Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics EASE 1 Pointers G11 2324
Physics EASE 1 Pointers G11 2324
Uploaded by
Ramadhan AmriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics EASE 1 Pointers G11 2324
Physics EASE 1 Pointers G11 2324
Uploaded by
Ramadhan AmriCopyright:
Available Formats
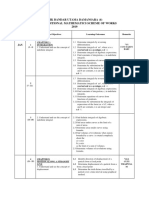
PHYSICS EASE 1 POINTERS GRADE 11 2023/2024
Question Difficutly
No. Topic Sub Topic Level
Indicator/Learning Objective
Type
01 understand that all physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and
1 Understanding 1
Physical a unit
quantities 02 make reasonable estimates of physical quantities included within the
2 Analyzing 1
syllabus
Physical quantities and units
03 recall the following SI base quantities and their units: mass (kg), length (m),
3 Knowing 1
time (s), current (A), temperature (K)
04 express derived units as products or quotients of the SI base units and use
4 Analyzing 2
the derived units for quantities listed in this syllabus as appropriate
SI Units
5 Analyzing 3 05 use SI base units to check the homogeneity of physical equations
06 recall and use the following prefixes and their symbols to indicate decimal
6 Analyzing 1 submultiples or multiples of both base and derived units: pico (p), nano (n),
micro (µ), milli (m), centi (c), deci (d), kilo (k), mega (M), giga (G), tera (T)
07 understand and explain the effects of systematic errors (including zero
7 Errors and Understanding 1
errors) and random errors in measurements
uncertainties
8 Analyzing 1 08 understand the distinction between precision and accuracy
10 understand the difference between scalar and vector quantities and give
9 Scalars and Understanding 1
examples of scalar and vector quantities included in the syllabus
vectors
10 Applying 1 11 add and subtract coplanar vector
11 Understanding 1 13 define and use distance, displacement, speed, velocity and acceleration
14 use graphical methods to represent distance, displacement, speed, velocity
12 Analyzing 2
and acceleration
13 Analyzing 2 15 determine displacement from the area under a velocity–time graph
Kinematics
14 Knowing 1 17 determine acceleration using the gradient of a velocity–time graph
Equations of 18 derive, from the definitions of velocity and acceleration, equations that
15 motion Understanding 1
represent uniformly acceleratedmotion in a straight line
19 solve problems using equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion
16 Analyzing 2 in a straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational
field without air resistance
21 describe and explain motion due to a uniform velocity in one direction and a
17 Understanding 1
uniform acceleration in a perpendicular direction
22 understand that mass is the property of an object that resists change in
18 Knowing 1
motion
23 recall F = ma and solve problems using it, understanding that acceleration
19 Analyzing 2
and resultant force are always in the same direction
Momentum
20 Knowing 1 24 define and use linear momentum as the product of mass and velocity
and Newton’s
21 laws of Knowing 1 25 define and use force as rate of change of momentum
22 motion Understanding 1 26 state and apply each of Newton’s laws of motion
27 describe and use the concept of weight as the effect of a gravitational field
23 Knowing 1 on a mass and recall that the weight of an object is equal to the product of its
Dynamics
mass and the acceleration of free fall
28 show a qualitative understanding of frictional forces and viscous/drag forces
including air resistance (no treatment of the coefficients of friction and viscosity
24 Understanding 1
is required, and a simple model of drag force increasing as speed increases is
Non-uniform sufficient)
motion 29 describe and explain qualitatively the motion of objects in a uniform
25 Understanding 1
gravitational field with air resistance
30 understand that objects moving against a resistive force may reach a
26 Understanding 1
terminal (constant) velocity
27 Linear Understanding 1 31 state the principle of conservation of momentum
momentum 32 apply the principle of conservation of momentum to solve simple problems,
and its including elastic and inelastic interactions between objects in both one and two
28 Applying 3
conservation dimensions (knowledge of the concept of coefficient of restitution is not
required)
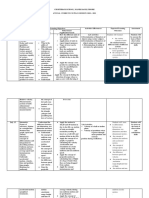
Question Difficutly
No. Topic Sub Topic Level
Indicator/Learning Objective
Type
33 recall that, for a perfectly elastic collision, the relative speed of approach is
29 Knowing 1
Dynamics
Linear equal to the relative speed of separation
momentum
and its
conservation 34 recall that, for a perfectly elastic collision, the relative speed of approach is
30 Applying 3
equal to the relative speed of separation
35. Understand that the weight of an object may be taken as acting at a single
31 Knowing 1
Turning point known as its centre of gravity
Force Density and Pressure
32 effects of Applying 1 36 Define and apply the moment of a force
37 Understand that a couple is a pair of forces that acts to produce rotation
33 forces Knowing 1
only
34 Understanding 1 38 Define and apply the torque of a couple
35 Equilibrium
Knowing 1 39 State and apply the principle of moments
40 Understand that, when there is no resultant force and no resultant torque, a
36 of forces Analyzing 1
system is in equilibrium
37 Understanding 1 42 Define and use density
38 Knowing 1 43 Define and use pressure
Density and 46 Derive, from the definitions of pressure and density, the equation for
39 Understanding 1
pressure hydrostatic pressure ?p = ?g?h
47 Calculate the upthrust acting on an object in a fluid using the equation F =
40 Applying 1
?gV (Archimedes’ principle)
You might also like
- Types of PurchasingDocument5 pagesTypes of PurchasingKARISHMAAT100% (2)
- I - Year-Most Expected Questions-2023-24-1Document14 pagesI - Year-Most Expected Questions-2023-24-1srishti.intlNo ratings yet
- Fisika Kelas X Semester I: With Both Analogue and Digital DisplaysDocument69 pagesFisika Kelas X Semester I: With Both Analogue and Digital DisplaysSilka AbyadatiNo ratings yet
- Physics Syllabus XI (2022-23)Document10 pagesPhysics Syllabus XI (2022-23)RAJU GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- Stem-Gen. Physics1 - q1Document13 pagesStem-Gen. Physics1 - q1Meldren TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Level Physics Teaching SchemesDocument29 pagesAdvanced Level Physics Teaching SchemesBeaugar MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Student 'S Copy: Prepared by Prof Madya Ahmad Abd Hamid, Jun 2013Document16 pagesStudent 'S Copy: Prepared by Prof Madya Ahmad Abd Hamid, Jun 2013Khairun HusnaNo ratings yet
- RPT 2023 Fizik (Versi Bi) - T4Document50 pagesRPT 2023 Fizik (Versi Bi) - T4norfaridatulakmarNo ratings yet
- Lessonplan 094 2018 Student'sDocument16 pagesLessonplan 094 2018 Student'sNur KhaizanNo ratings yet
- NEB - New CurriculumDocument110 pagesNEB - New CurriculumbalsaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterDocument46 pagesSenior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterSharifNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (861) : Paper I: Theory - Paper II: Practical - 3 Hours ... 15 MarksDocument11 pagesPHYSICS (861) : Paper I: Theory - Paper II: Practical - 3 Hours ... 15 MarksRoux CubeNo ratings yet
- ISC Physics 2026Document24 pagesISC Physics 2026btpirtaza123No ratings yet
- 2015 Physics As Revision Cards Paper 1 As NEWDocument53 pages2015 Physics As Revision Cards Paper 1 As NEWgalaxyhunter16No ratings yet
- Topic Learning Outcome Teachi NG Periods: Scheme of Work 2017 Physics - Lower Six First Term: MechanicsDocument5 pagesTopic Learning Outcome Teachi NG Periods: Scheme of Work 2017 Physics - Lower Six First Term: MechanicsNafa HashimNo ratings yet
- ISC Physics XI XII Revised 020424 2026Document24 pagesISC Physics XI XII Revised 020424 2026kshayoniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Term I Plan 2022 - 2023Document5 pagesGrade 12 Physics Term I Plan 2022 - 2023user nameNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Phy f4 2018Document16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Phy f4 2018TS ShongNo ratings yet
- 01 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument28 pages01 Physical Quantities and Unitsfisica2No ratings yet
- Scheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2013: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsDocument19 pagesScheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2013: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsbighaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Matematik Tingkatan 4 (DLP)Document18 pages2024 Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Matematik Tingkatan 4 (DLP)Fariz FdzNo ratings yet
- Newmark Method October 2018 Mac v3Document4 pagesNewmark Method October 2018 Mac v3Nikhil PotnuruNo ratings yet
- Physics As Level SyllabusDocument11 pagesPhysics As Level SyllabusOm Parkash Sarwan BheelNo ratings yet
- RPT Physics Lower 6 2015 Sem 1Document10 pagesRPT Physics Lower 6 2015 Sem 1Norhazli IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CASTRO, John Carlo - PHYSICS - MODULEDocument28 pagesCASTRO, John Carlo - PHYSICS - MODULEFatimaMendozaNo ratings yet
- A LevelphysicsDocument9 pagesA LevelphysicsOmar AamirNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Measurement and Vectors PDFDocument27 pagesUnit 1 Measurement and Vectors PDFSharneet ChettyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PHYSICS 1Document6 pagesSyllabus PHYSICS 1Re HanaNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Document11 pagesISC Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Jeevith Soumya SuhasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Planning F4 Physics 2010Document13 pagesYearly Planning F4 Physics 2010nickphysics4927No ratings yet
- Genaral Physics 1Document5 pagesGenaral Physics 1Nicole LagumbayNo ratings yet
- Phy Split UpDocument6 pagesPhy Split UpharjitjammujohalNo ratings yet
- Course Outline DBS1012 Jun 17 - UpdateDocument4 pagesCourse Outline DBS1012 Jun 17 - UpdateNasir RejabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tensor CalculusDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Tensor CalculusUsama hanifNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Document3 pagesMathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Physics EASE 1 Pointers G10 2324Document2 pagesPhysics EASE 1 Pointers G10 2324Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- Final GCC Syllabus-1Document13 pagesFinal GCC Syllabus-1ebsp7as7No ratings yet
- Vi Class Summer Fun Work For All OrientationsDocument4 pagesVi Class Summer Fun Work For All OrientationsSaraLakshmi ReddyNo ratings yet
- RPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPSarina ShariffNo ratings yet
- LO Grade 11 Term 1Document2 pagesLO Grade 11 Term 1dayh07117No ratings yet
- YEARLY LESSON PLAN F4 Physics 2020Document40 pagesYEARLY LESSON PLAN F4 Physics 2020Asdayanty AdlinNo ratings yet
- Pure and Mechanics Revision Checklist For Year 12 Assessment 2Document2 pagesPure and Mechanics Revision Checklist For Year 12 Assessment 2yuhitsanniNo ratings yet
- Practice 2 Classical Mechanics Laboratory ESIQIEDocument26 pagesPractice 2 Classical Mechanics Laboratory ESIQIEScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMathematics 2 PDFAbsolute ZeroNo ratings yet
- Physics Exercises 2018Document146 pagesPhysics Exercises 2018ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- C1. Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsDocument8 pagesC1. Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- DLL Blank Template (PHYSICAL SCIENCE) (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesDLL Blank Template (PHYSICAL SCIENCE) (AutoRecovered)Lembert Uyangurin CasinilloNo ratings yet
- ISC PhysicsDocument25 pagesISC PhysicsprinceNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Physics For The IscDocument2 pagesSyllabus in Physics For The IscPreshin SivanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum PhysicsDocument33 pagesCurriculum PhysicsMahad ArifNo ratings yet
- Reka Bentuk, Pembinaan Dan Pentadbiran UjianDocument9 pagesReka Bentuk, Pembinaan Dan Pentadbiran UjianAiman HazimNo ratings yet
- Form 1 PDFDocument32 pagesForm 1 PDFCLCNo ratings yet
- ISC PhysicsDocument25 pagesISC PhysicsMuhammed AkthusNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 2020Document8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1 2020Noorleha Manan100% (3)
- Yearly Scheme - Add Maths F5 2019Document8 pagesYearly Scheme - Add Maths F5 2019angelchen991No ratings yet
- Epartment OF Ngineering: Ourse BjectivesDocument4 pagesEpartment OF Ngineering: Ourse BjectivesNileshIndulkarNo ratings yet
- Phy F111 1015Document4 pagesPhy F111 1015IkshwakNo ratings yet
- As Level Physics Syllabus ContentDocument11 pagesAs Level Physics Syllabus ContentAYMAN HASANNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument12 pagesPhysics XIAshish UpretiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To DynamicsDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Dynamicsmustafa hassanNo ratings yet
- Order-Preserving Maps and Integration Processes. (AM-31), Volume 31From EverandOrder-Preserving Maps and Integration Processes. (AM-31), Volume 31No ratings yet
- Physics EASE 1 Pointers G10 2324Document2 pagesPhysics EASE 1 Pointers G10 2324Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- Ease 1 Physics 22-23 g12Document9 pagesEase 1 Physics 22-23 g12Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- (DLB) (PC) Harnden v. California Et Al - Document No. 3Document1 page(DLB) (PC) Harnden v. California Et Al - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Violations of OLSDocument64 pagesViolations of OLSOisín Ó CionaoithNo ratings yet
- A Writ of Attachment Creates A Lien On Real Property Belonging To The Judgment DebtorDocument7 pagesA Writ of Attachment Creates A Lien On Real Property Belonging To The Judgment DebtorHangul Si Kuya AliNo ratings yet
- Saurav Sah: SummaryDocument3 pagesSaurav Sah: SummarySaurav SahNo ratings yet
- Ped 201 Lab 5 sp14Document7 pagesPed 201 Lab 5 sp14api-241632865No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Kat Sajo50% (2)
- Hydraulic JumpDocument9 pagesHydraulic JumpAhmed Gamal100% (1)
- Computer Network Lesson Plan - UpdatedDocument2 pagesComputer Network Lesson Plan - UpdatedAmit Prakash SenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 "How Well Am I Doing?" - Financial Statement AnalysisDocument134 pagesChapter 16 "How Well Am I Doing?" - Financial Statement AnalysisTyra Joyce RevadaviaNo ratings yet
- Acta Pilati Alcock 2016Document19 pagesActa Pilati Alcock 2016roger_pearseNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFMohammed AL-sharafiNo ratings yet
- Film Genres SurveyDocument7 pagesFilm Genres SurveyMargarette OidilesNo ratings yet
- Entangled Gluons: Replies To Casati, Han, Kim, and YagisawaDocument11 pagesEntangled Gluons: Replies To Casati, Han, Kim, and YagisawaWittProfNo ratings yet
- Prevalent Moral Issues and Dubious Practices in The WorkplaceDocument1 pagePrevalent Moral Issues and Dubious Practices in The WorkplaceChristian Ü Fer Ibañez100% (1)
- Small Talk PhrasesDocument2 pagesSmall Talk Phrasesnurul syakirinNo ratings yet
- Palash Agrawal ResumeDocument1 pagePalash Agrawal ResumesgbhuNo ratings yet
- Se 2014 PDFDocument546 pagesSe 2014 PDFRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bertrand Russell's Theory of Empiricism PDFDocument204 pagesBertrand Russell's Theory of Empiricism PDFBrian WoodNo ratings yet
- JNTU ANATHAPUR B.TECH Mechanical Engineering R09 SyllabusDocument147 pagesJNTU ANATHAPUR B.TECH Mechanical Engineering R09 Syllabuspavankumar72No ratings yet
- Capacitive TransducerDocument21 pagesCapacitive Transducersourabhyadav14No ratings yet
- Alice A. Jardine, Shannon Lundeen, Kelly OliverDocument160 pagesAlice A. Jardine, Shannon Lundeen, Kelly OliverZenia YébenesNo ratings yet
- Towards Being A HumanDocument53 pagesTowards Being A HumanlarenNo ratings yet
- Middle School Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMiddle School Lesson Planapi-339151467No ratings yet
- Virginia Standards of Learning ObjectiveDocument7 pagesVirginia Standards of Learning ObjectiveHoney Grace CaballesNo ratings yet
- Criteo Vs SteelHouseDocument44 pagesCriteo Vs SteelHouseLaraNo ratings yet
- ES DLP 7-4-2017 Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument1 pageES DLP 7-4-2017 Plate Tectonics TheoryCharline A. RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Charmed - 1x06 - The Wedding From Hell - enDocument46 pagesCharmed - 1x06 - The Wedding From Hell - enGa ConNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument34 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyGazal ReyazNo ratings yet
- Government AccountingDocument56 pagesGovernment AccountingJoleaNo ratings yet