document3 pagesQ CE 6502 Oct-21Md. Shofiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Acceleration LabDocument7 pagesAcceleration Labapi-261954479No ratings yet
- University of Mumbai Institute of Distance Education MCA (Distance Education) ENTRANCE TEST - 2008Document4 pagesUniversity of Mumbai Institute of Distance Education MCA (Distance Education) ENTRANCE TEST - 2008Sushmita JkNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Document17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - 2 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal Exam - 2 PDFSyed Muhammad Moin Ud Din SajjadNo ratings yet
- Shajra AttariaDocument5 pagesShajra AttariaFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 2with AnswersDocument22 pagesUnit Test 2with AnswersPhysicshekNo ratings yet
- University Tenaga National College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesUniversity Tenaga National College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringabdallah baderNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet
- Internal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefDocument8 pagesInternal Verification of Assignment Briefs: Evaluation Criteria or 1 Draft Final BriefOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Assignment 3 Question PaperDocument3 pagesProblem Based Assignment 3 Question PaperarlandoNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Practice Has As Main Objective To Corroborate A Data That Was Obtained From The TheoryDocument6 pagesAn Experimental Practice Has As Main Objective To Corroborate A Data That Was Obtained From The TheoryAnonymous OP6R1ZSNo ratings yet
- Class 09 Science Motion Sample Test 03Document2 pagesClass 09 Science Motion Sample Test 03Govind ChettyNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Motion Test 03Document2 pages09 Science Motion Test 03Mrigendra MishraNo ratings yet
- (R) MCV4U Final Exam Review OutlineDocument3 pages(R) MCV4U Final Exam Review OutlinelaureniscapuletNo ratings yet
- UBGLXP-15-3 January 2016 PDFDocument4 pagesUBGLXP-15-3 January 2016 PDFLibraryNo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument8 pagesSummative Assessmentapi-376643450No ratings yet
- Graphics SyllabusDocument9 pagesGraphics SyllabusAdarsh RNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Practice Test 2015Document3 pagesKinematics Practice Test 2015BassilObeidiNo ratings yet
- Linear Motion Oct 1. 2018Document5 pagesLinear Motion Oct 1. 2018carlierosetalNo ratings yet
- The Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19Document5 pagesThe Moving Man Acceleration Simulation Lab 2013-08-19sk112No ratings yet
- 2.11.2 Project - Performance Task - The Parallax Problem (Project)Document16 pages2.11.2 Project - Performance Task - The Parallax Problem (Project)8xy2th9rwdNo ratings yet
- SPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedDocument10 pagesSPH3U 1-4I - Advanced Kinematics Problems Assignment UpdatedlarrylynnmailNo ratings yet
- General Physics For Engineering I (PHYS191) : L53 CRN: 11728Document7 pagesGeneral Physics For Engineering I (PHYS191) : L53 CRN: 11728Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Rotational DynamicsDocument2 pagesCircular Motion and Rotational DynamicsChasel Jane LaygoNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 WorksheetsDocument9 pagesAs Level Physics Topic 3 Kinematics Lessons 1 2 Worksheetsapi-183882946No ratings yet
- LacasseS PH 20 Lesson 3 Self-CheckDocument4 pagesLacasseS PH 20 Lesson 3 Self-Checkfuzzysamurai23No ratings yet
- AP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookDocument401 pagesAP Physics B 2013 Practice WorkbookGabby Tanaka0% (1)
- Bunda Mulia School (SPK) : GRADEDocument4 pagesBunda Mulia School (SPK) : GRADEScience MS/HSNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Linear Motion 2012Document18 pages2.1 Linear Motion 2012cikgusuriyatiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 SUVAT EquationsDocument8 pagesPart 2 SUVAT Equationsvian.gargNo ratings yet
- Part 2 SUVAT EquationsDocument8 pagesPart 2 SUVAT Equationsvian.gargNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Brill, J. P. and Mukherjee, H. - Multiphase Flow in WellsDocument149 pagesBrill, J. P. and Mukherjee, H. - Multiphase Flow in WellsMisael GarcíaNo ratings yet
- LWT - Food Science and Technology: A B C D ADocument6 pagesLWT - Food Science and Technology: A B C D AVidaluz VanegasNo ratings yet
- A Century of PhysicsDocument8 pagesA Century of PhysicsMohd Afiq AminNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument11 pagesThermal EngineeringParasNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGDocument3 pagesPowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGanon_370743546No ratings yet
- UPS2000-G - 1 kVA-3 kVADocument64 pagesUPS2000-G - 1 kVA-3 kVAsmart studioNo ratings yet
- Gearless Traction Machine Application: 1. General Speed Passenger ElevatorDocument4 pagesGearless Traction Machine Application: 1. General Speed Passenger ElevatorChang ChangNo ratings yet
- CO ECE - Criteria 3 CO PO Mapping 2018 2021Document33 pagesCO ECE - Criteria 3 CO PO Mapping 2018 2021Dr. Subhendu Sekhar Sahoo (EEE Dept)No ratings yet
- VelocityDocument3 pagesVelocityleizl MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)Document59 pagesCivil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)TrevorKetso100% (1)
- 03 Spectrophysics Rick Trebino Modern Physics Wide StudIPDocument35 pages03 Spectrophysics Rick Trebino Modern Physics Wide StudIPhansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4Saravanan MunusamyNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Faculty Name - Prof. Satya Prakash Program - B.Tech IV Batch - 2018-22 Course - Mine EnvironmentDocument8 pagesFaculty Name - Prof. Satya Prakash Program - B.Tech IV Batch - 2018-22 Course - Mine Environmentshivam raiNo ratings yet
- PowerTransmissionCourse2 2Document116 pagesPowerTransmissionCourse2 2Yan Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Document34 pagesScheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Malik HammadNo ratings yet
- Equipment: Unit Identification CardDocument7 pagesEquipment: Unit Identification CardMax Rojas100% (1)
- SIUI General ProbeDocument14 pagesSIUI General ProbeRudy Jaramillo100% (1)
- M&MV Lab Exp 5 Constant Acceleratin CamDocument12 pagesM&MV Lab Exp 5 Constant Acceleratin CamSyeda Sara BatoolNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction Volume 21, Supramolecular Aspects of Solvent Extraction (Bruce A Moyer) (Z-Library)Document290 pagesIon Exchange and Solvent Extraction Volume 21, Supramolecular Aspects of Solvent Extraction (Bruce A Moyer) (Z-Library)Alejandro VillalbaNo ratings yet
- 6 Exam Paper - IB HL - DifferentiationDocument35 pages6 Exam Paper - IB HL - DifferentiationDarshana JainNo ratings yet
- Thermo MCQDocument23 pagesThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Hagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesDocument48 pagesHagedorn-Brown Correlation: Multi-Phase Flow in PipesFarah Taha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- ABB-LVP in High AltitudesDocument13 pagesABB-LVP in High AltitudesRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERSDocument79 pagesTRANSDUCERSregi destawanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Apparatus and Devices Laboratory Exercise 1 TransformerDocument17 pagesElectrical Apparatus and Devices Laboratory Exercise 1 TransformerMary Grace CuevaNo ratings yet
- Multistage and Poly Stage ConverterDocument22 pagesMultistage and Poly Stage ConverterkirthikNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids (MRH)Document49 pagesCarboxylic Acids (MRH)Ali Akand AsifNo ratings yet