Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RSD Poster
RSD Poster
Uploaded by
KAUL.officialOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RSD Poster
RSD Poster
Uploaded by
KAUL.officialCopyright:
Available Formats
Developing a computational domain for the prediction
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
of in-cylinder phenomena in a Spark Ignition engine
IIT KANPUR
Vishesh Kaul
Introduction Methodology
• Validation of experimental data is essential to ensure the data used is
accurate. CAD model created and imported
• In-cylinder phenomena are important to understand for proper analysis
of experiments.
Geometry errors removed in
CONVERGE CFD
Asymmetric
Boundary conditions set along with
the whole case setup
Case run and observed for any errors
during runtime
Adjustment of allowable parameters
Fig. Temperature plot of cylinder at BDC Fig. Cylinder at TDC according to practice and intuition.
Computational domain
Case re-run and observed
Test data validated
Results tabulated
Fig. computational domain with demarcated boundaries
Results and Discussion
• The results were obtained for motoring and not combustion.
• Increase in intake pressure led to an observed increase in peak in-cylinder
pressure.
• Increase in intake temperature led to a decrease in trapped mass.
Fig. initial diagnosis Fig. Final diagnosis
Analysis
Initial parameters:
Table 1: parameters initialised for the first run
Trapped-mass vs CAD variation with pressure
Deviation observed:
Table 2: Slight disagreement between model Scope of Future Work
1. The simulation can be further tuned and used to simulate Hydrogen ignition.
Fig. Experimental(Green) vs Simulation(Blue) in-cylinder pressure 2. Engine characteristics of the model with laser ignition can be studied.
Parameters for second run: Deviation was observed in the second
run: 3. Optimisation of injection timing with combustion modelling.
Table 3: recalibrated parameters for second run
Table 4: Comparison between experiment and simulation
References
[1]: Richards, K.J., Senecal, P.K., and Pomraning, E., CONVERGE 3.1, Convergent
Science, Madison, WI (2023).
Conclusions [2]: Ye, W., Pan, Y., He, L., Chen, B., Liu, J., Gao, J., Wang, Y., & Yang, Y. (2021).
Design with modelling techniques. Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
• The trapped mass observed was heavily overpredicted. (Second Edition), 109-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816673-4.00008-0
• The inlet valve opening was checked, along with the compression
curve. 2341648
• The Pressure peaks at around 2.08 MPa for 57% throttle, 50Nm VISHESH KAUL
Load and at stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. Prof. AVINASH KUMAR AGARWAL
• The experimental setup is being investigated for sources of error. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
You might also like
- 2008 Ford F-150 5.4L Electric Wiring DiagramsDocument61 pages2008 Ford F-150 5.4L Electric Wiring Diagramskamaleon dorado100% (3)
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual ECDocument1,314 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual ECAndy Dellinger100% (9)
- Ajax DPC 2804 O&M ManualDocument185 pagesAjax DPC 2804 O&M Manualmavericklf187% (30)
- Project Metrics DefinitionsDocument8 pagesProject Metrics DefinitionsSudharsana100% (6)
- Ingersoll Rand Irn55k-Cc, Irn75k-Cc, Irn75h-Cc, Irn100h-Cc Parts Catalog (Feb 2004)Document50 pagesIngersoll Rand Irn55k-Cc, Irn75k-Cc, Irn75h-Cc, Irn100h-Cc Parts Catalog (Feb 2004)J100% (2)
- 1jz-Gte InfoDocument8 pages1jz-Gte Info007jones007No ratings yet
- Automobile Parts and FunctionDocument11 pagesAutomobile Parts and FunctionMohith Choudhary100% (2)
- JCB ExcavatorDocument275 pagesJCB Excavatoraldy yasi71% (7)
- Torque Specifications: Service Specifications - 2Az-Fxe Engine MechanicalDocument3 pagesTorque Specifications: Service Specifications - 2Az-Fxe Engine MechanicaldiemnganNo ratings yet
- Toyota 3UR-FE V8 Tech GuideDocument8 pagesToyota 3UR-FE V8 Tech GuideAbin MathewNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CAD ELECTRICAL MACHINEDocument5 pagesUnit 6 CAD ELECTRICAL MACHINEPradhunya KambleNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Case Study PDFDocument29 pagesDC Motor Case Study PDFliling100% (1)
- Mechatronics DC Motor - Tachometer Closed-Loop Speed Control SystemDocument29 pagesMechatronics DC Motor - Tachometer Closed-Loop Speed Control SystemskheoNo ratings yet
- Dougherty2003 PDFDocument16 pagesDougherty2003 PDFpusikurac1234567No ratings yet
- S16 Crossflow Turbine - Final - PosterDocument1 pageS16 Crossflow Turbine - Final - PosterKashif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Journee SD EtudeDocument2 pagesJournee SD EtudenastaNo ratings yet
- Application of DOE To CAEDocument9 pagesApplication of DOE To CAETran ThaihongNo ratings yet
- NIST Gravimetric Calibration Volumetric Glassware SOP PDFDocument20 pagesNIST Gravimetric Calibration Volumetric Glassware SOP PDFStephenNo ratings yet
- Cymgrd 7.0 New Features: Efficient and Robust Substation Grounding AnalysisDocument2 pagesCymgrd 7.0 New Features: Efficient and Robust Substation Grounding Analysisjaneth lozanoNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Ignite3d A4Document2 pagesBrochure-Ignite3d A4CfdGNo ratings yet
- Petro Industry News - New Developments in On-Line Calorific Value Analysis - 02-2007Document2 pagesPetro Industry News - New Developments in On-Line Calorific Value Analysis - 02-2007zaffarNo ratings yet
- Andritz DTwin - Recaust - DTDocument10 pagesAndritz DTwin - Recaust - DTPavel JakobsonNo ratings yet
- Managing Fleet Performance 1.0Document23 pagesManaging Fleet Performance 1.0KURNIAWANNo ratings yet
- The How To's of Advanced Mixed-Signal VerificationDocument51 pagesThe How To's of Advanced Mixed-Signal VerificationNguyễn Sĩ NamNo ratings yet
- Dissimilar Welding JointsDocument12 pagesDissimilar Welding JointsAhmed ELmlahyNo ratings yet
- Training M2000 (M2000V200R012C00) Performance Management-20120417-C V1.0Document52 pagesTraining M2000 (M2000V200R012C00) Performance Management-20120417-C V1.0Mohammad KamruzzamanNo ratings yet
- CAE Techniques For Casting OptimizationDocument4 pagesCAE Techniques For Casting OptimizationArchana PathakNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Versus ResolutionDocument3 pagesAccuracy Versus ResolutionPablo BertoloneNo ratings yet
- An124 Tuning Control Loops With The IMC Tuning Method PDFDocument3 pagesAn124 Tuning Control Loops With The IMC Tuning Method PDFSyed Mian Fahim KakakhailNo ratings yet
- Measurement System AnalysisDocument80 pagesMeasurement System AnalysisVasant bhoknalNo ratings yet
- Define: Understanding The Define: Operation/Unit Measure: Creation of The Analyze and Improve: Use Control: Final Checking ofDocument1 pageDefine: Understanding The Define: Operation/Unit Measure: Creation of The Analyze and Improve: Use Control: Final Checking ofRaymund RascoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Simulation Model of The Compression Ignition EngineDocument4 pagesThermodynamic Simulation Model of The Compression Ignition EngineAhmed S. El DenNo ratings yet
- MINI PROJECT REPORT (Centrifugal Pump)Document54 pagesMINI PROJECT REPORT (Centrifugal Pump)HEMANT SONINo ratings yet
- Project Name: Cycle Time Reduction. Project Owner: S.N. Parmar, Ajay Kumar ChoudhariDocument50 pagesProject Name: Cycle Time Reduction. Project Owner: S.N. Parmar, Ajay Kumar Choudhariblitzkrig100% (1)
- Benchmarking Quantum Annealing Controls With Portfolio OptimizationDocument14 pagesBenchmarking Quantum Annealing Controls With Portfolio OptimizationMunawar Ali RahimoonNo ratings yet
- Ever QDocument8 pagesEver QOTNo ratings yet
- ORAN ProposalDocument7 pagesORAN Proposallitoc60255No ratings yet
- 1/28/2017 Ronald Morgan Shewchuk 1Document80 pages1/28/2017 Ronald Morgan Shewchuk 1SudhagarNo ratings yet
- Calculations in Process EngineeringDocument3 pagesCalculations in Process EngineeringAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Hioki 3511-50Document4 pagesHioki 3511-50martin JeongNo ratings yet
- ACR 2018 DM QC ProgramDocument43 pagesACR 2018 DM QC ProgramMario PadillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Q-400 Digital Image Correlation V2Document5 pagesIntroduction To Q-400 Digital Image Correlation V2Alex J. GonzálezNo ratings yet
- ASTM - D3967 - 16 Splitting Tensile Strength ...Document5 pagesASTM - D3967 - 16 Splitting Tensile Strength ...Italo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Simcenter STAR-CCM+ Combustion-Heat Transfer (Furnaces, Heaters, Kilns) - Application Spotlight PresentationDocument80 pagesSimcenter STAR-CCM+ Combustion-Heat Transfer (Furnaces, Heaters, Kilns) - Application Spotlight Presentationvivek shajiNo ratings yet
- Adam Equipment: PGW Precision BalancesDocument40 pagesAdam Equipment: PGW Precision Balancesslim ben hassineNo ratings yet
- Gea32885 Bouchain Whitepaper Final Aug 2016 PDFDocument8 pagesGea32885 Bouchain Whitepaper Final Aug 2016 PDFMd. Humayun Kabir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Calibration in Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument82 pagesCalibration in Pharmaceutical Industryosama kamel100% (2)
- Lecture3 CPS RequirementsDocument14 pagesLecture3 CPS RequirementszahraNo ratings yet
- Aiche 2016 - Dynamic Simulation For Apc Total-InprocessDocument29 pagesAiche 2016 - Dynamic Simulation For Apc Total-InprocesscbqucbquNo ratings yet
- Kolgomorov WawanDocument3 pagesKolgomorov WawanadhiexvNo ratings yet
- Troitsky Novikova Bannatyne en ReDocument4 pagesTroitsky Novikova Bannatyne en ReGurinderjeet01No ratings yet
- Optimization of Casting Shapes: Technical PaperDocument5 pagesOptimization of Casting Shapes: Technical PaperAndyNo ratings yet
- Sop 29 Assignment of Uncertainty 20190506Document12 pagesSop 29 Assignment of Uncertainty 20190506Andi Yuliani RusliNo ratings yet
- GT2017 63591Document12 pagesGT2017 63591DeckrunNo ratings yet
- Onl9 Monitoring of TransformerDocument4 pagesOnl9 Monitoring of TransformerMTECH IPSNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma BustedDocument7 pagesSix Sigma BustedOmar AlasNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of A Centrifugal Pump Impeller With Ansys - OptislangDocument3 pagesDesign and Optimization of A Centrifugal Pump Impeller With Ansys - OptislangHayderAlSamawiNo ratings yet
- Conical Diffuser Modelling Using Simulated AnnealingDocument10 pagesConical Diffuser Modelling Using Simulated AnnealingOKORIENo ratings yet
- Tunneling ProductivityDocument56 pagesTunneling ProductivitySiddharth Patel100% (1)
- OASIcs iPMVM 2020 6Document18 pagesOASIcs iPMVM 2020 6Kakashi ZXNo ratings yet
- PID Tuning MethodsDocument52 pagesPID Tuning Methodsarash esfahanNo ratings yet
- Sop 29 Assignment of Uncertainty 20180131Document11 pagesSop 29 Assignment of Uncertainty 20180131Misael NavarroNo ratings yet
- Swep20 Act ScottDocument11 pagesSwep20 Act Scottkorray1No ratings yet
- SOP - Double Check PDFDocument12 pagesSOP - Double Check PDFNURUL YAZIDNo ratings yet
- UserCom TA 6Document24 pagesUserCom TA 6rubenssanNo ratings yet
- Max Plus at Work: Modeling and Analysis of Synchronized Systems: A Course on Max-Plus Algebra and Its ApplicationsFrom EverandMax Plus at Work: Modeling and Analysis of Synchronized Systems: A Course on Max-Plus Algebra and Its ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication SystemsNo ratings yet
- Catalogo FiltriDocument221 pagesCatalogo Filtrisancsa_74No ratings yet
- Piston Rider RingsDocument1 pagePiston Rider Ringscontango O&GNo ratings yet
- Instalacion Motor Serie S270S PDFDocument80 pagesInstalacion Motor Serie S270S PDFMarlene Sanmartin MazaNo ratings yet
- 320C - Esquema de Lubrificação 3066Document3 pages320C - Esquema de Lubrificação 3066Marcus ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Entire Group Ref. Note Part No. Part Name 167-0994-PRODUCT Pump Gp-PistonDocument4 pagesEntire Group Ref. Note Part No. Part Name 167-0994-PRODUCT Pump Gp-PistonLenin GullapalliNo ratings yet
- Tool 3164067 Silicone Sealant: Engine Family: AllDocument2 pagesTool 3164067 Silicone Sealant: Engine Family: AllFaisal ImamNo ratings yet
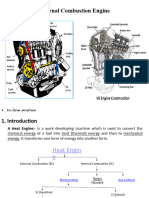
- ICE (CH 1)Document41 pagesICE (CH 1)xyonieNo ratings yet
- B1550HSTDDocument312 pagesB1550HSTDalexNo ratings yet
- Development of Quiescent Combustion System (MIQCS) PDFDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Quiescent Combustion System (MIQCS) PDFpeterNo ratings yet
- Jet 4 125Document178 pagesJet 4 125HonoluluNo ratings yet
- Ata 73Document61 pagesAta 73Jorge Ignacio Lara CeballosNo ratings yet
- C201 DieselDocument67 pagesC201 Dieselsergio ramirez60% (5)
- TVX 900 Sprężarka Tłokowa MehrerDocument2 pagesTVX 900 Sprężarka Tłokowa MehrerZamriNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: Groups 21-26 EDocument248 pagesWorkshop Manual: Groups 21-26 EmeltemNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of A Low Head Propeller TurbineDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of A Low Head Propeller TurbineChidolue OnyinyechukwuNo ratings yet
- Bx250aefin (2014) PDFDocument97 pagesBx250aefin (2014) PDFAlbert DepanoNo ratings yet
- Amte 226 Lesson 2: Magneto and Distributor VentingDocument13 pagesAmte 226 Lesson 2: Magneto and Distributor VentingKim RioverosNo ratings yet
- Connecting Rod Vs Stroke RatioDocument11 pagesConnecting Rod Vs Stroke RatioJameel Khan0% (1)
- Introduction To ME-GI Engines (Dual Fuel)Document23 pagesIntroduction To ME-GI Engines (Dual Fuel)Lucinio PittiNo ratings yet
- 2SP3 1t2sp470e1Document54 pages2SP3 1t2sp470e1Bahar SkNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 01: B.Tech. 7Th Sem.-Me 7me5-11 (Internal Combustion Engine)Document4 pagesLecture - 01: B.Tech. 7Th Sem.-Me 7me5-11 (Internal Combustion Engine)Kalyan SinghNo ratings yet