Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smart Task 03
Smart Task 03
Uploaded by
Rachit GuptaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smart Task 03
Smart Task 03
Uploaded by
Rachit GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
VCE Summer Internship Program 2021
Smart Task Submission Format
[ Download This Format in .DOCX format and then Edit it and SUBMIT ]
Intern’s Details
Name Rachit Gupta
Email-ID rachitgupta1148@gmail.com
Smart Task No. 03
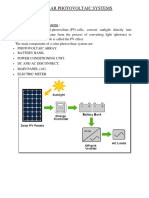
Project Topic Solar PV
Smart Task (Solution)
Task Q1 : Please write down each and every term with the definitions and explanation from any PVSyst Report.
Task Q1 Solution :
These terms are commonly used in a PVSyst report to assess the performance, efficiency, and various factors affecting
the energy production of a PV system.
1. Meteo Data: Meteorological data refers to information related to weather conditions, such as solar radiation,
ambient temperature, wind speed, and other relevant parameters. PVSyst uses this data to simulate the
performance of the PV system.
2. Albedo: Albedo is a measure of the reflectivity of the ground surface. In the context of a PVSyst report, it
represents the amount of solar radiation that is reflected by the ground and reaches the PV panels.
3. Backtracking Strategy: Backtracking is a tracking strategy used in PV systems with tracking mechanisms. It
involves adjusting the position of the PV panels to optimize their orientation with respect to the sun's position
throughout the day, maximizing energy production.
4. Tracker Spacing: Tracker spacing refers to the distance between individual solar trackers in a PV system. It
affects the layout and arrangement of the trackers in an array and is an important factor in optimizing energy
production.
5. Array Global Power: Array Global Power represents the total power output of the PV system, taking into
account all the individual modules or panels in the array.
6. Inverter Pack: Inverter Pack refers to the group of inverters used in a PV system. It represents the configuration
and capacity of the inverters installed to convert DC power generated by the panels to AC power for use in the
electrical grid.
7. Array Soiling Loss: Array soiling loss refers to the reduction in energy production due to the accumulation of
dirt, dust, or other contaminants on the PV panels, which can block sunlight and reduce their efficiency.
8. Thermal Loss Factor: The thermal loss factor represents the losses incurred in the PV system due to
temperature effects. It takes into account the decrease in panel efficiency as temperature increases, leading to
a reduction in energy output.
9. Wiring Ohmic Loss: Wiring ohmic loss refers to the energy loss that occurs due to the resistance of the
electrical wiring in the PV system. It accounts for the power dissipated as heat when electricity flows through
ST Solution Page 1 https://techvardhan.com
VCE Summer Internship Program 2021
Smart Task Submission Format
the wiring.
10. Series Diode Loss: Series diode loss represents the energy loss that occurs across the series diodes in the PV
system. Diodes are electronic components that allow current flow in one direction. However, they introduce a
small voltage drop and result in power losses.
11. LID - Light-Induced Degradation: LID is a phenomenon observed in some PV modules, particularly those with
crystalline silicon technology. It refers to the initial decrease in module efficiency due to exposure to light, which
stabilizes over time. PVSyst considers this degradation in its performance calculations.
12. Module Quality Loss: Module quality loss accounts for the decrease in energy production due to lower quality
or degraded PV modules. It can occur due to factors such as manufacturing defects, material degradation, or
module aging.
13. Module Mismatch Loss: Module mismatch loss refers to the reduction in energy output caused by mismatched
characteristics of individual PV modules within an array. Variations in module performance, such as different
current-voltage characteristics, can lead to reduced overall system efficiency.
14. Incidence Effect (IAM): The incidence effect, also known as the incidence angle modifier (IAM), represents the
change in module performance based on the angle at which sunlight strikes the PV module's surface. It
accounts for the variation in energy output with different incident angles of sunlight.
15. Near Shadings: Near shadings refer to obstructions or shading caused by nearby objects such as buildings,
trees, or other structures. PVSyst considers the impact of near shadings on the PV system's energy production.
16. Nominal Power: Nominal power refers to the rated power output of a PV module or an entire PV system under
standard test conditions (STC). It represents the power that the module or system is designed to deliver.
17. Performance Ratio: The performance ratio (PR) is a measure of the overall efficiency and performance of the
PV system. It is calculated as the ratio of the actual energy output of the system to the expected energy output,
considering losses and other factors.
18. Horizontal Global Irradiation: Horizontal global irradiation represents the total solar radiation received on a
horizontal surface. It includes both direct sunlight and diffuse sky radiation.
19. Horizontal Diffuse Irradiation: Horizontal diffuse irradiation refers to the solar radiation received on a horizontal
surface due to scattering and diffusion of sunlight by the Earth's atmosphere. It does not include direct sunlight.
20. Ambient Temperature: Ambient temperature refers to the temperature of the surrounding air or environment
where the PV system is installed. It affects the performance and efficiency of the PV modules as temperature
changes can impact their electrical characteristics and energy production.
21. Global Incident in Coil Plane: Global incident in coil plane represents the total solar radiation incident on a
specific plane or surface of the PV module or collector. It takes into account both direct sunlight and diffuse sky
radiation.
22. Far Shadings: Far shadings refer to obstructions or shading caused by objects located at a distance from the
PV system. These obstructions can cast shadows on the PV modules and reduce their exposure to sunlight,
affecting energy production.
23. Effective Irradiance on Collectors: Effective irradiance on collectors represents the actual amount of solar
irradiance received by the PV collectors or modules after considering various factors such as shading, soiling,
and other losses.
ST Solution Page 2 https://techvardhan.com
VCE Summer Internship Program 2021
Smart Task Submission Format
24. PV Conversion: PV conversion refers to the process by which sunlight is converted into electricity by the
photovoltaic modules. It involves the use of semiconductor materials within the PV cells to generate a flow of
electrons when exposed to sunlight.
25. Active Energy: Active energy refers to the actual usable electrical energy produced or consumed by the PV
system or any other electrical device. It represents the real power that is transferred to the load.
26. Reactive Energy: Reactive energy, also known as reactive power, is the component of electrical energy that
alternates between the load and the power source without being converted into useful work. It is required for
certain types of equipment but does not contribute to active power or real energy transfer.
500 Words (Max.)
ST Solution Page 3 https://techvardhan.com
You might also like
- Soalan Tugasan Jan 2023Document19 pagesSoalan Tugasan Jan 2023NURUL AIN BINTI RAPIAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 24 31artical1123Document9 pages24 31artical1123Sersio BordiosNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument36 pagesChapter OneStanleyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Electrical Energy With SolarDocument4 pagesCalculation of Electrical Energy With Solarmohamed parvez100% (1)
- Design and Sizing of Stand Alone Solar Power SystemDocument6 pagesDesign and Sizing of Stand Alone Solar Power Systemनिपुण कुमार100% (1)
- A10020115 KTI AJER InternasionalDocument15 pagesA10020115 KTI AJER Internasionalarief ndartoNo ratings yet
- DPR Manipur 5 MW Solar PV: Submitted By: Meghraj Capital Advisors Private LimitedDocument52 pagesDPR Manipur 5 MW Solar PV: Submitted By: Meghraj Capital Advisors Private LimitedPrathap kumar100% (4)
- Design of A Photovoltaic System For A Rural House: M.Aminy, N.Barhemmati, A.Hadadian, F.ValiDocument5 pagesDesign of A Photovoltaic System For A Rural House: M.Aminy, N.Barhemmati, A.Hadadian, F.ValiHypnotic KnightNo ratings yet
- How A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465Document9 pagesHow A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465ahmed abusnoubarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Output DC Current Injection in 100kW Grid Connected VACON 8000 Solar InverterDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Output DC Current Injection in 100kW Grid Connected VACON 8000 Solar InverteriaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- MainDocument25 pagesMainDurgaprasadNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Systems and How To Design ItDocument5 pagesWhat Is Solar Systems and How To Design Itabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Anupam Vinay Surin 12PS05F P & Es, NitkDocument20 pagesAnupam Vinay Surin 12PS05F P & Es, NitkchethanNo ratings yet
- Design and Comparative Analysis of Grid-Connected BIPV System With Monocrystalline Silicon and Polycrystalline Silicon in Kandahar ClimateDocument10 pagesDesign and Comparative Analysis of Grid-Connected BIPV System With Monocrystalline Silicon and Polycrystalline Silicon in Kandahar ClimateAhmad Shah IrshadNo ratings yet
- Zachariah2020 - Direct Solar PV-LED Lighting SystemDocument3 pagesZachariah2020 - Direct Solar PV-LED Lighting SystemAlexisNo ratings yet
- ANN BASED MPPT TECHNIQUE UNDER PARTIALLY SHADED CONDITIONS FOR GRID CONNECTED PV APPLICATIONS Ijariie23373Document8 pagesANN BASED MPPT TECHNIQUE UNDER PARTIALLY SHADED CONDITIONS FOR GRID CONNECTED PV APPLICATIONS Ijariie23373ntsuandihNo ratings yet
- Modified Algorithm For Drift Avoidance in PV System Using Neural NetworkDocument6 pagesModified Algorithm For Drift Avoidance in PV System Using Neural NetworkIIR indiaNo ratings yet
- Video1 - TranscripcionDocument3 pagesVideo1 - TranscripcionPedro AranaNo ratings yet
- Tese Grid Connected PV 2001Document124 pagesTese Grid Connected PV 2001chauhan303No ratings yet
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 54Document1 pageSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 54mydearteacherNo ratings yet
- NEOM ProjectDocument11 pagesNEOM Projectsahilsagar 2K20A1470No ratings yet
- Study On MPP MismatchDocument8 pagesStudy On MPP MismatchJean Venturin DestefaniNo ratings yet
- ChaptersDocument47 pagesChaptersAitha DeepakNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Roof Top Solar SystemDocument47 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction To Roof Top Solar Systemjonnalagadda harithaNo ratings yet
- Design & Implementation of 17.25 KVA Solar Power Plant-IJAERDV04I0237283Document8 pagesDesign & Implementation of 17.25 KVA Solar Power Plant-IJAERDV04I0237283Editor IJAERDNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three DesignDocument20 pagesChapter Three DesignADEFRIS BELACHEWNo ratings yet
- The Techno City Project Trivandrum, Kerala, India Latest Technologies Report For MEP ServicesDocument28 pagesThe Techno City Project Trivandrum, Kerala, India Latest Technologies Report For MEP ServicesSyraj HamzaNo ratings yet
- Training Module Photovoltaic Project Analysis: Clean Energy Project Analysis Course Speaker'S NotesDocument14 pagesTraining Module Photovoltaic Project Analysis: Clean Energy Project Analysis Course Speaker'S NotespikermiNo ratings yet
- Development of Bidirectional Net Meter in Grid Connected Solar PV System For Domestic ConsumersDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Bidirectional Net Meter in Grid Connected Solar PV System For Domestic ConsumersHariprasad RNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan May 08, 2024Document8 pagesAdobe Scan May 08, 2024ACR Talks malayalamNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell System Design-2Document12 pagesSolar Cell System Design-2spotifyladderNo ratings yet
- Zeta PDFDocument5 pagesZeta PDFCrispNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 80Kw Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Power Plant Using SisifoDocument14 pagesAnalysis of 80Kw Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Power Plant Using SisifoTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Design and Sizing of Solar Photovoltaic Systems R2Document125 pagesDesign and Sizing of Solar Photovoltaic Systems R2Andrei TaranuNo ratings yet
- PRJP - 1425Document11 pagesPRJP - 1425gourav VermaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfideDocument6 pagesPhotovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfidetroy_asubNo ratings yet
- PGTDU AssignmentDocument5 pagesPGTDU AssignmentNorest SitchaNo ratings yet
- 22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02Document25 pages22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02jayeshdeore398No ratings yet
- Report 3 D Solar Cell...Document15 pagesReport 3 D Solar Cell...Pankaj DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- My ReportDocument27 pagesMy Reportboluayomide2020No ratings yet
- Intelligent PV Module For Grid-Connected PV System PDFDocument8 pagesIntelligent PV Module For Grid-Connected PV System PDFAnjas WibisanaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System Efficiency Improvement MethodsDocument24 pagesPhotovoltaic System Efficiency Improvement MethodsradiNo ratings yet
- Report On Visit To Solar Power PlantDocument16 pagesReport On Visit To Solar Power Plantsm4513848No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solar PowerDocument112 pagesChapter 2 Solar PowerBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- Solar Technology: Seminar ContentsDocument19 pagesSolar Technology: Seminar ContentsObichere OnyekachiNo ratings yet
- Smart Task 1 Solar PVDocument7 pagesSmart Task 1 Solar PVShubham AroraNo ratings yet
- Chapter:-1: 1.1 Introduction To Solar EnergyDocument15 pagesChapter:-1: 1.1 Introduction To Solar EnergySwaroopNo ratings yet
- AES CEP ReportDocument10 pagesAES CEP ReportMoiz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Inverter White PaperDocument10 pagesPhotovoltaic Inverter White PapergubiliNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Utilization - Part3Document52 pagesSolar Energy Utilization - Part3Joyce CheungNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of A GriDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of A GriSidiabdoulah dahNo ratings yet
- Emma ProjectDocument48 pagesEmma ProjectChristianNo ratings yet
- Project Main Documentation (1) .Docx Edit-1Document66 pagesProject Main Documentation (1) .Docx Edit-1Best Dp's EverNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document33 pagesModule 2Vibin NivasNo ratings yet
- TH - EnglishDocument87 pagesTH - EnglishBacamarteNo ratings yet
- Pratikruti-2 17: Grid Connected Solar Rooftop SystemDocument1 pagePratikruti-2 17: Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Systems3ct0r 10No ratings yet
- Electrical Installation System in The Building Group No. 2Document15 pagesElectrical Installation System in The Building Group No. 2shada aidaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IDocument6 pagesEffect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IM VetriselviNo ratings yet
- SPIP TaskDocument5 pagesSPIP TaskRachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- TaskDocument5 pagesTaskRachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- CSD TaskDocument4 pagesCSD TaskRachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Final Internship ReportDocument34 pagesFinal Internship ReportRachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Smart Task 02Document6 pagesSmart Task 02Rachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- TD13 enDocument12 pagesTD13 enkiyong namNo ratings yet
- LC Vco ThesisDocument8 pagesLC Vco Thesissarareedannarbor100% (2)
- Design Optimization of Gating and FeedinDocument9 pagesDesign Optimization of Gating and FeedinJoao LuisNo ratings yet
- Case 3.1: "Ethical Selling at Perfect Solutions: The Case of The Delayed Product"Document3 pagesCase 3.1: "Ethical Selling at Perfect Solutions: The Case of The Delayed Product"Shan Danielle MortejoNo ratings yet
- 1 Continuous Process ImprovementDocument45 pages1 Continuous Process ImprovementlisahunNo ratings yet
- A Review of Passive Micromixers With A ComparativeDocument25 pagesA Review of Passive Micromixers With A ComparativeSadia SiddiqaNo ratings yet
- Scratch - SearchDocument1 pageScratch - Search180657126No ratings yet
- Sidiq Subandriyanto Setyawan: Statement of ParticipationDocument2 pagesSidiq Subandriyanto Setyawan: Statement of Participationsetyawan punkNo ratings yet
- +++ James Arthur Ray - The Science of Success +++Document92 pages+++ James Arthur Ray - The Science of Success +++simona_simona_1982100% (4)
- 1lmd Eng 1Document15 pages1lmd Eng 1Yassine HamdiaNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument3 pagesPower SystemMogaka LucasNo ratings yet
- Lab 06: Arrays & Functions Objective(s) :: ExercisesDocument4 pagesLab 06: Arrays & Functions Objective(s) :: ExercisesAhsan Ali GopangNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AI DevelopmentDocument8 pagesIntroduction of AI DevelopmentKeystrideNo ratings yet
- CH 3 OBDocument15 pagesCH 3 OBBuraq FarisNo ratings yet
- Reservoir EngineeringDocument13 pagesReservoir EngineeringhasanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- T 87 PG 101-102 PDFDocument2 pagesT 87 PG 101-102 PDFJossimar PerezNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawDocument46 pagesEnvironmental LawRohit100% (1)
- Csc271 Exam 9Document5 pagesCsc271 Exam 9NabiLNo ratings yet
- SUBMITTED-full - TRUESOILDocument103 pagesSUBMITTED-full - TRUESOILAndi Alfi SyahrinNo ratings yet
- Ryna Du PlooyDocument8 pagesRyna Du PlooyRosel.RamosNo ratings yet
- Activity Report City-Wide CleanUp DriveDocument4 pagesActivity Report City-Wide CleanUp DrivePamela TabayNo ratings yet
- Regallian DoctrineDocument1 pageRegallian DoctrineMary Joy SumapidNo ratings yet
- 2 6 2 English L - LDocument16 pages2 6 2 English L - LAyush RajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XIIDocument18 pagesChemistry XIISayantan DasNo ratings yet
- 30 Must Read Bestsellers in Infographics by HeadwayDocument69 pages30 Must Read Bestsellers in Infographics by HeadwaykateNo ratings yet
- Tecsis P3276Document4 pagesTecsis P3276benNo ratings yet
- IRFB59N10D - International RectifierDocument11 pagesIRFB59N10D - International RectifierStevenNo ratings yet
- MeteoroidsDocument8 pagesMeteoroidsCharisse FelicildaNo ratings yet
- Cep80n15 CetDocument4 pagesCep80n15 CetLuis LealNo ratings yet