Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Based Audit of FS
Risk Based Audit of FS
Uploaded by
NavsCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Activity 6Document12 pagesActivity 6danica gomezNo ratings yet
- Accounting Abm 12Document9 pagesAccounting Abm 12veronica aban0% (1)
- CA Final Audit RISK ASSESSMENT AND INTERNAL CONTROL NotesDocument21 pagesCA Final Audit RISK ASSESSMENT AND INTERNAL CONTROL NotesSARASWATHI S100% (1)
- Chapter 11 A Risk Based Audit Approach - PPT 302925165Document12 pagesChapter 11 A Risk Based Audit Approach - PPT 302925165Clar Aaron Bautista50% (2)
- Test 1 Aud679Document2 pagesTest 1 Aud679Izham Asri100% (1)
- Cash Disbursement PolicyDocument5 pagesCash Disbursement PolicyRia Dumapias100% (1)
- Risk Assesment & Internal ControlDocument56 pagesRisk Assesment & Internal Controlkaran kapadiaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Risk AssessmentDocument35 pagesCH 4 - Risk AssessmentSUMIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AuditDocument9 pagesReviewer AuditElisha BascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - : - Risk Assessment and Internal ControlDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - : - Risk Assessment and Internal ControlTamanna AroraNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementDocument3 pagesLS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- 4 5850471109056532138Document39 pages4 5850471109056532138Yehualashet MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Risk and MaterialityDocument4 pagesRisk and MaterialitymsyllNo ratings yet
- Ca PDFDocument3 pagesCa PDFHindutav aryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Risk Assement & Internal ControlDocument54 pagesChapter 3 Risk Assement & Internal ControlRohit Kumar SantukaNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReviewerDocument2 pagesAuditing ReviewerQueenie de BorjaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 24, 2022Document14 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 24, 2022Emmanuel PenullarNo ratings yet
- AKSK - Sesi#4 - Risk & ControlDocument20 pagesAKSK - Sesi#4 - Risk & Controlantia saraswatiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 - Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageGROUP 8 - Risk AssessmentRhad Lester C. MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Assessing Risks of Material MisstatementsDocument2 pagesIdentifying and Assessing Risks of Material MisstatementsCattleyaNo ratings yet
- AT 4 Audit Risk and MaterialityDocument6 pagesAT 4 Audit Risk and MaterialityLhea ClomaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3e - Risk and MaterialityDocument33 pagesTOPIC 3e - Risk and MaterialityLANGITBIRUNo ratings yet
- 74937bos60526-Cp4 UnlockedDocument72 pages74937bos60526-Cp4 Unlockedhrudaya boysNo ratings yet
- IAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Document16 pagesIAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Bianca Marie PedrozoNo ratings yet
- Audit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & ADocument86 pagesAudit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & Asantosh pandeyNo ratings yet
- SA Flowcharts 2Document33 pagesSA Flowcharts 2partymonger71% (7)
- Audit PlanningDocument22 pagesAudit Planningdomenick sadamaNo ratings yet
- Internal Control DocumentationDocument42 pagesInternal Control DocumentationJhoe Marie Balintag100% (1)
- Types of Audits: Audit - An OverviewDocument31 pagesTypes of Audits: Audit - An OverviewRanel Clark D. TabiosNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasYuliana rahayuNo ratings yet
- AUDITING Concepts & ApplicationsDocument2 pagesAUDITING Concepts & ApplicationsClarish S. TanNo ratings yet
- AACONAPPS1 - Chapter 8 - Overview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessDocument15 pagesAACONAPPS1 - Chapter 8 - Overview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessClarisse Angela PostreNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlDocument34 pagesEvaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlClene DoconteNo ratings yet
- Midterms 2Document2 pagesMidterms 2moreNo ratings yet
- Audit Charts FullDocument80 pagesAudit Charts FullsummaiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Risk Assessment & Internal ControlDocument1 pageChapter 3 - Risk Assessment & Internal Controlthuzh007No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsDocument6 pagesAuditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Kitcb D01.nhóm 7Document44 pagesKitcb D01.nhóm 7Mạnh hưng LêNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Knowledge of The BusinessDocument10 pages3.2.2 Knowledge of The BusinessAkkamaNo ratings yet
- Aa 3101Document3 pagesAa 3101Lance UrichNo ratings yet
- Audit RiskDocument17 pagesAudit RiskStephenly TongganoNo ratings yet
- Chapter+2+ +Audit+Planning+and+Internal+Controls+Considerations+ +part+1Document16 pagesChapter+2+ +Audit+Planning+and+Internal+Controls+Considerations+ +part+1Dan MorettoNo ratings yet
- At.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDocument10 pagesAt.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Blessed OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Materiality, Risk Assessment and IC - QRDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Materiality, Risk Assessment and IC - QRAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amendments For May 2021: Chapter 1: Quality Control and Engagement StandardsDocument13 pagesAmendments For May 2021: Chapter 1: Quality Control and Engagement StandardsSneha BharathiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Internal Control - E-NotesDocument55 pagesRisk Assessment and Internal Control - E-NotesManavNo ratings yet
- Qna IvDocument3 pagesQna Ivparrishya7No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - A017 2010 IAASB Handbook ISA 315Document13 pagesMicrosoft Word - A017 2010 IAASB Handbook ISA 315JENNETH AMINAO CASINONo ratings yet
- AT.3608 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control RiskDocument9 pagesAT.3608 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control Riskrichshielanghag627No ratings yet
- Relationship of Objectives To Risk Assessment & Control ActivitiesDocument2 pagesRelationship of Objectives To Risk Assessment & Control ActivitiesHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Role of Auditing: Introduction - Regulatory FrameworkDocument19 pagesRole of Auditing: Introduction - Regulatory FrameworkGabrielle AndreaNo ratings yet
- AT.111 - Undestanding The Entity's Internal ControlDocument6 pagesAT.111 - Undestanding The Entity's Internal Controlandrew dacullaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F8知识要点汇总 (上)Document37 pagesACCA F8知识要点汇总 (上)Freya SunNo ratings yet
- Auditorsdesk EQCR Reporting ChecklistDocument5 pagesAuditorsdesk EQCR Reporting ChecklistHARSHA REDDYNo ratings yet
- AU 9 Consideration of ICDocument11 pagesAU 9 Consideration of ICJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5AHMAD FAIZUL ADAM BIN MD NOOR (BG)No ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument4 pagesAudit Planningneo14No ratings yet
- Section 3: Appendix: 1. Audit Checklist: Risk Management ProcessDocument3 pagesSection 3: Appendix: 1. Audit Checklist: Risk Management Processpgupta101No ratings yet
- Major Phases of AuditDocument8 pagesMajor Phases of AuditCamille SantosNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Entity and Its Environment: Phase I-CDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Entity and Its Environment: Phase I-CMarjorieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document3 pagesChapter 01John Rey EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Fair Lending Compliance: Intelligence and Implications for Credit Risk ManagementFrom EverandFair Lending Compliance: Intelligence and Implications for Credit Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XDocument3 pagesLAW Title XNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIVDocument3 pagesLAW Title XIVNavsNo ratings yet
- Prelim-Exam REVIEWERDocument56 pagesPrelim-Exam REVIEWERNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVIIDocument3 pagesLAW Title XVIINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title IXDocument4 pagesLAW Title IXNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIIIDocument8 pagesLAW Title XIIINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIDocument4 pagesLAW Title XINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW2Document41 pagesLAW2NavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVIDocument4 pagesLAW Title XVINavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Financial Assets and Amortized CostDocument3 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Financial Assets and Amortized CostNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVDocument4 pagesLAW Title XVNavsNo ratings yet
- What Lies Beneath The Temptation: by Kathleah P. ErmitaDocument2 pagesWhat Lies Beneath The Temptation: by Kathleah P. ErmitaNavsNo ratings yet
- What Lies Beneath The TemptationDocument2 pagesWhat Lies Beneath The TemptationNavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Investments in Associates and Additional ConceptsDocument2 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Investments in Associates and Additional ConceptsNavsNo ratings yet
- The Son of Man Has Come To Seek and Save The LostDocument2 pagesThe Son of Man Has Come To Seek and Save The LostNavsNo ratings yet
- What Are Special JournalsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Special JournalsNavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Receivable FinancingDocument2 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Receivable FinancingNavsNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument4 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Cues Notes: 1. Introduction To Accounting ProcessDocument2 pagesCues Notes: 1. Introduction To Accounting ProcessNavsNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument6 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Intermediate Accounting Delinquent SharesDocument2 pagesLecture Notes Intermediate Accounting Delinquent SharesNavsNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice Santika TMIIDocument4 pagesProforma Invoice Santika TMIIAngga Ciro BamsNo ratings yet
- Problem 15-4 Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesProblem 15-4 Multiple ChoiceMobi Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Non-Current AssetsDocument6 pagesNon-Current AssetsMaryam EhsanNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorDocument20 pagesModule - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- English Assignment: Name: Fioren Patricia Venesa Kaunang ID No. 19304036 Accounting A, Sem 3Document3 pagesEnglish Assignment: Name: Fioren Patricia Venesa Kaunang ID No. 19304036 Accounting A, Sem 3Fioren KaunangNo ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemmas in Artificial Intelligence Development - EditedDocument3 pagesEthical Dilemmas in Artificial Intelligence Development - EditedPoetic YatchyNo ratings yet
- e-StatementBRImo 385201001647508 Nov2023 20231117 133133Document2 pagese-StatementBRImo 385201001647508 Nov2023 20231117 133133yazidfadillah2019No ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument11 pagesCash Flow StatementDuke CyraxNo ratings yet
- Ac110 24032023Document4 pagesAc110 24032023Lyana InaniNo ratings yet
- Limba Engleza Si Comunicare de Specialitate I Si II - Suport de Curs IDDocument120 pagesLimba Engleza Si Comunicare de Specialitate I Si II - Suport de Curs IDLuizaNo ratings yet
- Kang Gray (2011)Document31 pagesKang Gray (2011)Oshiie AeNo ratings yet
- LM Publications Catalogue 2019 2020 JuneDocument15 pagesLM Publications Catalogue 2019 2020 Junekucing kerongNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument12 pagesManagement Information SystemAssad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Solution MERGER & ACQUISITION, CA-FINAL-SFM by CA PRAVINN MAHAJANDocument51 pagesSolution MERGER & ACQUISITION, CA-FINAL-SFM by CA PRAVINN MAHAJANPravinn_Mahajan80% (5)
- Problem ADocument3 pagesProblem ALisel SalibioNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Ifrs: Consolidated Financial Statements: Redefining ControlDocument80 pagesPractical Guide To Ifrs: Consolidated Financial Statements: Redefining Controldavidwijaya1986No ratings yet
- Go Airways Private LimitedDocument62 pagesGo Airways Private Limitedshubham ranaNo ratings yet
- Add'l Exercises For Merchandising - Jenny Boo, 12 Dwight MoodyDocument6 pagesAdd'l Exercises For Merchandising - Jenny Boo, 12 Dwight MoodyJenny BooNo ratings yet
- Theory Mas OverviewDocument6 pagesTheory Mas OverviewAdrian RoxasNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping Lesson 1 Different Book AccountsDocument19 pagesBookkeeping Lesson 1 Different Book AccountsAiram EtteniotnaNo ratings yet
- Aman SharmaDocument2 pagesAman SharmaRachin PandeyNo ratings yet
- Romney Ais14 CH 16 General Ledger and Reporting SystemDocument11 pagesRomney Ais14 CH 16 General Ledger and Reporting SystemHabteweld EdluNo ratings yet
- Rais12 SM CH11Document24 pagesRais12 SM CH11Hero BirawanNo ratings yet
- New GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Document29 pagesNew GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Tani ShabNo ratings yet
- resume - بالعربىDocument2 pagesresume - بالعربىsherifsss7001No ratings yet
- Terminal Sample 2 SolvedDocument11 pagesTerminal Sample 2 SolvedFami FamzNo ratings yet
- IASDocument12 pagesIASJeanne Therese Miranda100% (1)
Risk Based Audit of FS
Risk Based Audit of FS
Uploaded by
NavsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Based Audit of FS
Risk Based Audit of FS
Uploaded by
NavsCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Note: A higher risk of material misstatement will require the
auditor to perform more effective and extensive audit
Identifying and Assessing Risks of Material procedures.
Misstatements (RoMM) through Understanding the
4. Determine the acceptable level of Audit Risk
Entity and its Environment
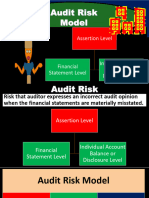
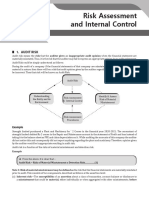
Audit risk is the risk that the auditor gives an inappropriate
Risk assessment procedures are audit procedures performed
audit opinion when the financial statements are materially
to obtain an understanding of the entity and its environment,
misstated.
including the entity’s internal control, to identify and assess the
risks of material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, at
the financial statement and assetion levels. Components of Audit Risk
Inherent Risk Control Risk Detection Risk
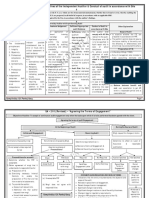
1. Obtain an understanding of the following:
i. Entity and its environment (the entity’s organizational • the susceptibility of an • is the possibility that • the risk that the
ABCOTD to a misstatement will auditor's
structure, ownership and governance, and its business misstatement before
consideration of any not be prevented or substantive
model, IT integration; industry, regulatory, and other related controls detected and procedures will not
corrected on a detect a
external factors; the measures used to assess the • Examples: timely basis by the misstatement that
Susceptibility to theft or accounting and exists in an
entity’s financial performance) fraudulent reporting, internal control ABCOTD that could
Complex accounting or systems be material
ii. Applicable financial reporting framework and calculations, Need for
judgment
accounting policies
iii. Entity’s system of internal control
The main purpose of the risk assessment procedures is to
enhance the understanding of the entity in order to The determination of acceptable level of audit risk is a matter of
specifically identify the applicable further audit professional judgment to be made by the auditor.
procedures (e.g. test of controls and substantive testing) and
to appropriately respond to the different risks assessed
5. Identify Detection Risk to determine the nature, timing and
related to the audit.
extent of further audit procedures
Detection risk is the function of the effectiveness of audit
procedures. When the auditor implements effective audit
procedures, detection risk will be low since there is a greater
possibility that the misstatement will be detected.
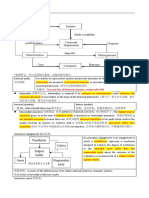
SCENARIO
Through the understanding of the entity obtained by the auditor
during planning actvities, there was ann increase in the assessed
level of control risk. How will this affect the different components
of audit risk?
The above scenario will require for a decrease in dectection
risk in order to maintain the acceptable level of audit risk.
Since the auditor only assesses the levels of IR and CR, the only
2. Consider Materiality way to maintain the acceptable level of audit risk when there is
Information is material if its omission or misstatement could an increase in CR is to change DR.
influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of
Lower DR Higher DR
the financial statements.
Nature More effective Less effective
procedures may be procedures may be
The concept of materiality is applied by the auditor in evaluating
applied applied
the effect of identified misstatements on the audit and of
uncorrected misstatements on the FS, and in forming the opinion Timing Procedures will be Procedures will be
of the auditor’s report. performed closer or performed at interim or
nearer to year-end several dates
Note: The lower materiality set will generally require the auditor Extent Larger sample size will Smaller sample size will
to perform more effective and extensive audit procedures. be tested be tested
3. Identify and Assess RoMMs
Using the unerstanding of the entity and its environment,
including its internal control, the auditor identifies and assesses
the risk of material misstatement at the following levels:
• risk of revenue overstatement due to cut-
Assertion off [assertion] error
• risk of understatement of trade payables
Level due to unrecorded purchase invoices
[completeness]
Financial
• risk that entity is not a going concern
Statement • significant risks of management fraud
Level
You might also like
- Activity 6Document12 pagesActivity 6danica gomezNo ratings yet
- Accounting Abm 12Document9 pagesAccounting Abm 12veronica aban0% (1)
- CA Final Audit RISK ASSESSMENT AND INTERNAL CONTROL NotesDocument21 pagesCA Final Audit RISK ASSESSMENT AND INTERNAL CONTROL NotesSARASWATHI S100% (1)
- Chapter 11 A Risk Based Audit Approach - PPT 302925165Document12 pagesChapter 11 A Risk Based Audit Approach - PPT 302925165Clar Aaron Bautista50% (2)
- Test 1 Aud679Document2 pagesTest 1 Aud679Izham Asri100% (1)
- Cash Disbursement PolicyDocument5 pagesCash Disbursement PolicyRia Dumapias100% (1)
- Risk Assesment & Internal ControlDocument56 pagesRisk Assesment & Internal Controlkaran kapadiaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Risk AssessmentDocument35 pagesCH 4 - Risk AssessmentSUMIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AuditDocument9 pagesReviewer AuditElisha BascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - : - Risk Assessment and Internal ControlDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - : - Risk Assessment and Internal ControlTamanna AroraNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementDocument3 pagesLS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- 4 5850471109056532138Document39 pages4 5850471109056532138Yehualashet MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Risk and MaterialityDocument4 pagesRisk and MaterialitymsyllNo ratings yet
- Ca PDFDocument3 pagesCa PDFHindutav aryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Risk Assement & Internal ControlDocument54 pagesChapter 3 Risk Assement & Internal ControlRohit Kumar SantukaNo ratings yet
- Auditing ReviewerDocument2 pagesAuditing ReviewerQueenie de BorjaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 24, 2022Document14 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 24, 2022Emmanuel PenullarNo ratings yet
- AKSK - Sesi#4 - Risk & ControlDocument20 pagesAKSK - Sesi#4 - Risk & Controlantia saraswatiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 - Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageGROUP 8 - Risk AssessmentRhad Lester C. MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Assessing Risks of Material MisstatementsDocument2 pagesIdentifying and Assessing Risks of Material MisstatementsCattleyaNo ratings yet
- AT 4 Audit Risk and MaterialityDocument6 pagesAT 4 Audit Risk and MaterialityLhea ClomaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3e - Risk and MaterialityDocument33 pagesTOPIC 3e - Risk and MaterialityLANGITBIRUNo ratings yet
- 74937bos60526-Cp4 UnlockedDocument72 pages74937bos60526-Cp4 Unlockedhrudaya boysNo ratings yet
- IAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Document16 pagesIAASB ISA 315 Revised 2019Bianca Marie PedrozoNo ratings yet
- Audit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & ADocument86 pagesAudit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & Asantosh pandeyNo ratings yet
- SA Flowcharts 2Document33 pagesSA Flowcharts 2partymonger71% (7)
- Audit PlanningDocument22 pagesAudit Planningdomenick sadamaNo ratings yet
- Internal Control DocumentationDocument42 pagesInternal Control DocumentationJhoe Marie Balintag100% (1)
- Types of Audits: Audit - An OverviewDocument31 pagesTypes of Audits: Audit - An OverviewRanel Clark D. TabiosNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasYuliana rahayuNo ratings yet
- AUDITING Concepts & ApplicationsDocument2 pagesAUDITING Concepts & ApplicationsClarish S. TanNo ratings yet
- AACONAPPS1 - Chapter 8 - Overview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessDocument15 pagesAACONAPPS1 - Chapter 8 - Overview of Risk-Based Audit ProcessClarisse Angela PostreNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlDocument34 pagesEvaluating The Design and Effectiveness of Internal ControlClene DoconteNo ratings yet
- Midterms 2Document2 pagesMidterms 2moreNo ratings yet
- Audit Charts FullDocument80 pagesAudit Charts FullsummaiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Risk Assessment & Internal ControlDocument1 pageChapter 3 - Risk Assessment & Internal Controlthuzh007No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsDocument6 pagesAuditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Kitcb D01.nhóm 7Document44 pagesKitcb D01.nhóm 7Mạnh hưng LêNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Knowledge of The BusinessDocument10 pages3.2.2 Knowledge of The BusinessAkkamaNo ratings yet
- Aa 3101Document3 pagesAa 3101Lance UrichNo ratings yet
- Audit RiskDocument17 pagesAudit RiskStephenly TongganoNo ratings yet
- Chapter+2+ +Audit+Planning+and+Internal+Controls+Considerations+ +part+1Document16 pagesChapter+2+ +Audit+Planning+and+Internal+Controls+Considerations+ +part+1Dan MorettoNo ratings yet
- At.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDocument10 pagesAt.3215 - Considering The Risk of Frauds Errors and NOCLARDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Blessed OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Materiality, Risk Assessment and IC - QRDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Materiality, Risk Assessment and IC - QRAnkita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amendments For May 2021: Chapter 1: Quality Control and Engagement StandardsDocument13 pagesAmendments For May 2021: Chapter 1: Quality Control and Engagement StandardsSneha BharathiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Internal Control - E-NotesDocument55 pagesRisk Assessment and Internal Control - E-NotesManavNo ratings yet
- Qna IvDocument3 pagesQna Ivparrishya7No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - A017 2010 IAASB Handbook ISA 315Document13 pagesMicrosoft Word - A017 2010 IAASB Handbook ISA 315JENNETH AMINAO CASINONo ratings yet
- AT.3608 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control RiskDocument9 pagesAT.3608 - Considering Internal Controls and Assessing Control Riskrichshielanghag627No ratings yet
- Relationship of Objectives To Risk Assessment & Control ActivitiesDocument2 pagesRelationship of Objectives To Risk Assessment & Control ActivitiesHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Role of Auditing: Introduction - Regulatory FrameworkDocument19 pagesRole of Auditing: Introduction - Regulatory FrameworkGabrielle AndreaNo ratings yet
- AT.111 - Undestanding The Entity's Internal ControlDocument6 pagesAT.111 - Undestanding The Entity's Internal Controlandrew dacullaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F8知识要点汇总 (上)Document37 pagesACCA F8知识要点汇总 (上)Freya SunNo ratings yet
- Auditorsdesk EQCR Reporting ChecklistDocument5 pagesAuditorsdesk EQCR Reporting ChecklistHARSHA REDDYNo ratings yet
- AU 9 Consideration of ICDocument11 pagesAU 9 Consideration of ICJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5AHMAD FAIZUL ADAM BIN MD NOOR (BG)No ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument4 pagesAudit Planningneo14No ratings yet
- Section 3: Appendix: 1. Audit Checklist: Risk Management ProcessDocument3 pagesSection 3: Appendix: 1. Audit Checklist: Risk Management Processpgupta101No ratings yet
- Major Phases of AuditDocument8 pagesMajor Phases of AuditCamille SantosNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Entity and Its Environment: Phase I-CDocument1 pageUnderstanding The Entity and Its Environment: Phase I-CMarjorieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document3 pagesChapter 01John Rey EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Fair Lending Compliance: Intelligence and Implications for Credit Risk ManagementFrom EverandFair Lending Compliance: Intelligence and Implications for Credit Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XDocument3 pagesLAW Title XNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIVDocument3 pagesLAW Title XIVNavsNo ratings yet
- Prelim-Exam REVIEWERDocument56 pagesPrelim-Exam REVIEWERNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVIIDocument3 pagesLAW Title XVIINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title IXDocument4 pagesLAW Title IXNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIIIDocument8 pagesLAW Title XIIINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XIDocument4 pagesLAW Title XINavsNo ratings yet
- LAW2Document41 pagesLAW2NavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVIDocument4 pagesLAW Title XVINavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Financial Assets and Amortized CostDocument3 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Financial Assets and Amortized CostNavsNo ratings yet
- LAW Title XVDocument4 pagesLAW Title XVNavsNo ratings yet
- What Lies Beneath The Temptation: by Kathleah P. ErmitaDocument2 pagesWhat Lies Beneath The Temptation: by Kathleah P. ErmitaNavsNo ratings yet
- What Lies Beneath The TemptationDocument2 pagesWhat Lies Beneath The TemptationNavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Investments in Associates and Additional ConceptsDocument2 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Investments in Associates and Additional ConceptsNavsNo ratings yet
- The Son of Man Has Come To Seek and Save The LostDocument2 pagesThe Son of Man Has Come To Seek and Save The LostNavsNo ratings yet
- What Are Special JournalsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Special JournalsNavsNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Answer Key Quiz - Receivable FinancingDocument2 pagesAccounting - Answer Key Quiz - Receivable FinancingNavsNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument4 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Cues Notes: 1. Introduction To Accounting ProcessDocument2 pagesCues Notes: 1. Introduction To Accounting ProcessNavsNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument6 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Intermediate Accounting Delinquent SharesDocument2 pagesLecture Notes Intermediate Accounting Delinquent SharesNavsNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice Santika TMIIDocument4 pagesProforma Invoice Santika TMIIAngga Ciro BamsNo ratings yet
- Problem 15-4 Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesProblem 15-4 Multiple ChoiceMobi Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Non-Current AssetsDocument6 pagesNon-Current AssetsMaryam EhsanNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorDocument20 pagesModule - 2 Auditor'S Report: Objectives of The AuditorVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- English Assignment: Name: Fioren Patricia Venesa Kaunang ID No. 19304036 Accounting A, Sem 3Document3 pagesEnglish Assignment: Name: Fioren Patricia Venesa Kaunang ID No. 19304036 Accounting A, Sem 3Fioren KaunangNo ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemmas in Artificial Intelligence Development - EditedDocument3 pagesEthical Dilemmas in Artificial Intelligence Development - EditedPoetic YatchyNo ratings yet
- e-StatementBRImo 385201001647508 Nov2023 20231117 133133Document2 pagese-StatementBRImo 385201001647508 Nov2023 20231117 133133yazidfadillah2019No ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument11 pagesCash Flow StatementDuke CyraxNo ratings yet
- Ac110 24032023Document4 pagesAc110 24032023Lyana InaniNo ratings yet
- Limba Engleza Si Comunicare de Specialitate I Si II - Suport de Curs IDDocument120 pagesLimba Engleza Si Comunicare de Specialitate I Si II - Suport de Curs IDLuizaNo ratings yet
- Kang Gray (2011)Document31 pagesKang Gray (2011)Oshiie AeNo ratings yet
- LM Publications Catalogue 2019 2020 JuneDocument15 pagesLM Publications Catalogue 2019 2020 Junekucing kerongNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument12 pagesManagement Information SystemAssad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Solution MERGER & ACQUISITION, CA-FINAL-SFM by CA PRAVINN MAHAJANDocument51 pagesSolution MERGER & ACQUISITION, CA-FINAL-SFM by CA PRAVINN MAHAJANPravinn_Mahajan80% (5)
- Problem ADocument3 pagesProblem ALisel SalibioNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Ifrs: Consolidated Financial Statements: Redefining ControlDocument80 pagesPractical Guide To Ifrs: Consolidated Financial Statements: Redefining Controldavidwijaya1986No ratings yet
- Go Airways Private LimitedDocument62 pagesGo Airways Private Limitedshubham ranaNo ratings yet
- Add'l Exercises For Merchandising - Jenny Boo, 12 Dwight MoodyDocument6 pagesAdd'l Exercises For Merchandising - Jenny Boo, 12 Dwight MoodyJenny BooNo ratings yet
- Theory Mas OverviewDocument6 pagesTheory Mas OverviewAdrian RoxasNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping Lesson 1 Different Book AccountsDocument19 pagesBookkeeping Lesson 1 Different Book AccountsAiram EtteniotnaNo ratings yet
- Aman SharmaDocument2 pagesAman SharmaRachin PandeyNo ratings yet
- Romney Ais14 CH 16 General Ledger and Reporting SystemDocument11 pagesRomney Ais14 CH 16 General Ledger and Reporting SystemHabteweld EdluNo ratings yet
- Rais12 SM CH11Document24 pagesRais12 SM CH11Hero BirawanNo ratings yet
- New GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Document29 pagesNew GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Tani ShabNo ratings yet
- resume - بالعربىDocument2 pagesresume - بالعربىsherifsss7001No ratings yet
- Terminal Sample 2 SolvedDocument11 pagesTerminal Sample 2 SolvedFami FamzNo ratings yet
- IASDocument12 pagesIASJeanne Therese Miranda100% (1)