Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ec3551 TLRF
Ec3551 TLRF
Uploaded by
Maadhesh100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
380 views2 pagesThis document provides a summary of a continuous internal assessment test for a transmission lines and RF systems course. The test contains two parts:
- Part A contains 10 multiple choice questions worth 2 marks each about topics like transmission line power delivery, standing wave ratio, and line parameters.
- Part B contains two long-form questions worth 15 marks each about topics like waveform distortion, transmission line constants, input impedance calculation, and line termination problems. The test aims to assess student understanding of transmission line analysis and high frequency system design.
Original Description:
Tlrf study
Original Title
EC3551 TLRF
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a summary of a continuous internal assessment test for a transmission lines and RF systems course. The test contains two parts:
- Part A contains 10 multiple choice questions worth 2 marks each about topics like transmission line power delivery, standing wave ratio, and line parameters.
- Part B contains two long-form questions worth 15 marks each about topics like waveform distortion, transmission line constants, input impedance calculation, and line termination problems. The test aims to assess student understanding of transmission line analysis and high frequency system design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
380 views2 pagesEc3551 TLRF
Ec3551 TLRF
Uploaded by
MaadheshThis document provides a summary of a continuous internal assessment test for a transmission lines and RF systems course. The test contains two parts:
- Part A contains 10 multiple choice questions worth 2 marks each about topics like transmission line power delivery, standing wave ratio, and line parameters.
- Part B contains two long-form questions worth 15 marks each about topics like waveform distortion, transmission line constants, input impedance calculation, and line termination problems. The test aims to assess student understanding of transmission line analysis and high frequency system design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CONTINUOUS INTERNAL ASSESSMENT – I
Branch: ECE Semester: V Date:08/09/2023(FN) Duration: 90 min
Subject code & Name EC3551-Transmission Lines & RF Systems Max. Marks: 50
Course Outcomes: RBT
CO1 Compute line parameters and various losses of transmission lines [AP]
Calculate the standing wave ratio and input impedance in high
CO2 [AP]
frequency transmission lines
Part – A (10 x 02 = 20 Marks) RBT CO Marks
Answer All Questions
1 When will a transmission line deliver maximum power to the load? U 1 2
2 A 50Ω line is terminated into an infinite line. If it is fed by a 10V.50Ω
AP 1 2
source .Find the reflected and power transmitted into infinite line.
3 Why we need loading in transmission lines? U 1 2
4 Calculate the load reflection coefficient of an open and short
AP 1 2
circuited line.
5 If a line is to have neither frequency nor delay distortion, how do you
relate attenuation constant and velocity of propagation to U 2
1
frequency?
6 What are the assumptions made for the analysis of performance of
U 1 2
the lines at high frequency?
7 For the line of Zero dissipation, what will be the values of attenuation
U 1 2
and propagation constant?
8 Compare the expressions for inductance L of open wire line and
U 2 2
coaxial Line?
9 Distinguish between the nodes and antinodes on a Transmission lines U 2 2
10 Write the expression of voltage and current equation of dissipation
U 2 2
less line?
Part – B (02 x 15 = 30 Marks) RBT CO Marks
Answer All Questions
11(a) Define wave form distortion on a transmission line. Determine the
condition for distortion less transmission line. How can a U 1 (15)
transmission line be made distortion less?
(OR)
11(b) What are the salient aspects of primary constants of two wire
transmission lines? Determine the voltages and current expression U 1 (15)
of two wire transmission lines?
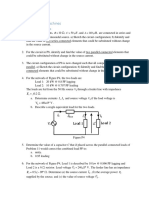
12(a) A generator of 1V 1kHz supplies power to a 100km long line
terminated in Z0 and having the following constants.
R=10.4Ω/km, L=0.00367H/km, G=0.8 X10-6 mho/km,
AP 1 (15)
C=0.00835X10-6 F/km. Calculate Input impedance attenuation
,propagation constant wavelength and phase velocity. Also
Calculate received current, voltage and power.
(OR)
12(b)(i) The constants of transmission lines are R=6Ω/km, L=2.2mH/km,
G=0.25 X10-6 mho/km, C=0.005X10-6F/km. Determine the (8)
characteristics impedance and propagation constant at 1000Hz.
(ii) A 2 meter long transmission lines with characteristic impedance AP 1
of 60+j40Ω are operating at 106 rad/sec has attenuation
constants of 0.921 Np/m and phase shift constant of 0 rad/m. If
(7)
the lines are terminated by a load of 20+j50Ω, determine the
input impedance of this line.
Faculty-In-Charge IQAC-Coordinator HoD/ECE Principal
You might also like
- Transient Signals On Transmission Lines PDFDocument154 pagesTransient Signals On Transmission Lines PDFEmeka N Obikwelu50% (2)
- ECE 220 Midterm 1 73 Total PointsDocument8 pagesECE 220 Midterm 1 73 Total PointsCarlosGomezNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2266Document33 pagesScientech 2266sarikapravinNo ratings yet
- ProblemsAC FundamentalsDocument3 pagesProblemsAC Fundamentalskrishneel100% (1)
- Sat Comm Sys EngineeringDocument34 pagesSat Comm Sys EngineeringHamis RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- User's Guide: RF Toolbox™Document786 pagesUser's Guide: RF Toolbox™Amardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- KrausCarver Electromagnetics TextDocument850 pagesKrausCarver Electromagnetics TextJosé Miguel Martínez100% (3)
- Transmission Line and Waveguides Unit Notes Unit - I - Transmission Line Theory Part ADocument24 pagesTransmission Line and Waveguides Unit Notes Unit - I - Transmission Line Theory Part AJk OkNo ratings yet
- Assignment TX LineDocument3 pagesAssignment TX LineMynam Meghana0% (1)
- LIC Manual NewDocument84 pagesLIC Manual NewVandhana PramodhanNo ratings yet
- Powersystem ExerciseDocument3 pagesPowersystem ExerciseHabib FirdausNo ratings yet
- EE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3Document1 pageEE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3vineet mishraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: Unit 3 Resonant CircuitsDocument36 pagesCircuit Theory: Unit 3 Resonant CircuitsSuganthi ShanmugasundarNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFDocument15 pagesPulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFlakshmanNo ratings yet
- Ec3551 TLRF Unit-1 QBDocument3 pagesEc3551 TLRF Unit-1 QBkaviya100% (1)
- LIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsDocument4 pagesLIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 DC CircuitsDocument40 pagesCh.1 DC Circuitsaattish100% (1)
- 15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesDocument2 pages15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesRadhika MahankaliNo ratings yet
- Eca Lab Manual Final Print PDFDocument41 pagesEca Lab Manual Final Print PDFvineethaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Analog MultipliersDocument17 pages3.1 Analog MultipliersMarykutty CyriacNo ratings yet
- PART IV. Instrument TransformersDocument30 pagesPART IV. Instrument TransformersuplbselesNo ratings yet
- FM Balanced Slope DetectorDocument5 pagesFM Balanced Slope DetectorPujjalPandeyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Low Pass RC and High Pass RL Filter Circuits: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Low Pass RC and High Pass RL Filter Circuits: Objectiveayesha amjad100% (1)
- DualityDocument16 pagesDualityRohanNo ratings yet
- Ec6701 - Vii SemDocument20 pagesEc6701 - Vii SemaniNo ratings yet
- EDC BitsDocument12 pagesEDC BitsKumar Goud.K0% (1)
- Edc Bit Paper - II EceDocument2 pagesEdc Bit Paper - II Ecevenkiscribd444No ratings yet
- Gate 1991 EeDocument15 pagesGate 1991 EeParayatham ManasaNo ratings yet
- BSNL JTO 2009 Question Paper SolutionsDocument25 pagesBSNL JTO 2009 Question Paper SolutionsGurwinder DhindsaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3 PDFDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3 PDFgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Cmos AnswersDocument8 pagesCmos AnswersOnu SamNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis HandoutDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis Handoutmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Physics Excellent QuestionsDocument98 pagesPhysics Excellent QuestionsShashank Rai0% (1)
- Signals and SystemsDocument17 pagesSignals and SystemsSanthosh Vegeta Goku GNo ratings yet
- Transito RampDocument30 pagesTransito RampMarium AliNo ratings yet
- ch11 PDFDocument43 pagesch11 PDFmri_leon100% (1)
- Experiment 2Document2 pagesExperiment 2Sunidhi Chauhan100% (1)
- Experiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportShahzad JameelNo ratings yet
- DC-DC ConvertersDocument30 pagesDC-DC ConvertersTema HassanNo ratings yet
- Eee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyDocument4 pagesEee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyMike ShakespeareNo ratings yet
- DADocument40 pagesDAkrishneel sharmaNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- Sem - Course - Curriculum-ECE - DTU - 3rd SemDocument8 pagesSem - Course - Curriculum-ECE - DTU - 3rd SemRohit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: Reference: Slides From Alexander-Sadiku Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument57 pagesElectric Circuits: Reference: Slides From Alexander-Sadiku Fundamentals of Electric Circuitsthuan phamNo ratings yet
- Lab10 PDFDocument12 pagesLab10 PDFJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document62 pagesChapter 1Bennie Bailey100% (4)
- Unit 3Document33 pagesUnit 3Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocument2 pages9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Energy Levels of Semiconductor, Conductors and InsulatorsDocument53 pagesEnergy Levels of Semiconductor, Conductors and InsulatorsTawki BakiNo ratings yet
- TRANSMISSION LINES JNTUK Question BankDocument5 pagesTRANSMISSION LINES JNTUK Question BankMunni 1123No ratings yet
- Triangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsDocument6 pagesTriangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- Nic LD PDFDocument349 pagesNic LD PDFCeilortNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercise - 2018 PDFDocument2 pagesAdditional Exercise - 2018 PDFCarlos GamioNo ratings yet
- EM Waves & Transmission LinesDocument7 pagesEM Waves & Transmission LinesShaik vaseem akramNo ratings yet
- EE-391 Manual 02Document68 pagesEE-391 Manual 02Deb Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument15 pagesLab Reportaeoliano0% (1)
- 2 ND UnitDocument3 pages2 ND UnitB.BijuNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Vlsi CIA IDocument5 pagesAnswer Key - Vlsi CIA IMaadheshNo ratings yet
- AcademicDocument66 pagesAcademicManimegalaiNo ratings yet
- Imp Qstions TLRFDocument16 pagesImp Qstions TLRFSinan SinanNo ratings yet
- Imp Qstions TLRFDocument16 pagesImp Qstions TLRFSinan SinanNo ratings yet
- TLWG qb1Document17 pagesTLWG qb1balasaravanan0408No ratings yet
- 3 RD UnitDocument2 pages3 RD UnitB.BijuNo ratings yet
- MengECE D512 Problem Set 2Document1 pageMengECE D512 Problem Set 2Jc GarciaNo ratings yet
- Design Formula For Inset Fed Micro StripDocument6 pagesDesign Formula For Inset Fed Micro StripGaurav MehtaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Protection of Transmission Lines PDFDocument107 pages11 - Protection of Transmission Lines PDFWahed Imtiaz100% (2)
- The Authoritative Dictionary of IEEE Terms ML12089A535Document4 pagesThe Authoritative Dictionary of IEEE Terms ML12089A535sebastiannistorNo ratings yet
- Pinoybix Communication: Series of MCQ Part 1. Transmission FundamentalsDocument41 pagesPinoybix Communication: Series of MCQ Part 1. Transmission Fundamentalsmark stephen yapNo ratings yet
- Powsurge Module1.2Document26 pagesPowsurge Module1.2JasperNo ratings yet
- CT11 Distance Protection F21 Setting GuideDocument44 pagesCT11 Distance Protection F21 Setting GuidecesarchiletNo ratings yet
- Computational Design of A Broadband In-Line Coaxial-to-Rectangular Waveguide TransitionDocument15 pagesComputational Design of A Broadband In-Line Coaxial-to-Rectangular Waveguide TransitionVladimir ShkolnikovNo ratings yet
- Emtl Question Bank Imp QsDocument9 pagesEmtl Question Bank Imp QsSri MurthyNo ratings yet
- The Future of MM-Wave PackagingDocument11 pagesThe Future of MM-Wave PackagingTribu Vaquero JimenezNo ratings yet
- AllanGreenwood Capitulos 1 y 2Document48 pagesAllanGreenwood Capitulos 1 y 2Paul RamosNo ratings yet
- Travelling Waves 1Document12 pagesTravelling Waves 1Shareef ChampNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media and Antenna Systems B: Course ContentDocument26 pagesTransmission Media and Antenna Systems B: Course ContentWyndale John JastillanoNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument130 pagesOutput18131A0230 GEDDU TARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Bip: Gummel-Poon Bipolar Transistor Model: Appendix ADocument7 pagesBip: Gummel-Poon Bipolar Transistor Model: Appendix AdeancjenningsNo ratings yet
- QB ComputationDocument16 pagesQB ComputationLakshmi ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Booklet - Telecom Cables Used in Indian RailwaysDocument41 pagesBooklet - Telecom Cables Used in Indian RailwayssatheeskrsnaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies A ReviDocument15 pagesDynamic Equivalents in Power System Studies A ReviRong GuoNo ratings yet
- High Speed Memory Design Techniques An4010 12Document6 pagesHigh Speed Memory Design Techniques An4010 12Luis Daniel BinsakNo ratings yet
- Corum-Tesla Coils and The Failure of Lumped-Element Circuit TheoryDocument9 pagesCorum-Tesla Coils and The Failure of Lumped-Element Circuit TheoryMilan KulichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Transmission Line Theory: 11/01/15 1 ELCT564Document29 pagesChapter 2: Transmission Line Theory: 11/01/15 1 ELCT564Frew FrewNo ratings yet
- One Eighth Wave Line - The Quarter Wave Line and Half Wave Line. Single Stub Matching and Double Stub MatchingDocument11 pagesOne Eighth Wave Line - The Quarter Wave Line and Half Wave Line. Single Stub Matching and Double Stub MatchingSaravanan ManavalanNo ratings yet
- TSTL6 - Switched Transmission Lines ExampleDocument2 pagesTSTL6 - Switched Transmission Lines ExampleNick FlintNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Literature Survey 1. Compact Triple-Band Antenna For Wimaxand Wlan ApplicationsDocument49 pages1.2 Literature Survey 1. Compact Triple-Band Antenna For Wimaxand Wlan ApplicationsRampratheep vNo ratings yet
- HD26LS31Document12 pagesHD26LS31Joao Stuard Herrera QuerevalúNo ratings yet