Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set 2
Problem Set 2
Uploaded by
Dylan BobCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Yi Hong LowNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Course Code: ME-636 Course Name: Combustion Technology Instructor: Dr. Pradeep KumarDocument4 pagesAssignment 1: Course Code: ME-636 Course Name: Combustion Technology Instructor: Dr. Pradeep KumarRajan KumarNo ratings yet
- AromaticsDocument5 pagesAromaticskinepela853No ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SET - 3 - AnswerDocument5 pagesPROBLEM - SET - 3 - AnswerDylan BobNo ratings yet
- Cuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Document35 pagesCuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Monica BravoNo ratings yet
- (P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Document11 pages(P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Addison JuttieNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor Theory: Unit 1Document3 pagesChemical Reactor Theory: Unit 1rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document3 pagesPs 1Anonymous s4HW3TX0IHNo ratings yet
- C D1031 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Questions. Each Question Carries 15 MarksDocument2 pagesC D1031 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Questions. Each Question Carries 15 MarksMidhunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document2 pagesChapter 10JoyantaNo ratings yet
- 2021 July CHT202-ADocument3 pages2021 July CHT202-AAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- A Brief Catalyst Study On Direct Methane Conversion Using: Antonius IndartoDocument16 pagesA Brief Catalyst Study On Direct Methane Conversion Using: Antonius Indartoapi-3728640No ratings yet
- Simultaneous Reaction-Deactivation Kinetics in N-Octane and Methylcyclopentane Reforming Reactions On Platinum-Containing CatalystsDocument18 pagesSimultaneous Reaction-Deactivation Kinetics in N-Octane and Methylcyclopentane Reforming Reactions On Platinum-Containing CatalystsLuis Enrique Jiménez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Tut1 2016 QDocument5 pagesTut1 2016 QAbhishek SardaNo ratings yet
- Cuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Document35 pagesCuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Monica BravoNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Assignment For Chem 103Document1 pageSupplementary Assignment For Chem 103madhur sharmaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 QuestionDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 Questionnur hidayatiNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic FBR DesignDocument10 pagesAdiabatic FBR DesignRana UzairNo ratings yet
- 2024 Jan. CHT202-EDocument3 pages2024 Jan. CHT202-EAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- BCT Important QuestionDocument5 pagesBCT Important QuestionliaayeongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5Saints Burner ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Semibullvalene SynthesisDocument5 pagesSemibullvalene SynthesisKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Conformational AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractice Questions-Conformational AnalysisHarry Zgambo100% (1)
- Assignment 2 3Document3 pagesAssignment 2 3Sandeep Challa0% (1)
- Gases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LDocument11 pagesGases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 3 ProblemsSteve HoNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia PlantDocument8 pagesModeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia PlantAbdulrazzaqAL-MalikyNo ratings yet
- CHE 140A Problem Set No. 8: Hill, 4-1, Pg. 120Document3 pagesCHE 140A Problem Set No. 8: Hill, 4-1, Pg. 120Anthony RoqueNo ratings yet
- DQE January 2001: Additional InformationDocument12 pagesDQE January 2001: Additional InformationryezhuNo ratings yet
- Sdarticle 008Document29 pagesSdarticle 008geo angNo ratings yet
- In Silico Folding of A Three Helix Protein and Characterization of Its Free-Energy LandscapeDocument4 pagesIn Silico Folding of A Three Helix Protein and Characterization of Its Free-Energy LandscapevictorNo ratings yet
- Ch3+o2 OldDocument26 pagesCh3+o2 OldJorge David Romero ChamacaNo ratings yet
- Resonance Interactions in Acyclic Systems: IupacDocument8 pagesResonance Interactions in Acyclic Systems: IupacAmOo ChurailNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions: Bt8302 Applied Thermodynamics For BiotechnologistsDocument1 pagePart B & Part C Questions: Bt8302 Applied Thermodynamics For BiotechnologistsKathir Vel.kNo ratings yet
- 2023 June CHT202-CDocument4 pages2023 June CHT202-CAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument51 pagesModule 5 - Chemical Energeticspoopoodotcom23No ratings yet
- Cet IiDocument4 pagesCet IiAnanya DaveNo ratings yet
- Chelate Effect and Its Thermodynamic Origin AbstractDocument2 pagesChelate Effect and Its Thermodynamic Origin AbstractSubodh DholpuriaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Unit2 1Document9 pagesExercises Unit2 1Clara Carrera0% (1)
- Direct Methanol Fuel CellDocument6 pagesDirect Methanol Fuel CellMarilynYunLingNo ratings yet
- Kin 20149Document6 pagesKin 20149Bruna ButkeNo ratings yet
- PS5Document3 pagesPS5Truong CaiNo ratings yet
- Houk Hydroboration TetDocument18 pagesHouk Hydroboration TetSuavo Tekka MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- HW2 2009 SolnsDocument13 pagesHW2 2009 SolnsMatthew RichardsonNo ratings yet
- DFT Calculations On Theretro-Ene Reactions, Part Iii: Allyl Benzyl Sulfide Pyrolysis in The Gas PhaseDocument5 pagesDFT Calculations On Theretro-Ene Reactions, Part Iii: Allyl Benzyl Sulfide Pyrolysis in The Gas Phaseiky77No ratings yet
- CL324 - 2023 - Tutorial 02Document2 pagesCL324 - 2023 - Tutorial 02Prince KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 5+Collision+Model+StudentDocument4 pages5 5+Collision+Model+StudentJannah ElmaghrabyNo ratings yet
- CHE3044F, 2013: Reactor Design 1: TUTORIAL 3Document3 pagesCHE3044F, 2013: Reactor Design 1: TUTORIAL 3nmhatityeNo ratings yet
- 12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFDocument13 pages12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Models - Chem.round Jet BurnerDocument44 pagesModels - Chem.round Jet BurnerLe Nguyen Phuc ThienNo ratings yet
- Computational and Theoretical ChemistryDocument8 pagesComputational and Theoretical ChemistryEdward AlexanderNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument6 pagesExampiyushdua01No ratings yet
- Detailed Solutions To ExercisesDocument123 pagesDetailed Solutions To Exerciseslutfi awn100% (5)
- ChenCatChem SilaneDocument7 pagesChenCatChem SilaneHimadri SahaNo ratings yet
- ModelQuestionsCh16 AKDocument5 pagesModelQuestionsCh16 AKYasmeen ElsawafNo ratings yet
- (Grupo 3) Photocatalyzed Direct Α-Alkylation of Esters Using Styrenes Adv Synth Catal - 2023 - WangDocument6 pages(Grupo 3) Photocatalyzed Direct Α-Alkylation of Esters Using Styrenes Adv Synth Catal - 2023 - Wangjuan.ceballos.anayaNo ratings yet
- John B. Bell Et Al - Numerical Simulation of The Combustion of PETN/TNT Products With Air in Closed ChambersDocument9 pagesJohn B. Bell Et Al - Numerical Simulation of The Combustion of PETN/TNT Products With Air in Closed ChambersFraosmNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Theory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFrom EverandTheory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFernanda DuarteNo ratings yet
Problem Set 2
Problem Set 2
Uploaded by
Dylan BobOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set 2
Problem Set 2
Uploaded by
Dylan BobCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 5000 Homework 2 (Due Nov.
14th)
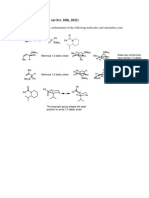
1. Draw the most stable conformation of the following molecules
2. a) using “arrow-pushing” convention, outline a reasonable mechanism for the
following transformation:
b) “this reaction is thermodynamically controlled” explain what is implied by this
statement.
c) draw the most stable conformations of compounds 2 and 3, on the basis of the
statement in b), predict which is the major product of the reaction shown above, and
explain what factors make it the thermodynamic product.
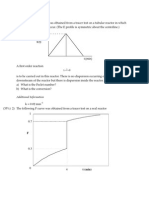
3. The diastereoselectivity of alkyl radical addition to substituted alkylidene malononitriles is a
function of the size of the attacking radical when there is a bulky substituent at the -carbon.
Conformational analysis of the reactant indicates that it prefers conformation a over b by 3.0
kcal/mol. Suggest a TS structure, showing reactant conformation and reagent trajectory that is in
accord with these results. Use the Curtin-Hammet principle (p. 296) to construct a reaction energy
diagram that illustrates the product composition in terms of TS energy.
4. The A vaule of -CH3 in mono substituted cyclohexane is about 1.74 kacal/mol while for H it
would be 0. But in N-substituted piperidine derivatives, the A value for H would be 0.36 kcal/mol.
For -CH3, the A value could be up to 3.0 kcal/mol. Please explain this observation.
5. Explain why the exchange for deuterium of the proton of HC(CF3)3 catalyzed by MeONa in
MeOD is 109 times faster than the exchange reaction of the proton of HCF3 under the same
condition (start from writing down a chemical reaction according to the above description).
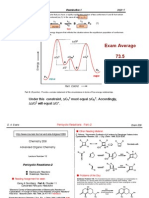
6. A mechanism for alkene arylation catalyzed by Pd(II) is outlined below. The isotope effect
kH/kD was found to be 5 when benzene-d6 was used. There was no isotope effect when styrene-β-
d2 was used. Which steps in the reaction mechanism could be rate determining, given this
information on isotope effects?
7. refer to textbook, Carey & Sundberg Advanced Organic Chemistry (Part A) Chapter 2: 2.26
You might also like
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Yi Hong LowNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Course Code: ME-636 Course Name: Combustion Technology Instructor: Dr. Pradeep KumarDocument4 pagesAssignment 1: Course Code: ME-636 Course Name: Combustion Technology Instructor: Dr. Pradeep KumarRajan KumarNo ratings yet
- AromaticsDocument5 pagesAromaticskinepela853No ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SET - 3 - AnswerDocument5 pagesPROBLEM - SET - 3 - AnswerDylan BobNo ratings yet
- Cuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Document35 pagesCuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Monica BravoNo ratings yet
- (P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Document11 pages(P01, C01, C02, C2, C3) : Confidential EH/JUN 2014/CHE584/594Addison JuttieNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor Theory: Unit 1Document3 pagesChemical Reactor Theory: Unit 1rajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document3 pagesPs 1Anonymous s4HW3TX0IHNo ratings yet
- C D1031 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Questions. Each Question Carries 15 MarksDocument2 pagesC D1031 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Questions. Each Question Carries 15 MarksMidhunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document2 pagesChapter 10JoyantaNo ratings yet
- 2021 July CHT202-ADocument3 pages2021 July CHT202-AAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- A Brief Catalyst Study On Direct Methane Conversion Using: Antonius IndartoDocument16 pagesA Brief Catalyst Study On Direct Methane Conversion Using: Antonius Indartoapi-3728640No ratings yet
- Simultaneous Reaction-Deactivation Kinetics in N-Octane and Methylcyclopentane Reforming Reactions On Platinum-Containing CatalystsDocument18 pagesSimultaneous Reaction-Deactivation Kinetics in N-Octane and Methylcyclopentane Reforming Reactions On Platinum-Containing CatalystsLuis Enrique Jiménez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Tut1 2016 QDocument5 pagesTut1 2016 QAbhishek SardaNo ratings yet
- Cuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Document35 pagesCuaderno de Trabajo - 2019-2Monica BravoNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Assignment For Chem 103Document1 pageSupplementary Assignment For Chem 103madhur sharmaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 QuestionDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 Questionnur hidayatiNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic FBR DesignDocument10 pagesAdiabatic FBR DesignRana UzairNo ratings yet
- 2024 Jan. CHT202-EDocument3 pages2024 Jan. CHT202-EAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- BCT Important QuestionDocument5 pagesBCT Important QuestionliaayeongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5Saints Burner ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Semibullvalene SynthesisDocument5 pagesSemibullvalene SynthesisKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Conformational AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractice Questions-Conformational AnalysisHarry Zgambo100% (1)
- Assignment 2 3Document3 pagesAssignment 2 3Sandeep Challa0% (1)
- Gases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LDocument11 pagesGases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 3 ProblemsSteve HoNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia PlantDocument8 pagesModeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia PlantAbdulrazzaqAL-MalikyNo ratings yet
- CHE 140A Problem Set No. 8: Hill, 4-1, Pg. 120Document3 pagesCHE 140A Problem Set No. 8: Hill, 4-1, Pg. 120Anthony RoqueNo ratings yet
- DQE January 2001: Additional InformationDocument12 pagesDQE January 2001: Additional InformationryezhuNo ratings yet
- Sdarticle 008Document29 pagesSdarticle 008geo angNo ratings yet
- In Silico Folding of A Three Helix Protein and Characterization of Its Free-Energy LandscapeDocument4 pagesIn Silico Folding of A Three Helix Protein and Characterization of Its Free-Energy LandscapevictorNo ratings yet
- Ch3+o2 OldDocument26 pagesCh3+o2 OldJorge David Romero ChamacaNo ratings yet
- Resonance Interactions in Acyclic Systems: IupacDocument8 pagesResonance Interactions in Acyclic Systems: IupacAmOo ChurailNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions: Bt8302 Applied Thermodynamics For BiotechnologistsDocument1 pagePart B & Part C Questions: Bt8302 Applied Thermodynamics For BiotechnologistsKathir Vel.kNo ratings yet
- 2023 June CHT202-CDocument4 pages2023 June CHT202-CAkshay A BijuNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDocument51 pagesModule 5 - Chemical Energeticspoopoodotcom23No ratings yet
- Cet IiDocument4 pagesCet IiAnanya DaveNo ratings yet
- Chelate Effect and Its Thermodynamic Origin AbstractDocument2 pagesChelate Effect and Its Thermodynamic Origin AbstractSubodh DholpuriaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Unit2 1Document9 pagesExercises Unit2 1Clara Carrera0% (1)
- Direct Methanol Fuel CellDocument6 pagesDirect Methanol Fuel CellMarilynYunLingNo ratings yet
- Kin 20149Document6 pagesKin 20149Bruna ButkeNo ratings yet
- PS5Document3 pagesPS5Truong CaiNo ratings yet
- Houk Hydroboration TetDocument18 pagesHouk Hydroboration TetSuavo Tekka MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- HW2 2009 SolnsDocument13 pagesHW2 2009 SolnsMatthew RichardsonNo ratings yet
- DFT Calculations On Theretro-Ene Reactions, Part Iii: Allyl Benzyl Sulfide Pyrolysis in The Gas PhaseDocument5 pagesDFT Calculations On Theretro-Ene Reactions, Part Iii: Allyl Benzyl Sulfide Pyrolysis in The Gas Phaseiky77No ratings yet
- CL324 - 2023 - Tutorial 02Document2 pagesCL324 - 2023 - Tutorial 02Prince KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 5+Collision+Model+StudentDocument4 pages5 5+Collision+Model+StudentJannah ElmaghrabyNo ratings yet
- CHE3044F, 2013: Reactor Design 1: TUTORIAL 3Document3 pagesCHE3044F, 2013: Reactor Design 1: TUTORIAL 3nmhatityeNo ratings yet
- 12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFDocument13 pages12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Models - Chem.round Jet BurnerDocument44 pagesModels - Chem.round Jet BurnerLe Nguyen Phuc ThienNo ratings yet
- Computational and Theoretical ChemistryDocument8 pagesComputational and Theoretical ChemistryEdward AlexanderNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument6 pagesExampiyushdua01No ratings yet
- Detailed Solutions To ExercisesDocument123 pagesDetailed Solutions To Exerciseslutfi awn100% (5)
- ChenCatChem SilaneDocument7 pagesChenCatChem SilaneHimadri SahaNo ratings yet
- ModelQuestionsCh16 AKDocument5 pagesModelQuestionsCh16 AKYasmeen ElsawafNo ratings yet
- (Grupo 3) Photocatalyzed Direct Α-Alkylation of Esters Using Styrenes Adv Synth Catal - 2023 - WangDocument6 pages(Grupo 3) Photocatalyzed Direct Α-Alkylation of Esters Using Styrenes Adv Synth Catal - 2023 - Wangjuan.ceballos.anayaNo ratings yet
- John B. Bell Et Al - Numerical Simulation of The Combustion of PETN/TNT Products With Air in Closed ChambersDocument9 pagesJohn B. Bell Et Al - Numerical Simulation of The Combustion of PETN/TNT Products With Air in Closed ChambersFraosmNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Theory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFrom EverandTheory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFernanda DuarteNo ratings yet