Professional Documents
Culture Documents
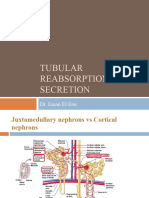
Lecture Objectives and Copy 5
Lecture Objectives and Copy 5
Uploaded by
mickey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe document discusses normal glucose, PAH, and urea processing by the nephron. Glucose is nearly 100% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule via transporters, though the transporters can become saturated leading to glucose spillage in the urine. Urea is partially reabsorbed passively in the proximal tubule. The key transport properties of the proximal tubule are also outlined, including its role in reabsorbing 65-70% of the glomerular filtrate isotonicly through tight coupling of water and sodium resorption.
Original Description:
bio
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses normal glucose, PAH, and urea processing by the nephron. Glucose is nearly 100% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule via transporters, though the transporters can become saturated leading to glucose spillage in the urine. Urea is partially reabsorbed passively in the proximal tubule. The key transport properties of the proximal tubule are also outlined, including its role in reabsorbing 65-70% of the glomerular filtrate isotonicly through tight coupling of water and sodium resorption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageLecture Objectives and Copy 5
Lecture Objectives and Copy 5
Uploaded by
mickeyThe document discusses normal glucose, PAH, and urea processing by the nephron. Glucose is nearly 100% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule via transporters, though the transporters can become saturated leading to glucose spillage in the urine. Urea is partially reabsorbed passively in the proximal tubule. The key transport properties of the proximal tubule are also outlined, including its role in reabsorbing 65-70% of the glomerular filtrate isotonicly through tight coupling of water and sodium resorption.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
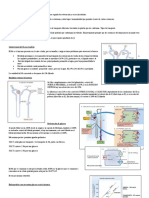
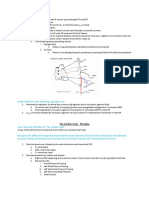
Diagram normal glucose processing by the nephron.
What are the limitations in glucose processing or any transporter mediated process?
Transporters can become saturated so the solute will spill into urine and get excreted instead of 100% reabsorbed
Diagram normal PAH processing by the nephron.
Diagram normal urea processing by the nephron.
Partial reabsorption?
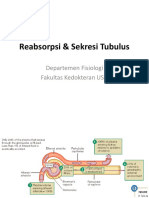
Proximal Tubule Isotonic Reabsorption Wednesday
List the key transport properties of the proximal tubule.
1. 65-70% of the glomerular filtrate is normally reabsorbed here. The reabsorbate is always isosmotic.
a. Isosmotic Resorption- tight coupling between water and Na resorption
2. Where sugars, amino acids, metabolic intermediates, etc., are nearly 100% reabsorbed, and where organic acids and
bases are secreted.
3. Urea is partially reabsorbed here- passive mechanism.
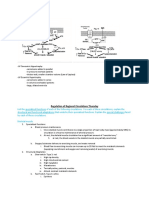
4. The tight junctions of the epithelium are very leaky to Na+ and Cl–
a. Therefore, the electrochemical gradients of Na+ and Cl– across the junctions significantly affects the
amount of filtrate absorbed.
5. Solute reabsorption in the late proximal tubule uses quite different mechanisms than in early proximal tubule.
a. Reabsorption is rate-limited by uptake of fluid by the peritubular capillaries. Peritubular hemodynamic
forces modulate net reabsorption.
6. The proximal tubule exhibits glomerulotubular balance.
You might also like
- Cerner Basic Competencies 08-2019Document195 pagesCerner Basic Competencies 08-2019mickeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 GuytonDocument6 pagesChapter 27 GuytonGabriella ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- (PHYSIO B) 1.2 Renal Physio Pt. 3Document8 pages(PHYSIO B) 1.2 Renal Physio Pt. 3miguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Lecture ObjectivesCopy 6Document2 pagesLecture ObjectivesCopy 6mickeyNo ratings yet
- L5&6-Tubular Reabsorption& SecretionDocument38 pagesL5&6-Tubular Reabsorption& SecretionsairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Manejo Tubular de SolutosDocument4 pagesManejo Tubular de SolutosAnghelussNo ratings yet
- GUS1-K6-Reabsorpsi & Sekresi TubulusDocument33 pagesGUS1-K6-Reabsorpsi & Sekresi TubulusMarieta RitongaNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument21 pagesTubular Reabsorption and SecretionAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- SHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionDocument61 pagesSHS.108.Lect-10 Tubular ReabsorptionAzlan YasirNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption & SecretionDocument25 pagesTubular Reabsorption & SecretionRishabh DangiNo ratings yet
- Tubular ReabsorptionDocument42 pagesTubular Reabsorptionmina mounirNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology BY Dr. Olasupo. S. AdeniyiDocument6 pagesRenal Physiology BY Dr. Olasupo. S. AdeniyiUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- TubularDocument12 pagesTubularShana LeeNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryDocument34 pagesPart 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryFarah Bashar Al-RawachyNo ratings yet
- Reabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Document28 pagesReabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Ayesha IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Kidney DR SeenaaDocument15 pagesLec 2 - Kidney DR Seenaaحسين علاوي طاميNo ratings yet
- Applied Renal PhysiologyDocument18 pagesApplied Renal PhysiologyDamián ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument56 pagesRenal PhysiologyfinazkyaloNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal FunctionDocument52 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal Functionliakot prantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24. The Kidney.: 1. The Structure and Function of The NephronDocument8 pagesChapter 24. The Kidney.: 1. The Structure and Function of The NephronjeskevandiemenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 14th EdDocument90 pagesChapter 28 14th EdchayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation and Its CompositionDocument22 pagesUrine Formation and Its CompositionZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes and Renal FunctionDocument7 pagesElectrolytes and Renal FunctionUhjafwnuijhnfa KmerkgoeNo ratings yet
- REN Revision LectureDocument43 pagesREN Revision Lecturegyamfi.rolandNo ratings yet
- After Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able To - .Document59 pagesAfter Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able To - .Deepika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Excretion in InsectsDocument58 pagesExcretion in InsectsMani VasagamNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument29 pagesTubular Reabsorption and SecretionenriNo ratings yet
- Lec2-Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument18 pagesLec2-Tubular Reabsorption and Secretionمحمد يوسفNo ratings yet
- DCT and Collecting DuctDocument29 pagesDCT and Collecting DuctayeshaNo ratings yet
- Glomerular FiltrationDocument4 pagesGlomerular FiltrationJohn MusaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - The Urinary System: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument28 pagesChapter 19 - The Urinary System: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceSara SabraNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument195 pagesRenal System7bzhbznbdmNo ratings yet
- Transport Mech 09192011Document38 pagesTransport Mech 09192011Wesley SeeNo ratings yet
- Role of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D SiwaleDocument84 pagesRole of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D Siwalenoahngoma41No ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Renal Functions @BVSC6thDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of Renal Functions @BVSC6thDr. Prakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDocument49 pagesTubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- Distal Tubule Balance and Tubuloglomerular Feedback-Group 2Document42 pagesDistal Tubule Balance and Tubuloglomerular Feedback-Group 2Chuleha SethNo ratings yet
- Proximal Tubule Function and Response To Acidosis: Norman P. Curthoys and Orson W. MoeDocument12 pagesProximal Tubule Function and Response To Acidosis: Norman P. Curthoys and Orson W. Moehrol31060No ratings yet
- Inulin Clearance Is Indeed The Hallmark Method For Measuring GFRDocument12 pagesInulin Clearance Is Indeed The Hallmark Method For Measuring GFRVanathy KarunamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Handling of Certain Important Solutes by The Renal TubulesDocument14 pagesHandling of Certain Important Solutes by The Renal TubulesOsama MohamedNo ratings yet
- Physio 2Document6 pagesPhysio 2Mohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- L3 +L4 Renal System 2023Document31 pagesL3 +L4 Renal System 2023mizare29gNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base and Potassium HomeostasisDocument8 pagesAcid-Base and Potassium HomeostasisVeronica WongNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System 2013Document52 pagesThe Urinary System 2013adystiNo ratings yet
- 6-Drugs Acting On The Renal System - 2Document65 pages6-Drugs Acting On The Renal System - 2Hamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sistem UrinariaDocument51 pagesKuliah Sistem Urinaria6. Putu Arbita DivyaNo ratings yet
- Tubular Processing of The Glomerular FiltrateDocument8 pagesTubular Processing of The Glomerular FiltrateOsama MohamedNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation PDFDocument15 pagesUrine Formation PDFGene PabayosNo ratings yet
- Expt 29 Urine Formation PDFDocument15 pagesExpt 29 Urine Formation PDFGene PabayosNo ratings yet
- Expt. 29 Urine FormationDocument15 pagesExpt. 29 Urine Formationapi-3769252100% (5)
- Expt 29 Urine Formation PDFDocument15 pagesExpt 29 Urine Formation PDFGene PabayosNo ratings yet
- Renalphysiology3 150323053336 Conversion Gate01Document33 pagesRenalphysiology3 150323053336 Conversion Gate01Hema KamatNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Ery HermawatiDocument96 pagesUrinary System: Ery HermawatiAnonymous 8pxwZTNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesThe Urinary SystemMuhamed Shexbzeny100% (1)
- KidneyDocument25 pagesKidneytiba.qasem2000No ratings yet
- Kidney 2 AdelinaVladDocument65 pagesKidney 2 AdelinaVladGiorgos Doukas KaranasiosNo ratings yet
- Urinary System2Document23 pagesUrinary System2nasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Renal FunctionDocument2 pagesRenal FunctionlenoNo ratings yet
- L4 Regional Transport 2023Document4 pagesL4 Regional Transport 2023bgj9cddvxhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-5Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-5mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-7Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-7mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-3Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-3mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-4Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-4mickeyNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam Vital SignsDocument4 pagesPhysical Exam Vital SignsmickeyNo ratings yet
- 1 OutlineDocument5 pages1 OutlinemickeyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneyDocument53 pagesGastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneymickeyNo ratings yet