Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are The Important Topics of The General Anat
What Are The Important Topics of The General Anat
Uploaded by
Sanjeev Verma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThis document provides an overview of several topics in human anatomy and genetics. It discusses the stages of mitosis and types of genes and chromosomes. It also summarizes the skeletal system including bone structure and classification. Additionally, it reviews the circulatory system by comparing arteries and veins. Other systems covered include the lymphatic system, muscles, fascia, nervous system, skin, and connective tissues. Genetic disorders like Down syndrome and types of joints are also mentioned.
Original Description:
Anatomy mbbs first year
Original Title
What are the important topics of the General Anat…
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of several topics in human anatomy and genetics. It discusses the stages of mitosis and types of genes and chromosomes. It also summarizes the skeletal system including bone structure and classification. Additionally, it reviews the circulatory system by comparing arteries and veins. Other systems covered include the lymphatic system, muscles, fascia, nervous system, skin, and connective tissues. Genetic disorders like Down syndrome and types of joints are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageWhat Are The Important Topics of The General Anat
What Are The Important Topics of The General Anat
Uploaded by
Sanjeev VermaThis document provides an overview of several topics in human anatomy and genetics. It discusses the stages of mitosis and types of genes and chromosomes. It also summarizes the skeletal system including bone structure and classification. Additionally, it reviews the circulatory system by comparing arteries and veins. Other systems covered include the lymphatic system, muscles, fascia, nervous system, skin, and connective tissues. Genetic disorders like Down syndrome and types of joints are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1.
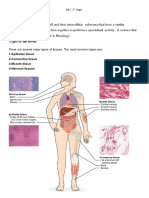
Genetics :
1. Stages of Mitosis : Prophase, Prometaphase,
Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
2. Types of Genes : Dominant and Recessive genes,
Carrier genes, Co-dominant gene, Sex-linked
genes, Sex-limited genes,Structural genes and
Regulatory genes.
3. Structure of chromosome : One Chromosome —
Two Chromatid.
4. Types of Chromosomes : Metacentric, Sub-
Metacentric and Acrocentric.
5. Barr Body(Sex chromatin) : This is an inactivated
X chromosome attached with the nuclear
membrane.
6. Karyotyping : Identification of chromosomes.
7. Down Syndrome : Also called Trisomy 21,
because there is trisomy of chromosome number
21.
8. Cri du chat Syndrome : Deletion of a part of ‘p’
arm in chromosome number 5.
9. Turner’s Syndrome : The genotype is 45X.
10. Klinefelter’s Syndrome : The genotype is 47
XXY.
11. Pedigree chart : To map chromosomal disorders
of a particular family.
12. Prenatal Diagnosis : This is the diagnosis of any
genetic abnormalities before the birth. This can be
done by various procedures like USG.
2. Skeletal System :
This mainly includes the bones and cartilages. The
whole framework of the body if formed by the skeletal
system.
1. Classification of Bones : Long bones, Short
bones, Flat bones, Irregular bones, Pneumatic
bones, Sesamoid bones and Accessory bones.
2. Gross Structure of an fully developed long
bone : Shaft(Periosteum, Cortex and the
Medullary cavity) and the two ends.
3. Parts of a developing bone : Epiphysis,
Diaphysis, Metaphysis and the Epiphyseal plate of
cartilage.
4. Blood Supply of the Bone : Arterial Supply of
Lone bones(Nutrient artery, Periosteal arteries,
epiphyseal arteries, Metaphysial arteries) and
Venous drainage.
5. Cartilage : Types(Hyaline cartilage, Fibrocartlage,
Elastic cartilage)
3. Joints :
These are the junctions between two or more bones.
1. Structural Classification : Fibrous Joint,
Cartilaginous joint and Synovial joint
4. Circulator System :
1. Components of the Circulatory System are : Heart,
Arteries, veins and Capillaries.
2. Types of Circulation of blood : systemic circulation,
Pulmonary circulation, portal circulation.
Arteries Veins
1. Carry oxygenated 1. Carry deoxygenated
blood(except pulmonary blood(except pulmonary
artery) from the heart. vein) to the heart.
2. Normally bright red in 2. Normally dark red in
color. color.
3. Walls are elastic and
3. Thin walls or less
thick that expand with
elastic.
surge of blood.
4. No valves are present 4. Valves are present.
5. Pulse can be felt. 5. Pulse cannot be felt.
5. Lymphatic System :
Immunity providing lymphatic system has mainly 6
components :
1. Lymph capillaries and lymph vessles
2. Central lymphoid tissues
3. Peripheralymphoid organs
4. Circulating lymphocytes
5. Epithelio-Lymphoid system
6. Mononuclear phagocyte system
6. Muscles and Fascia :
1. Types of Muscles : Striated/Skeletal, Non-
Striated/Smooth and Cardiac Muscles.
2. Parts of Muscle : Two ends(Origin & Insertion),
Two parts ( Fleshy part, Fibrous parts).
3. Nerve supply of Skeletal muscle : Motor nerve
fibres(60%), Sensory fibres(40%)
4. Nerve supply of smooth muscle : Single-unit
types and Multi-unit type.
1. Fascia are of two types : Superficial and Deep
fascia.
2. Superficial fascia : This ones are the general
covering of the body beneath the skin, made up of
loose areolar tissue with varying amount of fat.
3. Deep fascia : These are tough inelastic fibrous
sheet which invades the body beneath the
superficial fascia.
7. Nervous System :
Parts of the nervous system :
1. Central nervous system : Brain, Spinal cord
2. Peripheral nervous system : Cerebrospinal
nervous system and Peripheral autonomic nervous
system.
Cell types of the nervous system : Neuron and
Neuroglia
8. Skin :
This is the general covering of the entire covering of
the body.
1. Pigments of Skin : Melanin, Melanoid, Carotene,
Haemoglobin and Oxyhaemoglobin.
2. Structure of the Skin : Epidermis, Dermis.
3. Appendages of skin : Nails, Hair, Sweat glands,
Sebaceous glands.
9. Connective tissue :
Classification :
1. Loose connective tissue – Areolar tissue,
adipose tissue, myxomatous tissue and reticular
tissue.
2. Dense Irregular connective tissue – tendon,
Cartilage and bones.
10. Ligaments and Raphe :
Ligaments : these are fibrous bands connect the
adjacent bones.
Raphe : These are linear fibrous band formed by
interdigitation of the tendinous or aponeurotic ends
of the muscles, like the two lateral half of the
tongue.
You might also like
- Veterinary AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary AnatomyKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Biology Noteskatwal0986% (21)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes - Full CourseDocument278 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes - Full CourseJamye CarrNo ratings yet
- A&P1 Final Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesA&P1 Final Exam Study GuideRhett Clark100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- K02 Histology of Muscle TissueDocument43 pagesK02 Histology of Muscle TissueagnesNo ratings yet
- A&p 1Document44 pagesA&p 1HARI KRISHNA G LNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Lecture 2+lab 2Document19 pagesHISTOLOGY Lecture 2+lab 2anaNo ratings yet
- Histo SPMDocument11 pagesHisto SPMdizarroNo ratings yet
- Histology - Name QuestionsDocument12 pagesHistology - Name QuestionsMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Structure and Function of Animal TissueDocument32 pagesStructure and Function of Animal TissueFajar Oktavia RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Anatomy AdhyapakDocument50 pagesAnatomy AdhyapakChief Nike - Clash RoyaleNo ratings yet
- 1-Introductin To AnatomyDocument56 pages1-Introductin To AnatomyJoxNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Anatomyandphysiology 131001192714 Phpapp01Document80 pagesChapter3 Anatomyandphysiology 131001192714 Phpapp01zestie38No ratings yet
- 03 Human Anatomy 1st YearDocument9 pages03 Human Anatomy 1st Yearit's EimyNo ratings yet
- Histology SummaryDocument24 pagesHistology SummaryaelsehamyNo ratings yet
- Histology ExamDocument12 pagesHistology Exammahdia18No ratings yet
- Histology: The Study of TissuesDocument39 pagesHistology: The Study of TissuesEla Santos100% (1)
- ANATOMY Lab 1 Exam NotesDocument15 pagesANATOMY Lab 1 Exam Notesbreanna coyneNo ratings yet
- B 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramDocument27 pagesB 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramSANTHIYA A/P MOHANA SUNDARAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells in The Human BodyDocument34 pagesTypes of Cells in The Human BodyJiezel CastorNo ratings yet
- التشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةDocument10 pagesالتشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةبايNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells, Tissues, and Organs - Exercise 12Document53 pagesAnimal Cells, Tissues, and Organs - Exercise 12James SiazonNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- Lab3 Human Anatomy 1 YearDocument51 pagesLab3 Human Anatomy 1 Yearnatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- There Are Four 1 Tissues in The Body:: Tissue A Group of Cells and Cell Products With Similar Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesThere Are Four 1 Tissues in The Body:: Tissue A Group of Cells and Cell Products With Similar Structure and FunctionBurak KıvırcıkNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle TissueFady FadyNo ratings yet
- Course 4Document9 pagesCourse 4bordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Hewan (Animal Tissue)Document28 pagesJaringan Hewan (Animal Tissue)Adi GunawanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesBIOLOGYKimberling SandovalNo ratings yet
- Microanatomy - Nervous System, Sense OrgansDocument13 pagesMicroanatomy - Nervous System, Sense Organsamnashaikh0204No ratings yet
- 15th Proper 1301 SeqDocument21 pages15th Proper 1301 SeqAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document35 pagesLecture 1Mian Mudassar AkramNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerDocument111 pagesBio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerMedjugorje Beltran DalanNo ratings yet
- M2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!Document3 pagesM2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!deep.deepkNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceMark timothy LumanlanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- General Pathology, Histopathologic and Cytologic TechniquesDocument28 pagesGeneral Pathology, Histopathologic and Cytologic TechniquesMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- Lecture 10 Overview 1Document44 pagesLecture 10 Overview 1mariam tarek100% (1)
- Types of TissuesDocument7 pagesTypes of TissuesKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Revision 3Document63 pagesRevision 3hope55ui0No ratings yet
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Document33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmune SystemCasper Irra Marcos100% (1)
- Submitted By: Mia Jeanne D.Palencia Submitted To: Merlyn M. AdlawanDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Mia Jeanne D.Palencia Submitted To: Merlyn M. AdlawanMaryGracePalenciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Histo Plus INTEGUMEN For MidwifeDocument107 pagesBasic Histo Plus INTEGUMEN For MidwifeAuliya ShintaNo ratings yet
- Ati Teas 7 Anatomy and Physiology Review With Questions and AnswersDocument48 pagesAti Teas 7 Anatomy and Physiology Review With Questions and AnswersSAMUEL WAMNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideDocument19 pagesAnatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideChetfalkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture Exam Study Guides 1Document200 pagesAnatomy Lecture Exam Study Guides 1prabh647No ratings yet
- Syllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Document54 pagesSyllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Vanshika SethiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - HistologyDocument90 pagesCHAPTER 3 - HistologyObsan AbdiiNo ratings yet
- 4 Main Groupsof TissuesDocument98 pages4 Main Groupsof TissuesKenvyne Quides-CalugayNo ratings yet
- 5 Connective Tissue 1Document40 pages5 Connective Tissue 1miladsherwanyNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesBiology Exam ReviewKate Wen Guan100% (2)
- Spleen and Palatine TonsilsDocument19 pagesSpleen and Palatine TonsilsJana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Science Review Harr Robert R.Document28 pagesMedical Laboratory Science Review Harr Robert R.Arriel A. Aranggo50% (2)
- Lymphoid OrgansDocument4 pagesLymphoid OrgansJadys Merill DiezNo ratings yet
- L12 Nerves TissueDocument8 pagesL12 Nerves Tissueعلي اياد شبيب حناشNo ratings yet
- Grade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Document55 pagesGrade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Purvi Prakash KNo ratings yet
- Examination Questions and Answers in BasDocument505 pagesExamination Questions and Answers in Basdelton100% (1)
- A Connective - Tissue1 16 12 14 PDFDocument41 pagesA Connective - Tissue1 16 12 14 PDFShobhit GargNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Connective Tissue NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Connective Tissue NotesBinadi JayNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - TissuesDocument11 pagesModule 4 - TissuesArianne Mae VillajuanNo ratings yet
- Animal Form & FunctionDocument157 pagesAnimal Form & FunctionRenz Soledad100% (1)
- Lab Report 1. Tissues: Fig. 1: Mammal Artery and Vein - Cross SectionDocument11 pagesLab Report 1. Tissues: Fig. 1: Mammal Artery and Vein - Cross Sectionapi-3798860100% (5)
- Entire Tissues UnitDocument32 pagesEntire Tissues Unitnao_gataNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Images of Tissue Types and Answers To Unit 2 AssesmentDocument2 pagesConcept Map Images of Tissue Types and Answers To Unit 2 AssesmentChristian CortnerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- STM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesSTM 007 Gen Biology ReviewerAllessandra AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Xi STD Reduced Syllabus - 2021-22 by AmDocument52 pagesXi STD Reduced Syllabus - 2021-22 by AmTwelegyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument21 pagesConnective TissueCalvin Lin Jia RongNo ratings yet
- Histology Practical PDF Bytom CnaanDocument65 pagesHistology Practical PDF Bytom CnaanMichel MunozNo ratings yet
- Animal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" Cellsapi-25965241No ratings yet
- BIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Document11 pagesBIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Tonya Oliver100% (1)
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Human Anatomy Lab Manual 3rd Edition PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Human Anatomy Lab Manual 3rd Edition PDF Ebookdaniel.welton458100% (42)
- Ncert Master Stroke Booklet Volume - 2Document122 pagesNcert Master Stroke Booklet Volume - 2Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 7th Edition SherwoodDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 7th Edition SherwoodFreddie Woodyard100% (42)
- Chapter 10 Understanding Meats and GameDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Understanding Meats and GameLazaga RavenNo ratings yet
- How Ba Gua's 12 Standing Postures Open The Meridians - IAIDocument9 pagesHow Ba Gua's 12 Standing Postures Open The Meridians - IAIramvvugt12100% (1)
- AgingDocument12 pagesAgingKarapati lathaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Connective TissueDocument1 pageAnatomy: Connective TissueSyimah UmarNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in Animalssrinu.lichflNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet