Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1
Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Sanjeet KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1
Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Sanjeet KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
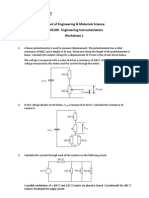
Department of Electrical Engineering
Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad
Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation (1st Sem) Assignment- 1
1. The torque of an ammeter varies as the square of the current through it. If a current of
5 A produces a deflection of 90º, what deflection will occur for a current of 3 A when
the instrument is (i) spring-controlled and (ii) gravity-controlled.
2. The inductance of a moving-iron ammeter with a full-scale deflection of 90° at 1.5 A
is given by L = (200 + 40θ - 4θ2 -θ3) μH where θ is the deflection in radian from the
zero position. Estimate the angular deflection of the pointer for a current of 1 A.
3. The law of deflection of a moving-iron ammeter is given by I = 4θn ampere, where θ is
the deflection in radian and n is a constant. The self-inductance when the meter current
is zero is 10 mH. The spring constant is 0.16 N-m/rad.
(a) Determine an expression for self-inductance of the meter as a function of θ and n.
(b)With n = 0.75, calculate the meter current and the deflection that corresponds to a
self-inductance of 60 mH.
4. A spring-controlled moving-iron voltmeter reads correctly on 250-V d.c. Calculate the
scale reading when 250-V a.c. is applied at 50 Hz. The instrument coil has a resistance
of 500 Ω and an inductance of 1 H and the series (non-reactive) resistance is 2000 Ω.
5. A moving-coil instrument has a resistance of 10 Ω and gives full-scale deflection when
carrying a current of 50 mA. Show how it can be adopted to measure voltage up to 750
V and currents upto 1000 A.
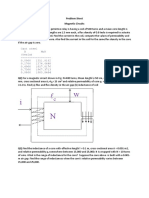
6. A permanent magnet moving-coil voltmeter gives full-scale deflection with a current
of 5 mA. The coil has 100 turns, effective depth of 3 cm and width of 2.5 cm. The
controlling torque of the spring is 0.5 cm for full-scale deflection. Estimate the flux
density in the gap.
7. A 50 V range spring-controlled electrodynamic voltmeter has an initial inductance of
0.25 H, the full scale deflection torque of 0.4 × 10-4 Nm and full scale deflection current
of 50 mA. Determine the difference between dc and 50 Hz ac reading at 50 volts if the
voltmeter inductance increases uniformly over the full scale of 90°.
8. Two wattmeters are connected to measure the power consumed by a 3-phase balanced
load. One of the wattmeters read 1500 Ω and the other 700 Ω. Find power factor of the
load, when (a) both the readings are positive, and (b) when the reading of the second
wattmeter is obtained after reversing its current coil connection.
9. A 230 V, single-phase watt hour meter records a constant load of 10 A for 4 hours at
unity power factor. If the meter disc makes 2760 revolutions during this period, what
is the meter constant in terms of revolutions per unit? Calculate the load power factor
if the number of revolutions made by the meter is 1104 when recording 5 A at 230 V
for 6 hours.
10. A dynamometer type wattmeter with its voltage coil connected across the load side of
the instrument reads 250 W. If the load voltage be 200 V, what power is being taken by
load? The voltage coil branch has a resistance of 2,000 Ω.
You might also like
- Classical Electromagnetism - H C VermaDocument526 pagesClassical Electromagnetism - H C VermaTushar Anand100% (3)
- Assignments StudentsDocument2 pagesAssignments StudentsManju Chakraborty100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 QDocument1 pageTutorial 2 QKaboyaone Keel KeelediweNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesDocument15 pagesPrinciplesvyronnekelly1No ratings yet
- Department of Instrumentation & Control EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Instrumentation & Control EngineeringBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Bee Theory and Nuerical Question BankDocument7 pagesBee Theory and Nuerical Question BankC1 314 Krishna GavaneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 PDFBala Subramanian50% (2)
- The Last ProblemsDocument4 pagesThe Last ProblemsAnirban SahaNo ratings yet
- End Sem 19-20Document2 pagesEnd Sem 19-20Soumya Ranjan NayakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 On Electromechanical InstrumentsDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 On Electromechanical InstrumentsSumit RaiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Sheet1Document2 pagesNumerical Sheet1debabratalogonNo ratings yet
- Measurement AssignmentDocument3 pagesMeasurement AssignmentAkash MittalNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFDocument56 pagesMeasurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFmadivala nagarajaNo ratings yet
- Engineering ContentDocument5 pagesEngineering ContentVikas ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MET-2.2 QuestionsDocument20 pagesMET-2.2 QuestionsApoorv SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic: Measuring Instrument Analogue InstrumentsDocument6 pagesTopic: Measuring Instrument Analogue InstrumentsParmanand AlvinNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect Galvanomter Into AmmterDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect Galvanomter Into Ammterpraveen godaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Xii Chapter 4,5,6Document7 pagesPhysics Xii Chapter 4,5,6SatvikNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 3Document6 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 3raghusabale1No ratings yet
- Magnetic Field-1Document1 pageMagnetic Field-1Muhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Bee 14 Question BankDocument10 pagesBee 14 Question BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- EDC NotesDocument47 pagesEDC NoteschitragowsNo ratings yet
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- R5310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument2 pagesR5310202 Electrical MeasurementssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment of EeeDocument4 pagesAssignment of EeeHarshilNo ratings yet
- Machines Tutorial Sheet #1Document4 pagesMachines Tutorial Sheet #1Shruthi reddyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet1 - Questions PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet1 - Questions PDFMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesTut Sheet PDFLalitSisodiaNo ratings yet
- EE Refresher 1Document3 pagesEE Refresher 1giophilipNo ratings yet
- EE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3Document1 pageEE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3vineet mishra100% (1)
- Emi and Ac AssignmentDocument5 pagesEmi and Ac AssignmentMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- D.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Document5 pagesD.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Pritam Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Assignment s6 - BDocument3 pagesAssignment s6 - BErick MwNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentDocument3 pagesAssignment On Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating CurrentAtharav GoyalNo ratings yet
- Numerical SheetDocument3 pagesNumerical SheetSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1 2 and 3 TASKDocument1 pageMeeting 1 2 and 3 TASKTerence VergaraNo ratings yet
- 17395.assignment 2 BeeDocument2 pages17395.assignment 2 BeevikrantNo ratings yet
- B M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Echanical Ngineering XaminationDocument3 pagesB M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Echanical Ngineering Xaminationrony RkNo ratings yet
- Class Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementDocument8 pagesClass Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementHello WorldNo ratings yet
- Exercises - Mag Circuits+ XFMRsDocument5 pagesExercises - Mag Circuits+ XFMRsMINH Nguyễn TuấnNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0537 EE PreBoard Exam 15Document1 pageIMG - 0537 EE PreBoard Exam 15let ramNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFDocument34 pagesElectrical Circuits Part 1 - Lecture PDFRyan Cortes0% (1)
- Assignment - Questions Electrical Machine 1 2024Document2 pagesAssignment - Questions Electrical Machine 1 2024saurabhsonkar821No ratings yet
- Solved Problems (1&2)Document27 pagesSolved Problems (1&2)Eyosiyas BeleteNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectricitymohametabdirahman334No ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetAJ REPECILONo ratings yet
- Synchronous MachineDocument3 pagesSynchronous MachineAvishek0% (1)
- 6-Sheet EE 346 3Document10 pages6-Sheet EE 346 3wasem.1048No ratings yet
- Exam-6-Set-A (Print)Document10 pagesExam-6-Set-A (Print)Dummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Notes of Instrumentation and MeasurementDocument8 pagesNotes of Instrumentation and MeasurementRavi Shankar 31No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument3 pagesTrigonometryJohnCarloTigue0% (1)
- Question Bank AC CircuitsDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank AC CircuitsVictor JoseNo ratings yet
- Class Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementDocument8 pagesClass Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementRafaelNo ratings yet
- 03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Document13 pages03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Alternating Current MetersDocument35 pagesChapter 3 - Alternating Current MetersANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Sheet EEx73Document3 pagesSheet EEx73mohamedsabah22No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocument2 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Edexcel Physics IGCSEThushanaNo ratings yet
- DPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Document12 pagesDPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Abhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument19 pagesChapter Fourgeorge manNo ratings yet
- Pelan Tindakan Subjek Fizik Igcse Tingkatan 4 2018Document2 pagesPelan Tindakan Subjek Fizik Igcse Tingkatan 4 2018Jamal RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Q4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 1Document3 pagesQ4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 1John Russel LanozaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems of ReflectionDocument13 pagesSolved Problems of ReflectionSadek PiashNo ratings yet
- Practical Magnetic Design - Inductors and Coupled Inductors (Article)Document23 pagesPractical Magnetic Design - Inductors and Coupled Inductors (Article)lokireddi kiran kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation Calculations - BasicDocument217 pagesElectrical Installation Calculations - BasicSnow John100% (1)
- Maxwell's EquationsDocument50 pagesMaxwell's EquationsDinake Lefhika MmopiNo ratings yet
- Asses Form Electrical Supervisor AdvancedDocument5 pagesAsses Form Electrical Supervisor AdvancedSUNDAR TNo ratings yet
- 6 Skin EffectDocument11 pages6 Skin EffectBuriro HayatNo ratings yet
- Notes On EnergyDocument5 pagesNotes On EnergyMoodely RuskynNo ratings yet
- TIMER Pag11Document63 pagesTIMER Pag11Luis SotoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus emDocument4 pagesSyllabus em100475175No ratings yet
- EE320 HW5 Solution AllDocument9 pagesEE320 HW5 Solution AllHussain SalmanNo ratings yet
- Central Model School Barrackpore Aissce, Cbse.: Investigatory Project FileDocument21 pagesCentral Model School Barrackpore Aissce, Cbse.: Investigatory Project Filearghadiproy012No ratings yet
- Forces - Day 1 Quarter 1.Document24 pagesForces - Day 1 Quarter 1.junalyn franciscoNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument2 pagesWave NotesHITECH ARMYNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere 13 00593 v2Document24 pagesAtmosphere 13 00593 v2ricardo calderon garciaNo ratings yet
- AIEEE - Current Electricity - 1Document5 pagesAIEEE - Current Electricity - 1Amit KashyapNo ratings yet
- L2 Phys 2021 P2Document20 pagesL2 Phys 2021 P2Magd O.No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7Taylor JammiesonNo ratings yet
- Mirzaei Ripka Grim A Novel Eddy Current Speed Sensor With Ferrite ECore (2020) AAM 341533Document5 pagesMirzaei Ripka Grim A Novel Eddy Current Speed Sensor With Ferrite ECore (2020) AAM 341533Karthikeyan LNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field ThesisDocument7 pagesMagnetic Field Thesisafcnahwvk100% (2)
- ELECTROMAGNETISM (Short Inside Book)Document17 pagesELECTROMAGNETISM (Short Inside Book)daniyal.king55No ratings yet
- Bhramastra Revision Patrika Physics Electromagnetic Induction MindmapsDocument2 pagesBhramastra Revision Patrika Physics Electromagnetic Induction Mindmapsyuvrajjadav882No ratings yet
- PHSC2112 Q2 Long Quiz 2Document8 pagesPHSC2112 Q2 Long Quiz 2RussianOmeleteNo ratings yet
- Solution Engg Physics RGPV Main Paper 2016 JuneDocument17 pagesSolution Engg Physics RGPV Main Paper 2016 JuneDr. Rakesh SohalNo ratings yet
- Composite ConductorsDocument6 pagesComposite ConductorsAmresh KumarNo ratings yet