Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G5 Plant Notes 1
G5 Plant Notes 1
Uploaded by
Hi ByeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- GR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesGR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerlegendarychampionthorNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Seed Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesSeed Structure and FunctionJohn AplerhNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument14 pagesGerminationPhoo Pyae Pyae KyawNo ratings yet
- Class-5 Science Plant ReproductionDocument4 pagesClass-5 Science Plant ReproductionSandeep Shaw100% (1)
- Agr122 Lab Report 4Document8 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- Cruise School, Addis Ababa: Science I Handout For Grade 6 Continued From Unit 4Document3 pagesCruise School, Addis Ababa: Science I Handout For Grade 6 Continued From Unit 4Dawit AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Science Book 1 Chapter 6Document49 pagesScience Book 1 Chapter 624 Jefferson Κoh JingNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document4 pagesExercise 5Cindy jabilloNo ratings yet
- Final SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2Document2 pagesFinal SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2l.a. lopezNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 STD 10Document19 pagesChapter 3 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Growing PlantsDocument4 pagesGrowing Plantsveerpat45No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsDocument23 pagesPlant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsJose CariasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeyDocument21 pagesChapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeySUHANEERIYA100% (1)
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- Seed Report OutlineDocument2 pagesSeed Report OutlineAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- Bio Project 12Document28 pagesBio Project 12sounav biswasNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument7 pagesSeed Germinationganeshbalak2000No ratings yet
- Biology Ss3 Weeks7-9Document7 pagesBiology Ss3 Weeks7-9Oshokeonoso MaizaNo ratings yet
- FORM 5 6.0 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument37 pagesFORM 5 6.0 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsIsmail ZueNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- What Do Beans, Tomatoes, Cucumbers, and Okra Have in Common?: All of These Are Containing SeedsDocument18 pagesWhat Do Beans, Tomatoes, Cucumbers, and Okra Have in Common?: All of These Are Containing SeedsClemente MontillaNo ratings yet
- Class7 Answers CH 12Document4 pagesClass7 Answers CH 12Vibhuti Bhushan RaiNo ratings yet
- 1506231856511463Document3 pages1506231856511463chikenbiriyanieaterNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Sauri ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SeedDocument1 pageParts of SeedScarlet Danielle CASASNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyMark Allen L. VicenteNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Development: Lesson 2Document10 pagesPlant and Animal Development: Lesson 2hellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- CL 6 - SciDocument2 pagesCL 6 - SciK BhaiNo ratings yet
- Flowers and ReproductionDocument19 pagesFlowers and ReproductionRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Seeds and Germination - : Seed StructureDocument1 pageSeeds and Germination - : Seed StructureSundari Murugan50% (2)
- FRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerDocument4 pagesFRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerRona Mae JavateNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsasadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- All Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSDocument65 pagesAll Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument47 pagesBiology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsjackieaj093No ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- CPT 103 - Lecture3Document71 pagesCPT 103 - Lecture3Esperanza CañaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionDocument18 pages12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionJorifNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Document25 pagesBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufNo ratings yet
- All Types of SeedsDocument1 pageAll Types of SeedsIsmaël BikomamangaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Plantstex dibasNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- ASEXUAL: The Development of New Individual With Out The Fusion of MaleDocument10 pagesASEXUAL: The Development of New Individual With Out The Fusion of MaleRobert HookeNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SEED - PartiDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SEED - Partichristian capunongNo ratings yet
- How Plant Grow and ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Plant Grow and ReproduceFrinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- g12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024Document13 pagesg12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024mwashikakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. SEEDDocument3 pagesLesson 13. SEEDSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Growth and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNotes - Growth and DevelopmentNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- PERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesDocument11 pagesPERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesErnie Rosemarie T. BucalenNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksFrom EverandHow Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksNo ratings yet
G5 Plant Notes 1
G5 Plant Notes 1
Uploaded by
Hi ByeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G5 Plant Notes 1
G5 Plant Notes 1
Uploaded by
Hi ByeCopyright:
Available Formats
GRADE V
SCIENCE
THEME-PLANTS
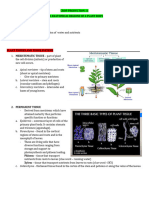
Internal Structure of a Seed
1. Seed coat- It is tough and waterproof. It covers and protects the embryo and food supply.
2. Embryo- It is the baby plant that has two parts-
a.Plumule- It grows upwards into stem, leaf, etc and forms the shoot system.
b.Radicle- It grows downwards into the ground and forms root system.
3. Cotyledons/Endosperm- These are also called seed leaves. These are parts of seed that contains
allthe food supply for embryo.
*Seeds with one cotyledon are called monocots or monocotyledons.
* Seeds with two cotyledons are called dicots or dicotyledons.
Difference between monocot and dicot seeds
Monocots Dicots
1. These seeds have one seed leaf or cotyledon These seeds have two seed leaves or cotyledons.
2. Plants having monocot seeds have a hollow stem Plants having dicot seeds have a solid stem
3.Plants having monocot seeds have fibrous root system Plants having dicot seeds have taproot system
3. Examples- corn, wheat, rice etc Examples-Bean, moong dal etc.
The process of a seed developing into a seedling is called germination.The three elements essential for seed
germination and growth are:
Air
Water
Sunlight
The largest seed in the world is Coco de mer.
The smallest seed in the world is black mustard seed.
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- GR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesGR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerlegendarychampionthorNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Seed Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesSeed Structure and FunctionJohn AplerhNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument14 pagesGerminationPhoo Pyae Pyae KyawNo ratings yet
- Class-5 Science Plant ReproductionDocument4 pagesClass-5 Science Plant ReproductionSandeep Shaw100% (1)
- Agr122 Lab Report 4Document8 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- Cruise School, Addis Ababa: Science I Handout For Grade 6 Continued From Unit 4Document3 pagesCruise School, Addis Ababa: Science I Handout For Grade 6 Continued From Unit 4Dawit AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Science Book 1 Chapter 6Document49 pagesScience Book 1 Chapter 624 Jefferson Κoh JingNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document4 pagesExercise 5Cindy jabilloNo ratings yet
- Final SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2Document2 pagesFinal SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2l.a. lopezNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 STD 10Document19 pagesChapter 3 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Growing PlantsDocument4 pagesGrowing Plantsveerpat45No ratings yet
- Plant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsDocument23 pagesPlant Diversity: The Evolution and Classification of PlantsJose CariasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeyDocument21 pagesChapter-4 Growing Plants Question Bank With Answer KeySUHANEERIYA100% (1)
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- Seed Report OutlineDocument2 pagesSeed Report OutlineAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- Bio Project 12Document28 pagesBio Project 12sounav biswasNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument7 pagesSeed Germinationganeshbalak2000No ratings yet
- Biology Ss3 Weeks7-9Document7 pagesBiology Ss3 Weeks7-9Oshokeonoso MaizaNo ratings yet
- FORM 5 6.0 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument37 pagesFORM 5 6.0 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsIsmail ZueNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- What Do Beans, Tomatoes, Cucumbers, and Okra Have in Common?: All of These Are Containing SeedsDocument18 pagesWhat Do Beans, Tomatoes, Cucumbers, and Okra Have in Common?: All of These Are Containing SeedsClemente MontillaNo ratings yet
- Class7 Answers CH 12Document4 pagesClass7 Answers CH 12Vibhuti Bhushan RaiNo ratings yet
- 1506231856511463Document3 pages1506231856511463chikenbiriyanieaterNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Nov 2022Sauri ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SeedDocument1 pageParts of SeedScarlet Danielle CASASNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyMark Allen L. VicenteNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Development: Lesson 2Document10 pagesPlant and Animal Development: Lesson 2hellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- CL 6 - SciDocument2 pagesCL 6 - SciK BhaiNo ratings yet
- Flowers and ReproductionDocument19 pagesFlowers and ReproductionRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Seeds and Germination - : Seed StructureDocument1 pageSeeds and Germination - : Seed StructureSundari Murugan50% (2)
- FRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerDocument4 pagesFRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerRona Mae JavateNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsasadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- All Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSDocument65 pagesAll Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument47 pagesBiology CL 12 - Chapter 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsjackieaj093No ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- CPT 103 - Lecture3Document71 pagesCPT 103 - Lecture3Esperanza CañaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionDocument18 pages12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionJorifNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Document25 pagesBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufNo ratings yet
- All Types of SeedsDocument1 pageAll Types of SeedsIsmaël BikomamangaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Plantstex dibasNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- ASEXUAL: The Development of New Individual With Out The Fusion of MaleDocument10 pagesASEXUAL: The Development of New Individual With Out The Fusion of MaleRobert HookeNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SEED - PartiDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SEED - Partichristian capunongNo ratings yet
- How Plant Grow and ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Plant Grow and ReproduceFrinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- g12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024Document13 pagesg12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024mwashikakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. SEEDDocument3 pagesLesson 13. SEEDSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Notes - Growth and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNotes - Growth and DevelopmentNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- PERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesDocument11 pagesPERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesErnie Rosemarie T. BucalenNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- How Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksFrom EverandHow Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksNo ratings yet